d776ca4d08b982e8266a522645974cae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
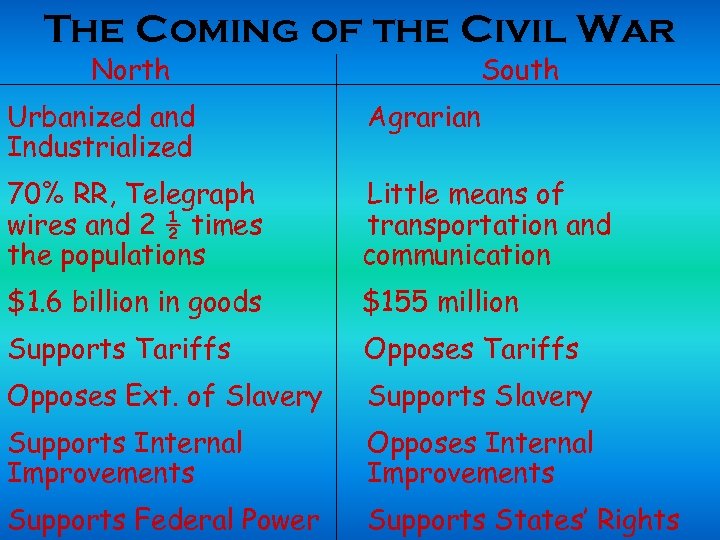 The Coming of the Civil War North South Urbanized and Industrialized Agrarian 70% RR, Telegraph wires and 2 ½ times the populations Little means of transportation and communication $1. 6 billion in goods $155 million Supports Tariffs Opposes Ext. of Slavery Supports Internal Improvements Opposes Internal Improvements Supports Federal Power Supports States’ Rights
The Coming of the Civil War North South Urbanized and Industrialized Agrarian 70% RR, Telegraph wires and 2 ½ times the populations Little means of transportation and communication $1. 6 billion in goods $155 million Supports Tariffs Opposes Ext. of Slavery Supports Internal Improvements Opposes Internal Improvements Supports Federal Power Supports States’ Rights
 The Civil War and Reconstruction
The Civil War and Reconstruction
 The Civil War (1861 -1865) The Union vs. The Confederacy • Throughout the 1850 s, sectionalism increased in the United States • Westward expansion fueled this rivalry between the sections because both free and slaves states were trying to increase their political power and control in Washington • Several attempts at compromise between the two sections failed and increased the tensions • Eventually, all of this would lead to the Southern States seceding from the United States – This will start the Civil War
The Civil War (1861 -1865) The Union vs. The Confederacy • Throughout the 1850 s, sectionalism increased in the United States • Westward expansion fueled this rivalry between the sections because both free and slaves states were trying to increase their political power and control in Washington • Several attempts at compromise between the two sections failed and increased the tensions • Eventually, all of this would lead to the Southern States seceding from the United States – This will start the Civil War
 Failure of Compromise: The Compromise of 1850 -California Gold Rush 1849 - application for statehood - Balance of Power and statehood - Compromise: California Admitted as Free State, Utah and New Mexico have popular sovereignty, Fugitive Slave Act
Failure of Compromise: The Compromise of 1850 -California Gold Rush 1849 - application for statehood - Balance of Power and statehood - Compromise: California Admitted as Free State, Utah and New Mexico have popular sovereignty, Fugitive Slave Act
 Reaction to the Compromise of 1850 Fugitive Slave Act - - Slave catchers - Defiance and Riots Harriet Beecher Stowe – Uncle Tom’s Cabin - Family Life and Eliza - Uncle Tom and Simon Legree - 300, 000 copies in 1 st year Cannibal’s All! - Southern Response
Reaction to the Compromise of 1850 Fugitive Slave Act - - Slave catchers - Defiance and Riots Harriet Beecher Stowe – Uncle Tom’s Cabin - Family Life and Eliza - Uncle Tom and Simon Legree - 300, 000 copies in 1 st year Cannibal’s All! - Southern Response
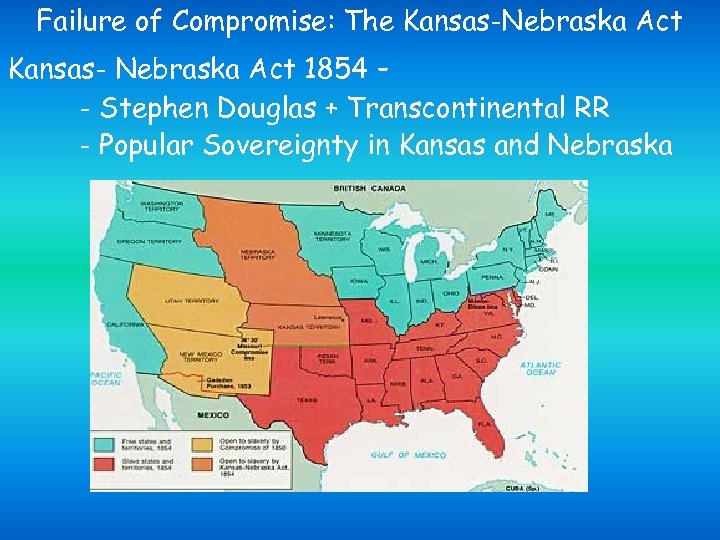 Failure of Compromise: The Kansas-Nebraska Act Kansas- Nebraska Act 1854 – - Stephen Douglas + Transcontinental RR - Popular Sovereignty in Kansas and Nebraska
Failure of Compromise: The Kansas-Nebraska Act Kansas- Nebraska Act 1854 – - Stephen Douglas + Transcontinental RR - Popular Sovereignty in Kansas and Nebraska
 Reaction to the Kansas-Nebraska Act 1. Bleeding Kansas - Free-Soilers and Pro-slavers (Missouri) - Two Constitutions and two capitals -Attack on Lawrence -John Brown and Pottawatomie Massacre -$2 mil in damages -200 people killed
Reaction to the Kansas-Nebraska Act 1. Bleeding Kansas - Free-Soilers and Pro-slavers (Missouri) - Two Constitutions and two capitals -Attack on Lawrence -John Brown and Pottawatomie Massacre -$2 mil in damages -200 people killed
 Reaction to the Kansas-Nebraska Act 2. Bleeding Sumner - Charles Sumner, Andrew Butler, and Preston Brooks 3. Republican Party Organized - Free Soil Platform
Reaction to the Kansas-Nebraska Act 2. Bleeding Sumner - Charles Sumner, Andrew Butler, and Preston Brooks 3. Republican Party Organized - Free Soil Platform
 The End of Compromise: The Dred Scott Decision Dred Scott v. Sanford – 1857 - Free Territory in Minnesota - Sued for his freedom Decision: - Slaves are property - 5 th Amendment - Missouri Compromise Unconstitutional - Federal Government cannot ban slavery in the territories
The End of Compromise: The Dred Scott Decision Dred Scott v. Sanford – 1857 - Free Territory in Minnesota - Sued for his freedom Decision: - Slaves are property - 5 th Amendment - Missouri Compromise Unconstitutional - Federal Government cannot ban slavery in the territories
 John Brown’s Raid – 1859 - Harpers Ferry Arsenal - Robert E Lee - Brown was convicted of treason + hanged - North considered him a martyr "Now, if it is deemed necessary that I should forfeit my life for the furtherance of the ends of justice, and mingle my blood further with the blood of millions in this slave country whose rights are disregarded by wicked, cruel, and unjust enactments, I say, let it be done. " -John Brown, statement at his sentencing on Nov. 2, 1859
John Brown’s Raid – 1859 - Harpers Ferry Arsenal - Robert E Lee - Brown was convicted of treason + hanged - North considered him a martyr "Now, if it is deemed necessary that I should forfeit my life for the furtherance of the ends of justice, and mingle my blood further with the blood of millions in this slave country whose rights are disregarded by wicked, cruel, and unjust enactments, I say, let it be done. " -John Brown, statement at his sentencing on Nov. 2, 1859
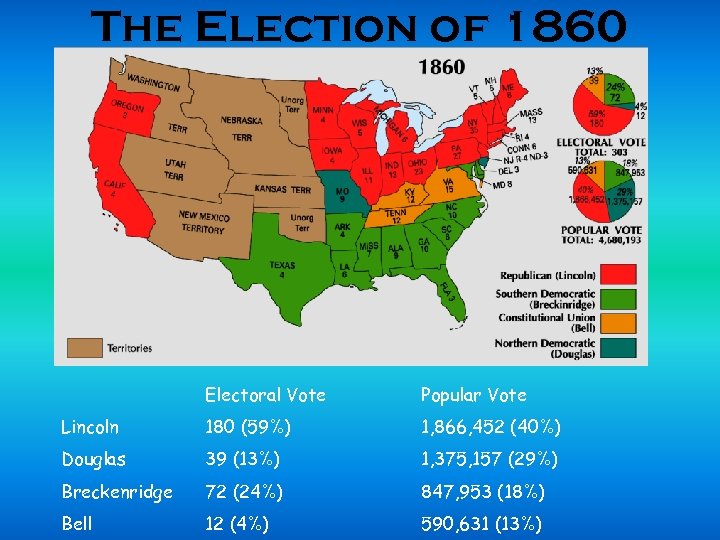 The Election of 1860 Electoral Vote Popular Vote Lincoln 180 (59%) 1, 866, 452 (40%) Douglas 39 (13%) 1, 375, 157 (29%) Breckenridge 72 (24%) 847, 953 (18%) Bell 12 (4%) 590, 631 (13%)
The Election of 1860 Electoral Vote Popular Vote Lincoln 180 (59%) 1, 866, 452 (40%) Douglas 39 (13%) 1, 375, 157 (29%) Breckenridge 72 (24%) 847, 953 (18%) Bell 12 (4%) 590, 631 (13%)
 Secession of the Southern States Lincoln’s Election - Free Soil Ideology Southern Response: - 12/20/60 – South Carolina Secedes - Miss, Fla, Ala, Geo, Lou, Texas follow - Crittenden Compromise - Feb 1861 – Confederate States of America - Jefferson Davis elected President Lincoln Comes to Power – March 1861 - Fort Sumter, South Carolina - Preserve the Union, secession is not constitutional - April 12, 1861 - Attack on Fort Sumter - Lincoln calls for volunteers - AK, TN, NC, VA all join the confederacy
Secession of the Southern States Lincoln’s Election - Free Soil Ideology Southern Response: - 12/20/60 – South Carolina Secedes - Miss, Fla, Ala, Geo, Lou, Texas follow - Crittenden Compromise - Feb 1861 – Confederate States of America - Jefferson Davis elected President Lincoln Comes to Power – March 1861 - Fort Sumter, South Carolina - Preserve the Union, secession is not constitutional - April 12, 1861 - Attack on Fort Sumter - Lincoln calls for volunteers - AK, TN, NC, VA all join the confederacy
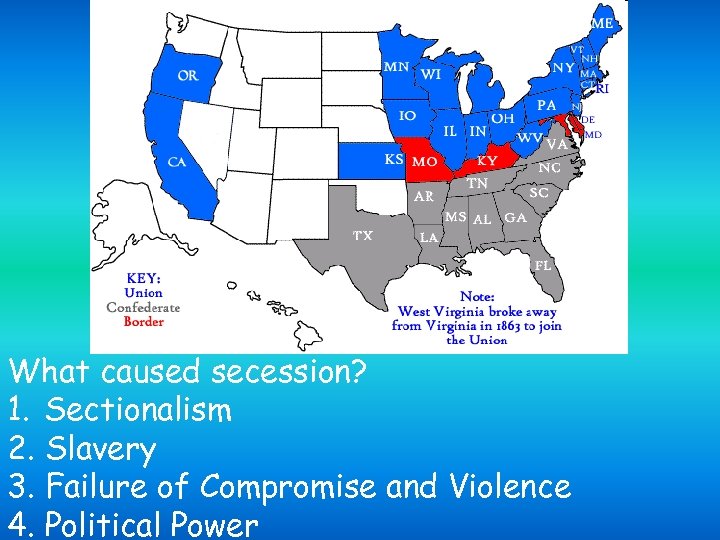 What caused secession? 1. Sectionalism 2. Slavery 3. Failure of Compromise and Violence 4. Political Power
What caused secession? 1. Sectionalism 2. Slavery 3. Failure of Compromise and Violence 4. Political Power
 Discuss the economic, political, and/or social differences between the North and the South that eventually led to the Civil War.
Discuss the economic, political, and/or social differences between the North and the South that eventually led to the Civil War.
 Discuss the economic, political, and/or social differences between the North and the South that eventually led to the Civil War.
Discuss the economic, political, and/or social differences between the North and the South that eventually led to the Civil War.
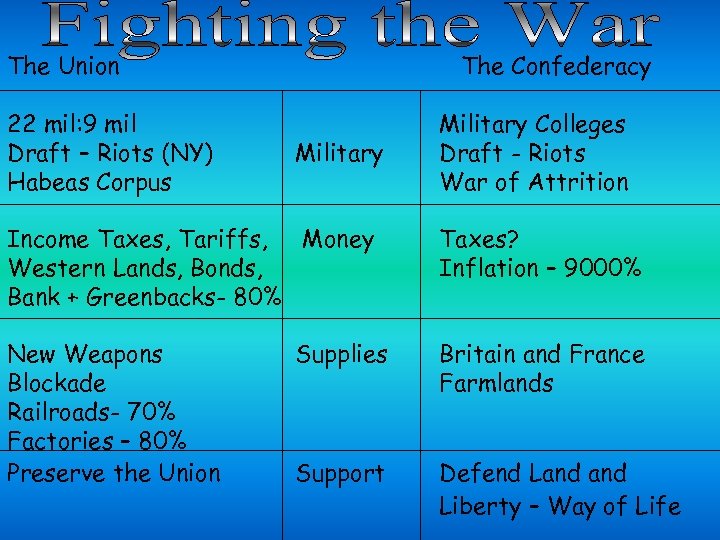 The Union 22 mil: 9 mil Draft – Riots (NY) Habeas Corpus The Confederacy Military Colleges Draft - Riots War of Attrition Income Taxes, Tariffs, Money Western Lands, Bonds, Bank + Greenbacks- 80% Taxes? Inflation – 9000% New Weapons Blockade Railroads- 70% Factories – 80% Preserve the Union Supplies Britain and France Farmlands Support Defend Land Liberty – Way of Life
The Union 22 mil: 9 mil Draft – Riots (NY) Habeas Corpus The Confederacy Military Colleges Draft - Riots War of Attrition Income Taxes, Tariffs, Money Western Lands, Bonds, Bank + Greenbacks- 80% Taxes? Inflation – 9000% New Weapons Blockade Railroads- 70% Factories – 80% Preserve the Union Supplies Britain and France Farmlands Support Defend Land Liberty – Way of Life
 The Emancipation Proclamation 1/1/63 – All slaves in rebel areas are free - Not Border States or Tennessee + Louisiana - Is this legal? Who is freed? What was the purpose of the Emancipation Proclamation? 1. Preserve the Union and stop the rebellion 2. Cause for the North – increased support 3. Harder for Confederates to fight 4. Britain and France? 5. Recruitment of black soldiers - 180, 000 – Massachusetts 54 th
The Emancipation Proclamation 1/1/63 – All slaves in rebel areas are free - Not Border States or Tennessee + Louisiana - Is this legal? Who is freed? What was the purpose of the Emancipation Proclamation? 1. Preserve the Union and stop the rebellion 2. Cause for the North – increased support 3. Harder for Confederates to fight 4. Britain and France? 5. Recruitment of black soldiers - 180, 000 – Massachusetts 54 th
 1861 - First Battle of Bull Run Anaconda Plan
1861 - First Battle of Bull Run Anaconda Plan
 Southern Victories - 1862 – Fredericksburg, 1863 – Chancellorsville Turning Point – July 4, 1863 - Robert E Lee – One more Victory - Gettysburg – 3 Day battle - Losses= N- 23, 000/ S- 28, 000 - Vicksburg – Mississippi River
Southern Victories - 1862 – Fredericksburg, 1863 – Chancellorsville Turning Point – July 4, 1863 - Robert E Lee – One more Victory - Gettysburg – 3 Day battle - Losses= N- 23, 000/ S- 28, 000 - Vicksburg – Mississippi River
 -Sherman – Atlanta and The March to the Sea - ‘War is all Hell’ – Sherman Bowties, Sherman stacks
-Sherman – Atlanta and The March to the Sea - ‘War is all Hell’ – Sherman Bowties, Sherman stacks
 - Ulysses S Grant + Virginia Campaign -April 9, 1865 – Appomattox Court House Surrender - Lincoln - Reelected in 1864 - 1865 – 13 th Amendment - April 14, 1865 – Lincoln’s Assassination
- Ulysses S Grant + Virginia Campaign -April 9, 1865 – Appomattox Court House Surrender - Lincoln - Reelected in 1864 - 1865 – 13 th Amendment - April 14, 1865 – Lincoln’s Assassination
 -Railroads, Cities, and Industry destroyed, Farmland burned -Casualties – 364, 000 N + 260, 000 S (1/5) -Plantation owners lost $3 billion in property - Freedmen – homeless, jobless, hungry, uneducated -Divided country - New President – Andrew Johnson Plans to repair the South and return the southern states to the Union were called Reconstruction.
-Railroads, Cities, and Industry destroyed, Farmland burned -Casualties – 364, 000 N + 260, 000 S (1/5) -Plantation owners lost $3 billion in property - Freedmen – homeless, jobless, hungry, uneducated -Divided country - New President – Andrew Johnson Plans to repair the South and return the southern states to the Union were called Reconstruction.
 Lincoln and Johnson’s Plan -Pardoned all southerners who swore allegiance - Iron Clad Oath -Once 10%/50% did states could have constitutional conventions -New constitutions had to void secession, abolish slavery, and ratify 13 th amendment -Then could hold elections and resume participation in Union -Freedmen’s Bureau
Lincoln and Johnson’s Plan -Pardoned all southerners who swore allegiance - Iron Clad Oath -Once 10%/50% did states could have constitutional conventions -New constitutions had to void secession, abolish slavery, and ratify 13 th amendment -Then could hold elections and resume participation in Union -Freedmen’s Bureau
 Problems with Presidential Reconstruction 1. Ex-Confederates elected to Congress – 1865 - 6 Cabinet Members, 4 Confederate Generals, 50 Congressmen and Senators, The Vice President of the Confederacy 2. Black Codes – Curfews, Labor Contracts, Vagrancy, Unemployment The Black Codes: In what ways were the black codes similar to the rules that regulated behavior during slavery? Who was in charge of executing these laws? What were the punishments for violating these codes? What impression did these codes give Northerners? Why were northerners outraged?
Problems with Presidential Reconstruction 1. Ex-Confederates elected to Congress – 1865 - 6 Cabinet Members, 4 Confederate Generals, 50 Congressmen and Senators, The Vice President of the Confederacy 2. Black Codes – Curfews, Labor Contracts, Vagrancy, Unemployment The Black Codes: In what ways were the black codes similar to the rules that regulated behavior during slavery? Who was in charge of executing these laws? What were the punishments for violating these codes? What impression did these codes give Northerners? Why were northerners outraged?
 - Radical Republicans elected to Congress – They will take over reconstruction plans (Radical/Congressional Reconstruction) - All Southern states were thrown back out of the union and Congress will take over Reconstruction -Passed 14 th Amendment – equal protection of the laws and citizenship -Military Reconstruction Act of 1867 - South divided into five military districts- martial law - Each under control of a General who oversaw the reconstruction of the district - had to write constitution that ratified 13 th and 14 th amendments and give all adult males the right to vote - Once reenter union – southerners who supported the confederacy could not vote
- Radical Republicans elected to Congress – They will take over reconstruction plans (Radical/Congressional Reconstruction) - All Southern states were thrown back out of the union and Congress will take over Reconstruction -Passed 14 th Amendment – equal protection of the laws and citizenship -Military Reconstruction Act of 1867 - South divided into five military districts- martial law - Each under control of a General who oversaw the reconstruction of the district - had to write constitution that ratified 13 th and 14 th amendments and give all adult males the right to vote - Once reenter union – southerners who supported the confederacy could not vote
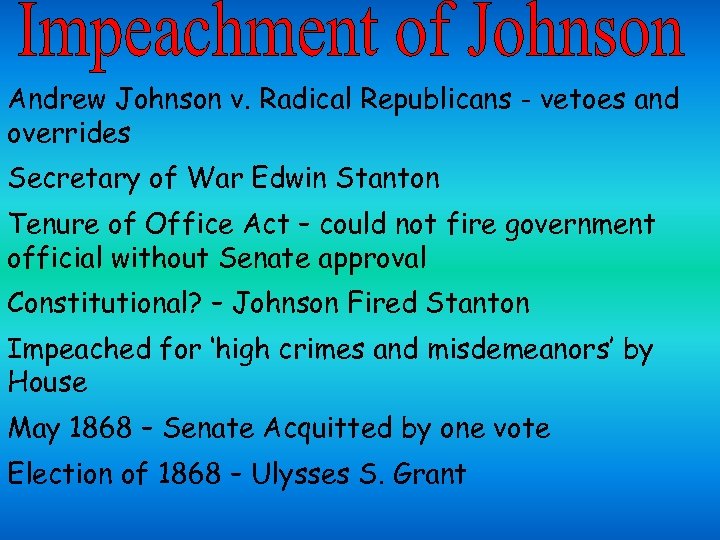 Andrew Johnson v. Radical Republicans - vetoes and overrides Secretary of War Edwin Stanton Tenure of Office Act – could not fire government official without Senate approval Constitutional? – Johnson Fired Stanton Impeached for ‘high crimes and misdemeanors’ by House May 1868 – Senate Acquitted by one vote Election of 1868 – Ulysses S. Grant
Andrew Johnson v. Radical Republicans - vetoes and overrides Secretary of War Edwin Stanton Tenure of Office Act – could not fire government official without Senate approval Constitutional? – Johnson Fired Stanton Impeached for ‘high crimes and misdemeanors’ by House May 1868 – Senate Acquitted by one vote Election of 1868 – Ulysses S. Grant
 Congressional Reconstruction National Economy + Internal Improvements - National Banking System - Internal Improvements: Transcontinental Railroad and Land Grants- 1867 - Homestead Act Rebuilding the South - Carpetbaggers and Scalawags - Republicans - Industry and Transportation - Public Education Rights for Freedmen - 13 th, 14 th, 15 th Amendments - Freedmen’s Bureau - KKK Acts
Congressional Reconstruction National Economy + Internal Improvements - National Banking System - Internal Improvements: Transcontinental Railroad and Land Grants- 1867 - Homestead Act Rebuilding the South - Carpetbaggers and Scalawags - Republicans - Industry and Transportation - Public Education Rights for Freedmen - 13 th, 14 th, 15 th Amendments - Freedmen’s Bureau - KKK Acts
 Election of 1876 - Rutherford B Hayes v. Samuel Tilden - Compromise of 1877 – Remove troops from the South Redeemers – take back control of the South - Jim Crow Laws – Segregation - Voting Restrictions – Poll Taxes, Literacy Tests, Grandfather Clauses - KKK, White League, Lynching - Sharecropping and Tenant Farming – Crop Lien System
Election of 1876 - Rutherford B Hayes v. Samuel Tilden - Compromise of 1877 – Remove troops from the South Redeemers – take back control of the South - Jim Crow Laws – Segregation - Voting Restrictions – Poll Taxes, Literacy Tests, Grandfather Clauses - KKK, White League, Lynching - Sharecropping and Tenant Farming – Crop Lien System
 Positive Results: - Union restored - Southern Industry and Transportation - Federal Gov’t power increased – role in economy and protection of minority rights (13 th, 14 th, 15 th) Negative Results: - Cycle of Poverty for Blacks – Tenant Farming and Sharecropping- Crop Lien - Redeemers – Gov’t in South - Racism and Rights – KKK, Jim Crow Laws, voting restrictions
Positive Results: - Union restored - Southern Industry and Transportation - Federal Gov’t power increased – role in economy and protection of minority rights (13 th, 14 th, 15 th) Negative Results: - Cycle of Poverty for Blacks – Tenant Farming and Sharecropping- Crop Lien - Redeemers – Gov’t in South - Racism and Rights – KKK, Jim Crow Laws, voting restrictions


