65c3a1efb56c205c13af4923d7cf7fce.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 The Common Assessment Framework (CAF) & Lead Professional (LP)
The Common Assessment Framework (CAF) & Lead Professional (LP)
 CAF & LP Awareness This is the awareness module for practitioners and managers delivering children and young people’s services in Lancashire. To complete this awareness raising module you should click through the main slides and these will give you the opportunity to get further information about CAF and Lead Professional. When you have gone through all the information you will need to complete the CAF/LP awareness checklist. The checklist will then be submitted and we will have records that you have completed CAF/LP awareness training. A confirmation of completion will also be provided for your records. Good Luck!
CAF & LP Awareness This is the awareness module for practitioners and managers delivering children and young people’s services in Lancashire. To complete this awareness raising module you should click through the main slides and these will give you the opportunity to get further information about CAF and Lead Professional. When you have gone through all the information you will need to complete the CAF/LP awareness checklist. The checklist will then be submitted and we will have records that you have completed CAF/LP awareness training. A confirmation of completion will also be provided for your records. Good Luck!
 Why CAF? -legislation The Common Assessment Framework and the Lead Professional are contributing elements to the delivery of integrated front line delivery of services, as outlined in the statutory guidance supporting section 10 (interagency cooperation) and section 11 (safeguarding and promoting the welfare of children) of the Children Act 2004.
Why CAF? -legislation The Common Assessment Framework and the Lead Professional are contributing elements to the delivery of integrated front line delivery of services, as outlined in the statutory guidance supporting section 10 (interagency cooperation) and section 11 (safeguarding and promoting the welfare of children) of the Children Act 2004.
 Why CAF – legislation • Section 10 of the Children Act 2004 places a duty on local authorities and their partners to co-operate in order to improve the well-being of children in that area. • The current government have removed the statutory duty to form Children’s Trusts, however Lancashire County Council has decided to continue to work with this model, with note to the guidance that describes the essential features of Children’s Trusts that will enable cooperation. • The CAF is one tool, along with the role of lead professional and information sharing guidance that supports the development of integrated working practices. • The CAF is an integral part of the plan to achieve Lancashire County Council’s Prevention and Early Intervention Strategic objectives. http: //www. lancashire. gov. uk/education/childrenstrusts/whats_involved/earl y_intervention/index. asp
Why CAF – legislation • Section 10 of the Children Act 2004 places a duty on local authorities and their partners to co-operate in order to improve the well-being of children in that area. • The current government have removed the statutory duty to form Children’s Trusts, however Lancashire County Council has decided to continue to work with this model, with note to the guidance that describes the essential features of Children’s Trusts that will enable cooperation. • The CAF is one tool, along with the role of lead professional and information sharing guidance that supports the development of integrated working practices. • The CAF is an integral part of the plan to achieve Lancashire County Council’s Prevention and Early Intervention Strategic objectives. http: //www. lancashire. gov. uk/education/childrenstrusts/whats_involved/earl y_intervention/index. asp
 Definitions The Common Assessment Framework (CAF) is a shared assessment, planning and reviewing tool for use across all Children’s Services in England. It: • is the key assessment process in context of Early Intervention. • supports early identification of additional need • promotes a co-ordinated approach to planned support • ensures a central record is kept to prevent duplication and facilitate communication
Definitions The Common Assessment Framework (CAF) is a shared assessment, planning and reviewing tool for use across all Children’s Services in England. It: • is the key assessment process in context of Early Intervention. • supports early identification of additional need • promotes a co-ordinated approach to planned support • ensures a central record is kept to prevent duplication and facilitate communication
 What does it do? • A national, more standardised approach to carry out an holistic assessment of children’s needs. • A means to support earlier identification and intervention by enabling practitioners to assess needs at an early stage and initiate a support plan. • A process for practitioners in all agencies so they can communicate more effectively, supporting inter-agency request of services and multi-agency working • An emerging ‘main method’ whereby needs are assessed by agencies, improving the coordination and consistency between assessment and reducing the number and scale of specialist assessments and duplication. • A supportive process – not another referral form
What does it do? • A national, more standardised approach to carry out an holistic assessment of children’s needs. • A means to support earlier identification and intervention by enabling practitioners to assess needs at an early stage and initiate a support plan. • A process for practitioners in all agencies so they can communicate more effectively, supporting inter-agency request of services and multi-agency working • An emerging ‘main method’ whereby needs are assessed by agencies, improving the coordination and consistency between assessment and reducing the number and scale of specialist assessments and duplication. • A supportive process – not another referral form
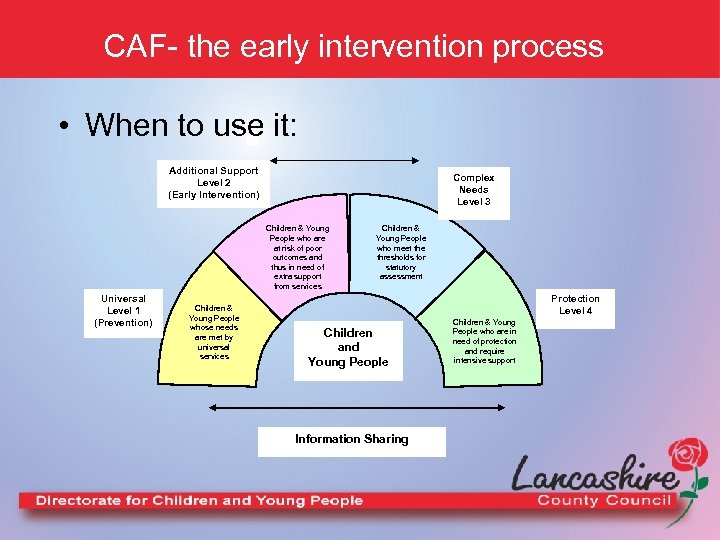 CAF- the early intervention process • When to use it: Additional Support Level 2 (Early Intervention) Complex Needs Level 3 Children & Young People who are at risk of poor outcomes and thus in need of extra support from services Universal Level 1 (Prevention) Children & Young People whose needs are met by universal services Children & Young People who meet the thresholds for statutory assessment Protection Level 4 Children and Young People Information Sharing Children & Young People who are in need of protection and require intensive support
CAF- the early intervention process • When to use it: Additional Support Level 2 (Early Intervention) Complex Needs Level 3 Children & Young People who are at risk of poor outcomes and thus in need of extra support from services Universal Level 1 (Prevention) Children & Young People whose needs are met by universal services Children & Young People who meet the thresholds for statutory assessment Protection Level 4 Children and Young People Information Sharing Children & Young People who are in need of protection and require intensive support
 When to use it… When a practitioner identifies that a child has got additional needs that cannot be met through universal services a CAF assessment should be actioned. Only once a full holistic assessment has been completed can an informed and confident decision on the appropriate support to meet identified needs be made. CAF can be used with any unborn baby, new baby, child or young person up to age 18 who has additional, unmet needs. In specific circumstances CAF may be used to support the transition into adult services. If at any stage of the process you suspect a child is being abused, at risk of being abused, self-harm or at risk or high risk of harming other follow safeguarding procedures
When to use it… When a practitioner identifies that a child has got additional needs that cannot be met through universal services a CAF assessment should be actioned. Only once a full holistic assessment has been completed can an informed and confident decision on the appropriate support to meet identified needs be made. CAF can be used with any unborn baby, new baby, child or young person up to age 18 who has additional, unmet needs. In specific circumstances CAF may be used to support the transition into adult services. If at any stage of the process you suspect a child is being abused, at risk of being abused, self-harm or at risk or high risk of harming other follow safeguarding procedures
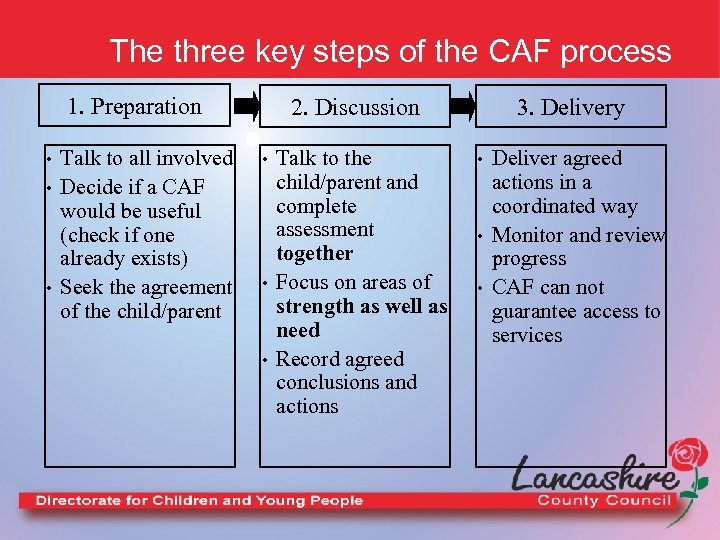 The three key steps of the CAF process 1. Preparation • • • Talk to all involved Decide if a CAF would be useful (check if one already exists) Seek the agreement of the child/parent 2. Discussion • • • Talk to the child/parent and complete assessment together Focus on areas of strength as well as need Record agreed conclusions and actions 3. Delivery • • • Deliver agreed actions in a coordinated way Monitor and review progress CAF can not guarantee access to services
The three key steps of the CAF process 1. Preparation • • • Talk to all involved Decide if a CAF would be useful (check if one already exists) Seek the agreement of the child/parent 2. Discussion • • • Talk to the child/parent and complete assessment together Focus on areas of strength as well as need Record agreed conclusions and actions 3. Delivery • • • Deliver agreed actions in a coordinated way Monitor and review progress CAF can not guarantee access to services
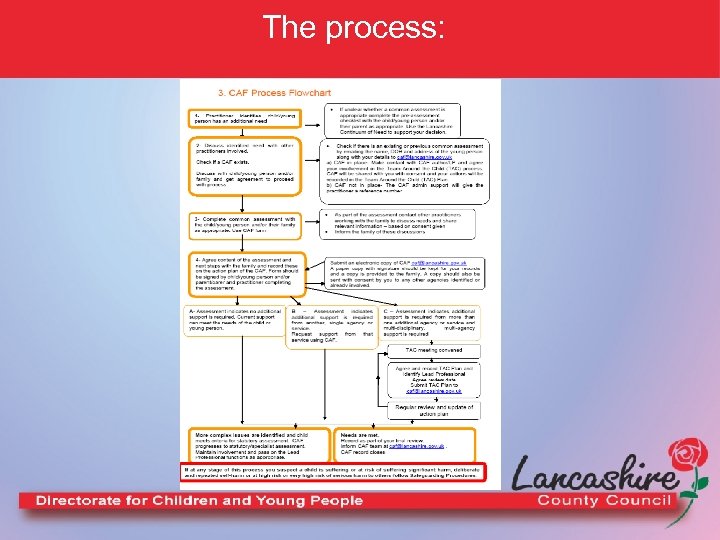 The process:
The process:
 Who will use the CAF? Every practitioner should: § Be able to recognise and respond to key signs of need § Have Knowledge of the Common Assessment Framework § Know how to complete a common assessment or who to contact in their agency to initiate one Every agency will train some staff to complete common assessments. Where more than one practitioner is involved with a child or young person, one will take the lead
Who will use the CAF? Every practitioner should: § Be able to recognise and respond to key signs of need § Have Knowledge of the Common Assessment Framework § Know how to complete a common assessment or who to contact in their agency to initiate one Every agency will train some staff to complete common assessments. Where more than one practitioner is involved with a child or young person, one will take the lead
 The lead professional role The lead professional (LP) is someone who takes the lead to co-ordinate provision and be a single point of contact for a child and their family, when a range of services are involved an integrated response is required. How to select – Ask the child and family; the CAF process is about listening to them and meeting their needs. Consider existing relationships and needs. The lead professional is not responsible or accountable for services delivered by other services.
The lead professional role The lead professional (LP) is someone who takes the lead to co-ordinate provision and be a single point of contact for a child and their family, when a range of services are involved an integrated response is required. How to select – Ask the child and family; the CAF process is about listening to them and meeting their needs. Consider existing relationships and needs. The lead professional is not responsible or accountable for services delivered by other services.
 Vision and functions of lead professional Vision: All children and young people with additional needs who require support from more than one practitioner should experience a seamless and effective service in which one practitioner takes a lead role to ensure that services are co-ordinated, coherent and achieving intended outcomes Core Functions Act as a single point of contact for the child or family Co-ordinate the delivery of actions agreed by the practitioners involved Reduce overlap and inconsistency in the services received
Vision and functions of lead professional Vision: All children and young people with additional needs who require support from more than one practitioner should experience a seamless and effective service in which one practitioner takes a lead role to ensure that services are co-ordinated, coherent and achieving intended outcomes Core Functions Act as a single point of contact for the child or family Co-ordinate the delivery of actions agreed by the practitioners involved Reduce overlap and inconsistency in the services received
 Selecting a lead professional The lead professional could be drawn from any of the people currently involved with the child or young person, and could be from either the statutory or voluntary sector. The lead professional should be the practitioner who is most relevant to the child or young person’s action plan and who has the most appropriate skills. This is not necessarily the first person to be involved with the child or young person nor the practitioner who carries out the common assessment. Deciding who is to be the lead professional can be done most effectively as part of the assessment and planning process.
Selecting a lead professional The lead professional could be drawn from any of the people currently involved with the child or young person, and could be from either the statutory or voluntary sector. The lead professional should be the practitioner who is most relevant to the child or young person’s action plan and who has the most appropriate skills. This is not necessarily the first person to be involved with the child or young person nor the practitioner who carries out the common assessment. Deciding who is to be the lead professional can be done most effectively as part of the assessment and planning process.
 Selection criteria • Criteria for selection could include: – the predominant needs of the child or family; – the level of trust built up and the existing or potential relationship with the child or family; – the wishes of the child or family; – primary or statutory responsibility for the work; and – the knowledge, skills, ability and capacity of the involved practitioners.
Selection criteria • Criteria for selection could include: – the predominant needs of the child or family; – the level of trust built up and the existing or potential relationship with the child or family; – the wishes of the child or family; – primary or statutory responsibility for the work; and – the knowledge, skills, ability and capacity of the involved practitioners.
 Key Accountabilities Each lead professional is accountable to their home agency for delivery of: – their part of the action plan; and – the lead professional functions The lead professional is not responsible or accountable for services delivered by other services. The lead professional will be responsible for gathering people together to review progress but it is up to the individuals to deliver on their agreed actions. A clear line of accountability for lead professionals would run from the practitioner, through their line management to the children’s trust arrangements.
Key Accountabilities Each lead professional is accountable to their home agency for delivery of: – their part of the action plan; and – the lead professional functions The lead professional is not responsible or accountable for services delivered by other services. The lead professional will be responsible for gathering people together to review progress but it is up to the individuals to deliver on their agreed actions. A clear line of accountability for lead professionals would run from the practitioner, through their line management to the children’s trust arrangements.
 Useful skills for lead professional functions Understand boundaries of own skills and knowledge Strong communication skills; diplomacy; sensitivity Knowledge of local and regional services for children and families Convene meetings and initiate discussions with relevant practitioners Establish a successful and trusting relationship with child/family Empower child/family to make decisions and challenge when appropriate Understand implications of the child’s assessment, for example in relation to risks and protective factors Work effectively Support and with practitioners from enable child / family a range of services to achieve their potential
Useful skills for lead professional functions Understand boundaries of own skills and knowledge Strong communication skills; diplomacy; sensitivity Knowledge of local and regional services for children and families Convene meetings and initiate discussions with relevant practitioners Establish a successful and trusting relationship with child/family Empower child/family to make decisions and challenge when appropriate Understand implications of the child’s assessment, for example in relation to risks and protective factors Work effectively Support and with practitioners from enable child / family a range of services to achieve their potential
 Further information More information about CAF/LP: www. everychildmatters. gov. uk www. cwdcouncil. org. uk/projects/integratedworking. htm Lancashire County Council Website gives further information and documentation regarding the Common Assessment Framework: www. lancashire. gov. uk/education/childrenstrusts/whatsinvol ved/caf/index. asp
Further information More information about CAF/LP: www. everychildmatters. gov. uk www. cwdcouncil. org. uk/projects/integratedworking. htm Lancashire County Council Website gives further information and documentation regarding the Common Assessment Framework: www. lancashire. gov. uk/education/childrenstrusts/whatsinvol ved/caf/index. asp
 Conclusion You have now gone through all the basic information about CAF and lead professional. Please complete the checklist and submit it. Thanks for completing the CAF/LP awareness module on line. On line checklist If you are experiencing difficulty accessing the Online checklist try copying the url below and pasting it into the address bar at the top of your browser window http: //forms. lancashire. gov. uk/AF 3/an/default. aspx/Render. Form/? F. Name=hs 8 U 2 amy. DPD
Conclusion You have now gone through all the basic information about CAF and lead professional. Please complete the checklist and submit it. Thanks for completing the CAF/LP awareness module on line. On line checklist If you are experiencing difficulty accessing the Online checklist try copying the url below and pasting it into the address bar at the top of your browser window http: //forms. lancashire. gov. uk/AF 3/an/default. aspx/Render. Form/? F. Name=hs 8 U 2 amy. DPD


