The concept and types of organizations.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20
 The concept and types of organizations
The concept and types of organizations
 • • 1. The concept of organization roles; 2. The concept of organizing; 3. What are the types of organization? 4. The concept of organization
• • 1. The concept of organization roles; 2. The concept of organizing; 3. What are the types of organization? 4. The concept of organization
 Organizational Roles • Organizational roles are the part or position that a person is assigned in the organization, for example the role of manager sales or your role as a student. People will cooperate effectively in organizations if they know the part they have to play in the organizations i. e. if they know their roles in the organization
Organizational Roles • Organizational roles are the part or position that a person is assigned in the organization, for example the role of manager sales or your role as a student. People will cooperate effectively in organizations if they know the part they have to play in the organizations i. e. if they know their roles in the organization
 Following are the requirement of organizational goals: • 1. Clear objectives; People must know the objectives that they have to achieve clearly. • 2. Clear idea of duties or activities: People must know their duties and activities that they must perform. E. g. , student duties are to study, be disciplined • 3. Clear area of authority: In organization people must know the extent of authority that they have.
Following are the requirement of organizational goals: • 1. Clear objectives; People must know the objectives that they have to achieve clearly. • 2. Clear idea of duties or activities: People must know their duties and activities that they must perform. E. g. , student duties are to study, be disciplined • 3. Clear area of authority: In organization people must know the extent of authority that they have.
 What is Organizing • Organizing means that there should be clear line of authority and all should know who reports to whom. Following are the main steps in organizing: • 1) Classification of activities: First all activities in organization must be classified i. e. activities similar in nature should be identified separately. • 2) Grouping of activities to achieve objectives: Similar activities should be grouped. • 3) Assigning a manager to each group of activities: A manager should be assigned • 4) Coordination of group of activities both horizontally and vertically: Coordination means the interrelationship among activities.
What is Organizing • Organizing means that there should be clear line of authority and all should know who reports to whom. Following are the main steps in organizing: • 1) Classification of activities: First all activities in organization must be classified i. e. activities similar in nature should be identified separately. • 2) Grouping of activities to achieve objectives: Similar activities should be grouped. • 3) Assigning a manager to each group of activities: A manager should be assigned • 4) Coordination of group of activities both horizontally and vertically: Coordination means the interrelationship among activities.
 Organization • Now we have talked about concepts of `roles' and `organizing', we will connect these two concepts with the concept of organization. Organization means a formalized intentional structure of roles and positions. Here we refer to organization as a structure in which people work. E. g. , school is organization.
Organization • Now we have talked about concepts of `roles' and `organizing', we will connect these two concepts with the concept of organization. Organization means a formalized intentional structure of roles and positions. Here we refer to organization as a structure in which people work. E. g. , school is organization.
 Types of Organization • Organizations can be categorized into following types: • 1. Formal Organizations • 2. Informal Organizations
Types of Organization • Organizations can be categorized into following types: • 1. Formal Organizations • 2. Informal Organizations
 • Formal organizations mean the intentional structure of roles in a formally organized enterprise. The structures are created by people to achieve certain defined goals. The formal organizations could be hospitals, schools, Water and Power Development authority (WAPDA).
• Formal organizations mean the intentional structure of roles in a formally organized enterprise. The structures are created by people to achieve certain defined goals. The formal organizations could be hospitals, schools, Water and Power Development authority (WAPDA).
 • Informal Organizations • A network of personal and social relations not established or required by the formal organization but arising spontaneously as people associate with each other is called informal organization. The example of informal organization is friendship within the organization amongst people working at various levels
• Informal Organizations • A network of personal and social relations not established or required by the formal organization but arising spontaneously as people associate with each other is called informal organization. The example of informal organization is friendship within the organization amongst people working at various levels
 DEPARTMENTALIZATION • What is Department • What are the Basis of Departmentalization • Advantages and Disadvantages of various types of Departmentalization • The Concept of Authority and Decentralization
DEPARTMENTALIZATION • What is Department • What are the Basis of Departmentalization • Advantages and Disadvantages of various types of Departmentalization • The Concept of Authority and Decentralization
 • Department "A department is a distinct area, division, or branch of organization over which manager hasauthority for performance of specified activities" • When activities and tasks are grouped according to some basis of similarity, it is called departmentalization
• Department "A department is a distinct area, division, or branch of organization over which manager hasauthority for performance of specified activities" • When activities and tasks are grouped according to some basis of similarity, it is called departmentalization
 Departmentalization by simple numbers • Departmentalization by number is done by putting people in group who are to perform the same duties. They are placed under supervision of a manager or supervisors. Example: Armies in old times, Unskilled labour in construction
Departmentalization by simple numbers • Departmentalization by number is done by putting people in group who are to perform the same duties. They are placed under supervision of a manager or supervisors. Example: Armies in old times, Unskilled labour in construction
 Departmentalization by time • Departmentalization by time is done at operational or lower levels of organizations where activities are grouped together on the basis of time. Example: People working in shifts in steel company, hospitals etc.
Departmentalization by time • Departmentalization by time is done at operational or lower levels of organizations where activities are grouped together on the basis of time. Example: People working in shifts in steel company, hospitals etc.
 Advantages • Departmentalization by time has two main advantages; These are: • 1. The usual timings of offices are eight hours, but if departmentalization is to be done beyond 8 hours, second shift or round the clock service can be provided. • 2. Equipment can be used more often in shifts: The tools, equipment and physical facilities can be used to full capacity.
Advantages • Departmentalization by time has two main advantages; These are: • 1. The usual timings of offices are eight hours, but if departmentalization is to be done beyond 8 hours, second shift or round the clock service can be provided. • 2. Equipment can be used more often in shifts: The tools, equipment and physical facilities can be used to full capacity.
 Disadvantages • 1. Lack of supervision: People working in shifts may not be supervised. • 2. Increase of overtime rates: There may be increase in expenditure due to payment to workers in shift
Disadvantages • 1. Lack of supervision: People working in shifts may not be supervised. • 2. Increase of overtime rates: There may be increase in expenditure due to payment to workers in shift
 Departmentalization by Enterprise Function • Departmentalization by function is the grouping of the activities in accordance with the functions of the enterprise (Functional Departmentalization). Example of functions of organization: Production, Budgeting, Accounts, Sales etc
Departmentalization by Enterprise Function • Departmentalization by function is the grouping of the activities in accordance with the functions of the enterprise (Functional Departmentalization). Example of functions of organization: Production, Budgeting, Accounts, Sales etc
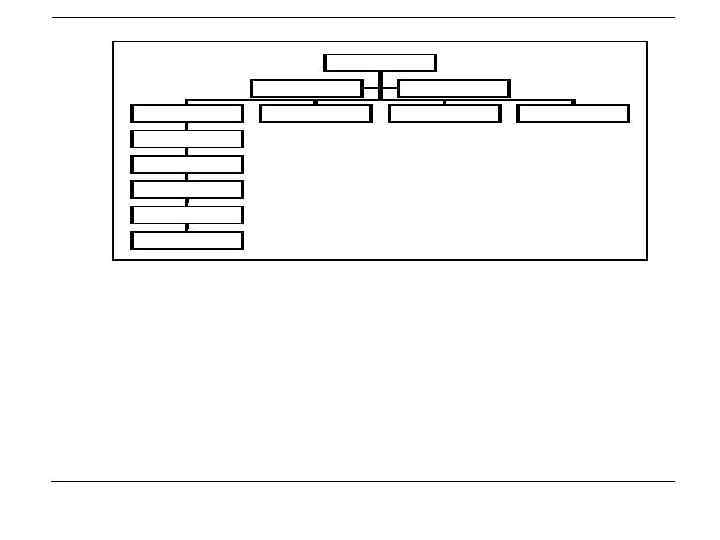
 • In figure 1 is the organization chart (also called organogram) of a private company. The functional departmentalization of a company is shown. There are 4 functional departments i. e. marketing, engineering, production and finance. Under the marketing department all market related activities are grouped i. e. marketing research, marketing planning, advertising and promotion, sales and administration. • Departmentalization by function is the most common form of departmentalization
• In figure 1 is the organization chart (also called organogram) of a private company. The functional departmentalization of a company is shown. There are 4 functional departments i. e. marketing, engineering, production and finance. Under the marketing department all market related activities are grouped i. e. marketing research, marketing planning, advertising and promotion, sales and administration. • Departmentalization by function is the most common form of departmentalization
 Advantages of Departmentalization by Function Following are the advantages of departmentalization by function: • 1. It is logical reflection of functions: This is more common and logical way of grouping activities. • 2. Maintains power of major functions: Certain functions in organization are more important as the main or core area. For example in universities the academic department will be major function. • 3. Simplifies training: Since people are grouped according to functional departmentalization, it becomes easier to provide training to employees in a particular functional area wise. • 4. Tight control on the top: Each department head can exercise control over its own functional area
Advantages of Departmentalization by Function Following are the advantages of departmentalization by function: • 1. It is logical reflection of functions: This is more common and logical way of grouping activities. • 2. Maintains power of major functions: Certain functions in organization are more important as the main or core area. For example in universities the academic department will be major function. • 3. Simplifies training: Since people are grouped according to functional departmentalization, it becomes easier to provide training to employees in a particular functional area wise. • 4. Tight control on the top: Each department head can exercise control over its own functional area
 Disadvantages of Departmentalization by Function Following are disadvantages of departmentalization by functions: • 1. Reduces coordination among functions: Since employees work in respective department; therefore, coordination amongst various department is reduced. • 2. Slow adaptation to changing environment: When people work for longtime in a department they become use to with the working and their styles become rigid. For example a police officer style of working would be different from that of a teacher. Therefore, they are slow to changing environment. • 3. Limits development of managers: Development of mangers is limited to a particular function only.
Disadvantages of Departmentalization by Function Following are disadvantages of departmentalization by functions: • 1. Reduces coordination among functions: Since employees work in respective department; therefore, coordination amongst various department is reduced. • 2. Slow adaptation to changing environment: When people work for longtime in a department they become use to with the working and their styles become rigid. For example a police officer style of working would be different from that of a teacher. Therefore, they are slow to changing environment. • 3. Limits development of managers: Development of mangers is limited to a particular function only.


