20149fe27a6c9ad7eba4b8d447d945bc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 The Cold War & Korean War
The Cold War & Korean War
 The Alliance of the “Big Three” Crumbled The hardline stances between the USSR & US led to over 4 decades of animosity The foreign policy and poor relations between the US and the Soviet Union from 1947 -1989 is called the Cold War
The Alliance of the “Big Three” Crumbled The hardline stances between the USSR & US led to over 4 decades of animosity The foreign policy and poor relations between the US and the Soviet Union from 1947 -1989 is called the Cold War
 Cold War of words, ideologies. The Cold War did turn “hot” on a few occasions Most major altercations in these years pitted the US against the USSR
Cold War of words, ideologies. The Cold War did turn “hot” on a few occasions Most major altercations in these years pitted the US against the USSR
 Origins of the Cold War Mutual Distrust US did not trust communism. Violence, lack of civil liberties USSR still angry at troop losses. Believed US and UK deliberately did not open a second front in WWII USSR did not allow free elections in Eastern Europe. Buffer-zone US kept the USSR out of reconstructing Japan Different ideas about post-war world
Origins of the Cold War Mutual Distrust US did not trust communism. Violence, lack of civil liberties USSR still angry at troop losses. Believed US and UK deliberately did not open a second front in WWII USSR did not allow free elections in Eastern Europe. Buffer-zone US kept the USSR out of reconstructing Japan Different ideas about post-war world
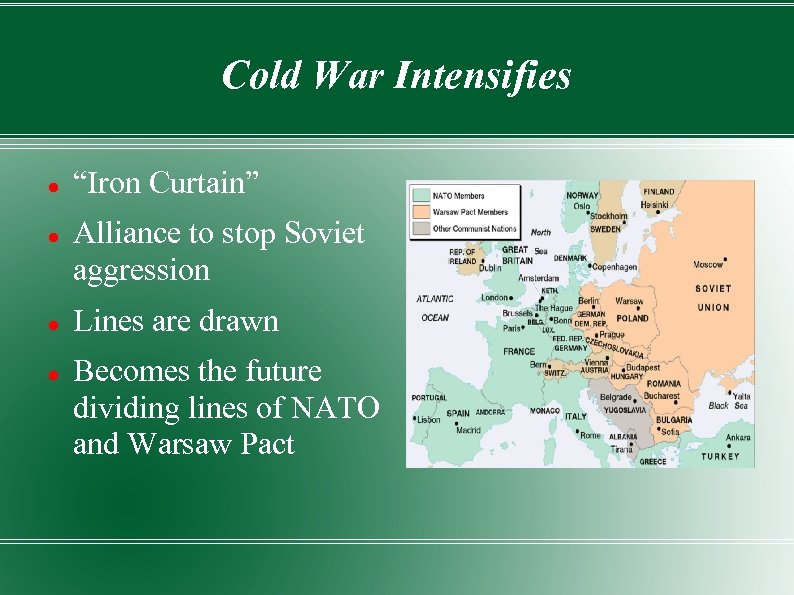 Cold War Intensifies “Iron Curtain” Alliance to stop Soviet aggression Lines are drawn Becomes the future dividing lines of NATO and Warsaw Pact
Cold War Intensifies “Iron Curtain” Alliance to stop Soviet aggression Lines are drawn Becomes the future dividing lines of NATO and Warsaw Pact
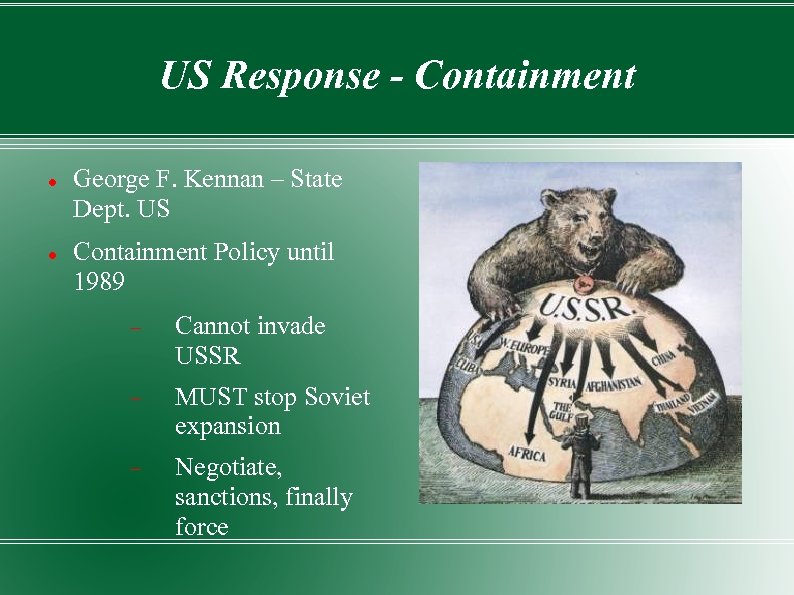 US Response - Containment George F. Kennan – State Dept. US Containment Policy until 1989 Cannot invade USSR MUST stop Soviet expansion Negotiate, sanctions, finally force
US Response - Containment George F. Kennan – State Dept. US Containment Policy until 1989 Cannot invade USSR MUST stop Soviet expansion Negotiate, sanctions, finally force
 Truman Doctrine Greece & Turkey. War against communist supported insurgents Doorway for USSR into Middle East and Western Europe Truman sent $400 M in aid to Greece & Turkey Pledged American aid to all “free peoples fighting oppression” US became a global police force against communism
Truman Doctrine Greece & Turkey. War against communist supported insurgents Doorway for USSR into Middle East and Western Europe Truman sent $400 M in aid to Greece & Turkey Pledged American aid to all “free peoples fighting oppression” US became a global police force against communism
 Marshall Plan 2 goals – Humanitarian Aid and contain/fight communism US gave $17 B in free aid to Western Europe to reconstruct the post-war economy Worked in Western Europe. Recovery, stopped spread of communism, promoted trade and helped US businesses
Marshall Plan 2 goals – Humanitarian Aid and contain/fight communism US gave $17 B in free aid to Western Europe to reconstruct the post-war economy Worked in Western Europe. Recovery, stopped spread of communism, promoted trade and helped US businesses
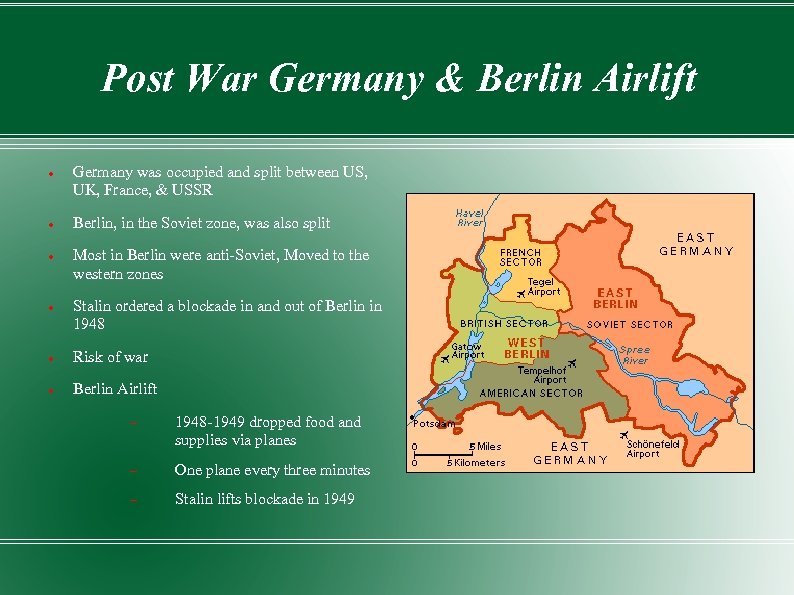 Post War Germany & Berlin Airlift Germany was occupied and split between US, UK, France, & USSR Berlin, in the Soviet zone, was also split Most in Berlin were anti-Soviet, Moved to the western zones Stalin ordered a blockade in and out of Berlin in 1948 Risk of war Berlin Airlift 1948 -1949 dropped food and supplies via planes One plane every three minutes Stalin lifts blockade in 1949
Post War Germany & Berlin Airlift Germany was occupied and split between US, UK, France, & USSR Berlin, in the Soviet zone, was also split Most in Berlin were anti-Soviet, Moved to the western zones Stalin ordered a blockade in and out of Berlin in 1948 Risk of war Berlin Airlift 1948 -1949 dropped food and supplies via planes One plane every three minutes Stalin lifts blockade in 1949
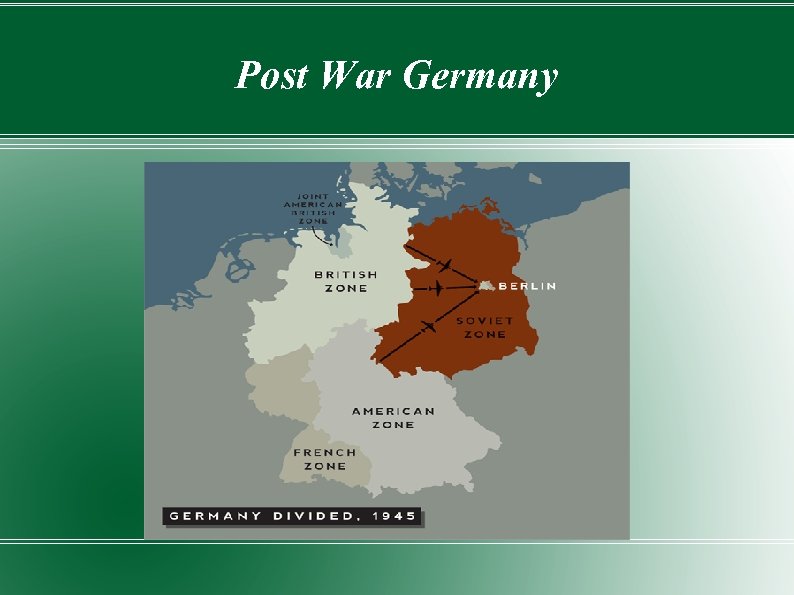 Post War Germany
Post War Germany
 Domestic Policy during the Cold War Election of 1948 Truman (Dem) – Expand New Deal, Civil Rights Strom Thurmond (Dixiecrat) – continue segregation Thomas Dewey (Rep. ), moderate Truman won in a very close election
Domestic Policy during the Cold War Election of 1948 Truman (Dem) – Expand New Deal, Civil Rights Strom Thurmond (Dixiecrat) – continue segregation Thomas Dewey (Rep. ), moderate Truman won in a very close election
 “Fair Deal” Truman wished to expand the New Deal – Called it the Fair Deal Raise minimum wage, expand social security Federal $ to public education (not passed) Promoted civil rights legislation (not passed) Wanted national health care (not passed)
“Fair Deal” Truman wished to expand the New Deal – Called it the Fair Deal Raise minimum wage, expand social security Federal $ to public education (not passed) Promoted civil rights legislation (not passed) Wanted national health care (not passed)
 Anti-Communism in the US Many in the US government also “waged war” on communism in the States HUAC – House Un. American Activities Committee Investigated government employees Promoted Hollywood anticommunist productions
Anti-Communism in the US Many in the US government also “waged war” on communism in the States HUAC – House Un. American Activities Committee Investigated government employees Promoted Hollywood anticommunist productions
 Mc. Carthyism Senator Joe Mc. Carthy from Wisconsin Used an anti-communist campaign to gain election Claimed that over 200 commies worked in the State Dept. Unsubstantiated charges, but very popular for a short time Condemned by Senate in 1954 in public/TV hearings
Mc. Carthyism Senator Joe Mc. Carthy from Wisconsin Used an anti-communist campaign to gain election Claimed that over 200 commies worked in the State Dept. Unsubstantiated charges, but very popular for a short time Condemned by Senate in 1954 in public/TV hearings
 The Korean War
The Korean War
 Asia after World War II US occupied Japan until 1952, but kept military bases there after 1952 Mao Tse-tung, receiving some aid from the USSR defeated Chiang Kai-Shek (US supported) Chiang and KMT evacuated to Taiwan US did not send troops
Asia after World War II US occupied Japan until 1952, but kept military bases there after 1952 Mao Tse-tung, receiving some aid from the USSR defeated Chiang Kai-Shek (US supported) Chiang and KMT evacuated to Taiwan US did not send troops
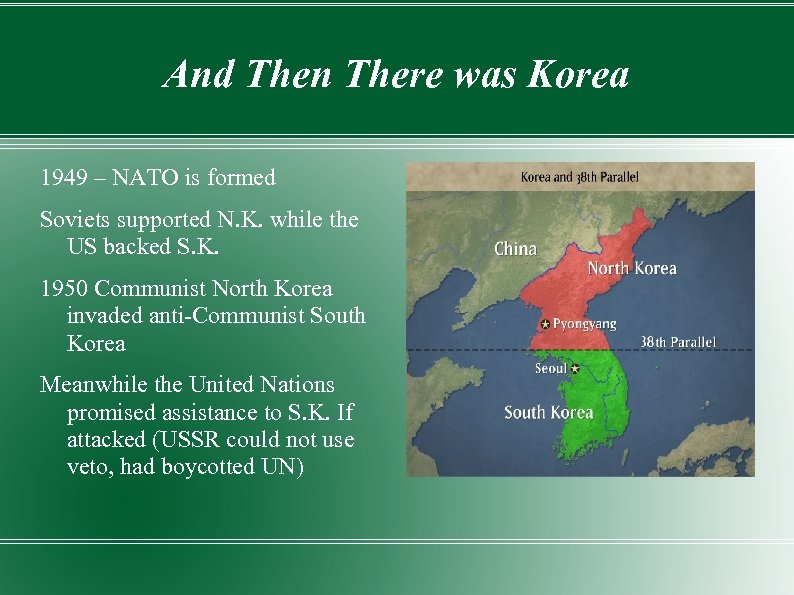 And Then There was Korea 1949 – NATO is formed Soviets supported N. K. while the US backed S. K. 1950 Communist North Korea invaded anti-Communist South Korea Meanwhile the United Nations promised assistance to S. K. If attacked (USSR could not use veto, had boycotted UN)
And Then There was Korea 1949 – NATO is formed Soviets supported N. K. while the US backed S. K. 1950 Communist North Korea invaded anti-Communist South Korea Meanwhile the United Nations promised assistance to S. K. If attacked (USSR could not use veto, had boycotted UN)
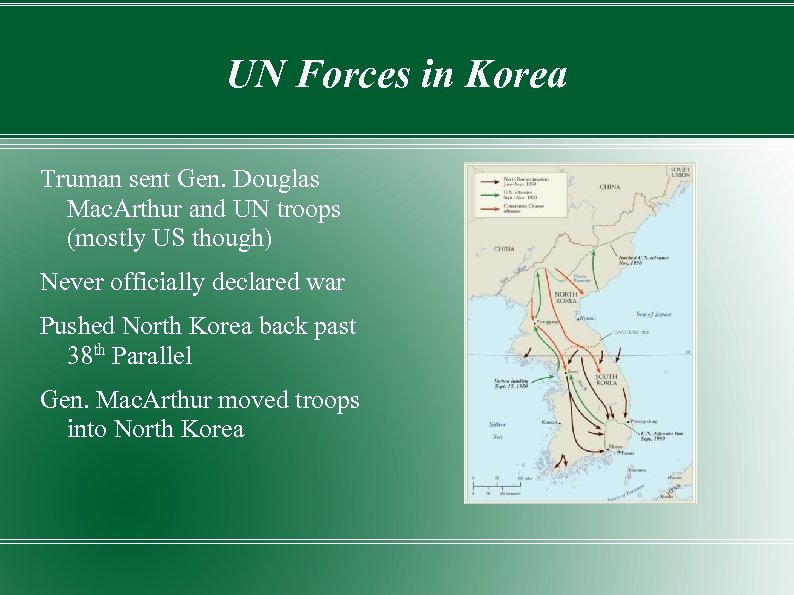 UN Forces in Korea Truman sent Gen. Douglas Mac. Arthur and UN troops (mostly US though) Never officially declared war Pushed North Korea back past 38 th Parallel Gen. Mac. Arthur moved troops into North Korea
UN Forces in Korea Truman sent Gen. Douglas Mac. Arthur and UN troops (mostly US though) Never officially declared war Pushed North Korea back past 38 th Parallel Gen. Mac. Arthur moved troops into North Korea
 Chinese Counterattack and the Second American Tie In Nov. 1950 China sent 300, 000 troops into Korea Pushed the UN forces back past the 38 th Parallel “Worst military setback. . . ” Stalemate Fallout between Truman and Mac. Arthur
Chinese Counterattack and the Second American Tie In Nov. 1950 China sent 300, 000 troops into Korea Pushed the UN forces back past the 38 th Parallel “Worst military setback. . . ” Stalemate Fallout between Truman and Mac. Arthur
 The Cold War Moving Forward A decade after WWII, the Cold War had intensified Neither the US nor the USSR was willing to risk direct action The Cold War turned “hot” in Korea and later in Vietnam American faith and confidence in Truman faltered Meanwhile, the Civil Rights Movement was picking up steam
The Cold War Moving Forward A decade after WWII, the Cold War had intensified Neither the US nor the USSR was willing to risk direct action The Cold War turned “hot” in Korea and later in Vietnam American faith and confidence in Truman faltered Meanwhile, the Civil Rights Movement was picking up steam


