e786de1fd0809a8753842c6bf24cd582.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 The Cold War
The Cold War
 The Cold War l Why “Cold” War? l What was the overarching dynamic? l How can we describe the spread of Communism during the twentieth century?
The Cold War l Why “Cold” War? l What was the overarching dynamic? l How can we describe the spread of Communism during the twentieth century?
 The Cold War
The Cold War
 The USSR under Stalin • Josef Stalin (1879 -1953) – Lenin’s successor – Chief propagandist of “Lenin cult” – Mysterious – “Socialism in one country” five-year plans
The USSR under Stalin • Josef Stalin (1879 -1953) – Lenin’s successor – Chief propagandist of “Lenin cult” – Mysterious – “Socialism in one country” five-year plans
 The USSR under Stalin
The USSR under Stalin
 The USSR under Stalin Tomb of Lenin, Red Square, Moscow
The USSR under Stalin Tomb of Lenin, Red Square, Moscow
 The USSR under Stalin • Collectivization – Kulaks dispossessed forcibly property to collective farms – Poorer peasants forced onto collectives – Results Women laboring on a collective (1941) • Millions lost lands • Approx. 10 million died (1929 -1933)!
The USSR under Stalin • Collectivization – Kulaks dispossessed forcibly property to collective farms – Poorer peasants forced onto collectives – Results Women laboring on a collective (1941) • Millions lost lands • Approx. 10 million died (1929 -1933)!
 The USSR under Stalin • Industrialization – Rapid industrialization competitive USSR! – Focus: heavy industry, infrastructure – New industrial cities – Slave labor in mines, canals, logging – 400% growth (1929 and 1940)!
The USSR under Stalin • Industrialization – Rapid industrialization competitive USSR! – Focus: heavy industry, infrastructure – New industrial cities – Slave labor in mines, canals, logging – 400% growth (1929 and 1940)!
 The USSR under Stalin • The Purges – “Show trials” (1936 -38) executions – Removed “threats” within army – Ordinary citizens arrested for “crimes against the state” – Punishments: execution, GULAGS
The USSR under Stalin • The Purges – “Show trials” (1936 -38) executions – Removed “threats” within army – Ordinary citizens arrested for “crimes against the state” – Punishments: execution, GULAGS
 The USSR under Stalin
The USSR under Stalin
 The USSR and Stalin • Attack on Religion – Objectives: eliminate religion, propagate atheism – Main target: Russian Orthodox Church • Clergy shot or sent to gulags • Churches closed • Revived during World War II
The USSR and Stalin • Attack on Religion – Objectives: eliminate religion, propagate atheism – Main target: Russian Orthodox Church • Clergy shot or sent to gulags • Churches closed • Revived during World War II
 The USSR under Stalin Demolition of Cathedral of Christ the Savior, Moscow (1931) Reconstructed church
The USSR under Stalin Demolition of Cathedral of Christ the Savior, Moscow (1931) Reconstructed church
 The USSR and Stalin • Questions?
The USSR and Stalin • Questions?
 The Cold War • The Cold War Begins – IRON CURTAIN – USA and USSR at odds over state of Eastern Europe – TRUMAN DOCTRINE (1947)
The Cold War • The Cold War Begins – IRON CURTAIN – USA and USSR at odds over state of Eastern Europe – TRUMAN DOCTRINE (1947)
 The Cold War • The First Showdown: Germany – Soviets’ goals: reparations, control – American goals • Strong West Germany to check Stalin • West German economic reconstruction, revival of political life
The Cold War • The First Showdown: Germany – Soviets’ goals: reparations, control – American goals • Strong West Germany to check Stalin • West German economic reconstruction, revival of political life
 The Cold War • The Berlin Blockade – Soviets halted traffic between West Berlin and West Germany (June 1948) – Response: Berlin airlift – Soviets lifted blockade (May 1949) The Berlin airlift
The Cold War • The Berlin Blockade – Soviets halted traffic between West Berlin and West Germany (June 1948) – Response: Berlin airlift – Soviets lifted blockade (May 1949) The Berlin airlift
 The Cold War • The Berlin Wall – Constructed 1961, and divided city – Purpose: keep East Berliners from fleeing
The Cold War • The Berlin Wall – Constructed 1961, and divided city – Purpose: keep East Berliners from fleeing
 The Cold War
The Cold War
 The Cold War • Questions?
The Cold War • Questions?
 The Cold War • Chinese Communism – Under MAO ZEDONG (1893 -1976) – Attractive to rural peasants – Red Army Mao Zedong
The Cold War • Chinese Communism – Under MAO ZEDONG (1893 -1976) – Attractive to rural peasants – Red Army Mao Zedong
 The Cold War • The Civil War (1946 -49) – Nationalists vs. Communists – Communist victory People’s Republic of China (Oct. 1, 1949) – Nationalists fled to Taiwan
The Cold War • The Civil War (1946 -49) – Nationalists vs. Communists – Communist victory People’s Republic of China (Oct. 1, 1949) – Nationalists fled to Taiwan
 The Cold War • Communist China – Mentored by USSR, resented by USA – Landlords targeted – Great Leap Forward (1958 -1960) • Collectivization • Self-industrialization of countryside
The Cold War • Communist China – Mentored by USSR, resented by USA – Landlords targeted – Great Leap Forward (1958 -1960) • Collectivization • Self-industrialization of countryside
 The Cold War
The Cold War
 The Cold War • The Cultural Revolution (1966 -69) – Goal: rid China of reverence for tradition – “Smash the four olds!” – Red Guards – Anarchy!
The Cold War • The Cultural Revolution (1966 -69) – Goal: rid China of reverence for tradition – “Smash the four olds!” – Red Guards – Anarchy!
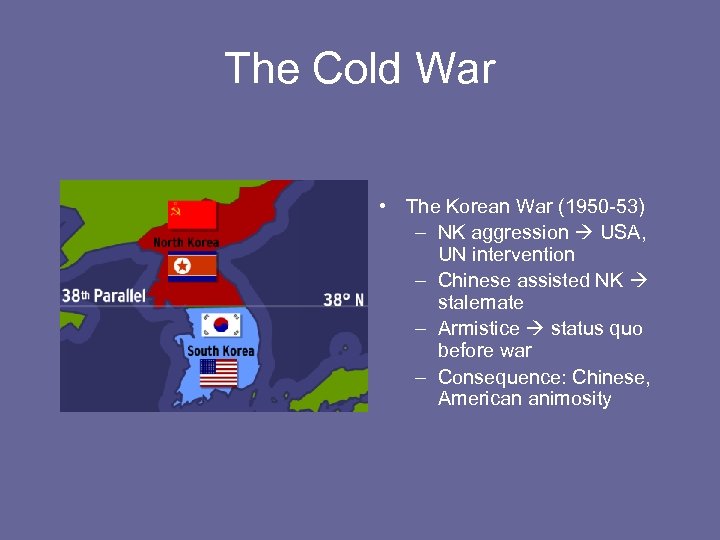 The Cold War • The Korean War (1950 -53) – NK aggression USA, UN intervention – Chinese assisted NK stalemate – Armistice status quo before war – Consequence: Chinese, American animosity
The Cold War • The Korean War (1950 -53) – NK aggression USA, UN intervention – Chinese assisted NK stalemate – Armistice status quo before war – Consequence: Chinese, American animosity
 The Cold War Ling-Ling and Hsing-Hsing
The Cold War Ling-Ling and Hsing-Hsing
 The Cold War
The Cold War
 The Cold War • Questions?
The Cold War • Questions?
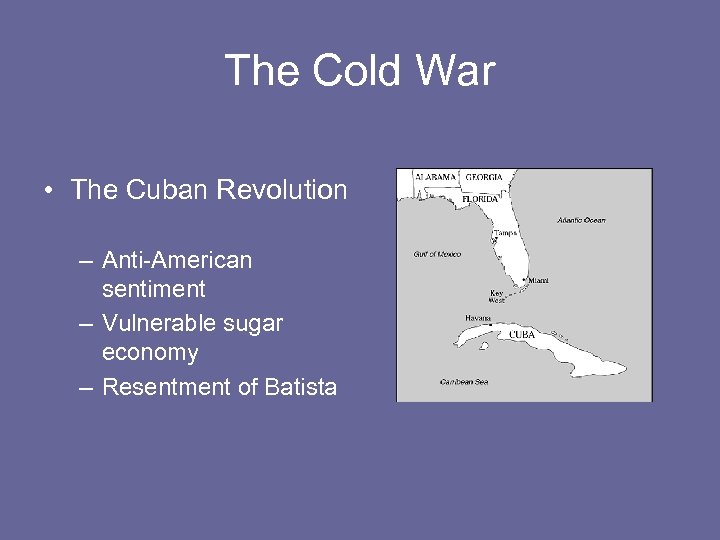 The Cold War • The Cuban Revolution – Anti-American sentiment – Vulnerable sugar economy – Resentment of Batista
The Cold War • The Cuban Revolution – Anti-American sentiment – Vulnerable sugar economy – Resentment of Batista
 The Cold War • Fidel Castro (1926 -2016) – Led victorious revolution (1959) – Very popular! – Cuban Communism • State-controlled economy • Nationalized US property, assets! • Allied with USSR
The Cold War • Fidel Castro (1926 -2016) – Led victorious revolution (1959) – Very popular! – Cuban Communism • State-controlled economy • Nationalized US property, assets! • Allied with USSR
 The Cold War Fidel and Raul Castro
The Cold War Fidel and Raul Castro
 The Cold War • The Cuban Missile Crisis (Autumn 1962) – Soviets missiles installed in Cuba – American response: naval blockade, ultimatum – Resolution • Missiles removed • US pledged not to invade Cuba, to remove missiles in Turkey
The Cold War • The Cuban Missile Crisis (Autumn 1962) – Soviets missiles installed in Cuba – American response: naval blockade, ultimatum – Resolution • Missiles removed • US pledged not to invade Cuba, to remove missiles in Turkey
 The Cold War
The Cold War
 The Cold War • Questions?
The Cold War • Questions?
 The Cold War • Ronald Reagan (1981 -89) – Former actor, president of Screen Actors’ Guild – Hated communism, concerned about arms race – Goal: confront USSR
The Cold War • Ronald Reagan (1981 -89) – Former actor, president of Screen Actors’ Guild – Hated communism, concerned about arms race – Goal: confront USSR
 The Cold War • Mikhail Gorbachev (1931 -) – Soviet premier (1985 -1991) – Reform-minded • Glasnost • Perestroika – Willing to negotiate with Reagan
The Cold War • Mikhail Gorbachev (1931 -) – Soviet premier (1985 -1991) – Reform-minded • Glasnost • Perestroika – Willing to negotiate with Reagan
 The Cold War • Nuclear Disarmament – Discussed over series of meetings (1985 -87) – The INF TREATY Reagan and Gorbachev signing the INF Treaty • Washington D. C. , December 8, 1987 • Superpowers must eliminate intermediaterange missiles
The Cold War • Nuclear Disarmament – Discussed over series of meetings (1985 -87) – The INF TREATY Reagan and Gorbachev signing the INF Treaty • Washington D. C. , December 8, 1987 • Superpowers must eliminate intermediaterange missiles
 The Cold War • The Cold War Ends – Berlin Wall fell (November 1989) – Republics of USSR began to defect – USSR abolished (December 1991) Destruction of Berlin Wall
The Cold War • The Cold War Ends – Berlin Wall fell (November 1989) – Republics of USSR began to defect – USSR abolished (December 1991) Destruction of Berlin Wall
 The Cold War Piece of Berlin Wall, Ronald Reagan Building, Washington D. C.
The Cold War Piece of Berlin Wall, Ronald Reagan Building, Washington D. C.
 The Cold War Reagan hammering at Berlin Wall (September 12, 1990)
The Cold War Reagan hammering at Berlin Wall (September 12, 1990)
 The Cold War • Questions?
The Cold War • Questions?
 The Cold War l Why “Cold” War? l What was the overarching dynamic? l How can we describe the spread of Communism during the twentieth century?
The Cold War l Why “Cold” War? l What was the overarching dynamic? l How can we describe the spread of Communism during the twentieth century?


