84ee9f0ace7d9ea3cafd031223631d6a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71
 The Cold War and the American Dream, 1945– 1960 Conflict develops between the United States and the Soviet Union. Americans react to the economic prosperity and rapid change of the postwar period. The Final Frost Barrier!—a magazine advertisement for General Motors’ Frost. Proof Imperial Freezer (1959). NEXT
The Cold War and the American Dream, 1945– 1960 Conflict develops between the United States and the Soviet Union. Americans react to the economic prosperity and rapid change of the postwar period. The Final Frost Barrier!—a magazine advertisement for General Motors’ Frost. Proof Imperial Freezer (1959). NEXT
 The Cold War and the American Dream, 1945– 1960 SECTION 1 Peacetime Adjustments and the Cold War SECTION 2 The Korean War and Mc. Carthyism SECTION 3 The Fifties NEXT
The Cold War and the American Dream, 1945– 1960 SECTION 1 Peacetime Adjustments and the Cold War SECTION 2 The Korean War and Mc. Carthyism SECTION 3 The Fifties NEXT
 Section 1 Peacetime Adjustments and the Cold War Good Economics Americans look for prosperity after World War II. They also fight Communism in the Cold War. NEXT
Section 1 Peacetime Adjustments and the Cold War Good Economics Americans look for prosperity after World War II. They also fight Communism in the Cold War. NEXT
 SECTION 1 Peacetime Adjustments and the Cold War Adjusting to Peace • Industries lay off workers, returning servicemen flood job market • Veterans win out over female workers for jobs • Women get jobs in traditional women’s fields, office work, teaching Actress Grace Kelly (in 1950, a New York photographer’s model) demonstrating a Remington typewriter. NEXT
SECTION 1 Peacetime Adjustments and the Cold War Adjusting to Peace • Industries lay off workers, returning servicemen flood job market • Veterans win out over female workers for jobs • Women get jobs in traditional women’s fields, office work, teaching Actress Grace Kelly (in 1950, a New York photographer’s model) demonstrating a Remington typewriter. NEXT
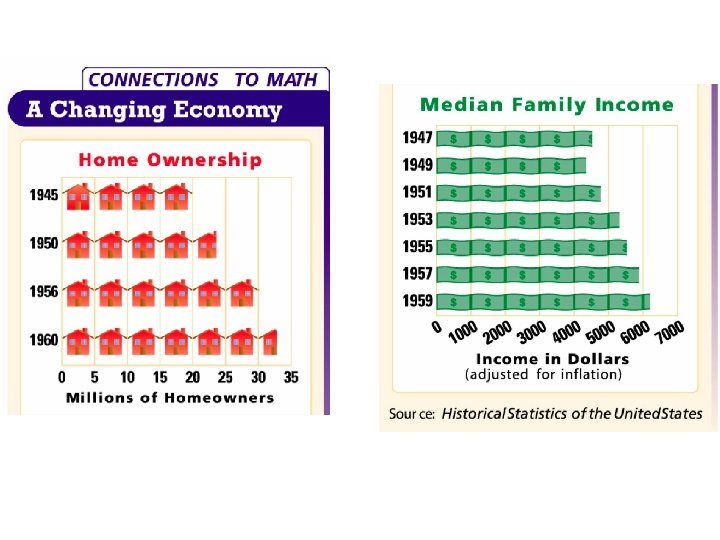
 SECTION 1 s di an m De high • People want more goods, factories start The Postwar Economy • e er f • th o e • e er us W ca be WII • W making needed products Controls on prices lifted, people have money, few goods to buy ion inflat Demand for goods increases, prices skyrocket William Levitt applies assembly-line technique to home building NY Start mass-producing affordable homes to meet demand for houses NEXT
SECTION 1 s di an m De high • People want more goods, factories start The Postwar Economy • e er f • th o e • e er us W ca be WII • W making needed products Controls on prices lifted, people have money, few goods to buy ion inflat Demand for goods increases, prices skyrocket William Levitt applies assembly-line technique to home building NY Start mass-producing affordable homes to meet demand for houses NEXT
 Developers: mass-produced, standardized homes built using assembly-line methods
Developers: mass-produced, standardized homes built using assembly-line methods
 SECTION 1 Labor Unrest and Civil Rights • Over 1 million workers join strikes, includes railway workers (1946) • President Harry S. Truman threatens to draft railway workers into army • WW II raises hopes of African Americans for more equality • African Americans still face prejudice, especially in the South • Truman wants Congress to pass equal rights laws, South resists proposals • Truman backs off issues, makes equal rights national issue NEXT
SECTION 1 Labor Unrest and Civil Rights • Over 1 million workers join strikes, includes railway workers (1946) • President Harry S. Truman threatens to draft railway workers into army • WW II raises hopes of African Americans for more equality • African Americans still face prejudice, especially in the South • Truman wants Congress to pass equal rights laws, South resists proposals • Truman backs off issues, makes equal rights national issue NEXT
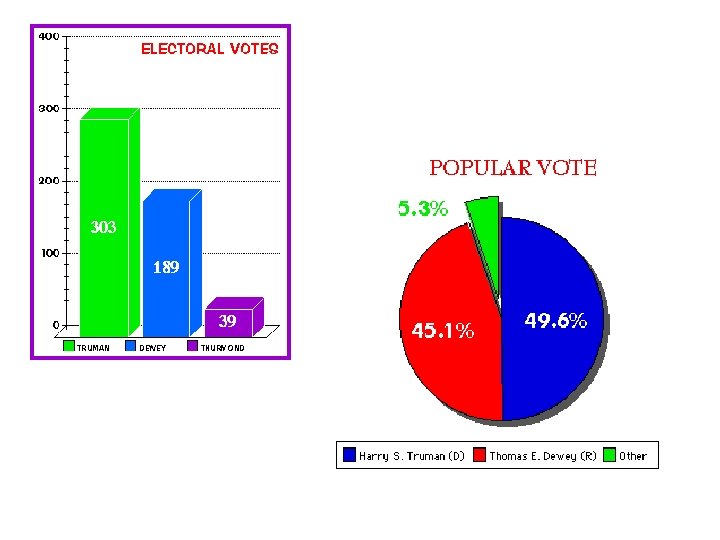
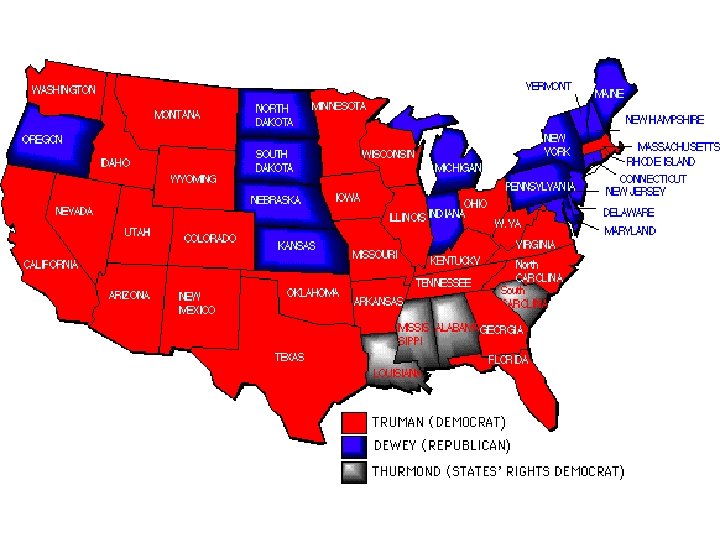
 SECTION 1 The Fair Deal • Republican Congress blocks Truman’s proposals, limits power of unions • Few people believe Truman will win 1948 presidential election • Truman takes campaign to the people, wins upset victory • Calls for Fair Deal, projects that: - create jobs, build public housing, end discrimination in hiring • Republicans, Southern Democrats block most of the programs NEXT
SECTION 1 The Fair Deal • Republican Congress blocks Truman’s proposals, limits power of unions • Few people believe Truman will win 1948 presidential election • Truman takes campaign to the people, wins upset victory • Calls for Fair Deal, projects that: - create jobs, build public housing, end discrimination in hiring • Republicans, Southern Democrats block most of the programs NEXT
 Truman v. Dewey Dem ocra ts Sp • Di lit xiec Stat rats es r – igh ts p • Ne arty w. P rog Par ress ty ive ues Iss s ght il Ri v • Ci bor i- La Ant s • tion Ac
Truman v. Dewey Dem ocra ts Sp • Di lit xiec Stat rats es r – igh ts p • Ne arty w. P rog Par ress ty ive ues Iss s ght il Ri v • Ci bor i- La Ant s • tion Ac


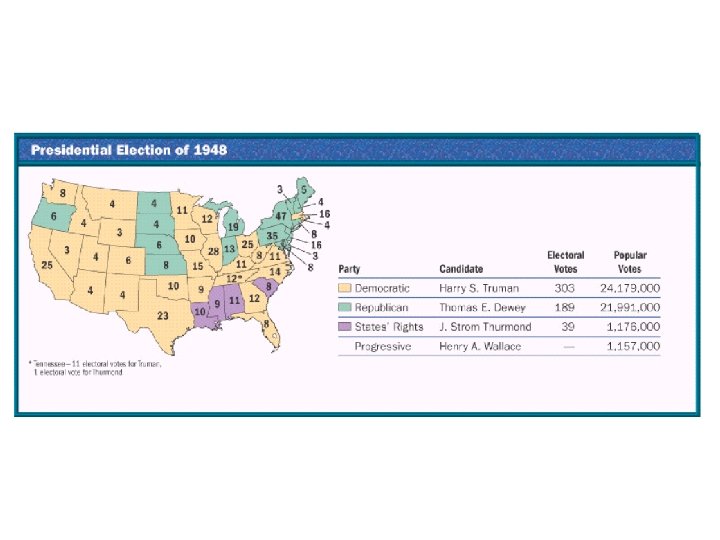
 Truman: threats to draft strikers Truman: integration of the armed forces
Truman: threats to draft strikers Truman: integration of the armed forces
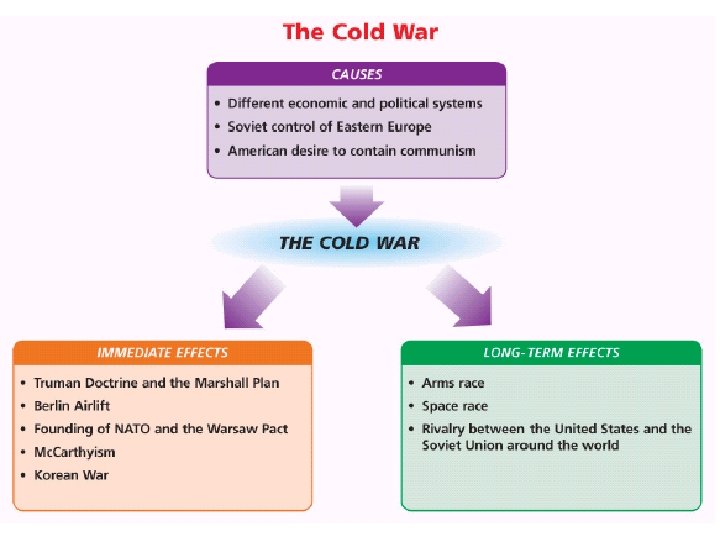
 SECTION 1 Origins of the Cold War • The West, Soviets allied against Nazis, Soviets free Eastern Europe • Stalin promises free elections but imposes Communism in Eastern Europe • Does not want anti-Soviet governments on the borders of Soviet Union • U. S. thinks Soviet leader Joseph Stalin wants to spread Communism • Cold War—U. S. /Soviet conflict, never directly fight on battlefield NEXT
SECTION 1 Origins of the Cold War • The West, Soviets allied against Nazis, Soviets free Eastern Europe • Stalin promises free elections but imposes Communism in Eastern Europe • Does not want anti-Soviet governments on the borders of Soviet Union • U. S. thinks Soviet leader Joseph Stalin wants to spread Communism • Cold War—U. S. /Soviet conflict, never directly fight on battlefield NEXT
 Thr eat out of all war exis ted Competition between the U. S. and the U. S. S. R. for global power and influence.
Thr eat out of all war exis ted Competition between the U. S. and the U. S. S. R. for global power and influence.
 Differences Soviet Union Untied States • Communist • Democracy • Individual Freedoms • State-run Economy • One-party rule • Capitalistic Economy • Suppression of Religion • Force to crush opposition
Differences Soviet Union Untied States • Communist • Democracy • Individual Freedoms • State-run Economy • One-party rule • Capitalistic Economy • Suppression of Religion • Force to crush opposition
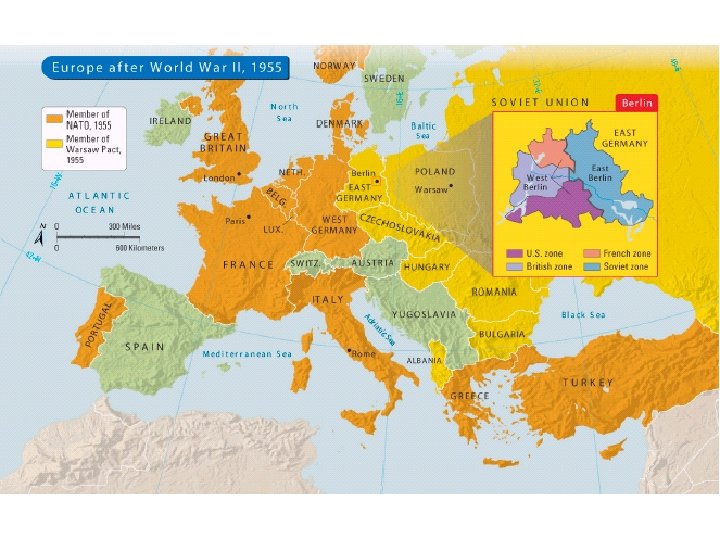
 SECTION 1 Containing Communism Abroad • Containment—use military, non-military ways to contain Communism • Truman Doctrine—promises to aid people resisting threats to democracy • North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO): - includes U. S. , Canada, 10 Western European countries - formed to counteract Communist control of Eastern Europe • Soviet Union, Eastern Europe form Warsaw Pact NEXT
SECTION 1 Containing Communism Abroad • Containment—use military, non-military ways to contain Communism • Truman Doctrine—promises to aid people resisting threats to democracy • North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO): - includes U. S. , Canada, 10 Western European countries - formed to counteract Communist control of Eastern Europe • Soviet Union, Eastern Europe form Warsaw Pact NEXT
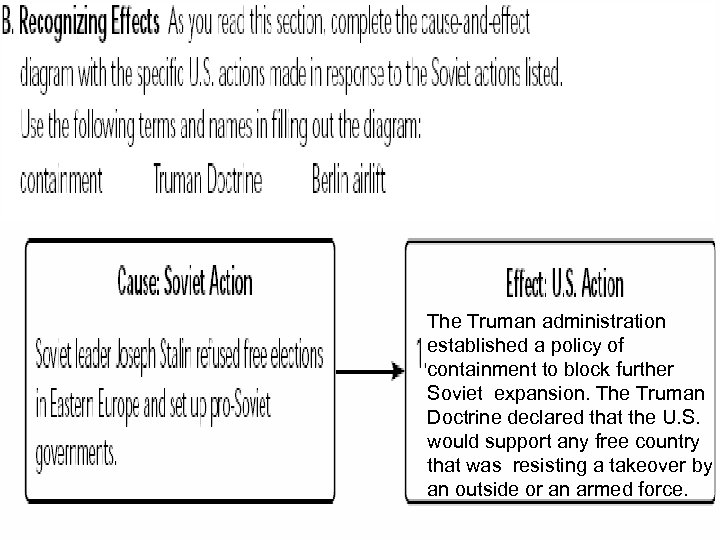 The Truman administration established a policy of containment to block further Soviet expansion. The Truman Doctrine declared that the U. S. would support any free country that was resisting a takeover by an outside or an armed force.
The Truman administration established a policy of containment to block further Soviet expansion. The Truman Doctrine declared that the U. S. would support any free country that was resisting a takeover by an outside or an armed force.
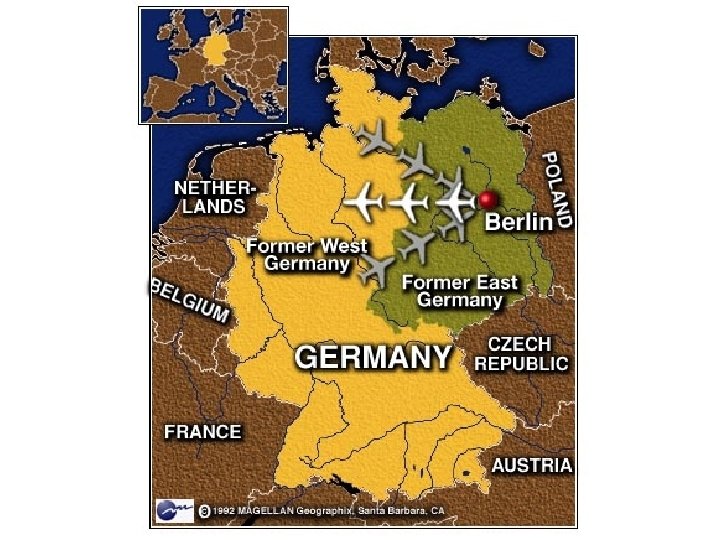
 SECTION 1 Marshall Plan and Berlin Airlift • Marshall Plan—$13 billion to help rebuild Western, Southern Europe • After WW II, Germany is divided into 4 zones controlled by: - Soviet Union - United States - France - Great Britain • Berlin in Soviet zone, city divided between East, West powers Continued. . . NEXT
SECTION 1 Marshall Plan and Berlin Airlift • Marshall Plan—$13 billion to help rebuild Western, Southern Europe • After WW II, Germany is divided into 4 zones controlled by: - Soviet Union - United States - France - Great Britain • Berlin in Soviet zone, city divided between East, West powers Continued. . . NEXT
 SECTION 1 continued Marshall Plan and Berlin Airlift • Soviets afraid Western powers will unite Germany • Block access to Berlin, Truman approves Berlin airlift: - U. S. , British planes carry supplies to city’s residents • Soviets call off blockade, Germany divided into: - Communist East Germany - Democratic West Germany NEXT
SECTION 1 continued Marshall Plan and Berlin Airlift • Soviets afraid Western powers will unite Germany • Block access to Berlin, Truman approves Berlin airlift: - U. S. , British planes carry supplies to city’s residents • Soviets call off blockade, Germany divided into: - Communist East Germany - Democratic West Germany NEXT
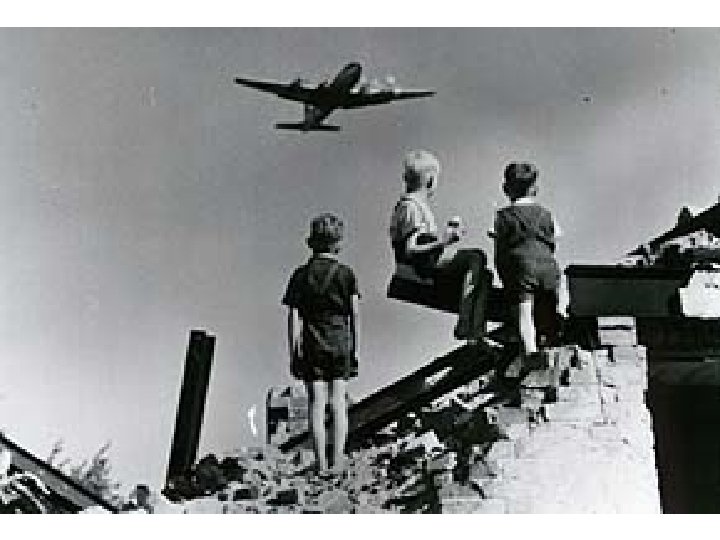
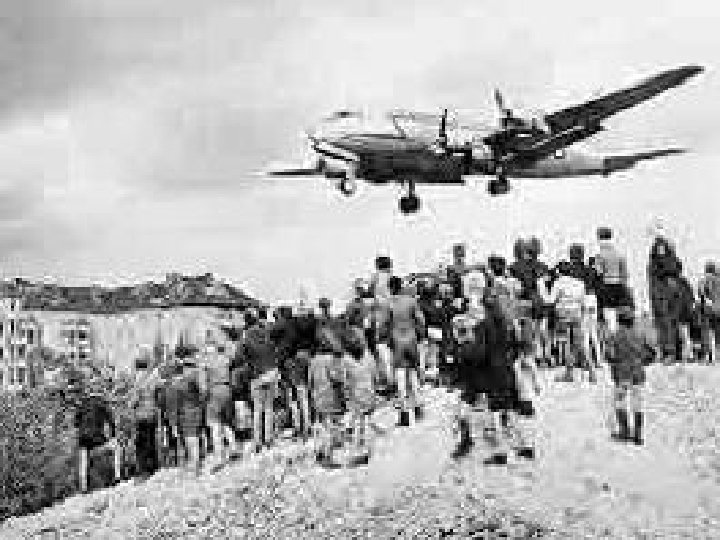
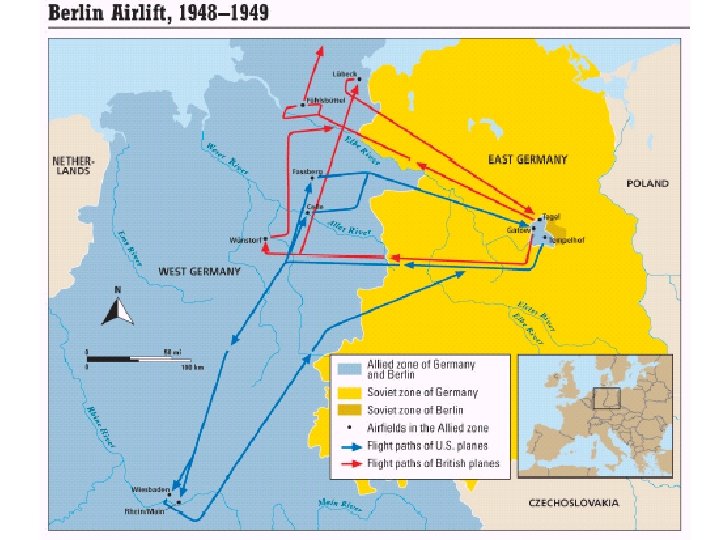


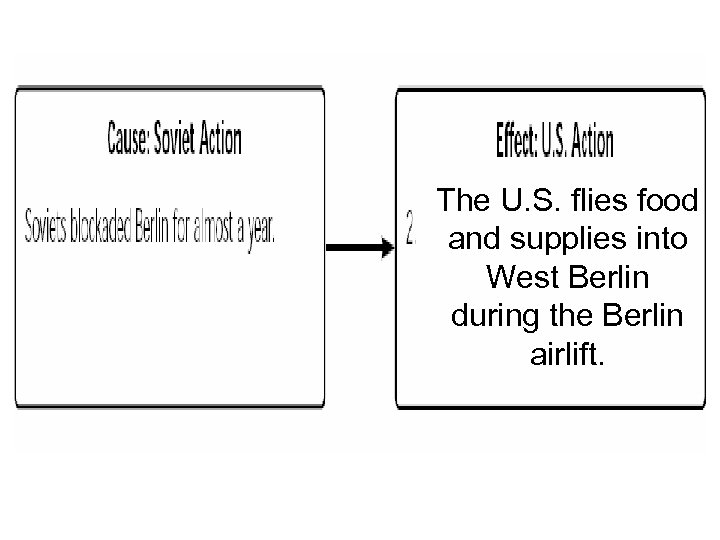 The U. S. flies food and supplies into West Berlin during the Berlin airlift.
The U. S. flies food and supplies into West Berlin during the Berlin airlift.
 SECTION 1 Fear of Communism at Home • Fear of Communism in the U. S. grows • Alger Hiss accused of giving military info to Soviets, sentenced 5 years • Ethel, Julius Rosenberg executed for passing atomic secrets to Russians • President Truman orders loyalty checks for federal workers • House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) issues blacklists: - names people (many in movie industry) thought to be Communists NEXT
SECTION 1 Fear of Communism at Home • Fear of Communism in the U. S. grows • Alger Hiss accused of giving military info to Soviets, sentenced 5 years • Ethel, Julius Rosenberg executed for passing atomic secrets to Russians • President Truman orders loyalty checks for federal workers • House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) issues blacklists: - names people (many in movie industry) thought to be Communists NEXT
 Actor Ronald Reagan, President of the Screen Actors Guild, testifying before the House Un-American Activities Committee (October 23, 1947).
Actor Ronald Reagan, President of the Screen Actors Guild, testifying before the House Un-American Activities Committee (October 23, 1947).

 Explain the significance of each of the following terms. Fair Deal Cold War Marshall Plan
Explain the significance of each of the following terms. Fair Deal Cold War Marshall Plan
 Section 2 The Korean War and Mc. Carthyism The Cold War and the Korean War produce a far-reaching form of Anti. Communism. NEXT
Section 2 The Korean War and Mc. Carthyism The Cold War and the Korean War produce a far-reaching form of Anti. Communism. NEXT
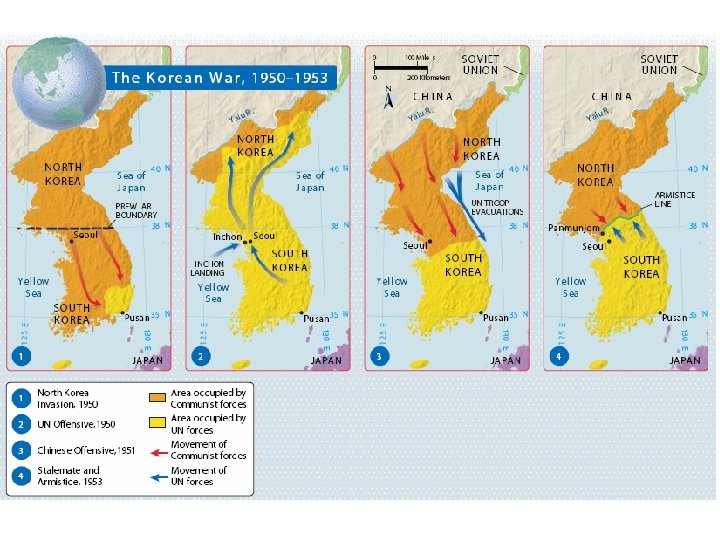
 SECTION 2 The Korean War and Mc. Carthyism Origins of the Korean War • Communists defeat U. S. -supported nationalists in China • Mao Zedong becomes head of Communist China • Communist takeover of China fuels Americans’ fear of communism • After WW II Korea is divided at the 38 th parallel, or line of latitude: - Soviets troops north of parallel - U. S. troops south of parallel • Soviets aid Communist government in North Korea NEXT
SECTION 2 The Korean War and Mc. Carthyism Origins of the Korean War • Communists defeat U. S. -supported nationalists in China • Mao Zedong becomes head of Communist China • Communist takeover of China fuels Americans’ fear of communism • After WW II Korea is divided at the 38 th parallel, or line of latitude: - Soviets troops north of parallel - U. S. troops south of parallel • Soviets aid Communist government in North Korea NEXT
 SECTION 2 Fighting Breaks Out in Korea • North Korean forces cross 38 th parallel into South Korea • Korean War—North Korean forces fight U. S. , UN, South Korean forces • U. S. General Mac. Arthur commands UN forces • North Koreans push South Koreans to Pusan • Mac. Arthur, troops push North Koreans back across 38 th parallel • Pursue enemy into North Korea • Women serve in armed forces, also join Army, Navy Nurse Corps NEXT
SECTION 2 Fighting Breaks Out in Korea • North Korean forces cross 38 th parallel into South Korea • Korean War—North Korean forces fight U. S. , UN, South Korean forces • U. S. General Mac. Arthur commands UN forces • North Koreans push South Koreans to Pusan • Mac. Arthur, troops push North Koreans back across 38 th parallel • Pursue enemy into North Korea • Women serve in armed forces, also join Army, Navy Nurse Corps NEXT
 United Nations forces fighting to recapture Seoul, South Korea, from communist invaders, September 1950
United Nations forces fighting to recapture Seoul, South Korea, from communist invaders, September 1950
 SECTION 2 China Enters the Conflict • China warns UN forces not to advance further, UN ignores warning • Chinese troops force UN troops south to the 38 th parallel • President Truman denies Mac. Arthur’s request to blockade, bomb China • Mac. Arthur goes over the president’s head to win support: - speaks, writes to newspapers, magazine publishers - writes Republican leaders • Truman fires Mac. Arthur, orders him home NEXT
SECTION 2 China Enters the Conflict • China warns UN forces not to advance further, UN ignores warning • Chinese troops force UN troops south to the 38 th parallel • President Truman denies Mac. Arthur’s request to blockade, bomb China • Mac. Arthur goes over the president’s head to win support: - speaks, writes to newspapers, magazine publishers - writes Republican leaders • Truman fires Mac. Arthur, orders him home NEXT
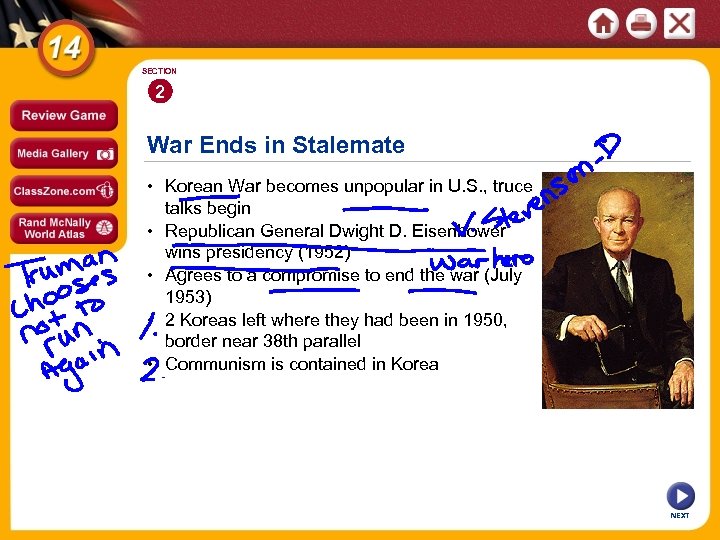 SECTION 2 War Ends in Stalemate • Korean War becomes unpopular in U. S. , truce talks begin • Republican General Dwight D. Eisenhower wins presidency (1952) • Agrees to a compromise to end the war (July 1953) • 2 Koreas left where they had been in 1950, border near 38 th parallel • Communism is contained in Korea NEXT
SECTION 2 War Ends in Stalemate • Korean War becomes unpopular in U. S. , truce talks begin • Republican General Dwight D. Eisenhower wins presidency (1952) • Agrees to a compromise to end the war (July 1953) • 2 Koreas left where they had been in 1950, border near 38 th parallel • Communism is contained in Korea NEXT
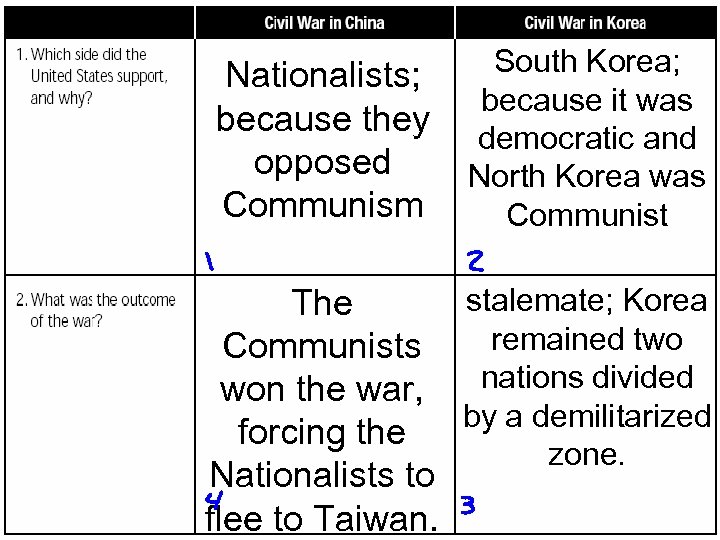 South Korea; Nationalists; because it was because they democratic and opposed North Korea was Communism Communist stalemate; Korea The remained two Communists won the war, nations divided by a demilitarized forcing the zone. Nationalists to flee to Taiwan.
South Korea; Nationalists; because it was because they democratic and opposed North Korea was Communism Communist stalemate; Korea The remained two Communists won the war, nations divided by a demilitarized forcing the zone. Nationalists to flee to Taiwan.
 SECTION 2 Mc. Carthy and Communism • Senator Joseph Mc. Carthy uses Korean War to fan fear of Communism • Conducts hunt for Communists in U. S. that ruins the careers of many • Term Mc. Carthyism stands for reckless charges against innocent • Senate holds Army-Mc. Carthy hearings: - Mc. Carthy accuses Army of “coddling Communists” - Army accuses Mc. Carthy of improper conduct Senator Joseph R. Mc. Carthy chairing the Senate Permanent Subcommittee on Investigation (February 26, 1954). NEXT
SECTION 2 Mc. Carthy and Communism • Senator Joseph Mc. Carthy uses Korean War to fan fear of Communism • Conducts hunt for Communists in U. S. that ruins the careers of many • Term Mc. Carthyism stands for reckless charges against innocent • Senate holds Army-Mc. Carthy hearings: - Mc. Carthy accuses Army of “coddling Communists” - Army accuses Mc. Carthy of improper conduct Senator Joseph R. Mc. Carthy chairing the Senate Permanent Subcommittee on Investigation (February 26, 1954). NEXT
 SECTION 2 Eisenhower and the Cold War • Secretary of State John Foster Dulles favors brinkmanship: - U. S. going to the brink of war to combat Communism • Arms race—U. S. , Soviets race to develop more destructive weapons • U. S. builds hydrogen bomb, H-bomb, Soviets soon develop weapon • U. S. , Soviet Union help allies, weaken enemies around the world Continued. . . NEXT
SECTION 2 Eisenhower and the Cold War • Secretary of State John Foster Dulles favors brinkmanship: - U. S. going to the brink of war to combat Communism • Arms race—U. S. , Soviets race to develop more destructive weapons • U. S. builds hydrogen bomb, H-bomb, Soviets soon develop weapon • U. S. , Soviet Union help allies, weaken enemies around the world Continued. . . NEXT
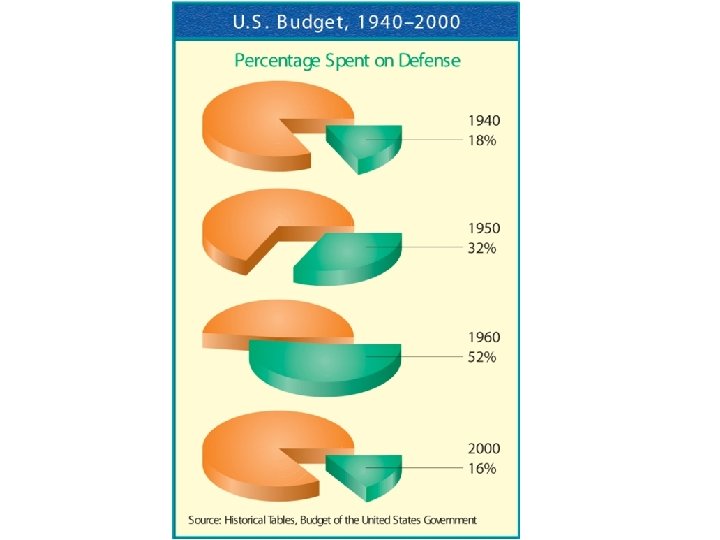
 SECTION 2 continued Eisenhower and the Cold War • Britain, U. S. withdraws aid to Soviet-friendly Egypt • Egypt seizes Suez Canal; Britain, U. S. , Israel attack Egypt • Soviet Union threatens to support Egypt, UN imposes cease-fire • Space race—U. S. , Soviet Union race to build satellites in space • Soviets shoot down U. S. spy plane, talks, U. S. , Soviets collapse NEXT
SECTION 2 continued Eisenhower and the Cold War • Britain, U. S. withdraws aid to Soviet-friendly Egypt • Egypt seizes Suez Canal; Britain, U. S. , Israel attack Egypt • Soviet Union threatens to support Egypt, UN imposes cease-fire • Space race—U. S. , Soviet Union race to build satellites in space • Soviets shoot down U. S. spy plane, talks, U. S. , Soviets collapse NEXT
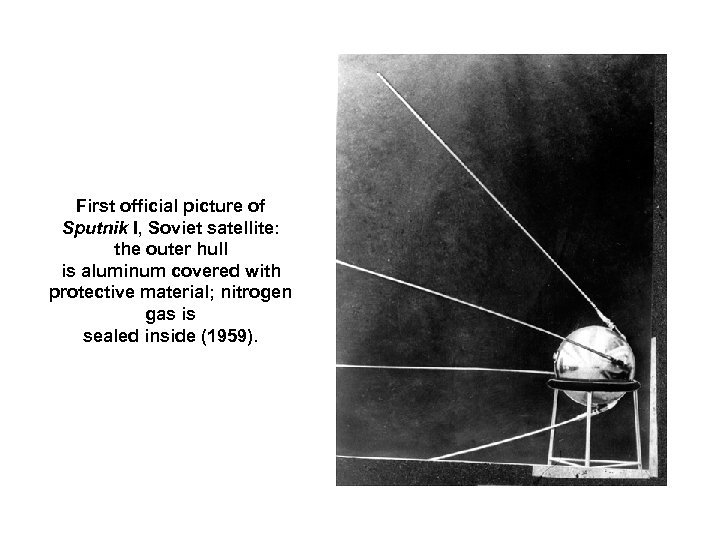 First official picture of Sputnik I, Soviet satellite: the outer hull is aluminum covered with protective material; nitrogen gas is sealed inside (1959).
First official picture of Sputnik I, Soviet satellite: the outer hull is aluminum covered with protective material; nitrogen gas is sealed inside (1959).
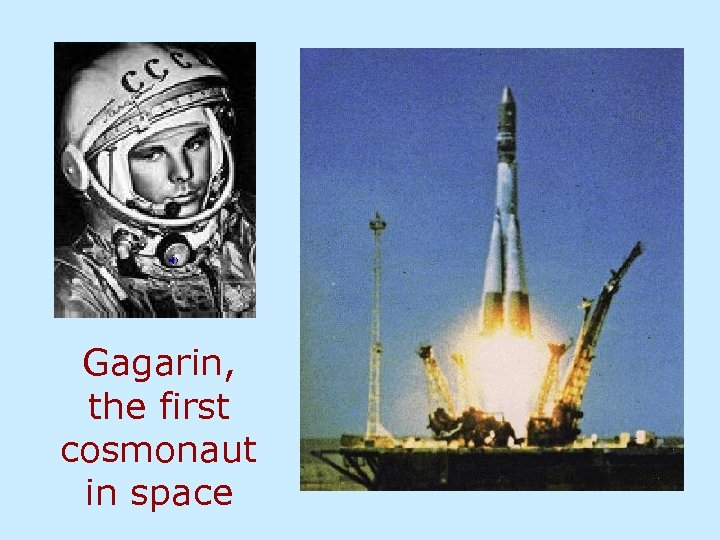 Gagarin, the first cosmonaut in space
Gagarin, the first cosmonaut in space
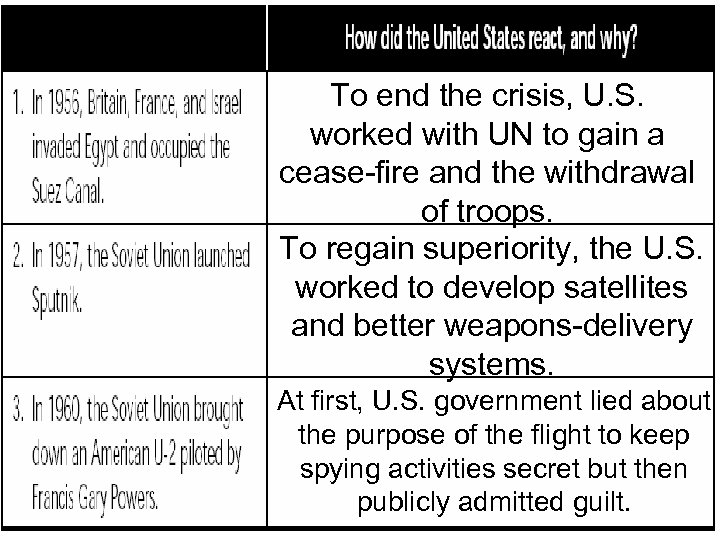 To end the crisis, U. S. worked with UN to gain a cease-fire and the withdrawal of troops. To regain superiority, the U. S. worked to develop satellites and better weapons-delivery systems. At first, U. S. government lied about the purpose of the flight to keep spying activities secret but then publicly admitted guilt.
To end the crisis, U. S. worked with UN to gain a cease-fire and the withdrawal of troops. To regain superiority, the U. S. worked to develop satellites and better weapons-delivery systems. At first, U. S. government lied about the purpose of the flight to keep spying activities secret but then publicly admitted guilt.
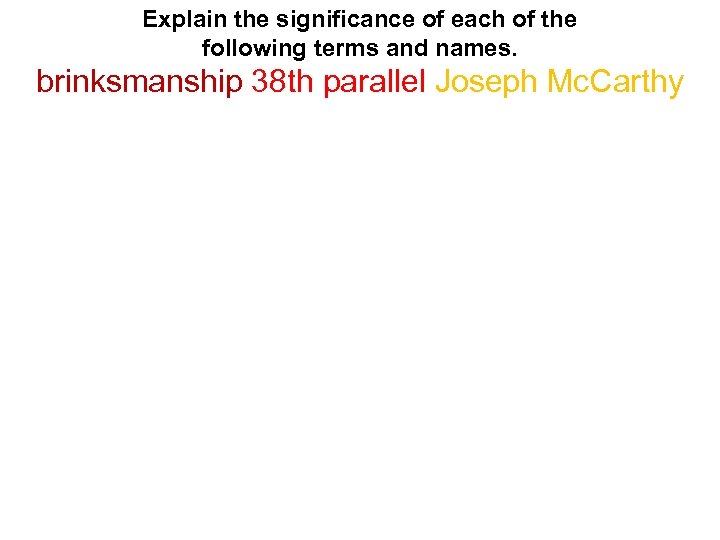 Explain the significance of each of the following terms and names. brinksmanship 38 th parallel Joseph Mc. Carthy
Explain the significance of each of the following terms and names. brinksmanship 38 th parallel Joseph Mc. Carthy
 Section 3 The Fifties With the United States locked in a Cold War, social and economic changes take place in American life. NEXT
Section 3 The Fifties With the United States locked in a Cold War, social and economic changes take place in American life. NEXT
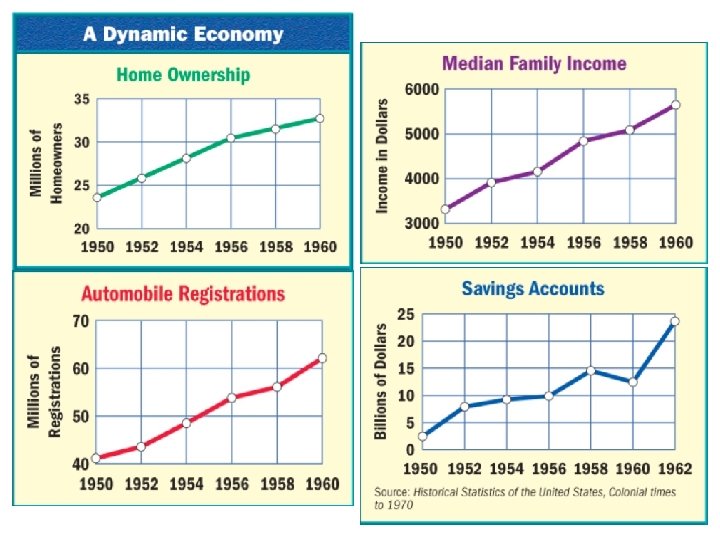
 SECTION 3 The Fifties The Domestic Scene in the Fifties • In 1957, one out of every five live in poverty, many live in cities • More well-to-do move to suburbs—residential areas surrounding a city • Mexican immigrants increase greatly, many cross border illegally • Some Mexicans stay in U. S. illegally after bracero program ends • President Eisenhower pleases liberals, conservatives • Keeps most New Deal programs, sets up Highway Act (1956) NEXT
SECTION 3 The Fifties The Domestic Scene in the Fifties • In 1957, one out of every five live in poverty, many live in cities • More well-to-do move to suburbs—residential areas surrounding a city • Mexican immigrants increase greatly, many cross border illegally • Some Mexicans stay in U. S. illegally after bracero program ends • President Eisenhower pleases liberals, conservatives • Keeps most New Deal programs, sets up Highway Act (1956) NEXT
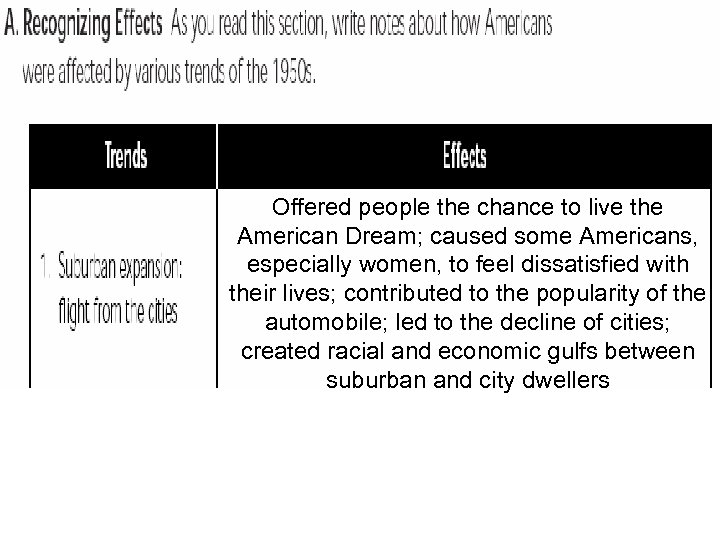 Offered people the chance to live the American Dream; caused some Americans, especially women, to feel dissatisfied with their lives; contributed to the popularity of the automobile; led to the decline of cities; created racial and economic gulfs between suburban and city dwellers
Offered people the chance to live the American Dream; caused some Americans, especially women, to feel dissatisfied with their lives; contributed to the popularity of the automobile; led to the decline of cities; created racial and economic gulfs between suburban and city dwellers
 SECTION 3 Changes Sweep America • During 1950 s, U. S. has baby boom—sharp birthrate increase after WW II • Baby boom spurs growth of suburbs • Shopping centers, restaurants built on former farmland, serve suburbs • Car sales explode because owning a car in the suburbs is a necessity • Many people move to sunbelt—warmer states in South, Southwest NEXT
SECTION 3 Changes Sweep America • During 1950 s, U. S. has baby boom—sharp birthrate increase after WW II • Baby boom spurs growth of suburbs • Shopping centers, restaurants built on former farmland, serve suburbs • Car sales explode because owning a car in the suburbs is a necessity • Many people move to sunbelt—warmer states in South, Southwest NEXT
 SECTION 3 The American Dream in the Fifties • Life for millions of white Americans in suburbs, the American Dream • Enjoy good schools, shopping malls, safe environment • Critics, people in suburbs forced to fit mold, willing to conform • Women have defined roles, limited job choices, some feel confined • Industry churns out goods, advertising encourages consumers to buy • Owning the latest car, appliance is symbol of social standing, success NEXT
SECTION 3 The American Dream in the Fifties • Life for millions of white Americans in suburbs, the American Dream • Enjoy good schools, shopping malls, safe environment • Critics, people in suburbs forced to fit mold, willing to conform • Women have defined roles, limited job choices, some feel confined • Industry churns out goods, advertising encourages consumers to buy • Owning the latest car, appliance is symbol of social standing, success NEXT
 New Kenmore Ranges from Sears!—magazine advertisement (1957).
New Kenmore Ranges from Sears!—magazine advertisement (1957).
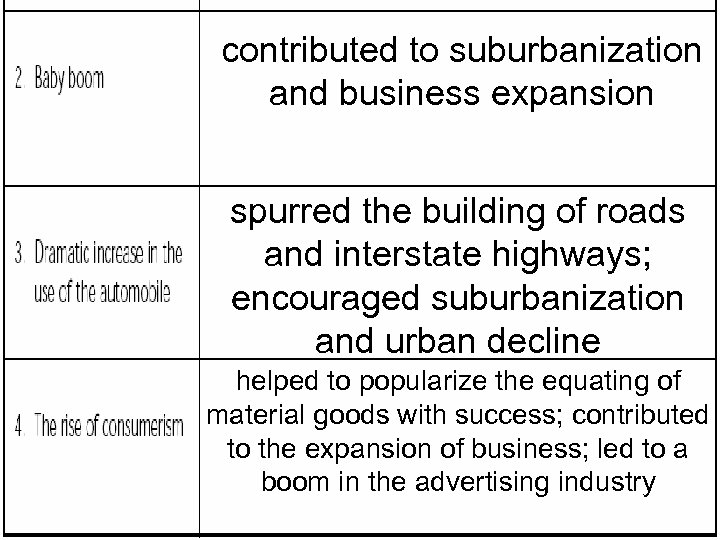 contributed to suburbanization and business expansion spurred the building of roads and interstate highways; encouraged suburbanization and urban decline helped to popularize the equating of material goods with success; contributed to the expansion of business; led to a boom in the advertising industry
contributed to suburbanization and business expansion spurred the building of roads and interstate highways; encouraged suburbanization and urban decline helped to popularize the equating of material goods with success; contributed to the expansion of business; led to a boom in the advertising industry
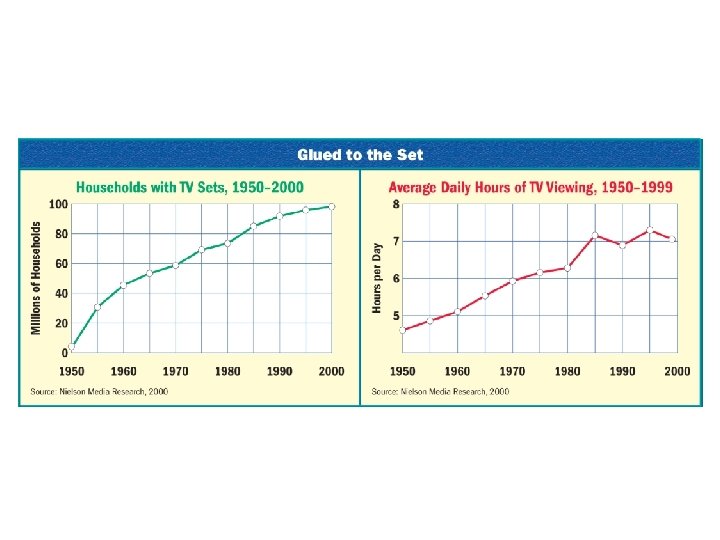
 SECTION 3 Pop Culture and Rock ’n’ Roll • Hollywood cranks out westerns, musicals, romances • Popularity of TV causes movie attendance to drop • Sitcoms show what many consider to be ideal families • Rock ’n’ Roll—style of popular music, has black, white musicians • Elvis Presley becomes the king of rock ’n’ roll • Allen Ginsberg, Jack Kerouac, “beatniks” criticize shallow U. S. society Elvis Presley performing at the Mississippi– Alabama State Fair in Tupelo, Mississippi (September 27, 1956). NEXT
SECTION 3 Pop Culture and Rock ’n’ Roll • Hollywood cranks out westerns, musicals, romances • Popularity of TV causes movie attendance to drop • Sitcoms show what many consider to be ideal families • Rock ’n’ Roll—style of popular music, has black, white musicians • Elvis Presley becomes the king of rock ’n’ roll • Allen Ginsberg, Jack Kerouac, “beatniks” criticize shallow U. S. society Elvis Presley performing at the Mississippi– Alabama State Fair in Tupelo, Mississippi (September 27, 1956). NEXT
 Howdy Doody and Buffalo Bob Smith Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz Mickey Mouse Club Lassie Father Knows Best THE LONE RANGER
Howdy Doody and Buffalo Bob Smith Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz Mickey Mouse Club Lassie Father Knows Best THE LONE RANGER
 Little Richard Jerry Lee Lewis Chuck Berry Elvis Presley
Little Richard Jerry Lee Lewis Chuck Berry Elvis Presley

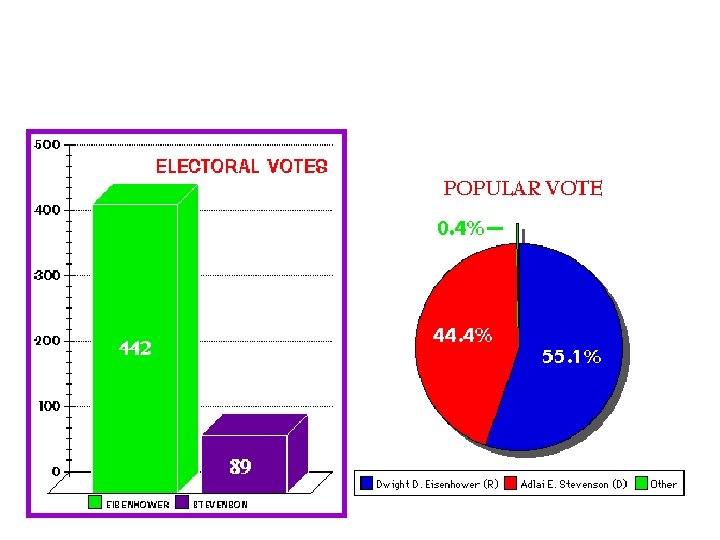
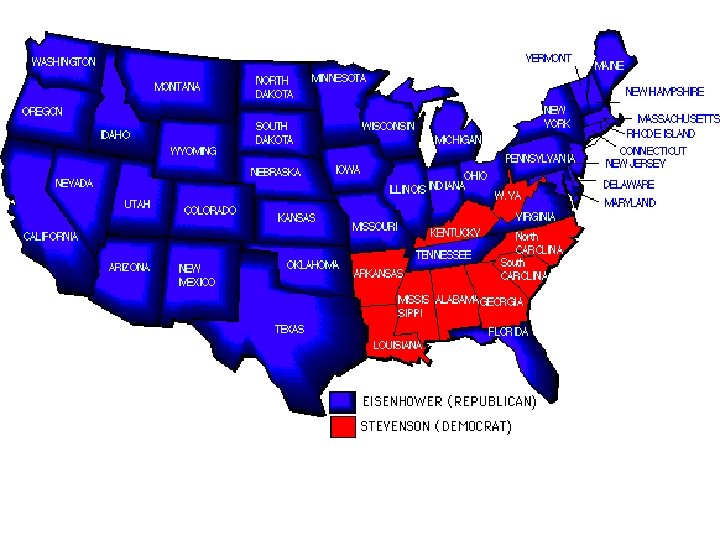
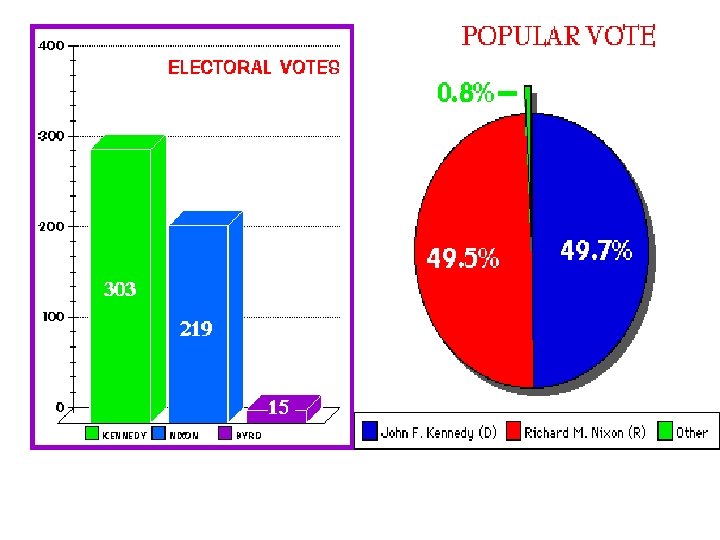
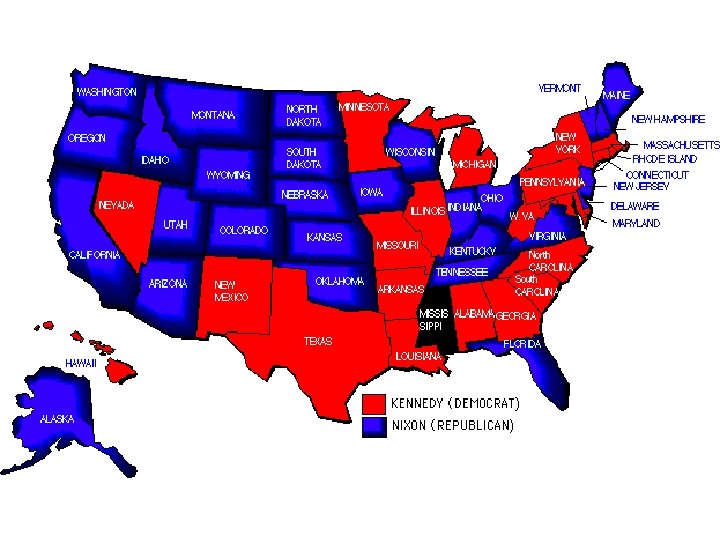
 SECTION 3 The Election of 1960 • 1960 presidential election, one of closest in U. S. history • Senator John Fitzgerald Kennedy, Democratic candidate • Richard M. Nixon, Republican candidate • Kennedy, Nixon stage 1 st televised presidential debates • Kennedy’s youthful energy, confidence helps him to win • Kennedy is nation’s youngest president, 1 st Catholic president NEXT
SECTION 3 The Election of 1960 • 1960 presidential election, one of closest in U. S. history • Senator John Fitzgerald Kennedy, Democratic candidate • Richard M. Nixon, Republican candidate • Kennedy, Nixon stage 1 st televised presidential debates • Kennedy’s youthful energy, confidence helps him to win • Kennedy is nation’s youngest president, 1 st Catholic president NEXT

 This is the end of the chapter presentation of lecture notes. Click the HOME or EXIT button. NEXT
This is the end of the chapter presentation of lecture notes. Click the HOME or EXIT button. NEXT
 Print Slide Show 1. On the File menu, select Print 2. In the pop-up menu, select Microsoft Power. Point If the dialog box does not include this pop-up, continue to step 4 3. In the Print what box, choose the presentation format you want to print: slides, notes, handouts, or outline 4. Click the Print button to print the Power. Point presentation Print Text Version 1. Click the Print Text button below; a text file will open in Adobe Acrobat 2. On the File menu, select Print 3. Click the Print button to print the entire document, or select the pages you want to print Print Text BACK
Print Slide Show 1. On the File menu, select Print 2. In the pop-up menu, select Microsoft Power. Point If the dialog box does not include this pop-up, continue to step 4 3. In the Print what box, choose the presentation format you want to print: slides, notes, handouts, or outline 4. Click the Print button to print the Power. Point presentation Print Text Version 1. Click the Print Text button below; a text file will open in Adobe Acrobat 2. On the File menu, select Print 3. Click the Print button to print the entire document, or select the pages you want to print Print Text BACK


