943a4a4ad0886f5caf6440b0ee8b081f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 The Constitution of the United States
The Constitution of the United States
 Drafting a Constitution • Articles were doomed to Fail – USA Lacked Central leadership – A Constitutional Convention was called in 1787 – Many states called for stronger central Government • Delegates – Revolutionary Veterans – Signers of Declaration of Independence – White, Landowning, males
Drafting a Constitution • Articles were doomed to Fail – USA Lacked Central leadership – A Constitutional Convention was called in 1787 – Many states called for stronger central Government • Delegates – Revolutionary Veterans – Signers of Declaration of Independence – White, Landowning, males
 Convention Problems that need to be solved: • Problem 1: Balance between State and Federal • Problem 2: Balance between North and South • Problem 3: Balance between BIG states and Small states • Two Plans proposed– The Virginia Plan & New Jersey Plan
Convention Problems that need to be solved: • Problem 1: Balance between State and Federal • Problem 2: Balance between North and South • Problem 3: Balance between BIG states and Small states • Two Plans proposed– The Virginia Plan & New Jersey Plan
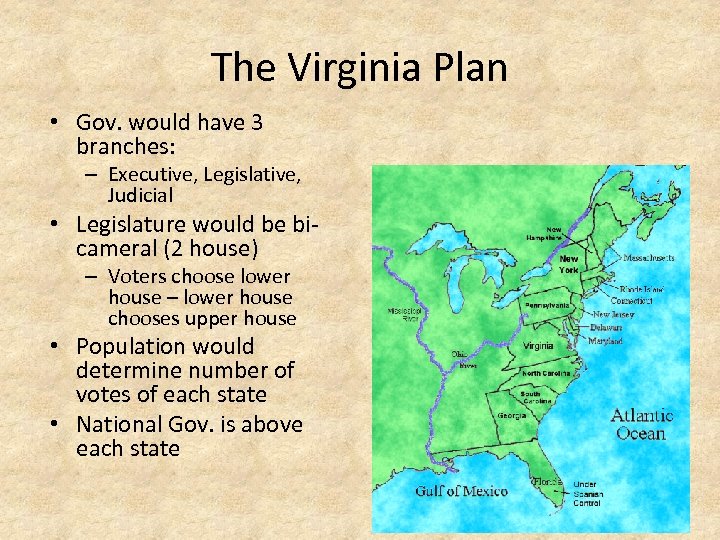 The Virginia Plan • Gov. would have 3 branches: – Executive, Legislative, Judicial • Legislature would be bicameral (2 house) – Voters choose lower house – lower house chooses upper house • Population would determine number of votes of each state • National Gov. is above each state
The Virginia Plan • Gov. would have 3 branches: – Executive, Legislative, Judicial • Legislature would be bicameral (2 house) – Voters choose lower house – lower house chooses upper house • Population would determine number of votes of each state • National Gov. is above each state
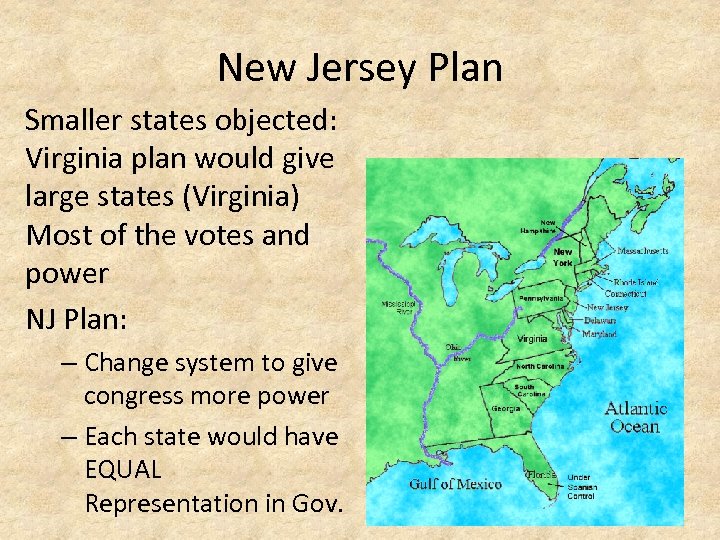 New Jersey Plan Smaller states objected: Virginia plan would give large states (Virginia) Most of the votes and power NJ Plan: – Change system to give congress more power – Each state would have EQUAL Representation in Gov.
New Jersey Plan Smaller states objected: Virginia plan would give large states (Virginia) Most of the votes and power NJ Plan: – Change system to give congress more power – Each state would have EQUAL Representation in Gov.
 “The Great Compromise” “The Two Ideas…ought to be combined; that one branch the people ought to be represented; in the other the states. ” • The Senate (upper house) would have 2 reps from each state • The Representatives (lower house) would be based on states population
“The Great Compromise” “The Two Ideas…ought to be combined; that one branch the people ought to be represented; in the other the states. ” • The Senate (upper house) would have 2 reps from each state • The Representatives (lower house) would be based on states population
 Compromise on Slavery Slave Population gave South huge Pop. Advantage – Also Raise taxes – Property Tax – Southerners wanted to count for Reps. But not for Taxes • 3/5 compromise – Slave = 3/5 person – Compromise on Reps. And Taxes
Compromise on Slavery Slave Population gave South huge Pop. Advantage – Also Raise taxes – Property Tax – Southerners wanted to count for Reps. But not for Taxes • 3/5 compromise – Slave = 3/5 person – Compromise on Reps. And Taxes
 Compromise on Slavery No Ban on Slavery Considered – Unity Needed more than Abolition • Agreed: – Importation would continue for 20 more years – then no more – Fugitive Slave Clause: A runaway slave to another state must be returned to its owner across state lines
Compromise on Slavery No Ban on Slavery Considered – Unity Needed more than Abolition • Agreed: – Importation would continue for 20 more years – then no more – Fugitive Slave Clause: A runaway slave to another state must be returned to its owner across state lines
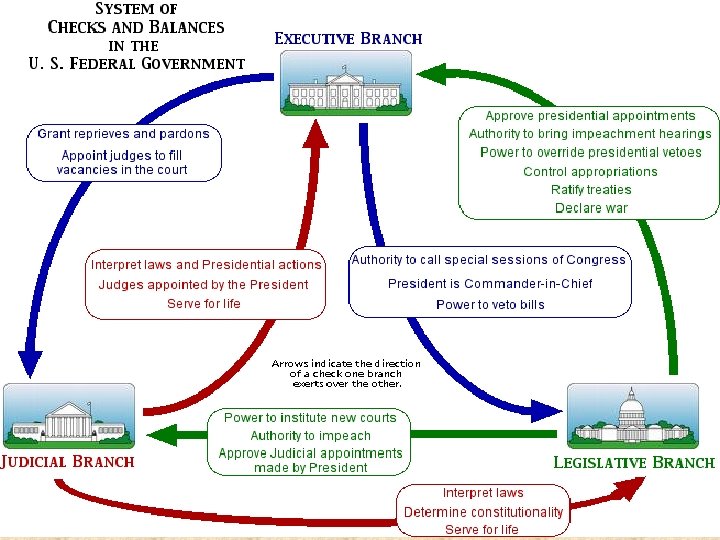
 Checks and Balances Enlightenment ideals states that effective governments need Checks & Balances • Balance between President/ Congress • Balance between States/ Federal • Convention gave MOST Power to the Congress (fear of Monarchy) • President elected by the states – Electoral College – States should follow popular vote
Checks and Balances Enlightenment ideals states that effective governments need Checks & Balances • Balance between President/ Congress • Balance between States/ Federal • Convention gave MOST Power to the Congress (fear of Monarchy) • President elected by the states – Electoral College – States should follow popular vote
 Checks and Balances • Office of VP – 2 nd place vote recipient • Each Branch had the ability to slow/stop another branch – Ensured no branch would have too much power – Ensured no branch could not dominate the others
Checks and Balances • Office of VP – 2 nd place vote recipient • Each Branch had the ability to slow/stop another branch – Ensured no branch would have too much power – Ensured no branch could not dominate the others
 Checks and Balances • Planning the Court System – Wanted courts to maintain independent status – Judges nominated by President/ Approved by Congress – Judges could not be fired without just cause
Checks and Balances • Planning the Court System – Wanted courts to maintain independent status – Judges nominated by President/ Approved by Congress – Judges could not be fired without just cause
 Federalists vs. Anti. Federalists • Fear of Strong Central Government • Federalists: Supporters of Constitution with strong central Gov. • Anti. Federalists: Opponents of the constitution in its present form and sought a weaker central Gov.
Federalists vs. Anti. Federalists • Fear of Strong Central Government • Federalists: Supporters of Constitution with strong central Gov. • Anti. Federalists: Opponents of the constitution in its present form and sought a weaker central Gov.
 The Federalists • Leaders: James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, John Adams, Washington, Franklin • Strong National Gov. = Republic Survives • Fed. Gov. could end chaos between states • Separation of Powers can prevent Tyranny
The Federalists • Leaders: James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, John Adams, Washington, Franklin • Strong National Gov. = Republic Survives • Fed. Gov. could end chaos between states • Separation of Powers can prevent Tyranny
 The Antifederalists Leaders: Sam Adams, Patrick Henry, Thomas Jefferson • Wanted a new Gov. but not the one proposed • Suspicious of Strong central Gov. = just left a strong Gov. • Feared Fed. Gov. would abuse states/ Individuals – Demanded a Bill of Rights for protection
The Antifederalists Leaders: Sam Adams, Patrick Henry, Thomas Jefferson • Wanted a new Gov. but not the one proposed • Suspicious of Strong central Gov. = just left a strong Gov. • Feared Fed. Gov. would abuse states/ Individuals – Demanded a Bill of Rights for protection
 Final Ratification? • Final draft was submitted to the states for approval • Some delegates refused to sign because it lacked 1 component – A Bill of Rights
Final Ratification? • Final draft was submitted to the states for approval • Some delegates refused to sign because it lacked 1 component – A Bill of Rights


