6d3603ef99f0943158cfb0002178a0ed.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

The common definitions and common symbols for EPBD related CEN standards Given in CEN Technical report CEN/TR 15615 ("Umbrella Document') Dick van Dijk 1), Johann Zirngibl 2) 1): dick. vandijk@tno. nl TNO Built Environment and Geosciences, The Netherlands 2): johann. zirngibl@cstb. fr CSTB, France CENSE Contract: EIE/07/069/SI 2. 466698 Duration: October 2007 – March 2010 Version: March 2010

Outline • The EU CENSE project • Introduction of the CEN Technical Report CEN TR 15615 in which the common definitions and symbols are presented • Background • Common definitions – including examples • Common symbols and subscripts – including examples • Frequently asked questions slide 2

The EU CENSE project (Oct. 2007 - March 2010) Aim of the project: To accelerate adoption and improved effectiveness of the EPBD related CEN- standards in the EU Member States These standards were successively published in the years 2007 -2008 and are being implemented or planned to be implemented in many EU Member States. However, the full implementation is not a trivial task Main project activities: A. To widely communicate role, status and content of these standards; to provide guidance on the implementation B. To collect comments and good practice examples from Member States aiming to remove obstacles C. To prepare recommendations to CEN for a “second generation” of standards on the integrated energy performance of buildings slide 3

Brief introduction A brief introduction to the CENSE project and the CEN-EPBD standards is provided in a separate presentation: slide 4

More information and downloads: www. iee-cense. eu Disclaimer: CENSE has received funding from the Community’s Intelligent Energy Europe programme under the contract EIE/07/069/SI 2. 466698. The content of this presentation reflects the authors view. The author(s) and the European Commission are not liable for any use that may be made of the information contained therein. Moreover, because this is an interim result of the project: any conclusions are only preliminary and may change in the course of the project based on further feedback from the contributors, additional collected information and/or increased insight. slide 5

Introduction of CEN Technical Report TR 15615 • CEN Technical Report, CEN/TR 15615, Explanation of the general relationship between various European standards and the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) - Umbrella Document, April 2008 • Relevant for this presentation: – Annex C provides an extensive list of common definitions – Annex D provides an extensive list of common symbols • Under responsibility of CEN/BT TF 173, Energy performance of buildings project group (currently called CEN/BT TC 371) slide 6

Background slide 7

Common definitions and symbols • Consequently: work started to prepare sets of common definitions and symbols on the main concepts and physical quantities • Due to timing constraints: in parallel with the development of the standards • Cover terms and data passing from one standard to another • Already applied in several key standards, such as: – EN 15217 (on energy performance rating) – EN 15603 (on overall assessment of energy performance) – EN ISO 13790 (on energy use for heating and cooling) slide 8

Common definitions: a few examples C. 5. 1, energy performance of a building calculated or measured amount of weighted net delivered energy actually used or estimated to meet different needs associated with a standardised use of a building, which may include, inter alia, energy used for heating, cooling, ventilation, domestic hot water and lighting C. 5. 2, energy performance requirement minimum level of energy performance that is to be achieved to obtain a right or an advantage: e. g. right to build, lower interest rate, quality label C. 5. 3, energy rating evaluation of the energy performance of a building based on the weighted sum of the calculated or measured use of energy carriers slide 9
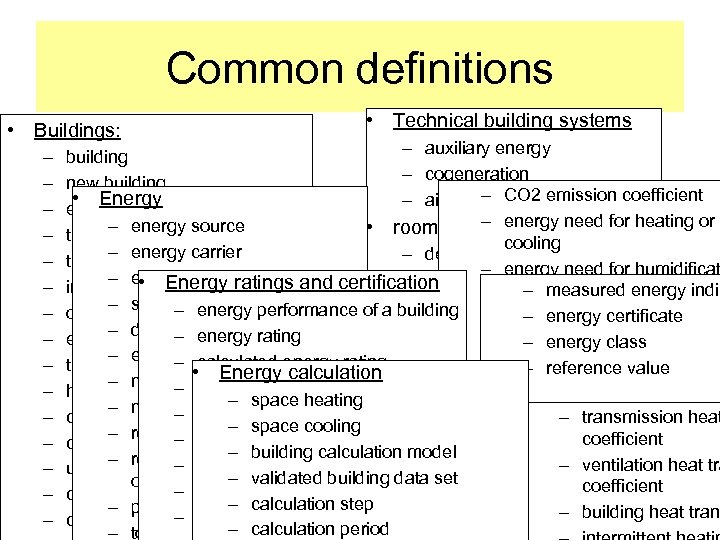
Common definitions • Buildings: – – – – • Technical building systems – auxiliary energy building – cogeneration new building – CO 2 emission coefficient • Energy – air conditioning system existing building – energy need for heating or – energy source • room conditioning system technical building system cooling – energy carrier – demand controlled ventilation technical building sub-system – energy need for humidificat – energyware – dehumidification • Energy ratings and certification internal dimension – measured energy indic or dehumidification – system boundary – humidification – energy performance of a building – energy need for domestic h overall internal dimension – energy certificate – delivered energy – ventilationwater – energy rating external dimension – energy class – exported energy – calculated energy rating – ventilation heat recovery – energy use for space heatin thermal envelope area – reference value • Energy calculation – net delivered energy cooling or domestic hot wat heated space– standard energy rating – part load operation – space heating – non-renewable energy – system thermal losstransmission heat – energy use for ventilation – design energy rating cooled space – – space cooling – renewable energy – recoverable system thermal – energy use for lighting – tailored energy rating conditioned space • Costs coefficient – building calculation model loss – grid electricity – renewable energy produced – ventilation heat tra – standard use data set unconditioned space – reasonably possible – validated building data set on the building site – recovered system thermal coefficient – gross calorific value – conditioned areameasured energy rating – reasonable cost – calculation step loss – primary energy – building heat trans – confidence interval conditioned zone – calculation period – total primary energy factor

More on the common symbols and subscripts • Most symbols are no surprise: ISO rules – – Q: heat E: energy T: temperature …. . • Subscripts: almost from scratch – Including rules how and when to use them
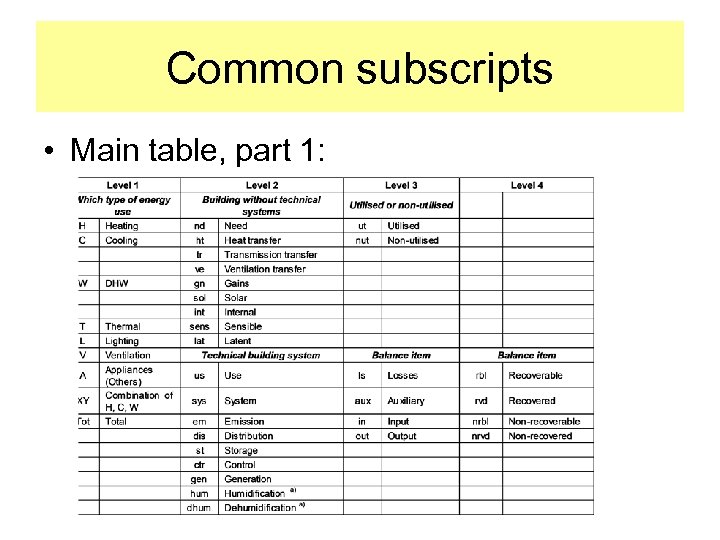
Common subscripts • Main table, part 1:
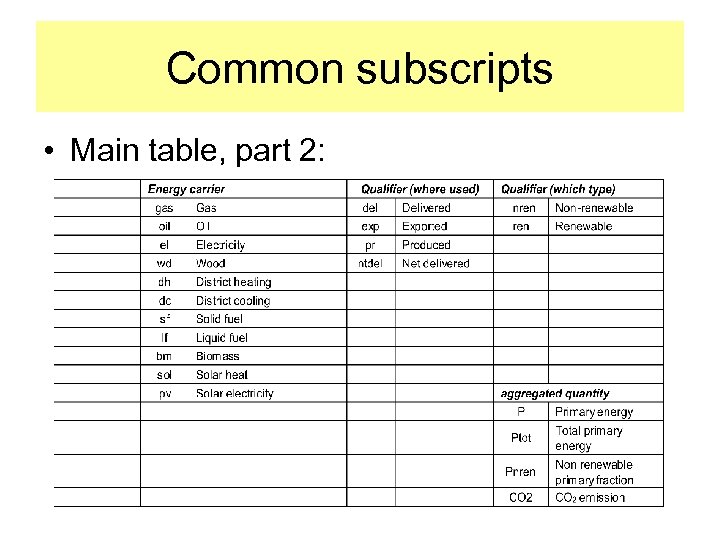
Common subscripts • Main table, part 2:

Examples: common symbols combined with subscripts • QH, nd – Energy need for heating • EHW, gen, in – Energy input to the common generator for heating and domestic hot water (= energy use for heating and DHW) • ET, exp, ren – Renewable part of the exported thermal energy
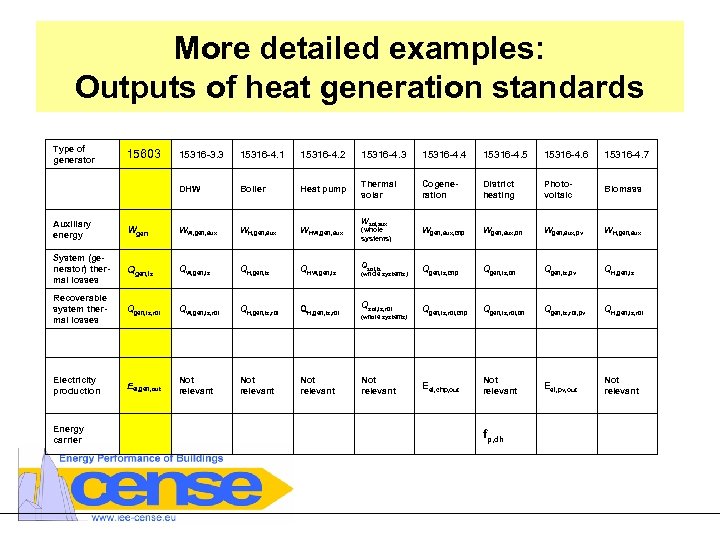
More detailed examples: Outputs of heat generation standards Type of generator 15603 15316 -3. 3 15316 -4. 1 15316 -4. 2 15316 -4. 3 15316 -4. 4 15316 -4. 5 15316 -4. 6 15316 -4. 7 DHW Boiler Heat pump Thermal solar Cogeneration District heating Photovoltaic Biomass (whole systems) Wgen, aux, chp Wgen, aux, dh Wgen, aux, pv WH, gen, aux Wsol, aux Auxiliary energy Wgen WW, gen, aux WHW, gen, aux System (generator) thermal losses Qgen, ls QW, gen, ls QHW, gen, ls Qsol, ls Qgen, ls, chp Qgen, ls, dh Qgen, ls, pv QH, gen, ls Recoverable system thermal losses Qgen, ls, rbl QW, gen, ls, rbl QH, gen, ls, rbl Qsol, ls, rbl Qgen, ls, rbl, chp Qgen, ls, rbl, dh Qgen, ls, rbl, pv QH, gen, ls, rbl Electricity production Eel, gen, out Not relevant Eel, chp, out Not relevant Eel, pv, out Not relevant Energy carrier (whole systems) fp, dh
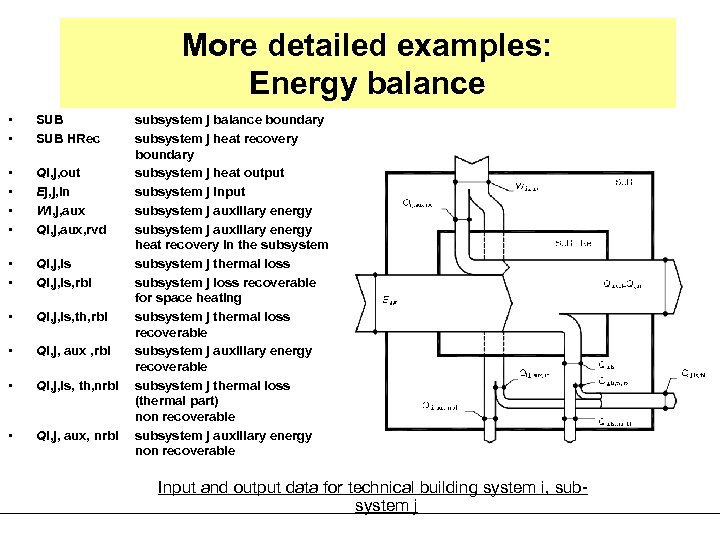
More detailed examples: Energy balance • • SUB HRec • • Qi, j, out Ej, j, in Wi, j, aux Qi, j, aux, rvd • • Qi, j, ls, rbl • Qi, j, ls, th, rbl • Qi, j, aux , rbl • Qi, j, ls, th, nrbl • Qi, j, aux, nrbl subsystem j balance boundary subsystem j heat recovery boundary subsystem j heat output subsystem j input subsystem j auxiliary energy heat recovery in the subsystem j thermal loss subsystem j loss recoverable for space heating subsystem j thermal loss recoverable subsystem j auxiliary energy recoverable subsystem j thermal loss (thermal part) non recoverable subsystem j auxiliary energy non recoverable Input and output data for technical building system i, subsystem j

Translations • Suggestion: to adopt the same set also in translated national standards – with English expression given as additional information, to explain the origin of the abbreviation • Example at next page
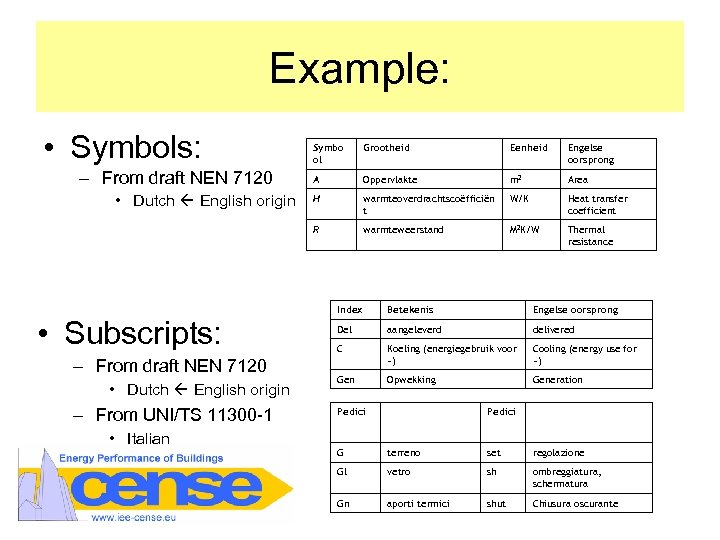
Example: • Symbols: • Dutch English origin • Subscripts: – From draft NEN 7120 • Dutch English origin – From UNI/TS 11300 -1 • Italian Grootheid Eenheid Engelse oorsprong A Oppervlakte m 2 Area H warmteoverdrachtscoëfficiën t W/K Heat transfer coefficient R – From draft NEN 7120 Symbo ol warmteweerstand M 2 K/W Thermal resistance Index Betekenis Engelse oorsprong Del aangeleverd delivered C Koeling (energiegebruik voor ~) Cooling (energy use for ~) Gen Opwekking Generation Pedici G terreno set regolazione Gl vetro sh ombreggiatura, schermatura Gn aporti termici shut Chiusura oscurante

Frequently Asked Questions • Are the common definitions given in CEN/TR 15615 mandatory? • Are the common symbols given in CEN/TR 15615 mandatory? • Why are the symbols in some of the EN ISO standards related to the EPBD not always the same as in the CEN standards to support the EPBD? r P 1 n Pape tio ma in Infor swers 54… n a See the slide 19

More information on this topic • P 154, Information paper on the common definitions and common symbols for EPBD related CEN standards, given in CEN Technical report CEN/TR 15615 ("Umbrella Document') • CEN Technical Report, CEN/TR 15615, Explanation of the general relationship between various European standards and the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) - Umbrella Document, April 2008 • Strongly related: Information Papers on the top level CEN standard EN 15603 (On assessment of overall energy performance): P 087, P 088 slide 20

More information and downloads: www. iee-cense. eu Disclaimer: CENSE has received funding from the Community’s Intelligent Energy Europe programme under the contract EIE/07/069/SI 2. 466698. The content of this presentation reflects the authors view. The author(s) and the European Commission are not liable for any use that may be made of the information contained therein. Moreover, because this is an interim result of the project: any conclusions are only preliminary and may change in the course of the project based on further feedback from the contributors, additional collected information and/or increased insight. slide 21
6d3603ef99f0943158cfb0002178a0ed.ppt