0014c4bf7bb1863eacd0aae25544580a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 THE COLD WAR A NEW INTERNATIONAL CONFLICT
THE COLD WAR A NEW INTERNATIONAL CONFLICT
 • After WWII, a new international conflict emerged, the Cold War – It was primarily an ideological conflict between the U. S. and the Soviet Union which dominated world politics from 1945 until the end of the 1980 s • Different forms of gov’t and economic systems, a conflict between communism and capitalist democracy
• After WWII, a new international conflict emerged, the Cold War – It was primarily an ideological conflict between the U. S. and the Soviet Union which dominated world politics from 1945 until the end of the 1980 s • Different forms of gov’t and economic systems, a conflict between communism and capitalist democracy
 The Cold War Begins • Nearing the end of WWII, Roosevelt and Churchill realized that millions of Soviets had taken possession of much of Eastern and Central Europe – They want self-determination and free elections in these nations – Stalin promises to allow this after the war – Roosevelt can’t anger Stalin, he needs the Soviet Union to declare war on Japan
The Cold War Begins • Nearing the end of WWII, Roosevelt and Churchill realized that millions of Soviets had taken possession of much of Eastern and Central Europe – They want self-determination and free elections in these nations – Stalin promises to allow this after the war – Roosevelt can’t anger Stalin, he needs the Soviet Union to declare war on Japan
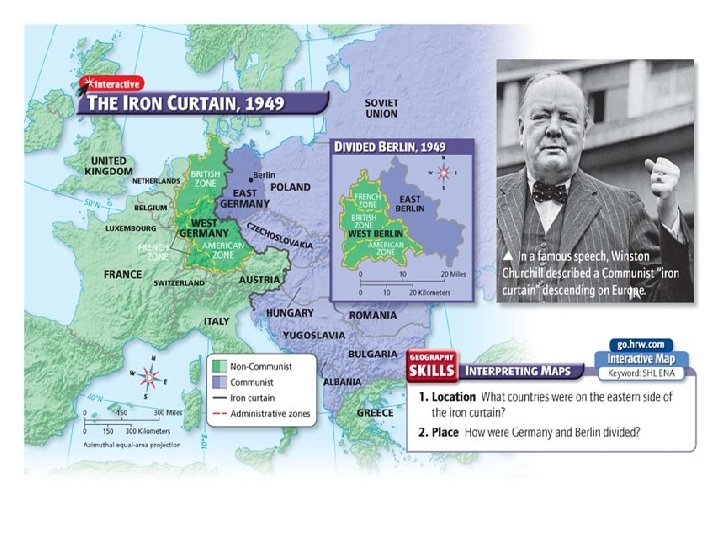
 • Potsdam Conference (July 1945) – Truman demands free elections in Eastern Europe and Stalin refuses – Stalin wants a communist buffer zone in Eastern Europe to guard against future attacks • Pro-Soviet Communist gov’ts are established in Eastern Europe – The only way to force free elections was to invade Soviet-held territories – no wants more war • Winston Churchill claims that “An Iron Curtain has descended across the continent” – This division is the beginning of the Cold War – U. S. fears communism and the Soviets fear the capitalist West
• Potsdam Conference (July 1945) – Truman demands free elections in Eastern Europe and Stalin refuses – Stalin wants a communist buffer zone in Eastern Europe to guard against future attacks • Pro-Soviet Communist gov’ts are established in Eastern Europe – The only way to force free elections was to invade Soviet-held territories – no wants more war • Winston Churchill claims that “An Iron Curtain has descended across the continent” – This division is the beginning of the Cold War – U. S. fears communism and the Soviets fear the capitalist West


 The United States Responds • In 1947 Soviet-backed Communists threaten the gov’t of Greece – The British can’t help because their economy is in bad shape, so the U. S. steps in • Truman Doctrine – 1947 President Truman issues this doctrine that states the U. S. would give money to countries threatened by Communist expansion • Afraid communism would spread if unchecked – Greece is able to stop the Communists
The United States Responds • In 1947 Soviet-backed Communists threaten the gov’t of Greece – The British can’t help because their economy is in bad shape, so the U. S. steps in • Truman Doctrine – 1947 President Truman issues this doctrine that states the U. S. would give money to countries threatened by Communist expansion • Afraid communism would spread if unchecked – Greece is able to stop the Communists
 • Marshall Plan (June 1947) – also known as the European Recovery Program – Set up to rebuild war-torn Europe • Theory that communism is successful in places with economic problems • U. S. spends 13 billion rebuilding Europe – Money is offered to the Soviet Union and its politically dependent Eastern European satellite states, but Stalin refuses the aid • Council for Mutual Assistance (COMECON) – Set up in 1949 by the Soviets in response to the Marshall Plan to help rebuild Eastern Europe – Fails due to the fact that the Soviets have no money
• Marshall Plan (June 1947) – also known as the European Recovery Program – Set up to rebuild war-torn Europe • Theory that communism is successful in places with economic problems • U. S. spends 13 billion rebuilding Europe – Money is offered to the Soviet Union and its politically dependent Eastern European satellite states, but Stalin refuses the aid • Council for Mutual Assistance (COMECON) – Set up in 1949 by the Soviets in response to the Marshall Plan to help rebuild Eastern Europe – Fails due to the fact that the Soviets have no money


 • Policy of Containment – Adopted by the U. S. in 1947 to keep communism within its existing boundaries and prevent further Soviet aggressive moves – Main U. S. foreign policy for the next 45 years – stop the spread of communism, will lead to two wars
• Policy of Containment – Adopted by the U. S. in 1947 to keep communism within its existing boundaries and prevent further Soviet aggressive moves – Main U. S. foreign policy for the next 45 years – stop the spread of communism, will lead to two wars
 Germany Divided • 1948 the U. S. , Britain, and France work to unify the three western sections of Germany and Berlin to create a democratic gov’t – The Soviets oppose this and set up a blockade of West Berlin – The U. S. and British respond with the Berlin Air Lift to fly supplies to West Berlin – It is successful and the Soviets end the blockade in May 1949 • West Germany is created in Sept. 1949 • East Germany set up by the Soviets a month later
Germany Divided • 1948 the U. S. , Britain, and France work to unify the three western sections of Germany and Berlin to create a democratic gov’t – The Soviets oppose this and set up a blockade of West Berlin – The U. S. and British respond with the Berlin Air Lift to fly supplies to West Berlin – It is successful and the Soviets end the blockade in May 1949 • West Germany is created in Sept. 1949 • East Germany set up by the Soviets a month later
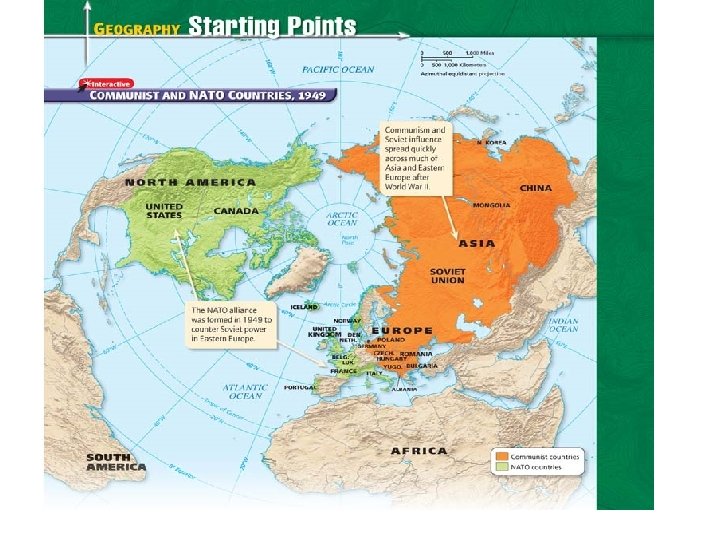
 Spread of the Cold War and New Alliances • China falls to Chinese Communists led by Mao Zedong in 1949 • The Soviet Union explodes its first atomic bomb – The U. S. and Soviet Union begin an arms race, each trying to gain an advantage in weapons – Both sides began to stockpile nuclear weapons – Deterrence = the development or maintenance of military power to prevent an attack
Spread of the Cold War and New Alliances • China falls to Chinese Communists led by Mao Zedong in 1949 • The Soviet Union explodes its first atomic bomb – The U. S. and Soviet Union begin an arms race, each trying to gain an advantage in weapons – Both sides began to stockpile nuclear weapons – Deterrence = the development or maintenance of military power to prevent an attack
 • Nato = North Atlantic Treaty Organization (1949) – Military alliance set up by the U. S. , Canada, Britain, France, and most of Western Europe to provide help if any member was attacked • Warsaw Pact (1955) – Military alliance between the Soviet Union and the Communist nations of Eastern Europe: Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Poland, and East Germany • The U. S. also made other alliances in Southeast Asia and Central America
• Nato = North Atlantic Treaty Organization (1949) – Military alliance set up by the U. S. , Canada, Britain, France, and most of Western Europe to provide help if any member was attacked • Warsaw Pact (1955) – Military alliance between the Soviet Union and the Communist nations of Eastern Europe: Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Poland, and East Germany • The U. S. also made other alliances in Southeast Asia and Central America
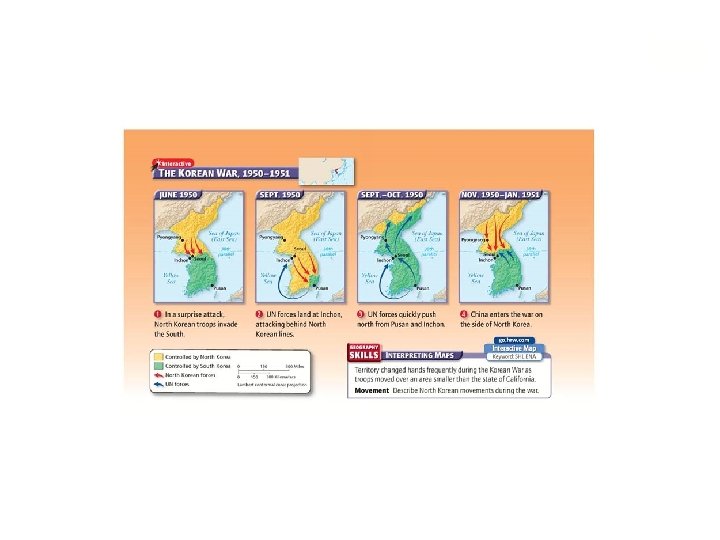
 Korean War (1950 -1953) • After the surrender of Japan, the U. S. and S. U. temporarily divided Korea – The Soviets establish a communist gov’t in North Korea, while the U. S. supports a non-communist gov’t in the South • War begins when the Communist gov’t of North Korea tries to take over South Korean and unite the country under a communist gov’t (June 1950) – Confirms U. S. fears of Communist expansion and the U. S. asks the United Nations to approve the use of force to stop the invasion
Korean War (1950 -1953) • After the surrender of Japan, the U. S. and S. U. temporarily divided Korea – The Soviets establish a communist gov’t in North Korea, while the U. S. supports a non-communist gov’t in the South • War begins when the Communist gov’t of North Korea tries to take over South Korean and unite the country under a communist gov’t (June 1950) – Confirms U. S. fears of Communist expansion and the U. S. asks the United Nations to approve the use of force to stop the invasion
 • The UN sends a military force with soldiers from 17 nations, although most of the soldiers are from the U. S. – These forces, led by General Mac. Arthur, push the North Koreans out of South Korea – Keep going deep into North Korea • China sends troop to aid the North Koreans and the UN forces are driven out of North Korea – Leads to a stalemate and in 1953 both sides agree to an armistice • Divided at the 38 th Parallel – DMZ – 54, 246 U. S. dead in three years, 103, 284 wounded – 4 million Koreans die
• The UN sends a military force with soldiers from 17 nations, although most of the soldiers are from the U. S. – These forces, led by General Mac. Arthur, push the North Koreans out of South Korea – Keep going deep into North Korea • China sends troop to aid the North Koreans and the UN forces are driven out of North Korea – Leads to a stalemate and in 1953 both sides agree to an armistice • Divided at the 38 th Parallel – DMZ – 54, 246 U. S. dead in three years, 103, 284 wounded – 4 million Koreans die
 Conflicts • Trouble in the Suez (1956) – Egypt takes over the Suez Canal, greatly angering Great Britain and France – Britain, France, and Israel then attack Egypt, and the Soviet Union threatens to fight on Egypt’s side – The U. S. steps in and tells its Allies to back down to prevent a larger war • Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961) – In 1959 Fidel Castro establishes a Communist gov’t in Cuba and makes an alliance with the Soviets – President Kennedy approves a secret plan for Cuban exiles to invade Cuba to remove Castro
Conflicts • Trouble in the Suez (1956) – Egypt takes over the Suez Canal, greatly angering Great Britain and France – Britain, France, and Israel then attack Egypt, and the Soviet Union threatens to fight on Egypt’s side – The U. S. steps in and tells its Allies to back down to prevent a larger war • Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961) – In 1959 Fidel Castro establishes a Communist gov’t in Cuba and makes an alliance with the Soviets – President Kennedy approves a secret plan for Cuban exiles to invade Cuba to remove Castro
 • The CIA secretly trains these 1500 Cubans and sends them to invade Cuba – The invasion fails – no air support • Berlin Wall (1961) – Soviets have the East German gov’t build a wall to stop the flow of East Germans escaping to West Berlin – By 1961 approximately 1, 000 people a day were leaving East Germany through Berlin – Wall is heavily guarded with machine guns, barbed wire, and attack dogs
• The CIA secretly trains these 1500 Cubans and sends them to invade Cuba – The invasion fails – no air support • Berlin Wall (1961) – Soviets have the East German gov’t build a wall to stop the flow of East Germans escaping to West Berlin – By 1961 approximately 1, 000 people a day were leaving East Germany through Berlin – Wall is heavily guarded with machine guns, barbed wire, and attack dogs

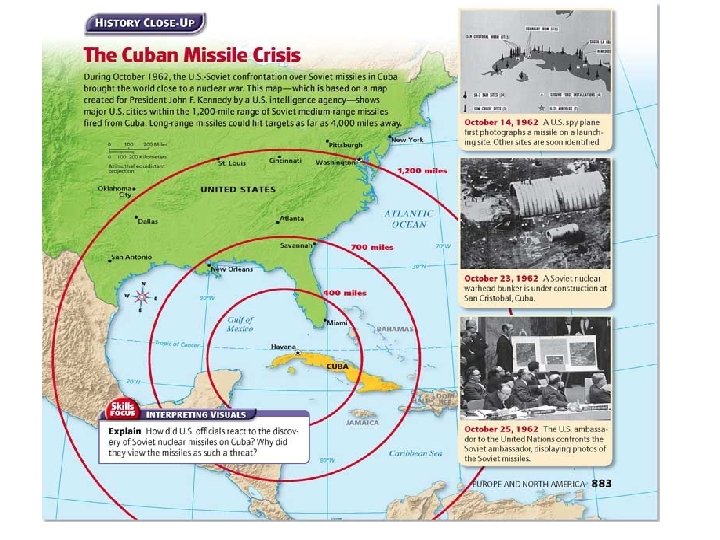
 • Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) – Soviet leader Khrushchev begins to place nuclear missiles in Cuba to counteract U. S. nuclear weapons placed in Turkey – In October, Kennedy finds out that Soviet ships carrying nuclear missiles are heading to Cuba • Orders the blockade of Cuba • The ships meet eye-to-eye, world on edge of a nuclear war • The Soviets turn back – Khrushchev removes the missiles from Cuba and Kennedy promises not to invade Cuba again
• Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) – Soviet leader Khrushchev begins to place nuclear missiles in Cuba to counteract U. S. nuclear weapons placed in Turkey – In October, Kennedy finds out that Soviet ships carrying nuclear missiles are heading to Cuba • Orders the blockade of Cuba • The ships meet eye-to-eye, world on edge of a nuclear war • The Soviets turn back – Khrushchev removes the missiles from Cuba and Kennedy promises not to invade Cuba again

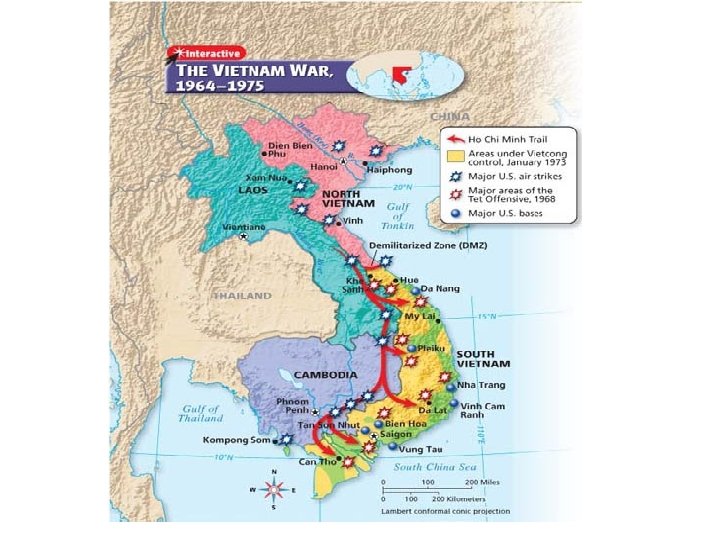
 Vietnam War (1964 -1975) • Domino theory = idea that if one country falls to communism, neighboring countries will also fall – Purpose of the Vietnam War was to keep the Communist gov’t of North Vietnam from gaining control of South Vietnam – Afraid if South Vietnam fell, so would other nations in Asia • Starts off as a war for independence from France – After WWII France worked to regain its colonies and fought against the Vietminh, who wanted independence from France
Vietnam War (1964 -1975) • Domino theory = idea that if one country falls to communism, neighboring countries will also fall – Purpose of the Vietnam War was to keep the Communist gov’t of North Vietnam from gaining control of South Vietnam – Afraid if South Vietnam fell, so would other nations in Asia • Starts off as a war for independence from France – After WWII France worked to regain its colonies and fought against the Vietminh, who wanted independence from France
 • The leader of the Vietminh was Ho Chi Minh, a Communist who received aid from the Soviet Union – The French pull out of Vietnam after their military base of Dien Bien Phu falls in 1954 • Vietnam was divided, with the Vietminh and Ho Chi Minh getting control of North Vietnam • The U. S. supported South Vietnam to keep it from being taken over by the North – The leader of South Vietnam was brutal and corrupt – A group called the Vietcong (Vietnamese Communists) formed to overthrown his gov’t and reunite Vietnam
• The leader of the Vietminh was Ho Chi Minh, a Communist who received aid from the Soviet Union – The French pull out of Vietnam after their military base of Dien Bien Phu falls in 1954 • Vietnam was divided, with the Vietminh and Ho Chi Minh getting control of North Vietnam • The U. S. supported South Vietnam to keep it from being taken over by the North – The leader of South Vietnam was brutal and corrupt – A group called the Vietcong (Vietnamese Communists) formed to overthrown his gov’t and reunite Vietnam
 • North Vietnamese forces entered South Vietnam to fight alongside the Vietcong – The U. S. sent thousands of military advisors to help South Vietnam • Tonkin Gulf Incident (1964) – North Vietnamese destroyer mistakenly fires on 2 U. S. ships • President Johnson informs Congress of this unprovoked attack – Congress passes the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution • Gives Johnson the power to expand U. S. involvement without a formal declaration of war • Hundreds of thousands of soldiers sent to Vietnam
• North Vietnamese forces entered South Vietnam to fight alongside the Vietcong – The U. S. sent thousands of military advisors to help South Vietnam • Tonkin Gulf Incident (1964) – North Vietnamese destroyer mistakenly fires on 2 U. S. ships • President Johnson informs Congress of this unprovoked attack – Congress passes the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution • Gives Johnson the power to expand U. S. involvement without a formal declaration of war • Hundreds of thousands of soldiers sent to Vietnam
 • Tet Offensive (1968) – Massive attack by the Vietcong and North Vietnamese forces – Ultimately a failure offensively, but it greatly weakened American support for the war • Antiwar movement in the U. S. – Draft instituted, people want out of the war – Kent State University (1970) four students are killed by the national guard • My Lai (1968) – Lt. William Calley and his troops murder almost an entire village in S. Vietnam – kill hundreds
• Tet Offensive (1968) – Massive attack by the Vietcong and North Vietnamese forces – Ultimately a failure offensively, but it greatly weakened American support for the war • Antiwar movement in the U. S. – Draft instituted, people want out of the war – Kent State University (1970) four students are killed by the national guard • My Lai (1968) – Lt. William Calley and his troops murder almost an entire village in S. Vietnam – kill hundreds
 • 1973 President Nixon pulls the U. S. out of the war – 58, 226 Americans killed – War resumes without U. S. intervention and within two years Vietnam is forcibly reunited by Communist armies from the North when Saigon falls in 1975
• 1973 President Nixon pulls the U. S. out of the war – 58, 226 Americans killed – War resumes without U. S. intervention and within two years Vietnam is forcibly reunited by Communist armies from the North when Saigon falls in 1975
 A Thaw in the Cold War • Détente = relaxation of tensions and improved relations between the superpowers – In the 1970 s American-Soviet relations enter a new phase – Strategic Arms Limitations Talks (SALT) • Agree to limit the number of nuclear weapons they have • 1979 détente collapses when the Soviets invade Afghanistan to restore a pro-Soviet regime – U. S. cancels American participation in the 1980 Olympics in Moscow – CIA trains people in Afghanistan to fight the Soviets, including Osama bin Laden
A Thaw in the Cold War • Détente = relaxation of tensions and improved relations between the superpowers – In the 1970 s American-Soviet relations enter a new phase – Strategic Arms Limitations Talks (SALT) • Agree to limit the number of nuclear weapons they have • 1979 détente collapses when the Soviets invade Afghanistan to restore a pro-Soviet regime – U. S. cancels American participation in the 1980 Olympics in Moscow – CIA trains people in Afghanistan to fight the Soviets, including Osama bin Laden


