 The Conjunction
The Conjunction
 It is a part of speech which denotes connections between objects and phenomena. It connects pats of the sentence, clauses, and sentences.
It is a part of speech which denotes connections between objects and phenomena. It connects pats of the sentence, clauses, and sentences.
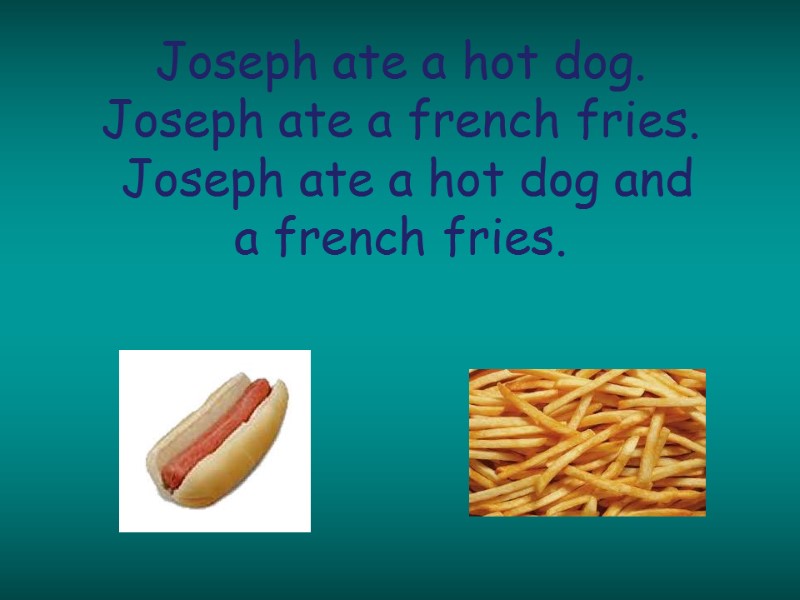 Joseph ate a hot dog. Joseph ate a french fries. Joseph ate a hot dog and a french fries.
Joseph ate a hot dog. Joseph ate a french fries. Joseph ate a hot dog and a french fries.
 According to their morphological structure conjunctions are divided into the folowing groups: simple: and, or, but, till, after, that, so, where, when, etc.; derivative: until, unless, etc.; compound: however, whereas, wherever, etc.; composite: as well as, as long as, in case, for fear (that), on the ground that, for the reason that, etc. some conjunctions are used in pairs: both…and, either…or, not only…but (also), neither … nor, whether … or.
According to their morphological structure conjunctions are divided into the folowing groups: simple: and, or, but, till, after, that, so, where, when, etc.; derivative: until, unless, etc.; compound: however, whereas, wherever, etc.; composite: as well as, as long as, in case, for fear (that), on the ground that, for the reason that, etc. some conjunctions are used in pairs: both…and, either…or, not only…but (also), neither … nor, whether … or.
 As to their function conjunctions fall under two classes: Coordinating conjunctions; Subordinating conjunctions.
As to their function conjunctions fall under two classes: Coordinating conjunctions; Subordinating conjunctions.
 Copulative: and, nor, as well as, both … and, not only … but (also), neither … nor. Not only she is a pretty girl, but also smart.
Copulative: and, nor, as well as, both … and, not only … but (also), neither … nor. Not only she is a pretty girl, but also smart.
 Disjunctive: or, either … or, or else, else. Mary should study hard, or else she won’t pass exams.
Disjunctive: or, either … or, or else, else. Mary should study hard, or else she won’t pass exams.
 Adversative: but, while, whereas. Sam has won the first prize, but he doesn’t seem too satisfied.
Adversative: but, while, whereas. Sam has won the first prize, but he doesn’t seem too satisfied.
 Causative-consecutive: so, for. I drank a cup of strong coffee, so I couldn’t fall asleep for a long time.
Causative-consecutive: so, for. I drank a cup of strong coffee, so I couldn’t fall asleep for a long time.
 Subordinating conjunctions: The conjunction that introduces subject clauses, object clauses, predicative clauses, adverbial clauses, and attributive clauses. The conjunction if introduces object clauses and adverbial clauses of condition. The conjunction as introduces adverbial clauses of time, of cause, and of comparison. The conjunction while may express both coordination and subordination. Conjunctions such as as if, as though, though, if are used in simple sentences.
Subordinating conjunctions: The conjunction that introduces subject clauses, object clauses, predicative clauses, adverbial clauses, and attributive clauses. The conjunction if introduces object clauses and adverbial clauses of condition. The conjunction as introduces adverbial clauses of time, of cause, and of comparison. The conjunction while may express both coordination and subordination. Conjunctions such as as if, as though, though, if are used in simple sentences.























