7f48848c9c4b4904275713b56c733a2c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 The Cold War Mr. Thomas Sothars De Smet Jesuit HS
The Cold War Mr. Thomas Sothars De Smet Jesuit HS
 Communist Takeover in Czechoslovakia w Feb. 1948 w Key members of Czech gov’t die mysteriously w Pro-western President forced to resign, new constitution ratified – Complete takeover by Czech communists
Communist Takeover in Czechoslovakia w Feb. 1948 w Key members of Czech gov’t die mysteriously w Pro-western President forced to resign, new constitution ratified – Complete takeover by Czech communists
 Berlin Airlift w Blockade of Berlin began on June 24, ’ 48 w From June 1948 to May 1949, U. S. and British planes airlift 1. 5 million tons of supplies to the residents of West Berlin. w After 200, 000 flights, the Soviet Union lifts the blockade.
Berlin Airlift w Blockade of Berlin began on June 24, ’ 48 w From June 1948 to May 1949, U. S. and British planes airlift 1. 5 million tons of supplies to the residents of West Berlin. w After 200, 000 flights, the Soviet Union lifts the blockade.
 Operation Vittles w All of the necessities for the city's 2. 5 million residents -- an estimated 4, 500 tons of food, coal and other materials each day -- had to enter the city by air. w On its biggest day, the "Easter parade" of April 16, 1949, the airlift sent 1, 398 flights into Berlin - one every minute. w Before it was all over, more than 278, 000 flights would carry 2. 3 million tons of relief supplies.
Operation Vittles w All of the necessities for the city's 2. 5 million residents -- an estimated 4, 500 tons of food, coal and other materials each day -- had to enter the city by air. w On its biggest day, the "Easter parade" of April 16, 1949, the airlift sent 1, 398 flights into Berlin - one every minute. w Before it was all over, more than 278, 000 flights would carry 2. 3 million tons of relief supplies.
 Berlin Airlift w The airlift marked a rise in tensions between the West and the Soviets, but it also helped heal divisions left by World War II. w Almost immediately, The United States, Great Britain, and France shifted from Germany's conquerors to its protectors. w "The airlift was the starting point for Germany's inclusion in the West and for the reconciliation with the Western powers, " Berlin Mayor Eberhard Diepgen says. w Allied cooperation paved way formation of new military alliance, North Atlantic Treaty Organization, NATO w Soviets formed their own alliance called Warsaw Pact in 1955
Berlin Airlift w The airlift marked a rise in tensions between the West and the Soviets, but it also helped heal divisions left by World War II. w Almost immediately, The United States, Great Britain, and France shifted from Germany's conquerors to its protectors. w "The airlift was the starting point for Germany's inclusion in the West and for the reconciliation with the Western powers, " Berlin Mayor Eberhard Diepgen says. w Allied cooperation paved way formation of new military alliance, North Atlantic Treaty Organization, NATO w Soviets formed their own alliance called Warsaw Pact in 1955
 1949 – Fall of China w In June, Jiang Jieshi defeated by Mao – Flee to island of Taiwan w Oct 1, Mao proclaims People’s Republic of China (PRC) w Two months later, Mao travels to Moscow, – negotiates the Sino. Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Alliance and Mutual Assistance.
1949 – Fall of China w In June, Jiang Jieshi defeated by Mao – Flee to island of Taiwan w Oct 1, Mao proclaims People’s Republic of China (PRC) w Two months later, Mao travels to Moscow, – negotiates the Sino. Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Alliance and Mutual Assistance.
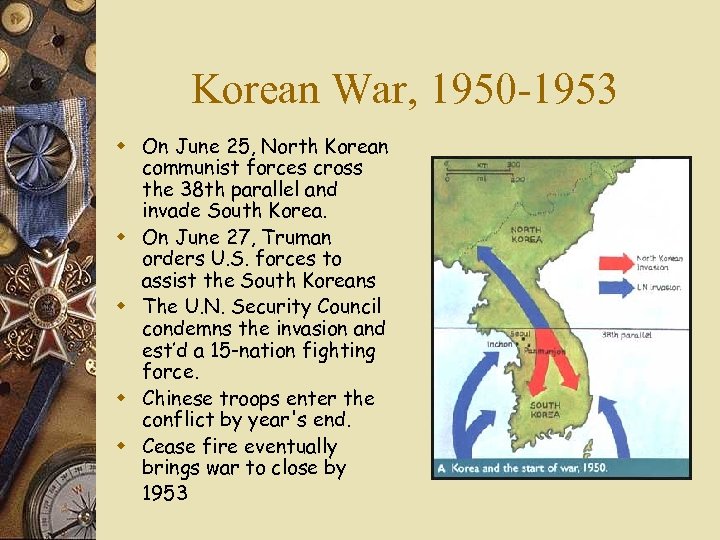 Korean War, 1950 -1953 w On June 25, North Korean communist forces cross the 38 th parallel and invade South Korea. w On June 27, Truman orders U. S. forces to assist the South Koreans w The U. N. Security Council condemns the invasion and est’d a 15 -nation fighting force. w Chinese troops enter the conflict by year's end. w Cease fire eventually brings war to close by 1953
Korean War, 1950 -1953 w On June 25, North Korean communist forces cross the 38 th parallel and invade South Korea. w On June 27, Truman orders U. S. forces to assist the South Koreans w The U. N. Security Council condemns the invasion and est’d a 15 -nation fighting force. w Chinese troops enter the conflict by year's end. w Cease fire eventually brings war to close by 1953
 Dien Bien Phu w After a long siege, Vietnamese communists under Ho Chi Minh defeat French colonial forces at Dien Bien Phu on May 7. w In July, the Geneva Accords divide the country at the 17 th parallel, creating a North and South Vietnam. w The United States assumes the chief responsibility of providing anti-communist aid to South Vietnam.
Dien Bien Phu w After a long siege, Vietnamese communists under Ho Chi Minh defeat French colonial forces at Dien Bien Phu on May 7. w In July, the Geneva Accords divide the country at the 17 th parallel, creating a North and South Vietnam. w The United States assumes the chief responsibility of providing anti-communist aid to South Vietnam.
 General Vo Nguyen Giap.
General Vo Nguyen Giap.
 Massive Retaliation w On January 12, 1955 U. S. Secretary of State John Foster Dulles first announces the doctrine of Massive Retaliation. w It threatens fullscale nuclear attack on the Soviet Union in response to communist aggression anywhere in the world. John Foster Dulles and Mac. Arthur in Korea, 1950
Massive Retaliation w On January 12, 1955 U. S. Secretary of State John Foster Dulles first announces the doctrine of Massive Retaliation. w It threatens fullscale nuclear attack on the Soviet Union in response to communist aggression anywhere in the world. John Foster Dulles and Mac. Arthur in Korea, 1950
 1956 - Khrushchev's 'secret speech' w In a speech, February 14, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev denounces the policies of Stalin. w He rejects the Leninist idea of the inevitability of war and calls for a doctrine of "peaceful coexistence" between capitalist and communist systems. 1959 Kitchen debate
1956 - Khrushchev's 'secret speech' w In a speech, February 14, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev denounces the policies of Stalin. w He rejects the Leninist idea of the inevitability of war and calls for a doctrine of "peaceful coexistence" between capitalist and communist systems. 1959 Kitchen debate
 1959 - Castro takes power w January 1, 1959 leftist forces under Fidel Castro overthrow Fulgencio Batista w Castro nationalizes the sugar industry and signs trade agreements with the Soviet Union. w The next year, Castro seizes U. S. assets on the island.
1959 - Castro takes power w January 1, 1959 leftist forces under Fidel Castro overthrow Fulgencio Batista w Castro nationalizes the sugar industry and signs trade agreements with the Soviet Union. w The next year, Castro seizes U. S. assets on the island.
 1960 - The U-2 Affair w On May 1, an American highaltitude U-2 spy plane is shot down on a mission over the Soviet Union. w After the Soviets announce the capture of pilot Francis Gary Powers, the United States recants earlier assertions that the plane was on a weather research mission.
1960 - The U-2 Affair w On May 1, an American highaltitude U-2 spy plane is shot down on a mission over the Soviet Union. w After the Soviets announce the capture of pilot Francis Gary Powers, the United States recants earlier assertions that the plane was on a weather research mission.
 The U-2 Affair • Suffering major embarrassment, Eisenhower was forced to admit the truth behind the mission and the U-2 program, although he refused to publicly apologize to Khrushchev. • This refusal caused the Paris Summit to collapse when Khrushchev stormed out of negotiations. w Powers was sentenced to ten years in prison, including seven years of hard labor, following an infamous showtrial. w He served less than two years, however, and was released in 1962 in exchange for Soviet spy Rudolf Abel.
The U-2 Affair • Suffering major embarrassment, Eisenhower was forced to admit the truth behind the mission and the U-2 program, although he refused to publicly apologize to Khrushchev. • This refusal caused the Paris Summit to collapse when Khrushchev stormed out of negotiations. w Powers was sentenced to ten years in prison, including seven years of hard labor, following an infamous showtrial. w He served less than two years, however, and was released in 1962 in exchange for Soviet spy Rudolf Abel.
 Kennedy’s Election w John F. Kennedy – from a wealthy, politically powerful family w Good looking, young, and comfortable in front of the television cameras w People felt Kennedy represented the future w Election of 1960 – Adopted the term “new frontier” – Played on the nation’s Cold War fears – Claimed the nation’s prosperity was not reaching the poor – Rallied the African American vote when Kennedy called Coretta King after Martin Luther King Jr. was arrested; Robert Kennedy persuaded the judge to release King – One of the closest elections in history
Kennedy’s Election w John F. Kennedy – from a wealthy, politically powerful family w Good looking, young, and comfortable in front of the television cameras w People felt Kennedy represented the future w Election of 1960 – Adopted the term “new frontier” – Played on the nation’s Cold War fears – Claimed the nation’s prosperity was not reaching the poor – Rallied the African American vote when Kennedy called Coretta King after Martin Luther King Jr. was arrested; Robert Kennedy persuaded the judge to release King – One of the closest elections in history
 Kennedy Takes Office Inaugural Address • Focused on change • Strong anti-Communist tone • Did not specify his domestic policy goals because so much division existed over domestic issues Kennedy’s Advisors • Gathered a group some called “the best and the brightest” as his advisors • Most of Kennedy’s advisors were young. • Closest advisor was his brother, Robert (“Bobby”) Kennedy • Cabinet members had less influence than White House advisors.
Kennedy Takes Office Inaugural Address • Focused on change • Strong anti-Communist tone • Did not specify his domestic policy goals because so much division existed over domestic issues Kennedy’s Advisors • Gathered a group some called “the best and the brightest” as his advisors • Most of Kennedy’s advisors were young. • Closest advisor was his brother, Robert (“Bobby”) Kennedy • Cabinet members had less influence than White House advisors.
 Bay of Pigs Invasion Background • Fidel Castro was in power in Cuba. • Came to power after a guerrilla war, promised to restore people’s rights and freedoms • Once in power, he seized private businesses and made overtures to Soviet Union. Kennedy • Kennedy learned that the CIA was training troops to invade Cuba and topple Castro. • His advisors were mixed. • Kennedy was worried about Communism spreading to Latin America. • Kennedy gave the go-ahead. The Invasion • Bay of Pigs invasion failed. • Information was leaked early. • Air strikes failed. • Castro prepared for a land attack. • Invaders were captured and ransomed back to United States. • Strengthened Castro’s ties to the Soviet Union
Bay of Pigs Invasion Background • Fidel Castro was in power in Cuba. • Came to power after a guerrilla war, promised to restore people’s rights and freedoms • Once in power, he seized private businesses and made overtures to Soviet Union. Kennedy • Kennedy learned that the CIA was training troops to invade Cuba and topple Castro. • His advisors were mixed. • Kennedy was worried about Communism spreading to Latin America. • Kennedy gave the go-ahead. The Invasion • Bay of Pigs invasion failed. • Information was leaked early. • Air strikes failed. • Castro prepared for a land attack. • Invaders were captured and ransomed back to United States. • Strengthened Castro’s ties to the Soviet Union
 1961 - Bay of Pigs Captured Cubans w U. S. -organized invasion force of 1, 400 Cuban exiles is defeated by Castro's government forces on Cuba's south coast at the Bay of Pigs. w Launched from Guatemala in ships and planes provided by the United States, the invaders surrender on April 20 after three days of fighting. w Kennedy takes full responsibility for the disaster.
1961 - Bay of Pigs Captured Cubans w U. S. -organized invasion force of 1, 400 Cuban exiles is defeated by Castro's government forces on Cuba's south coast at the Bay of Pigs. w Launched from Guatemala in ships and planes provided by the United States, the invaders surrender on April 20 after three days of fighting. w Kennedy takes full responsibility for the disaster.
 The Berlin Crisis Berlin’s Significance w Khrushchev demanded that the United States recognize East Germany as an independent Communist nation. w West Berlin was an island of freedom. w Many East Germans fled to West Germany through Berlin. w Kennedy refused to be bullied, sent troops into West Germany, built nuclear shelters, and waited for Khrushchev’s next move. The Berlin Wall w On August 13, 1961, Khrushchev closed the crossing points between East and West Berlin. w A high concrete wall was built to prevent further escapes to freedom. w Kennedy sent more troops, and Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson visited West Berlin. w Kennedy said “A wall is a … lot better than a war. ” w Over time, the wall was extended and fortified.
The Berlin Crisis Berlin’s Significance w Khrushchev demanded that the United States recognize East Germany as an independent Communist nation. w West Berlin was an island of freedom. w Many East Germans fled to West Germany through Berlin. w Kennedy refused to be bullied, sent troops into West Germany, built nuclear shelters, and waited for Khrushchev’s next move. The Berlin Wall w On August 13, 1961, Khrushchev closed the crossing points between East and West Berlin. w A high concrete wall was built to prevent further escapes to freedom. w Kennedy sent more troops, and Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson visited West Berlin. w Kennedy said “A wall is a … lot better than a war. ” w Over time, the wall was extended and fortified.
 1961 - Berlin Wall w On August 15, communist authorities begin construction on the Berlin Wall to prevent East Germans from fleeing to West Berlin.
1961 - Berlin Wall w On August 15, communist authorities begin construction on the Berlin Wall to prevent East Germans from fleeing to West Berlin.
 JFK in Berlin http: //www. npr. org/templates/story. php? story. Id=5359589
JFK in Berlin http: //www. npr. org/templates/story. php? story. Id=5359589
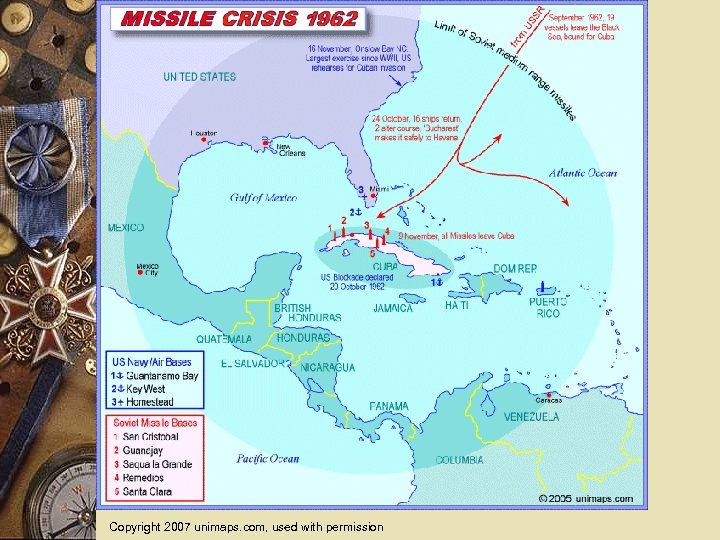
 1962 - Cuban Missile Crisis w After Bay of Pigs invasion, the Soviet Union installed nuclear missiles in Cuba. w After U-2 flights Kennedy ordered a naval blockade of Cuba on October 22 until the Soviet Union removed its missiles. w On October 28, the Soviets agreed to remove the missiles, defusing one of the most dangerous confrontations of the Cold War.
1962 - Cuban Missile Crisis w After Bay of Pigs invasion, the Soviet Union installed nuclear missiles in Cuba. w After U-2 flights Kennedy ordered a naval blockade of Cuba on October 22 until the Soviet Union removed its missiles. w On October 28, the Soviets agreed to remove the missiles, defusing one of the most dangerous confrontations of the Cold War.
 The Cuban Missile Crises w U. S. actions in the Bay of Pigs and Berlin crises encouraged hard -line leaders in the Soviet Union. Buildup w The Soviets were worried about another invasion of Cuba and U. S. nuclear missiles placed in Turkey. w Kennedy was worried about accusations of being “soft on communism. ” Crisis Begins w A U. S. U-2 spy plane detected Soviet surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) in Cuba. w The Soviets argued that the SAMs were defensive missiles and swore that they didn’t have offensive missiles in Cuba. w Later U-2 flights showed that the Soviets had lied.
The Cuban Missile Crises w U. S. actions in the Bay of Pigs and Berlin crises encouraged hard -line leaders in the Soviet Union. Buildup w The Soviets were worried about another invasion of Cuba and U. S. nuclear missiles placed in Turkey. w Kennedy was worried about accusations of being “soft on communism. ” Crisis Begins w A U. S. U-2 spy plane detected Soviet surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) in Cuba. w The Soviets argued that the SAMs were defensive missiles and swore that they didn’t have offensive missiles in Cuba. w Later U-2 flights showed that the Soviets had lied.
 The Cuban Missile Crisis w Managing the Crisis Kennedy assembled a group of advisors, known as the Ex. Comm, to help him plan a response. – Ex. Comm military members favored an air strike, perhaps followed by a land invasion of Cuba. – Others argued for a naval blockade. Kennedy agreed with this plan. The world watched as Soviet ships carrying missile parts approached the naval blockade. They turned back. w Effects of the Crisis w Khrushchev agreed to dismantle the missiles if the United States pledged to never invade Cuba. w Both Kennedy and Khrushchev took steps to ease tensions between their countries. w They set up a hotline to allow direct communication during times of crisis. w The Limited Nuclear Test Ban Treaty was signed, ending atmospheric and underwater testing of nuclear weapons.
The Cuban Missile Crisis w Managing the Crisis Kennedy assembled a group of advisors, known as the Ex. Comm, to help him plan a response. – Ex. Comm military members favored an air strike, perhaps followed by a land invasion of Cuba. – Others argued for a naval blockade. Kennedy agreed with this plan. The world watched as Soviet ships carrying missile parts approached the naval blockade. They turned back. w Effects of the Crisis w Khrushchev agreed to dismantle the missiles if the United States pledged to never invade Cuba. w Both Kennedy and Khrushchev took steps to ease tensions between their countries. w They set up a hotline to allow direct communication during times of crisis. w The Limited Nuclear Test Ban Treaty was signed, ending atmospheric and underwater testing of nuclear weapons.
 Copyright 2007 unimaps. com, used with permission
Copyright 2007 unimaps. com, used with permission


