cc836f061bef7d42dc83096917f64a06.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 THE COLD WAR & POST WWII WORLD RELATIONS The Onset from 1945 -1950
THE COLD WAR & POST WWII WORLD RELATIONS The Onset from 1945 -1950
 t. HE UNIt. Ed Nat. Io. Ns A. Post-war International peacekeeping organization 1. Created August 1945
t. HE UNIt. Ed Nat. Io. Ns A. Post-war International peacekeeping organization 1. Created August 1945
 1. Fifty nations met in San Francisco, CA, to establish the UN on April 25, 1945 (Before WWII even came to an end) 2. It officially came into existence on October 24, 1945, when it was ratified by China, France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, the United States, and a majority of other signatories.
1. Fifty nations met in San Francisco, CA, to establish the UN on April 25, 1945 (Before WWII even came to an end) 2. It officially came into existence on October 24, 1945, when it was ratified by China, France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, the United States, and a majority of other signatories.
 3. Permanent headquarters are now located in NYC. 4. Originally had 50 members; now has 192. 5. Delegates developed a General Assembly and a Security Council. 6. Security Council has 15 members: 5 permanent (US, GB, USSR, France, & China) and 10 rotating members.
3. Permanent headquarters are now located in NYC. 4. Originally had 50 members; now has 192. 5. Delegates developed a General Assembly and a Security Council. 6. Security Council has 15 members: 5 permanent (US, GB, USSR, France, & China) and 10 rotating members.
 7. According to the Charter, the UN has four purposes: a. to maintain international peace and international peace security b. to develop friendly relations among nations c. to cooperate in solving international problems and in promoting respect for human rights d. to be a center for harmonizing the actions of nations.
7. According to the Charter, the UN has four purposes: a. to maintain international peace and international peace security b. to develop friendly relations among nations c. to cooperate in solving international problems and in promoting respect for human rights d. to be a center for harmonizing the actions of nations.
 II. Two Major Meetings to decide the Postwar Setup of the World: Yalta & Potsdam
II. Two Major Meetings to decide the Postwar Setup of the World: Yalta & Potsdam
 a. Yalta
a. Yalta
 1. February, 1945 2. The Yalta Conference was seen as the beginning of the Cold War. 3. FDR (US), Churchill (GB), and Stalin (Russia) met on the Crimean southern border of the Black Sea Feb. 4 -11, 1945. 4. At this time, Stalin had control of the largest army in Europe (12 million soldiers).
1. February, 1945 2. The Yalta Conference was seen as the beginning of the Cold War. 3. FDR (US), Churchill (GB), and Stalin (Russia) met on the Crimean southern border of the Black Sea Feb. 4 -11, 1945. 4. At this time, Stalin had control of the largest army in Europe (12 million soldiers).
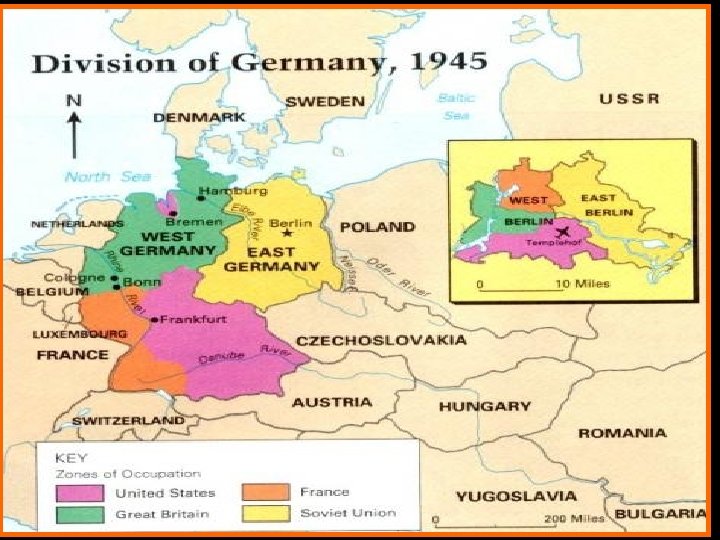
 5. MAJOR POINTS a. Germany (and the city of Berlin) would be divided into U. S. , British, French, and Soviet occupation zones b. Berlin, although in the quadrant controlled by the Soviets, would be divided as well.
5. MAJOR POINTS a. Germany (and the city of Berlin) would be divided into U. S. , British, French, and Soviet occupation zones b. Berlin, although in the quadrant controlled by the Soviets, would be divided as well.
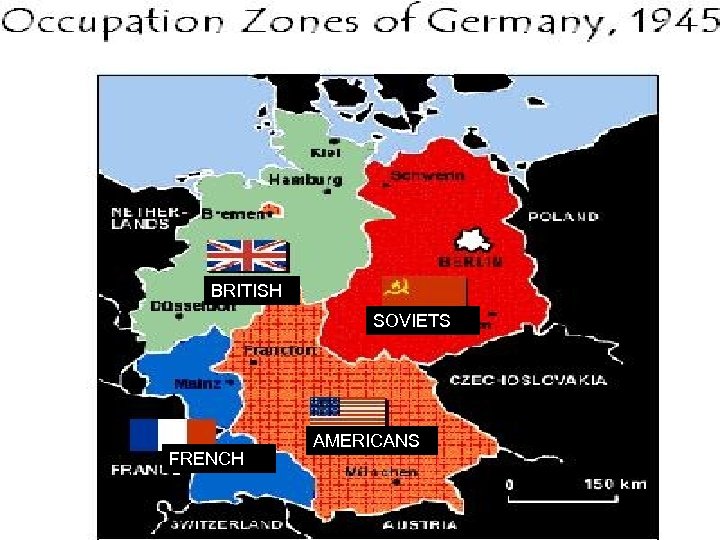 BRITISH SOVIETS FRENCH AMERICANS
BRITISH SOVIETS FRENCH AMERICANS
 c. US and GB let the Soviet occupation of Poland continue in the hopes of retaining Soviet alliance. Stalin did, however, promise to be fair with elections in Poland.
c. US and GB let the Soviet occupation of Poland continue in the hopes of retaining Soviet alliance. Stalin did, however, promise to be fair with elections in Poland.
 b. Potsdam
b. Potsdam
 1. July 16 - August 2, 1945 2. Stalin, Truman, and Churchill (who was replaced during the conference by new PM of GB Clement Atlee) met near Berlin. 3. The “Big Three” finalized the divisions of Germany and Berlin, establishing the borders and occupation zones. 4. The leaders also offered an ultimatum to Japan- surrender or be annihilated.
1. July 16 - August 2, 1945 2. Stalin, Truman, and Churchill (who was replaced during the conference by new PM of GB Clement Atlee) met near Berlin. 3. The “Big Three” finalized the divisions of Germany and Berlin, establishing the borders and occupation zones. 4. The leaders also offered an ultimatum to Japan- surrender or be annihilated.
 5. Nuremberg Trials: 1945 -1949 a. After the war, some of those responsible for crimes of the Holocaust were brought to trial in Nuremberg, Germany. b. Judges from the Allied powers (GB, France, the USSR, and the US) presided over the hearings of 21 major Nazi criminals. 12 prominent Nazis were sentenced to death.
5. Nuremberg Trials: 1945 -1949 a. After the war, some of those responsible for crimes of the Holocaust were brought to trial in Nuremberg, Germany. b. Judges from the Allied powers (GB, France, the USSR, and the US) presided over the hearings of 21 major Nazi criminals. 12 prominent Nazis were sentenced to death.
 6. Japan’s War Crimes Trials: 1946 -1948 a. Took place in Tokyo, under direction of General Mac. Arthur. b. Tojo was among those sentenced to execution. (7 in all sentenced to death)
6. Japan’s War Crimes Trials: 1946 -1948 a. Took place in Tokyo, under direction of General Mac. Arthur. b. Tojo was among those sentenced to execution. (7 in all sentenced to death)
 "The crimes which we seek to condemn and punish have been so calculated, so malignant and so devastating, that civilization cannot tolerate their being ignored, because it cannot survive their being repeated. “ ~ Robert Jackson , US Supreme Court
"The crimes which we seek to condemn and punish have been so calculated, so malignant and so devastating, that civilization cannot tolerate their being ignored, because it cannot survive their being repeated. “ ~ Robert Jackson , US Supreme Court
 iii. THE COLD WAR
iii. THE COLD WAR
 A. The Cold War was the competition for global power and influence between the US and the USSR. B. It was waged on mostly political and economic fronts, but there was always a threat of all-out war.
A. The Cold War was the competition for global power and influence between the US and the USSR. B. It was waged on mostly political and economic fronts, but there was always a threat of all-out war.
![The Cold War [1945 -1991]: An Ideological Struggle Soviet & Eastern Bloc Nations [“Iron The Cold War [1945 -1991]: An Ideological Struggle Soviet & Eastern Bloc Nations [“Iron](https://present5.com/presentation/cc836f061bef7d42dc83096917f64a06/image-21.jpg) The Cold War [1945 -1991]: An Ideological Struggle Soviet & Eastern Bloc Nations [“Iron Curtain”] GOAL spread world-wide Communism METHODOLOGIES: US & the Western Democracies GOAL “Containment” of Communism & the eventual collapse of the Communist world. [George Kennan] 1. Espionage [KGB vs. CIA] 2. Arms Race [nuclear escalation] 3. Ideological Competition for the minds and hearts of Third World peoples [Communist govt. & command economy vs. democratic govt. & capitalist economy] “proxy wars” 5. Bi-Polarization of Europe [NATO vs. Warsaw Pact]
The Cold War [1945 -1991]: An Ideological Struggle Soviet & Eastern Bloc Nations [“Iron Curtain”] GOAL spread world-wide Communism METHODOLOGIES: US & the Western Democracies GOAL “Containment” of Communism & the eventual collapse of the Communist world. [George Kennan] 1. Espionage [KGB vs. CIA] 2. Arms Race [nuclear escalation] 3. Ideological Competition for the minds and hearts of Third World peoples [Communist govt. & command economy vs. democratic govt. & capitalist economy] “proxy wars” 5. Bi-Polarization of Europe [NATO vs. Warsaw Pact]
 !!!!! USSR tested its first atomic bomb in 1949!!!!! 1949
!!!!! USSR tested its first atomic bomb in 1949!!!!! 1949
 1. At the heart of the conflict were two very different world-views held by the two nations and their allies: a. The USSR viewed capitalism as a monster, which, if unchecked, would consume the entire world. b. America viewed Communism as an evil tool designed to destroy the rights and liberties of all mankind. 2. Both sides believed that the other was seeking world domination.
1. At the heart of the conflict were two very different world-views held by the two nations and their allies: a. The USSR viewed capitalism as a monster, which, if unchecked, would consume the entire world. b. America viewed Communism as an evil tool designed to destroy the rights and liberties of all mankind. 2. Both sides believed that the other was seeking world domination.
 C. RELATIONS AFTER WWII 1. US and GB aligned themselves with the USSR during WWII because of its location near Japan. Although the US and GB had many concerns about the type of rule in the Soviet Union, its lack of economic wealth, military power, and national unity made them a non-threatening ally. 2. However, after WWII, old dissentions over governmental ideals arose. Plus, the USSR had military and occupational strength that was not prominent before. strength
C. RELATIONS AFTER WWII 1. US and GB aligned themselves with the USSR during WWII because of its location near Japan. Although the US and GB had many concerns about the type of rule in the Soviet Union, its lack of economic wealth, military power, and national unity made them a non-threatening ally. 2. However, after WWII, old dissentions over governmental ideals arose. Plus, the USSR had military and occupational strength that was not prominent before. strength
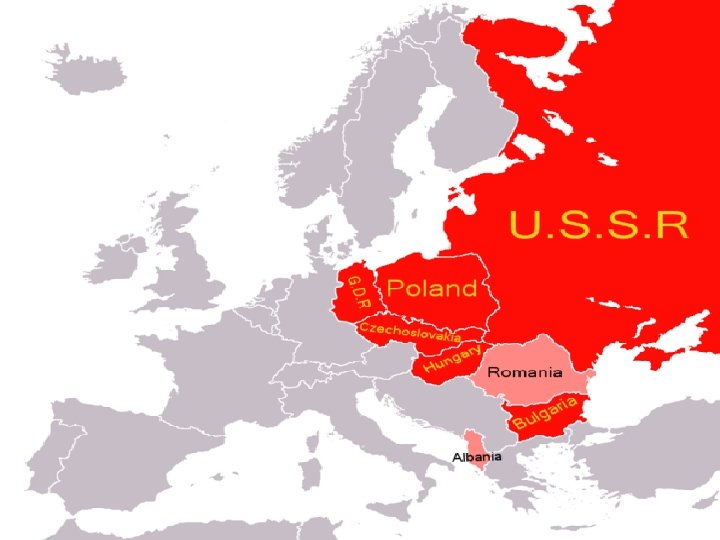
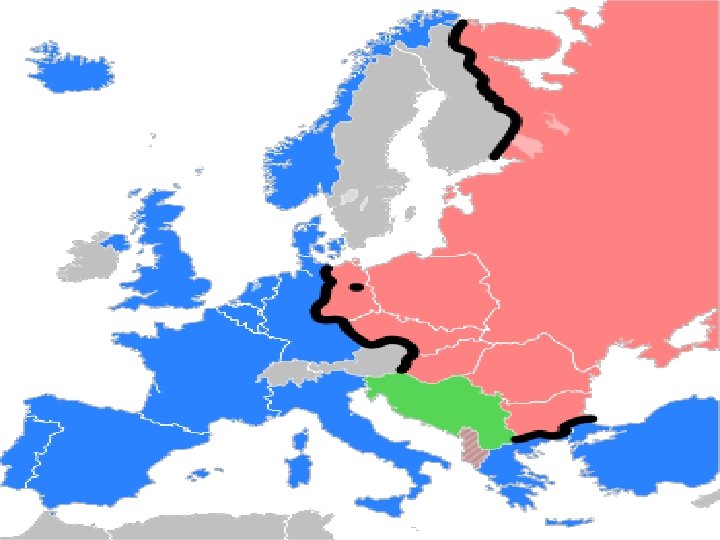
 D. SUSPICIONS AGAINST THE USSR 1. America feared that Soviet expansion would increase communism. 2. At this time, Soviet Union controlled most of Eastern Europe (satellite nations). nations 3. Soviet leaders promised free elections in their satellite nations; however, they did not follow through.
D. SUSPICIONS AGAINST THE USSR 1. America feared that Soviet expansion would increase communism. 2. At this time, Soviet Union controlled most of Eastern Europe (satellite nations). nations 3. Soviet leaders promised free elections in their satellite nations; however, they did not follow through.
 E. STALIN’S SUPPRESSIONS 1. The Soviet Union crushed all opposition in Eastern Europe (which it had liberated from Nazi control) after 1945, rigging elections in order to receive communist votes. 2. The Communists gained control by promising to abolish poverty, privilege, and private property.
E. STALIN’S SUPPRESSIONS 1. The Soviet Union crushed all opposition in Eastern Europe (which it had liberated from Nazi control) after 1945, rigging elections in order to receive communist votes. 2. The Communists gained control by promising to abolish poverty, privilege, and private property.
 3. By 1948, with the occupying Soviet Red Army always in the background, the communists had taken over the governments of 8 Eastern European countries.
3. By 1948, with the occupying Soviet Red Army always in the background, the communists had taken over the governments of 8 Eastern European countries.
 Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (RFE/RL) is a broadcaster funded by the US Congress that provides news, information, and analysis to countries in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, and the Middle East“ where the free flow of information is either banned by government authorities or not fully developed” Founded as an anti-communist propaganda source during the Cold War
Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (RFE/RL) is a broadcaster funded by the US Congress that provides news, information, and analysis to countries in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, and the Middle East“ where the free flow of information is either banned by government authorities or not fully developed” Founded as an anti-communist propaganda source during the Cold War
 F. THE IRON CURTAIN 1. 3/12/1946: Fulton, Missouri 2. Winston Churchill visited Winston Churchill Westminster College and summed up Soviet relations with the US and GB: “From Stettin on the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an Iron Curtain has descended across the Continent. ” 3. “Iron Curtain”: term used to describe Soviet control in Europe, 1945 -1990.
F. THE IRON CURTAIN 1. 3/12/1946: Fulton, Missouri 2. Winston Churchill visited Winston Churchill Westminster College and summed up Soviet relations with the US and GB: “From Stettin on the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an Iron Curtain has descended across the Continent. ” 3. “Iron Curtain”: term used to describe Soviet control in Europe, 1945 -1990.
 THE IRON CURTAIN Note to self: this is NOT the Berlin Wall!!!
THE IRON CURTAIN Note to self: this is NOT the Berlin Wall!!!
 G. CONTAINMENT 1. George Kennan- George Kennan. State Department official and Soviet expert- suggested the U. S. and Great Britain instill a policy of CONTAINMENT: restricting the expansion of Soviet communism.
G. CONTAINMENT 1. George Kennan- George Kennan. State Department official and Soviet expert- suggested the U. S. and Great Britain instill a policy of CONTAINMENT: restricting the expansion of Soviet communism.
 Good Afternoon! Complete bellringer on back of last class’s BR.
Good Afternoon! Complete bellringer on back of last class’s BR.
 2. Containment measures included: a. The Truman Doctrine b. The Marshall Plan c. The Berlin Airlift d. The Korean War e. The Eisenhower Doctrine (occurred later during the presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower)
2. Containment measures included: a. The Truman Doctrine b. The Marshall Plan c. The Berlin Airlift d. The Korean War e. The Eisenhower Doctrine (occurred later during the presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower)
 March 12, 1947 • It became "the policy of the United States to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures. " • Specifically targeted Greece and Turkey, who were fighting Communist forces. • $400 million sent to these 2 countries! - This replaced British support in Greece!
March 12, 1947 • It became "the policy of the United States to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures. " • Specifically targeted Greece and Turkey, who were fighting Communist forces. • $400 million sent to these 2 countries! - This replaced British support in Greece!
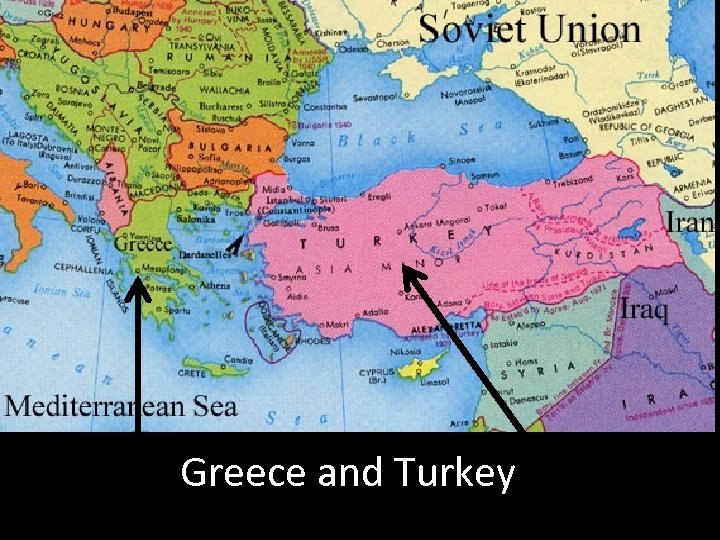 Greece and Turkey
Greece and Turkey
 • U. S. economic aid to Europe – try to contain Soviet influence on the continent!!! • Designed to help rebuild the Allied nations in Europe • $13 billion over four years! • Under influence of Stalin, Eastern Europe rejected the plan of aid. - Aka: European Recovery Program
• U. S. economic aid to Europe – try to contain Soviet influence on the continent!!! • Designed to help rebuild the Allied nations in Europe • $13 billion over four years! • Under influence of Stalin, Eastern Europe rejected the plan of aid. - Aka: European Recovery Program
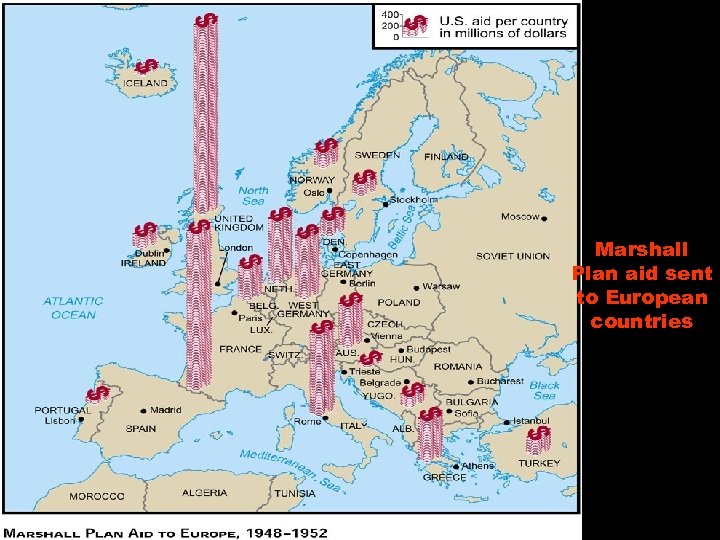 Marshall Plan aid sent to European countries
Marshall Plan aid sent to European countries

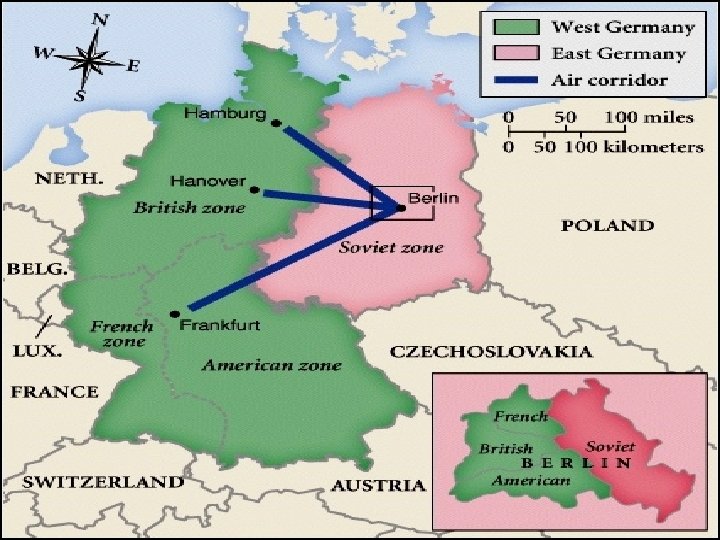
 • First major crisis of Cold War • June 24, 1948: USSR blocked railroad and street access to West Berlin. • American, British, and French forces airlifted food and other provisions to the Western-held sectors of Berlin. • USSR did not respond with force, and war was avoided! • Blockade ended on May 12, 1949
• First major crisis of Cold War • June 24, 1948: USSR blocked railroad and street access to West Berlin. • American, British, and French forces airlifted food and other provisions to the Western-held sectors of Berlin. • USSR did not respond with force, and war was avoided! • Blockade ended on May 12, 1949
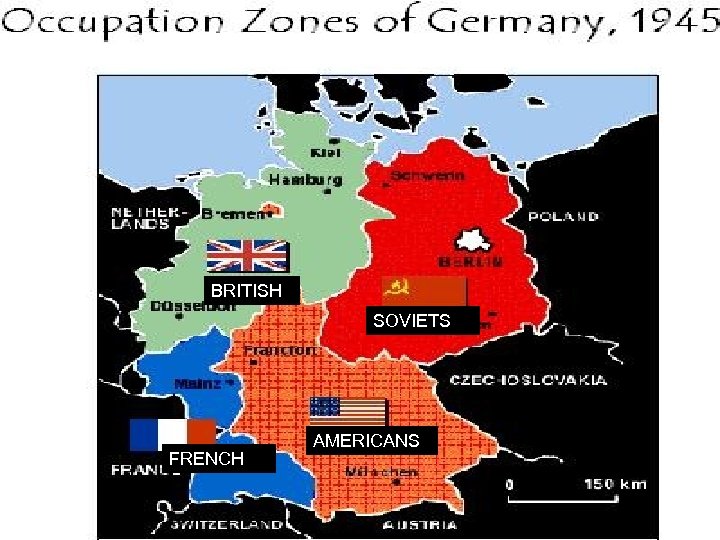 BRITISH SOVIETS FRENCH AMERICANS
BRITISH SOVIETS FRENCH AMERICANS
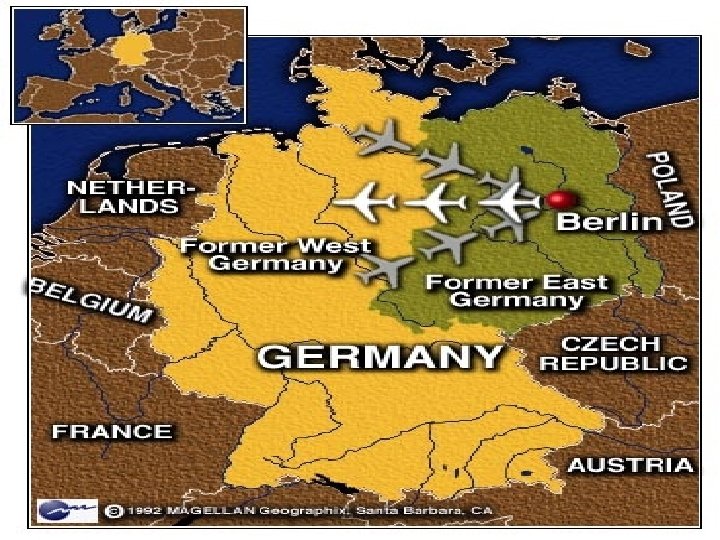
 The Berlin Airlift
The Berlin Airlift
 • Message to Congress on Jan 5, 1957 • Implied that U. S. would take military action in response to imminent or actual aggression to the U. S. • Countries that took stances opposed to communism would be given aid in various forms. • Applied to Middle East the next year (troops to Lebanon)
• Message to Congress on Jan 5, 1957 • Implied that U. S. would take military action in response to imminent or actual aggression to the U. S. • Countries that took stances opposed to communism would be given aid in various forms. • Applied to Middle East the next year (troops to Lebanon)
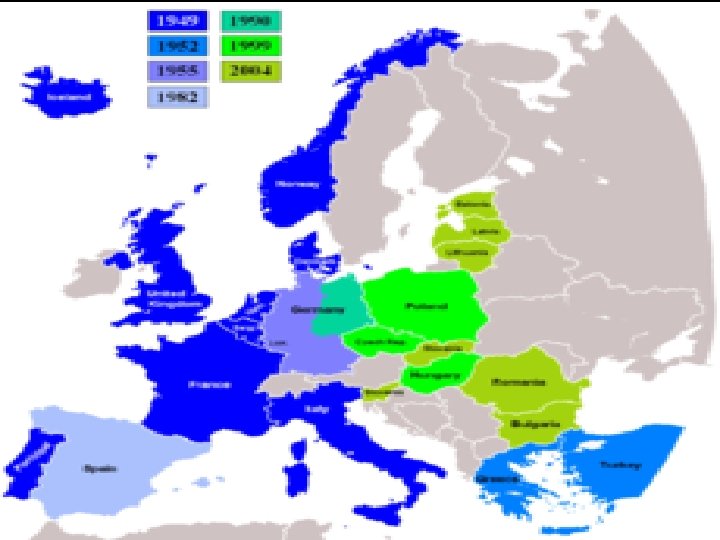
 H. NATO 1. In 1948, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization was formed. The organization established a system of collective security, in which its members pledged to defend the others in the case of an attack by an external party (communist nations were threat!) 2. The Communists later formed the Warsaw Pact to counter NATO.
H. NATO 1. In 1948, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization was formed. The organization established a system of collective security, in which its members pledged to defend the others in the case of an attack by an external party (communist nations were threat!) 2. The Communists later formed the Warsaw Pact to counter NATO.
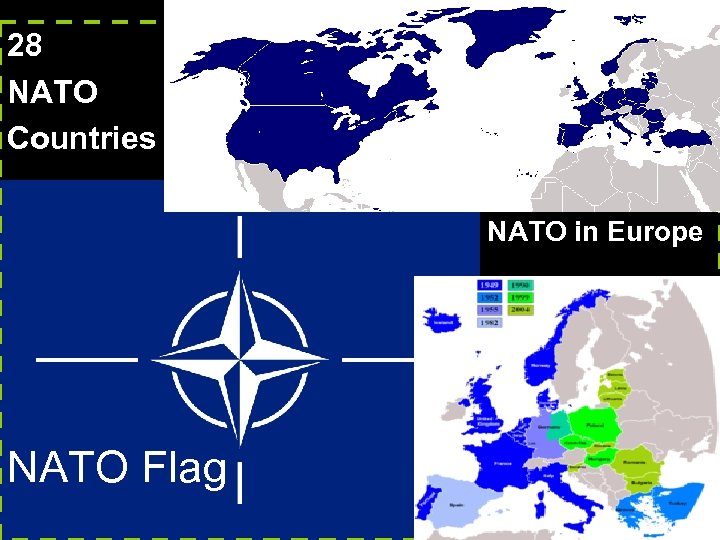 28 NATO Countries NATO in Europe NATO Flag
28 NATO Countries NATO in Europe NATO Flag
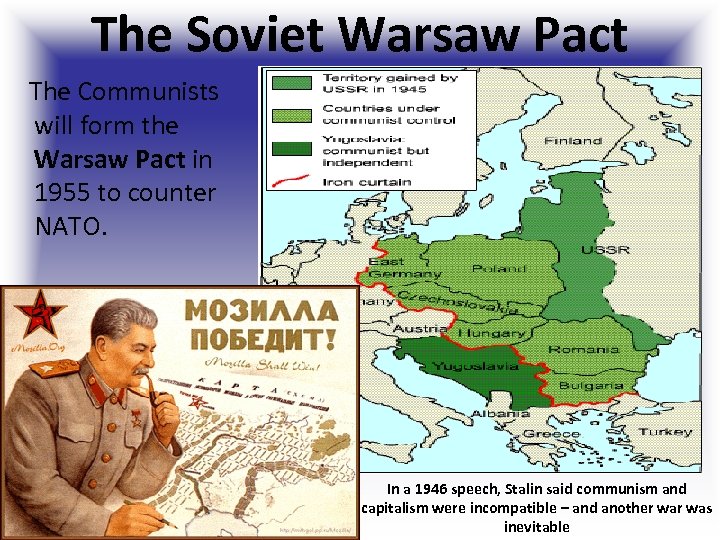 The Soviet Warsaw Pact The Communists will form the Warsaw Pact in 1955 to counter NATO. In a 1946 speech, Stalin said communism and capitalism were incompatible – and another was inevitable
The Soviet Warsaw Pact The Communists will form the Warsaw Pact in 1955 to counter NATO. In a 1946 speech, Stalin said communism and capitalism were incompatible – and another was inevitable
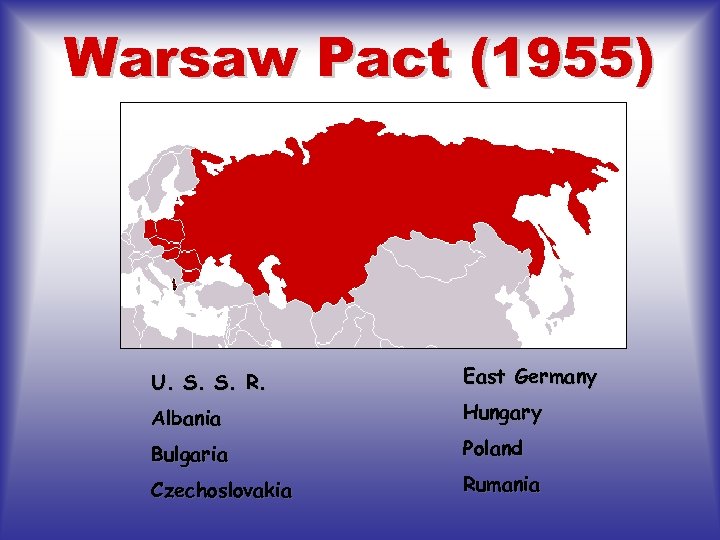 Warsaw Pact (1955) U. S. S. R. East Germany Albania Hungary Bulgaria Poland Czechoslovakia Rumania
Warsaw Pact (1955) U. S. S. R. East Germany Albania Hungary Bulgaria Poland Czechoslovakia Rumania
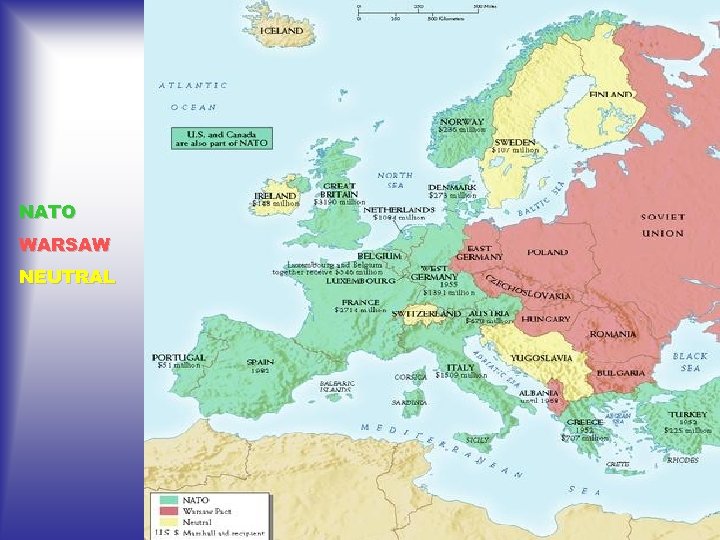 NATO WARSAW NEUTRAL
NATO WARSAW NEUTRAL
 I. Israel is Formed 1948: Following the massextermination of Jews by the Nazis during WWII, a homeland was established for the Israelites. This was preceded by more than 50 years of efforts to establish a sovereign nation as a homeland for Jews.
I. Israel is Formed 1948: Following the massextermination of Jews by the Nazis during WWII, a homeland was established for the Israelites. This was preceded by more than 50 years of efforts to establish a sovereign nation as a homeland for Jews.
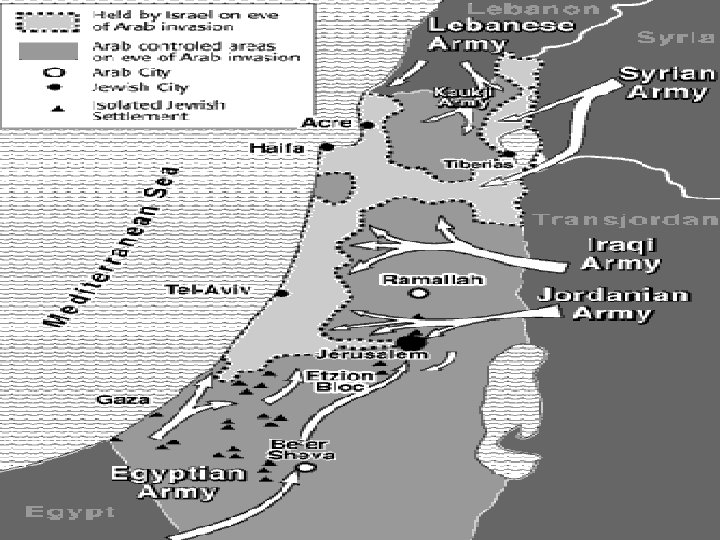
 The First Arab Israeli war The proclamation of an independent Israel brought immediate attack by the Arab nations surrounding Palestine. Although recognized by the US and Soviets the Arabs refused to recognize the Jewish state. The outnumbered Jews were able to defeat the Arabs armies of 4 nations and a UN negotiated armistice by Ralph Bunche ended the first conflict.
The First Arab Israeli war The proclamation of an independent Israel brought immediate attack by the Arab nations surrounding Palestine. Although recognized by the US and Soviets the Arabs refused to recognize the Jewish state. The outnumbered Jews were able to defeat the Arabs armies of 4 nations and a UN negotiated armistice by Ralph Bunche ended the first conflict.