fa59a49d897bcb3a241e9742758c9509.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78
 The Cold War: To what extent did ideological conflict affect international relations after the second world war? “It’s Iced Out Like A Freezer” Also “It’s Cooler than a Polar Bear’s Toenails”
The Cold War: To what extent did ideological conflict affect international relations after the second world war? “It’s Iced Out Like A Freezer” Also “It’s Cooler than a Polar Bear’s Toenails”
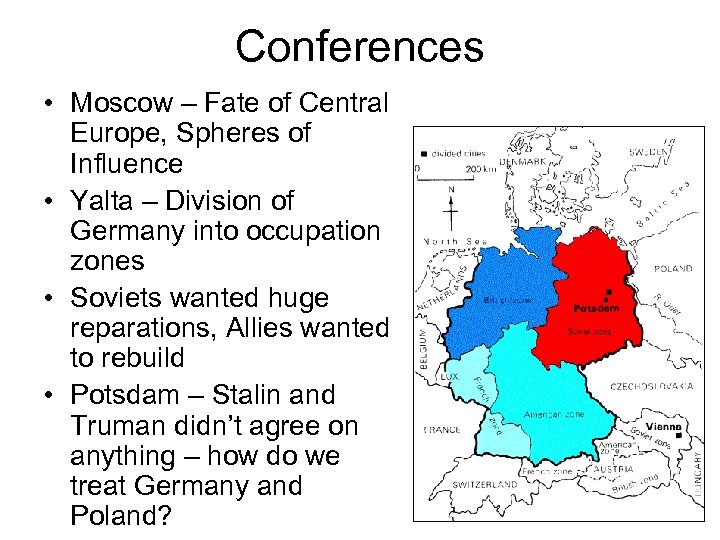 Conferences • Moscow – Fate of Central Europe, Spheres of Influence • Yalta – Division of Germany into occupation zones • Soviets wanted huge reparations, Allies wanted to rebuild • Potsdam – Stalin and Truman didn’t agree on anything – how do we treat Germany and Poland?
Conferences • Moscow – Fate of Central Europe, Spheres of Influence • Yalta – Division of Germany into occupation zones • Soviets wanted huge reparations, Allies wanted to rebuild • Potsdam – Stalin and Truman didn’t agree on anything – how do we treat Germany and Poland?
 Alliances of Cold War USA (Democratic/Capitalists USSR (Communist/CPE) Political: Truman Doctrine Economic: Marshal Plan Military: NATO (Europe&NA) SEATO ( S. E. Asia) • Political: Cominform • Economic: Comecon • Military: Warsaw Pact ANZUS(Aust/NZ/US) NORAD (US& Can. )
Alliances of Cold War USA (Democratic/Capitalists USSR (Communist/CPE) Political: Truman Doctrine Economic: Marshal Plan Military: NATO (Europe&NA) SEATO ( S. E. Asia) • Political: Cominform • Economic: Comecon • Military: Warsaw Pact ANZUS(Aust/NZ/US) NORAD (US& Can. )
 • • • • Events of Cold War Germany Issue Poland Issue-Containment of Communism of the USSR by USA Iran Issue –Truman Doctrine Turkey Greece-Marshal Plan Berlin Blockade-Iron Curtain-Berlin Wall 1945 -1948 Rejection to Illiberalism of the USSR – Hungarian Revolution of 1956 – Czechoslovakian Uprising: Prague Spring 1968 – Yugoslavia: Tito’s Defense Alignment: Whose is whose ally? Non-Alignment and Bandung Conference Détente to Deterence Canada in the Cold War France’s Dissuasion Policy Brinkmanship
• • • • Events of Cold War Germany Issue Poland Issue-Containment of Communism of the USSR by USA Iran Issue –Truman Doctrine Turkey Greece-Marshal Plan Berlin Blockade-Iron Curtain-Berlin Wall 1945 -1948 Rejection to Illiberalism of the USSR – Hungarian Revolution of 1956 – Czechoslovakian Uprising: Prague Spring 1968 – Yugoslavia: Tito’s Defense Alignment: Whose is whose ally? Non-Alignment and Bandung Conference Détente to Deterence Canada in the Cold War France’s Dissuasion Policy Brinkmanship
 GERMANY ISSUE • Allied Control Council – Management of Germany • West Berlin in middle of East Germany • Balance of Power – Equilibrium of alliances – checks on any one nation becoming too powerful • Sphere of Influence – extent to which a nation exerts influence beyond its own borders • Bipolar – world polarizes to USA+allies vs. USSR+allies
GERMANY ISSUE • Allied Control Council – Management of Germany • West Berlin in middle of East Germany • Balance of Power – Equilibrium of alliances – checks on any one nation becoming too powerful • Sphere of Influence – extent to which a nation exerts influence beyond its own borders • Bipolar – world polarizes to USA+allies vs. USSR+allies
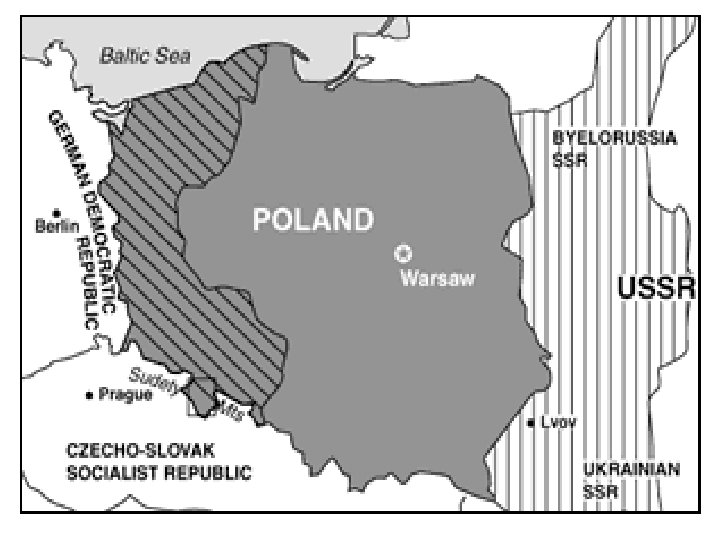
 Polish Question • What to do with Poland? • Who will govern, and where will borders go? • Government-in-exile in London – supported by West • Soviet puppet government in Lublin – suppressed freedoms (Poland in Soviet Sphere of Influence) • Soviet border moves USSR border further west, Poland compensated with German territory • West doesn’t really like it but not in a position to challenge
Polish Question • What to do with Poland? • Who will govern, and where will borders go? • Government-in-exile in London – supported by West • Soviet puppet government in Lublin – suppressed freedoms (Poland in Soviet Sphere of Influence) • Soviet border moves USSR border further west, Poland compensated with German territory • West doesn’t really like it but not in a position to challenge
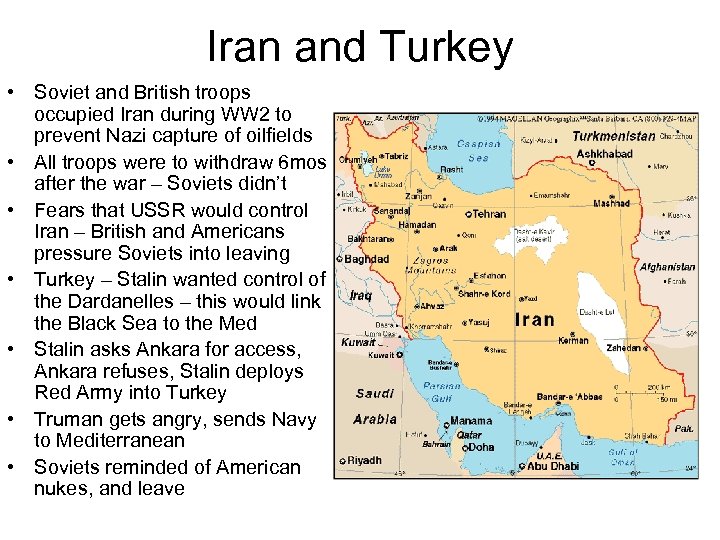 Iran and Turkey • Soviet and British troops occupied Iran during WW 2 to prevent Nazi capture of oilfields • All troops were to withdraw 6 mos after the war – Soviets didn’t • Fears that USSR would control Iran – British and Americans pressure Soviets into leaving • Turkey – Stalin wanted control of the Dardanelles – this would link the Black Sea to the Med • Stalin asks Ankara for access, Ankara refuses, Stalin deploys Red Army into Turkey • Truman gets angry, sends Navy to Mediterranean • Soviets reminded of American nukes, and leave
Iran and Turkey • Soviet and British troops occupied Iran during WW 2 to prevent Nazi capture of oilfields • All troops were to withdraw 6 mos after the war – Soviets didn’t • Fears that USSR would control Iran – British and Americans pressure Soviets into leaving • Turkey – Stalin wanted control of the Dardanelles – this would link the Black Sea to the Med • Stalin asks Ankara for access, Ankara refuses, Stalin deploys Red Army into Turkey • Truman gets angry, sends Navy to Mediterranean • Soviets reminded of American nukes, and leave
 Map of Turkey
Map of Turkey
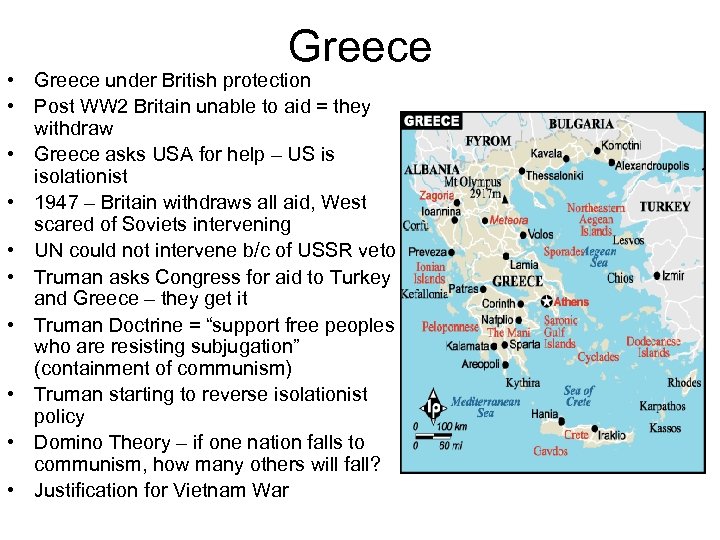 Greece • Greece under British protection • Post WW 2 Britain unable to aid = they withdraw • Greece asks USA for help – US is isolationist • 1947 – Britain withdraws all aid, West scared of Soviets intervening • UN could not intervene b/c of USSR veto • Truman asks Congress for aid to Turkey and Greece – they get it • Truman Doctrine = “support free peoples who are resisting subjugation” (containment of communism) • Truman starting to reverse isolationist policy • Domino Theory – if one nation falls to communism, how many others will fall? • Justification for Vietnam War
Greece • Greece under British protection • Post WW 2 Britain unable to aid = they withdraw • Greece asks USA for help – US is isolationist • 1947 – Britain withdraws all aid, West scared of Soviets intervening • UN could not intervene b/c of USSR veto • Truman asks Congress for aid to Turkey and Greece – they get it • Truman Doctrine = “support free peoples who are resisting subjugation” (containment of communism) • Truman starting to reverse isolationist policy • Domino Theory – if one nation falls to communism, how many others will fall? • Justification for Vietnam War
 • The Domino Theory
• The Domino Theory
 Stalin is an… Octopus?
Stalin is an… Octopus?
 Marshall Plan • Americans were scared of Soviet expansion into Western Europe • Best defence was to strengthen their economies • Economic aid to Turkey and Greece under the Truman Doctrine is expanded to Western Europe by the Marshall Plan • Soviets were in a recession but US economy boomed – resulting trade + Marshall Plan brought Western Europe close to USA and away from Eastern Europe
Marshall Plan • Americans were scared of Soviet expansion into Western Europe • Best defence was to strengthen their economies • Economic aid to Turkey and Greece under the Truman Doctrine is expanded to Western Europe by the Marshall Plan • Soviets were in a recession but US economy boomed – resulting trade + Marshall Plan brought Western Europe close to USA and away from Eastern Europe


 Berlin: 1945 -1949 • West Berlin: Thorn in Moscow’s side • Marshall Plan aid to West Germany means its economy was doing quite well • Soviets pillaged East Germany in order to bolster domestic economy • Spring 1948: Soviets block all access to Berlin – they feared a united Western Germany and wanted to push the Allies out of Berlin, also, the Allies won’t go to war over the enemy’s capital • Allies decide to supply Berlin by air – if Berlin falls, West Germany could fall, etc.
Berlin: 1945 -1949 • West Berlin: Thorn in Moscow’s side • Marshall Plan aid to West Germany means its economy was doing quite well • Soviets pillaged East Germany in order to bolster domestic economy • Spring 1948: Soviets block all access to Berlin – they feared a united Western Germany and wanted to push the Allies out of Berlin, also, the Allies won’t go to war over the enemy’s capital • Allies decide to supply Berlin by air – if Berlin falls, West Germany could fall, etc.
 • Americans, British airlift food, supplies to the city for nearly a year • Food consumption drops, energy requirements met by cutting trees in the city • Extremely stressful flying conditions – planes landed up to once every three minutes • To prevent the Soviets from shooting down cargo planes, US stationed B 29 s in Britain: nuclear monopoly • Blockade ineffective – lifted in May 1949 • British, US, French zones merge, become Federal Republic of Germany anyway -1949 • Soviet zone becomes Democratic Republic of Germany (DDR)
• Americans, British airlift food, supplies to the city for nearly a year • Food consumption drops, energy requirements met by cutting trees in the city • Extremely stressful flying conditions – planes landed up to once every three minutes • To prevent the Soviets from shooting down cargo planes, US stationed B 29 s in Britain: nuclear monopoly • Blockade ineffective – lifted in May 1949 • British, US, French zones merge, become Federal Republic of Germany anyway -1949 • Soviet zone becomes Democratic Republic of Germany (DDR)
 Berlin Blockade
Berlin Blockade
 European Containment
European Containment
 Super Power Dance?
Super Power Dance?
 Berlin Blockade
Berlin Blockade
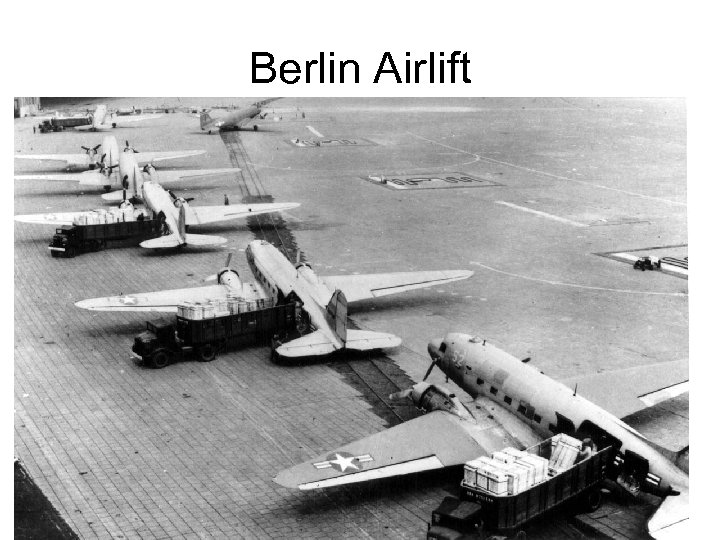 Berlin Airlift
Berlin Airlift
 Stalin’s Move over Europe
Stalin’s Move over Europe
 Rejections to Illiberalism of the USSR – Hungarian Revolution of 1956 – Czechoslovakian Uprising: Prague Spring 1968 – Yugoslavia: Tito’s Defense • Tito – A man Unwilling to accept Being pushed Around by Moscow
Rejections to Illiberalism of the USSR – Hungarian Revolution of 1956 – Czechoslovakian Uprising: Prague Spring 1968 – Yugoslavia: Tito’s Defense • Tito – A man Unwilling to accept Being pushed Around by Moscow
 Poland Hungary Labour unrest becomes wish for political freedom Gomulka gets elected – national communism – Khrushchev doesn’t go to war with him – Poland gains some freedom from USSR Hungary sees this and decides to try the same Hungary becomes communist after WW 2 – hard-line Stalinist in power = repression and poor living standards
Poland Hungary Labour unrest becomes wish for political freedom Gomulka gets elected – national communism – Khrushchev doesn’t go to war with him – Poland gains some freedom from USSR Hungary sees this and decides to try the same Hungary becomes communist after WW 2 – hard-line Stalinist in power = repression and poor living standards
 Czechoslovakia • 1946 – Communist PM elected in Czechoslovakia • Wanted Marshall Plan aid but Moscow ordered them to refuse • Tried to follow Moscow and be independent simultaneously • Foreign minister mysteriously dies. Jan Masaryk • Soviets were going to take control of Czechs – make it a satellite • Americans decided to extend Marshall Plan to prevent similar events elsewhere
Czechoslovakia • 1946 – Communist PM elected in Czechoslovakia • Wanted Marshall Plan aid but Moscow ordered them to refuse • Tried to follow Moscow and be independent simultaneously • Foreign minister mysteriously dies. Jan Masaryk • Soviets were going to take control of Czechs – make it a satellite • Americans decided to extend Marshall Plan to prevent similar events elsewhere
 Yugoslavia • Josip Broz = Tito • He liberates Yug from Nazis • Red Army shows up and commits assaults on Yugoslavs = tension with USSR • Issues over control – Stalin didn’t want Tito as equal • Tito freed Yugoslavia without major Allied help • He ruled independently of Moscow = angers Stalin • Tito asks Bulgaria for a trade union and doesn’t invite USSR – Stalin gets really angry
Yugoslavia • Josip Broz = Tito • He liberates Yug from Nazis • Red Army shows up and commits assaults on Yugoslavs = tension with USSR • Issues over control – Stalin didn’t want Tito as equal • Tito freed Yugoslavia without major Allied help • He ruled independently of Moscow = angers Stalin • Tito asks Bulgaria for a trade union and doesn’t invite USSR – Stalin gets really angry
 • Stalin asks Bulgarian, Yugoslav leaders to Moscow – Tito doesn’t attend – sends grunts • Stalin proposes union of Albania, Yug, Bulg • Tito views this as opportunity for Red Army to occupy Bulgaria and threaten Yugoslavia • Political differences in 1948 mean Yug expelled from Cominform • Soviets withdraw aid, so US gives aid • Tito allowed Greek communists to regroup in Yugoslavia – also supplied them – angers Stalin • “Can’t Touch This” attitude towards Moscow – geographical separation means Yug is hard to control • Stalin tries to reintegrate Yug, and fails • Yugoslavia presents alternative communist model – threat to USSR
• Stalin asks Bulgarian, Yugoslav leaders to Moscow – Tito doesn’t attend – sends grunts • Stalin proposes union of Albania, Yug, Bulg • Tito views this as opportunity for Red Army to occupy Bulgaria and threaten Yugoslavia • Political differences in 1948 mean Yug expelled from Cominform • Soviets withdraw aid, so US gives aid • Tito allowed Greek communists to regroup in Yugoslavia – also supplied them – angers Stalin • “Can’t Touch This” attitude towards Moscow – geographical separation means Yug is hard to control • Stalin tries to reintegrate Yug, and fails • Yugoslavia presents alternative communist model – threat to USSR
 Alignment: Whose is whose ally? USA (Democratic/Capitalists USSR (Communist/CPE) Political: Truman Doctrine Economic: Marshal Plan Military: NATO (Europe&NA) SEATO ( S. E. Asia) • Political: Cominform • Economic: Comecon • Military: Warsaw Pact ANZUS(Aust/NZ/US) NORAD (US& Can. )
Alignment: Whose is whose ally? USA (Democratic/Capitalists USSR (Communist/CPE) Political: Truman Doctrine Economic: Marshal Plan Military: NATO (Europe&NA) SEATO ( S. E. Asia) • Political: Cominform • Economic: Comecon • Military: Warsaw Pact ANZUS(Aust/NZ/US) NORAD (US& Can. )
 NATO • • NATO = North Atlantic Treaty Organization 1947 – Tensions between Soviets and West 1948 – Treaty of Brussels – Pooling of military resources of Br, Fr, Lux, Belg, Neth • Vandenberg Resolution – USA would align itself with regional alliances designed to promote security – allies with Brussels members = military union between US and Europe
NATO • • NATO = North Atlantic Treaty Organization 1947 – Tensions between Soviets and West 1948 – Treaty of Brussels – Pooling of military resources of Br, Fr, Lux, Belg, Neth • Vandenberg Resolution – USA would align itself with regional alliances designed to promote security – allies with Brussels members = military union between US and Europe
 • April 1949 – North Atlantic Treaty – Brussels members + US, Den, Ice, It, Nor, Por, Can • Attack any one of us means attack on us all • West would stand united against Soviet expansion = deterrent • US has nuclear monopoly until 1949
• April 1949 – North Atlantic Treaty – Brussels members + US, Den, Ice, It, Nor, Por, Can • Attack any one of us means attack on us all • West would stand united against Soviet expansion = deterrent • US has nuclear monopoly until 1949
 Cominform / Comecon / Warsaw • Communism International – Comintern – replaced by Communist Information Bureau – Cominform • Council for Mutual Economic Assistance – Comecon • Warsaw Pact – like NATO for Communists • Formed in response to Truman Doctrine, Marshall Plan, and NATO • Warsaw Pact dissolved in 1991
Cominform / Comecon / Warsaw • Communism International – Comintern – replaced by Communist Information Bureau – Cominform • Council for Mutual Economic Assistance – Comecon • Warsaw Pact – like NATO for Communists • Formed in response to Truman Doctrine, Marshall Plan, and NATO • Warsaw Pact dissolved in 1991
 SEATO / ANZUS • American policy also shifted towards a presence in Asia • 1951 - Australia – New Zealand – United States – US replaces Britain as protector • 1954 - Southeast Asia Treaty Organization • Mutual defense with US, Br, Fr, Aus, NZ, Philippines, Thailand • US also started to bolster Japan and start rearmament • Catalyzed rearmament of Europe • West Germany joins NATO • Military Defensive Alliance = maintain security through balance of power. Ex. NATO, Warsaw Pact
SEATO / ANZUS • American policy also shifted towards a presence in Asia • 1951 - Australia – New Zealand – United States – US replaces Britain as protector • 1954 - Southeast Asia Treaty Organization • Mutual defense with US, Br, Fr, Aus, NZ, Philippines, Thailand • US also started to bolster Japan and start rearmament • Catalyzed rearmament of Europe • West Germany joins NATO • Military Defensive Alliance = maintain security through balance of power. Ex. NATO, Warsaw Pact
 Non-Alignment & Bandung Conference, meeting of representatives of 29 African and Asian nations, held at Bandung, Indonesia, in 1955. The aim—to promote economic and cultural cooperation and to oppose colonialism—was more or less achieved in an atmosphere of cordiality. China played a prominent part and strengthened its friendly relations with other Asian nations. Not invited to the conference were South Africa, Israel, Taiwan, South Korea, and North Korea. The conference ultimately led to the establishment of the Nonaligned Movement in 1961. In later years, conflicts between the nonaligned nations eroded the solidarity expressed at Bandung.
Non-Alignment & Bandung Conference, meeting of representatives of 29 African and Asian nations, held at Bandung, Indonesia, in 1955. The aim—to promote economic and cultural cooperation and to oppose colonialism—was more or less achieved in an atmosphere of cordiality. China played a prominent part and strengthened its friendly relations with other Asian nations. Not invited to the conference were South Africa, Israel, Taiwan, South Korea, and North Korea. The conference ultimately led to the establishment of the Nonaligned Movement in 1961. In later years, conflicts between the nonaligned nations eroded the solidarity expressed at Bandung.
 Cold War Events 1950 -1991 • • • Korean War Khrushchev – Peaceful Co-existence Berlin Wall U 2 Spy Plane Castro Seizes power of Cuba Bay of Pigs Invasion Cuban Missile Crisis Vietnam War 1965 -1972 Afghanistan War 1979 -1989 Gorbachev take power 1985 and ends USSR
Cold War Events 1950 -1991 • • • Korean War Khrushchev – Peaceful Co-existence Berlin Wall U 2 Spy Plane Castro Seizes power of Cuba Bay of Pigs Invasion Cuban Missile Crisis Vietnam War 1965 -1972 Afghanistan War 1979 -1989 Gorbachev take power 1985 and ends USSR
 • Enter Korean War Korea • 1945 – Stalin and Truman jointly occupy Korea • June 1950 – North invades South – 38 Parallel – forceful unification • Truman sends military assistance to South Korea and Taiwan • If US didn’t help South Korea it would be a betrayal • US pushes resolution through the Security Council requesting assistance to Korea • At the time the Soviets were boycotting the UN – no veto • Shift in policy – Soviets would start to help other communist regimes – spread the red
• Enter Korean War Korea • 1945 – Stalin and Truman jointly occupy Korea • June 1950 – North invades South – 38 Parallel – forceful unification • Truman sends military assistance to South Korea and Taiwan • If US didn’t help South Korea it would be a betrayal • US pushes resolution through the Security Council requesting assistance to Korea • At the time the Soviets were boycotting the UN – no veto • Shift in policy – Soviets would start to help other communist regimes – spread the red
 Khrushchev • Stalin dies in ’ 53 • Khrushchev controls gov’t in 1956 • Austrian State Treaty – 1955 – Withdrawal of all Allied forces and forces Austrian neutrality – voluntary Soviet withdrawal = policy shift • De-Stalinization – purge horrors of Stalin • “many roads to socialism” – diversify Communism
Khrushchev • Stalin dies in ’ 53 • Khrushchev controls gov’t in 1956 • Austrian State Treaty – 1955 – Withdrawal of all Allied forces and forces Austrian neutrality – voluntary Soviet withdrawal = policy shift • De-Stalinization – purge horrors of Stalin • “many roads to socialism” – diversify Communism
 • Decolonization meant that extra nations could alter world order • Khrushchev decided to support new nations – Indian steel mill • PEACEFUL COEXISTENCE - Khrushchev recognized two social systems & advocated nonviolent transitions to communism • Agricultural reform fails – starts political demise of Khrushchev • Soviet thrust into Third World = weakened Sino. Soviet alliance • Many roads stimulated wishes for change in Poland Hungary
• Decolonization meant that extra nations could alter world order • Khrushchev decided to support new nations – Indian steel mill • PEACEFUL COEXISTENCE - Khrushchev recognized two social systems & advocated nonviolent transitions to communism • Agricultural reform fails – starts political demise of Khrushchev • Soviet thrust into Third World = weakened Sino. Soviet alliance • Many roads stimulated wishes for change in Poland Hungary
 • 1956 – Demonstrations against ruling regime – workers, students, intellectuals • USSR gets worried, sends army to put down the demonstrations, replace leaders • Hungarians wished to become autonomous and withdraw from Warsaw Pact = Soviets crush revolution • Over 20 k killed, 20 k jailed, 200 k fled Hungary • Invasion of Hungary violates Warsaw Pact • Force bound Eastern Bloc, not ideology • USSR prepared to use military means to force hegemony in Eastern Europe – vital to defense • US couldn’t help Hungary – open confrontation with USSR
• 1956 – Demonstrations against ruling regime – workers, students, intellectuals • USSR gets worried, sends army to put down the demonstrations, replace leaders • Hungarians wished to become autonomous and withdraw from Warsaw Pact = Soviets crush revolution • Over 20 k killed, 20 k jailed, 200 k fled Hungary • Invasion of Hungary violates Warsaw Pact • Force bound Eastern Bloc, not ideology • USSR prepared to use military means to force hegemony in Eastern Europe – vital to defense • US couldn’t help Hungary – open confrontation with USSR
 • • • Berlin Wall 1958 – Tension in Berlin West Germans very anti-Communist East Germany depressed and repressed – people fled to West Khrushchev threatened to attack West Berlin – West stood fast Khrushchev meets Eisenhower in 1959 – détente Summitry = tension can be removed by face to face talks of national leaders
• • • Berlin Wall 1958 – Tension in Berlin West Germans very anti-Communist East Germany depressed and repressed – people fled to West Khrushchev threatened to attack West Berlin – West stood fast Khrushchev meets Eisenhower in 1959 – détente Summitry = tension can be removed by face to face talks of national leaders
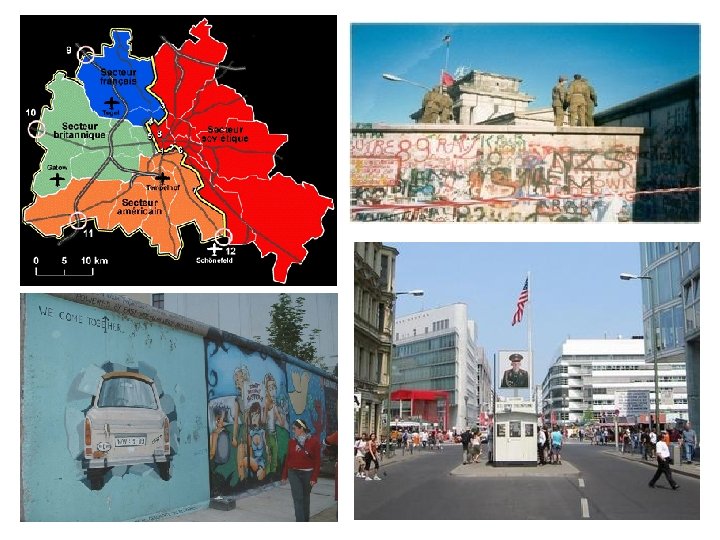
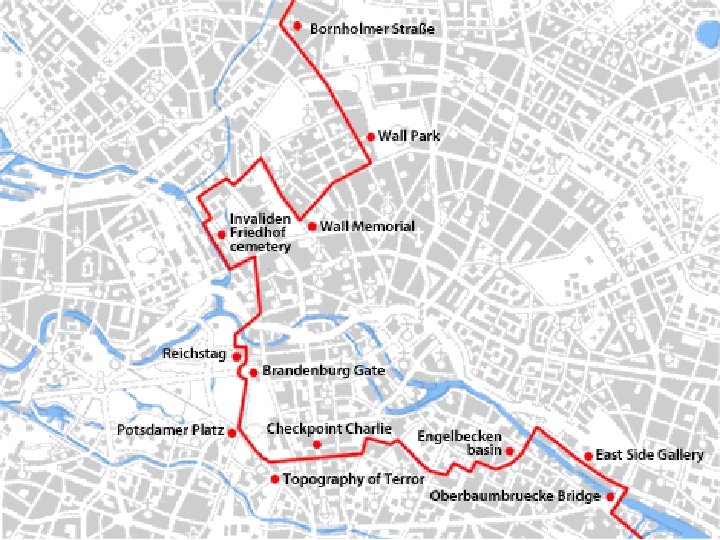
 BERLIN WALL • Constructed in 1961 to stop exodus of people to West Berlin
BERLIN WALL • Constructed in 1961 to stop exodus of people to West Berlin
 Gary Powers • Not related to Austin • Flew U 2 spy plane over Soviet Union, gets shot down
Gary Powers • Not related to Austin • Flew U 2 spy plane over Soviet Union, gets shot down
 • Soviets find out that US is flying over Russia – Paris summit is cancelled • Khrushchev gets criticized by Politburo and Chinese – declares he won’t negotiate with Eisenhower • JFK gets elected in 1961 • Khrushchev delivers ultimatum saying that US must withdraw from Berlin, announced Soviet military budget increased 33% • JFK responds by increasing draft calls, $3 billion to military • East Germans are going to West; Khrushchev decides to close border = Berlin Wall • Khrushchev criticized for backing down but he does let his tanks go “nose to nose” with US
• Soviets find out that US is flying over Russia – Paris summit is cancelled • Khrushchev gets criticized by Politburo and Chinese – declares he won’t negotiate with Eisenhower • JFK gets elected in 1961 • Khrushchev delivers ultimatum saying that US must withdraw from Berlin, announced Soviet military budget increased 33% • JFK responds by increasing draft calls, $3 billion to military • East Germans are going to West; Khrushchev decides to close border = Berlin Wall • Khrushchev criticized for backing down but he does let his tanks go “nose to nose” with US
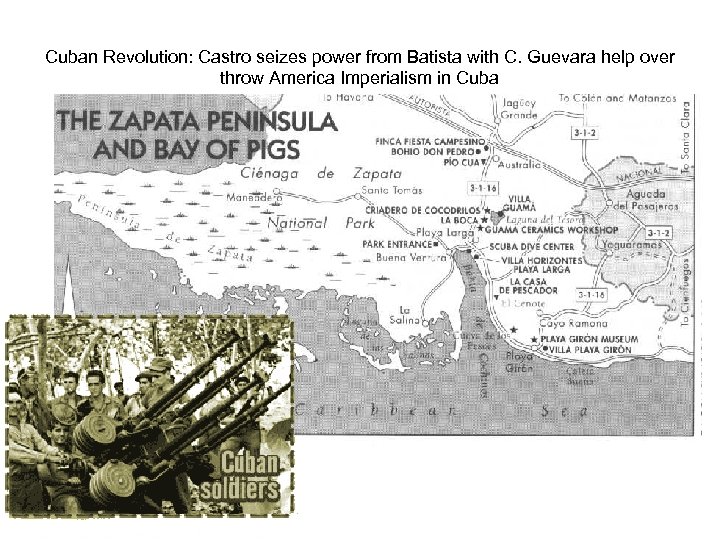 Cuban Revolution: Castro seizes power from Batista with C. Guevara help over throw America Imperialism in Cuba
Cuban Revolution: Castro seizes power from Batista with C. Guevara help over throw America Imperialism in Cuba
 Bay of Pigs • April 1961 – Invasion of Cuba – fails horribly
Bay of Pigs • April 1961 – Invasion of Cuba – fails horribly
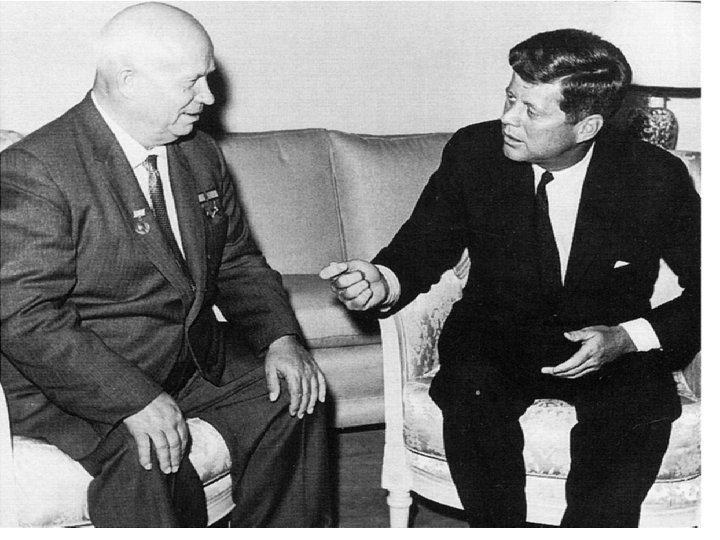
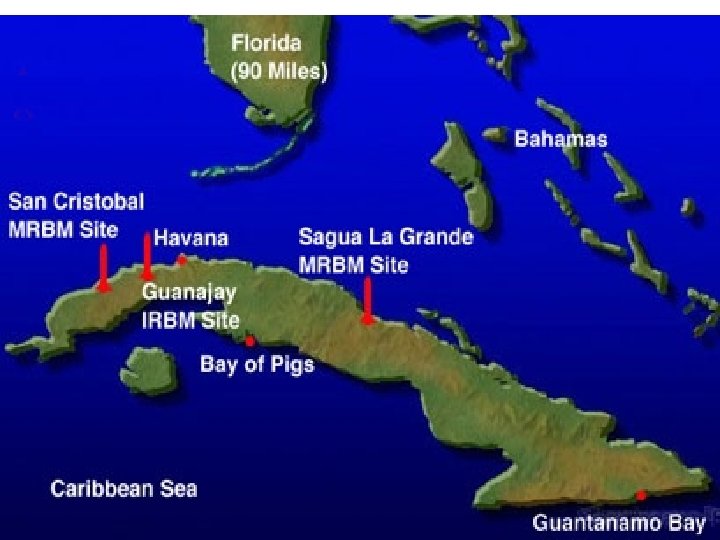
 Cuban Missile Crisis • 1962 – Khrushchev has idea of putting nuclear missiles on Cuba • Cuba is alright with it – Bay of Pigs, Soviet aid • October – U 2’s find missile sites on Cuba • What to do? • Hawks / Doves / Owls • Hawks – Direct Invasion or Airstrike Doves – Diplomacy – Barter Jupiters Owls – Middle of the Road – Blockade • Owls prevail – Kennedy announces nukes on Cuba, blockades • Blockade is technically and act of war, so Cuba was “quarantined”
Cuban Missile Crisis • 1962 – Khrushchev has idea of putting nuclear missiles on Cuba • Cuba is alright with it – Bay of Pigs, Soviet aid • October – U 2’s find missile sites on Cuba • What to do? • Hawks / Doves / Owls • Hawks – Direct Invasion or Airstrike Doves – Diplomacy – Barter Jupiters Owls – Middle of the Road – Blockade • Owls prevail – Kennedy announces nukes on Cuba, blockades • Blockade is technically and act of war, so Cuba was “quarantined”
 • Direct negotiation was used to solve crisis, not UN • establish compromise – Soviets would remove Cuban missiles, US would dismantle Turkish Jupiters the next year – save face for allies • Value of diplomacy realized = Hotline • Partial Test Ban treaty – prohibited nuclear testing in atmosphere, underwater, and in space – US, UK, USSR • 1963 – Beginning of Détente
• Direct negotiation was used to solve crisis, not UN • establish compromise – Soviets would remove Cuban missiles, US would dismantle Turkish Jupiters the next year – save face for allies • Value of diplomacy realized = Hotline • Partial Test Ban treaty – prohibited nuclear testing in atmosphere, underwater, and in space – US, UK, USSR • 1963 – Beginning of Détente

 The 2 Kennedy’s Plan to stop the USSR!
The 2 Kennedy’s Plan to stop the USSR!
 Krushchev and Castro prepare for war!
Krushchev and Castro prepare for war!
 Pictures of Missiles in Cuba
Pictures of Missiles in Cuba
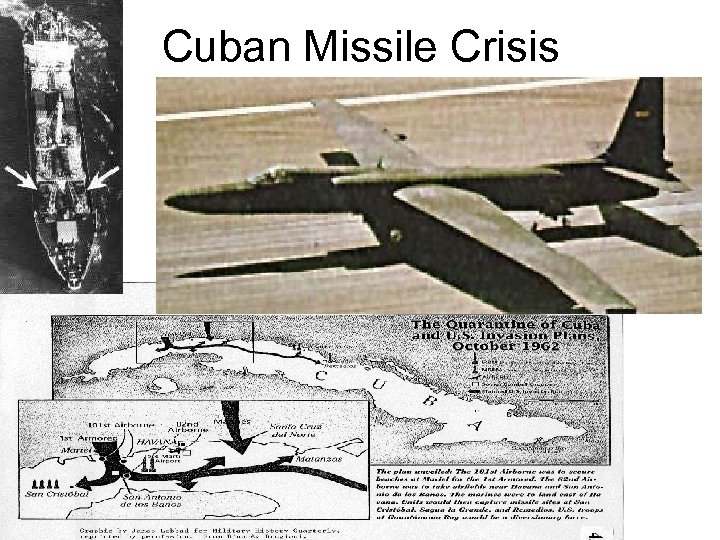 Cuban Missile Crisis
Cuban Missile Crisis
 Brinkmanship
Brinkmanship
 EXCOMM Kenedy and staffers
EXCOMM Kenedy and staffers
 President Kennedy signs proclamation for naval quarantine of Cuba, 23 October 1962.
President Kennedy signs proclamation for naval quarantine of Cuba, 23 October 1962.
 Soviet Military Build Up In Cuba, late October 1962
Soviet Military Build Up In Cuba, late October 1962
 MRBM Launch Site 1, 25 October 1962
MRBM Launch Site 1, 25 October 1962
 Soviet ship "Poltava" en route to Cuba
Soviet ship "Poltava" en route to Cuba
 Kennedy assassinated • Dallas, 1963 • Harvey Lee Oswald • Grassy Knoll
Kennedy assassinated • Dallas, 1963 • Harvey Lee Oswald • Grassy Knoll
 Opinion – Similarities to Pre. WWI? • Alliances – NATO and Warsaw Pact • Militarization – Arms Race and Nuclear Weapons • Imperialism – Spheres of Influence, Poland, Hungary • Nationalism – Anti-Communist sentiments in United States, Anti-Capitalist in Soviet Union • Lawlessness – Backdoor negotiations with Soviets during Cuban Missile Crisis
Opinion – Similarities to Pre. WWI? • Alliances – NATO and Warsaw Pact • Militarization – Arms Race and Nuclear Weapons • Imperialism – Spheres of Influence, Poland, Hungary • Nationalism – Anti-Communist sentiments in United States, Anti-Capitalist in Soviet Union • Lawlessness – Backdoor negotiations with Soviets during Cuban Missile Crisis
 IMPACT OF THE CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS ON US/SOVIET RELATIONS • • • Just over a month after the crisis began, on November 21, President Kennedy terminated the quarantine since Khrushchev finally withdrew the Soviet nuclear bombers from Cuba. On the 30 th anniversary of the Crisis, it was revealed that Soviet mobile tactical weapons and in excess of 40 000 Soviet Troops were in Cuba, ready to be deployed in the event of an American invasion. By the end of the 1960 s the Soviet Union had achieved strategic parity with the Americans. In overall military capability, the United States could no longer be considered pre-eminent. So in matters of arms control, the USSR could now negotiate from positions of equality. from the Cuban Missile Crisis, particularly after Khrushchev was relieved of his position as leader, there was a concerted effort on both parts for arms control, resulting in the signing of many bilateral agreements. the Cuban Missile Crisis highlighted the importance of a clear and direct system of communication between Moscow and Washington. During the crisis, the two leaders communicated with each other through letter writing, which proved to be a very slow form of communication, particularly in such a tense time. So, in 1963, an agreement was reached, the Hot-line Treaty, initially using teletype, telegraph and radio-telegraph communication links. Of course with the development of new technologies, these communication links have been upgraded.
IMPACT OF THE CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS ON US/SOVIET RELATIONS • • • Just over a month after the crisis began, on November 21, President Kennedy terminated the quarantine since Khrushchev finally withdrew the Soviet nuclear bombers from Cuba. On the 30 th anniversary of the Crisis, it was revealed that Soviet mobile tactical weapons and in excess of 40 000 Soviet Troops were in Cuba, ready to be deployed in the event of an American invasion. By the end of the 1960 s the Soviet Union had achieved strategic parity with the Americans. In overall military capability, the United States could no longer be considered pre-eminent. So in matters of arms control, the USSR could now negotiate from positions of equality. from the Cuban Missile Crisis, particularly after Khrushchev was relieved of his position as leader, there was a concerted effort on both parts for arms control, resulting in the signing of many bilateral agreements. the Cuban Missile Crisis highlighted the importance of a clear and direct system of communication between Moscow and Washington. During the crisis, the two leaders communicated with each other through letter writing, which proved to be a very slow form of communication, particularly in such a tense time. So, in 1963, an agreement was reached, the Hot-line Treaty, initially using teletype, telegraph and radio-telegraph communication links. Of course with the development of new technologies, these communication links have been upgraded.
 Vietnam War • • Between 1945 and 1954, the Vietnamese waged an anti-colonial war against France and received $2. 6 billion in financial support from the United States. The French defeat at the Dien Bien Phu was followed by a peace conference in Geneva, in which Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam received their independence and Vietnam was temporarily divided between an anti-Communist South and a Communist North. In 1956, South Vietnam, with American backing, refused to hold the unification elections. By 1958, Communist-led guerrillas known as the Viet Cong had begun to battle the South Vietnamese government. To support the South’s government, the United States sent in 2, 000 military advisors, a number that grew to 16, 300 in 1963. The military condition deteriorated, and by 1963 South Vietnam had lost the fertile Mekong Delta to the Vietcong. In 1965, Johnson escalated the war, commencing air strikes on North Vietnam and committing ground forces, which numbered 536, 000 in 1968. The 1968 Tet Offensive by the North Vietnamese turned many Americans against the war. The next president, Richard Nixon, advocated Vietnamization, withdrawing American troops and giving South Vietnam greater responsibility for fighting the war. His attempt to slow the flow of North Vietnamese soldiers and supplies into South Vietnam by sending American forces to destroy Communist supply bases in Cambodia in 1970 in violation of Cambodian neutrality provoked antiwar protests on the nation’s college campuses.
Vietnam War • • Between 1945 and 1954, the Vietnamese waged an anti-colonial war against France and received $2. 6 billion in financial support from the United States. The French defeat at the Dien Bien Phu was followed by a peace conference in Geneva, in which Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam received their independence and Vietnam was temporarily divided between an anti-Communist South and a Communist North. In 1956, South Vietnam, with American backing, refused to hold the unification elections. By 1958, Communist-led guerrillas known as the Viet Cong had begun to battle the South Vietnamese government. To support the South’s government, the United States sent in 2, 000 military advisors, a number that grew to 16, 300 in 1963. The military condition deteriorated, and by 1963 South Vietnam had lost the fertile Mekong Delta to the Vietcong. In 1965, Johnson escalated the war, commencing air strikes on North Vietnam and committing ground forces, which numbered 536, 000 in 1968. The 1968 Tet Offensive by the North Vietnamese turned many Americans against the war. The next president, Richard Nixon, advocated Vietnamization, withdrawing American troops and giving South Vietnam greater responsibility for fighting the war. His attempt to slow the flow of North Vietnamese soldiers and supplies into South Vietnam by sending American forces to destroy Communist supply bases in Cambodia in 1970 in violation of Cambodian neutrality provoked antiwar protests on the nation’s college campuses.
 Vietnam War • From 1968 to 1973 efforts were made to end the conflict through diplomacy. In January 1973, an agreement reached and U. S. forces were withdrawn from Vietnam and U. S. prisoners of war were released. In April 1975, South Vietnam surrendered to the North and Vietnam was reunited. CONSEQUENCES: • 1. The Vietnam War cost the United States 58, 000 lives and 350, 000 casualties. It also resulted in between one and two million Vietnamese deaths. • 2. Congress enacted the War Powers Act in 1973, requiring the president to receive explicit Congressional approval before committing American forces overseas. • It was the longest war in American history and the most unpopular American war of the twentieth century. It resulted in nearly 60, 000 American deaths and an estimated 2 million Vietnamese deaths. Even today, many Americans still ask whether the American effort in Vietnam was a sin, a blunder, a necessary war, or a noble cause, or an idealistic, if failed, effort to protect the South Vietnamese from totalitarian government
Vietnam War • From 1968 to 1973 efforts were made to end the conflict through diplomacy. In January 1973, an agreement reached and U. S. forces were withdrawn from Vietnam and U. S. prisoners of war were released. In April 1975, South Vietnam surrendered to the North and Vietnam was reunited. CONSEQUENCES: • 1. The Vietnam War cost the United States 58, 000 lives and 350, 000 casualties. It also resulted in between one and two million Vietnamese deaths. • 2. Congress enacted the War Powers Act in 1973, requiring the president to receive explicit Congressional approval before committing American forces overseas. • It was the longest war in American history and the most unpopular American war of the twentieth century. It resulted in nearly 60, 000 American deaths and an estimated 2 million Vietnamese deaths. Even today, many Americans still ask whether the American effort in Vietnam was a sin, a blunder, a necessary war, or a noble cause, or an idealistic, if failed, effort to protect the South Vietnamese from totalitarian government
 Afghanistan War • Afghanistan War, 1978– 92, conflict between anti-Communist Muslim Afghan guerrillas (mujahidin) and Afghan government and Soviet forces. The conflict had its origins in the 1978 coup that overthrew Afghan president Sardar Muhammad Daud Khan, who had come to power by ousting the king in 1973. The president was assassinated and a pro-Soviet Communist government under Noor Mohammed Taraki was established. In 1979 another coup, which brought Hafizullah Amin to power, provoked an invasion (Dec. , 1979) by Soviet forces and the installation of Babrak Karmal as president. • The Soviet invasion, which sparked Afghan resistance, intially involved an estimated 30, 000 troops, a force that ultimately grew to 100, 000. The mujahidin were supported by aid from the United States, China, and Saudi Arabia, channeled through Pakistan, and from Iran. Although the USSR had superior weapons and complete air control, the rebels successfully eluded them. The conflict largely settled into a stalemate, with Soviet and government forces controlling the urban areas, and the Afghan guerrillas operating fairly freely in mountainous rural regions. As the war progressed, the rebels improved their organization and tactics and began using imported and captured weapons, including U. S. antiaircraft missiles, to neutralize the technological advantages of the USSR.
Afghanistan War • Afghanistan War, 1978– 92, conflict between anti-Communist Muslim Afghan guerrillas (mujahidin) and Afghan government and Soviet forces. The conflict had its origins in the 1978 coup that overthrew Afghan president Sardar Muhammad Daud Khan, who had come to power by ousting the king in 1973. The president was assassinated and a pro-Soviet Communist government under Noor Mohammed Taraki was established. In 1979 another coup, which brought Hafizullah Amin to power, provoked an invasion (Dec. , 1979) by Soviet forces and the installation of Babrak Karmal as president. • The Soviet invasion, which sparked Afghan resistance, intially involved an estimated 30, 000 troops, a force that ultimately grew to 100, 000. The mujahidin were supported by aid from the United States, China, and Saudi Arabia, channeled through Pakistan, and from Iran. Although the USSR had superior weapons and complete air control, the rebels successfully eluded them. The conflict largely settled into a stalemate, with Soviet and government forces controlling the urban areas, and the Afghan guerrillas operating fairly freely in mountainous rural regions. As the war progressed, the rebels improved their organization and tactics and began using imported and captured weapons, including U. S. antiaircraft missiles, to neutralize the technological advantages of the USSR.
 Afghanistan War • In 1986, Karmal resigned and Mohammad Najibullah became head of a collective leadership. In Feb. , 1988, President Mikhail Gorbachev announced the withdrawal of USSR troops, which was completed one year later. Soviet citizens had become increasingly discontented with the war, which dragged on without success but with continuing casualties. In the spring of 1992, Najibullah's government collapsed and, after 14 years of rule by the People's Democratic party, Kabul fell to a coalition of mujahidin under the military leadership of Ahmed Shah Massoud. • The war left Afghanistan with severe political, economic, and ecological problems. More than 1 million Afghans died in the war and 5 million became refugees in neighboring countries. In addition, 15, 000 Soviet soldiers were killed and 37, 000 wounded. Economic production was drastically curtailed, and much of the land laid waste. At the end of the war more than 5 million mines saturated approximately 2% of the country, where they will pose a threat to human and animal life well into the 21 st cent. The disparate guerrilla forces that had triumphed proved unable to unite, and Afghanistan became divided into spheres of control. These political divisions set the stage for the rise of the Taliban later in the decade.
Afghanistan War • In 1986, Karmal resigned and Mohammad Najibullah became head of a collective leadership. In Feb. , 1988, President Mikhail Gorbachev announced the withdrawal of USSR troops, which was completed one year later. Soviet citizens had become increasingly discontented with the war, which dragged on without success but with continuing casualties. In the spring of 1992, Najibullah's government collapsed and, after 14 years of rule by the People's Democratic party, Kabul fell to a coalition of mujahidin under the military leadership of Ahmed Shah Massoud. • The war left Afghanistan with severe political, economic, and ecological problems. More than 1 million Afghans died in the war and 5 million became refugees in neighboring countries. In addition, 15, 000 Soviet soldiers were killed and 37, 000 wounded. Economic production was drastically curtailed, and much of the land laid waste. At the end of the war more than 5 million mines saturated approximately 2% of the country, where they will pose a threat to human and animal life well into the 21 st cent. The disparate guerrilla forces that had triumphed proved unable to unite, and Afghanistan became divided into spheres of control. These political divisions set the stage for the rise of the Taliban later in the decade.
 Gorbachev Ends Communism in USSR • • Gorbachev comes to Power in 1985 Glasnost Perestrokia Democratization 1989 Troop withdrawl from Afghanistan 1989 Coup attempt to overthrow Gorby 1991 Yeltsin rises to power
Gorbachev Ends Communism in USSR • • Gorbachev comes to Power in 1985 Glasnost Perestrokia Democratization 1989 Troop withdrawl from Afghanistan 1989 Coup attempt to overthrow Gorby 1991 Yeltsin rises to power
 Social and Personal Implications of Cold War • • Julius and Ethel Rosenberg Cold War Hysteria Threat of Nuclear War Espionage 1960 U-2 spy plane Mc. Carthysim and the Red Scare HUAC
Social and Personal Implications of Cold War • • Julius and Ethel Rosenberg Cold War Hysteria Threat of Nuclear War Espionage 1960 U-2 spy plane Mc. Carthysim and the Red Scare HUAC
 Rosenbergs - Manhattan Project – American atomic bomb construction project
Rosenbergs - Manhattan Project – American atomic bomb construction project
 Mc. Carthy • 1949 – Unacceptable to rearm Germany, US couldn’t send troops to Europe, Soviets get nukes – losing the Cold War • 1950 – Senator Mc. Carthy announces that 57 State Dept. members are communist • “Red Scare” • Stop communism before it takes over USA • NSC 68 – Huge military buildup = raise taxes – world’s police officer • Public wouldn’t support it without a crisis…
Mc. Carthy • 1949 – Unacceptable to rearm Germany, US couldn’t send troops to Europe, Soviets get nukes – losing the Cold War • 1950 – Senator Mc. Carthy announces that 57 State Dept. members are communist • “Red Scare” • Stop communism before it takes over USA • NSC 68 – Huge military buildup = raise taxes – world’s police officer • Public wouldn’t support it without a crisis…
 Mc. Carthyism
Mc. Carthyism
 Red Scare • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=ixy 5 F BLnh 7 o
Red Scare • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=ixy 5 F BLnh 7 o
 Détente and Treaties • • • Hotline 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty 1963 Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty 1968 SALT 1 1969 Helsinki Accords 1975 Soviet War in Afghanistan 1979 Reagan SDI 1980 START 1 1982 Intermediate-range Nuclear Forces Treaty INF Treaty 1987 • Mikhail Gorbachev becomes Soviet Premier end cold war by 1991.
Détente and Treaties • • • Hotline 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty 1963 Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty 1968 SALT 1 1969 Helsinki Accords 1975 Soviet War in Afghanistan 1979 Reagan SDI 1980 START 1 1982 Intermediate-range Nuclear Forces Treaty INF Treaty 1987 • Mikhail Gorbachev becomes Soviet Premier end cold war by 1991.
 Proxy Wars Assignment: Read pages 258 -259 and summarize: • Korean War • Vietnam War • Chile • Afghanistan War • The Iran-Contra Affair
Proxy Wars Assignment: Read pages 258 -259 and summarize: • Korean War • Vietnam War • Chile • Afghanistan War • The Iran-Contra Affair
 Cold War Legacies Assignment: Read pages 268 -269 and summarize the following: • Angola • Mozambique • Black Market
Cold War Legacies Assignment: Read pages 268 -269 and summarize the following: • Angola • Mozambique • Black Market


