d85ed0888268321c4401029a168a9684.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 The Cold War, 1945 -1953
The Cold War, 1945 -1953
 What Was the Cold War? n n n Conflict between the U. S. and Soviet Union Never directly attacked each other Fought each other around the globe in other countries Stand-off over economics, politics, military bases, resources Conflict in the Atomic Age 1945 -1989
What Was the Cold War? n n n Conflict between the U. S. and Soviet Union Never directly attacked each other Fought each other around the globe in other countries Stand-off over economics, politics, military bases, resources Conflict in the Atomic Age 1945 -1989
 Why Was it Significant? n n n C. W. influenced all international relations U. S. supported anti-communist dictators U. S. believed that all reforms were communist inspired Believed that Moscow wanted to expand around the globe and invade U. S. Massive military build-up $4. 5 trillion spent in U. S.
Why Was it Significant? n n n C. W. influenced all international relations U. S. supported anti-communist dictators U. S. believed that all reforms were communist inspired Believed that Moscow wanted to expand around the globe and invade U. S. Massive military build-up $4. 5 trillion spent in U. S.
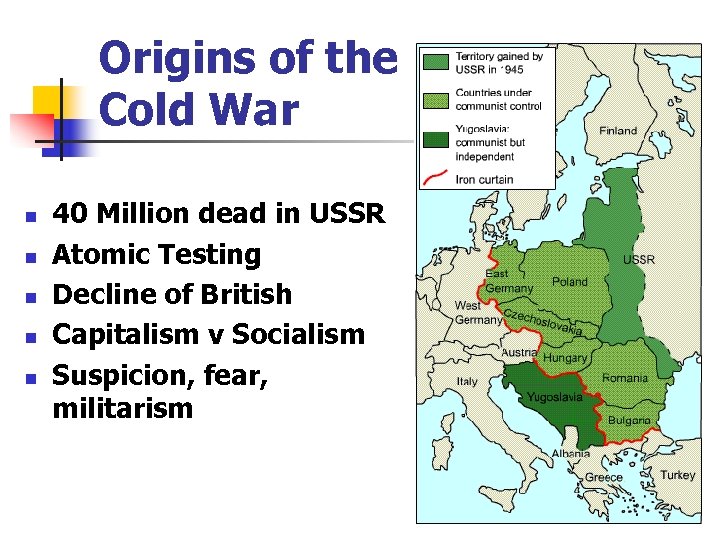 Origins of the Cold War n n n 40 Million dead in USSR Atomic Testing Decline of British Capitalism v Socialism Suspicion, fear, militarism
Origins of the Cold War n n n 40 Million dead in USSR Atomic Testing Decline of British Capitalism v Socialism Suspicion, fear, militarism
 Globalizing National Security n n n Defined everything in relation to it “Free Markets” led to democracy Other countries must consume U. S. products Socialist regimes threatened U. S. economic interests Perceived as communist threats Sanctioned invasions
Globalizing National Security n n n Defined everything in relation to it “Free Markets” led to democracy Other countries must consume U. S. products Socialist regimes threatened U. S. economic interests Perceived as communist threats Sanctioned invasions
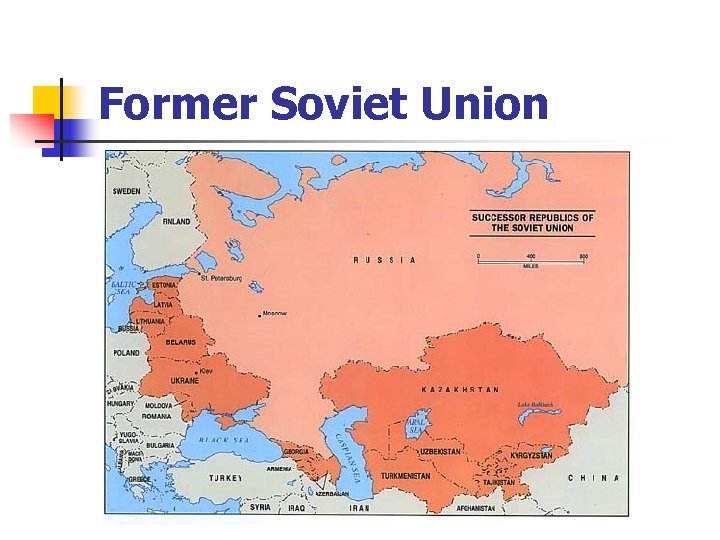 Former Soviet Union
Former Soviet Union
 Soviet Weaknesses n n n Economy destroyed Military deaths Small air force & navy Few international military bases Chinese independence
Soviet Weaknesses n n n Economy destroyed Military deaths Small air force & navy Few international military bases Chinese independence
 Containment Policy n n n George Kennan, Diplomat Architect of U. S. policy USSR was Insecure and paranoid Inherently expansionistic Open ended, constant war Contain communism
Containment Policy n n n George Kennan, Diplomat Architect of U. S. policy USSR was Insecure and paranoid Inherently expansionistic Open ended, constant war Contain communism
 Harry Truman n V. P. to FDR Agreed to A-Bomb Truman Doctrine n n Good v. Evil Two ways of life All nations must choose Exaggerated dangers for political gain
Harry Truman n V. P. to FDR Agreed to A-Bomb Truman Doctrine n n Good v. Evil Two ways of life All nations must choose Exaggerated dangers for political gain
 First Moves n 1945: Bombed Japan n n Mc. Arthur in Japan 1946: Iron Curtain 1947: Aid to Greece and Turkey 1947: Berlin Blockade 1948: Czechoslovakia
First Moves n 1945: Bombed Japan n n Mc. Arthur in Japan 1946: Iron Curtain 1947: Aid to Greece and Turkey 1947: Berlin Blockade 1948: Czechoslovakia
 Continued… n 1948 -52 Marshall Plan n n $13 billion European aid 1949: NATO U. S. atomic testing in the Pacific Soviet A-Bomb
Continued… n 1948 -52 Marshall Plan n n $13 billion European aid 1949: NATO U. S. atomic testing in the Pacific Soviet A-Bomb
 De-Colonization n n n n Liberation in countries controlled by Europeans Who would have power? ? ? Philippines, 1946 India, 1947 Middle East Israel in Palestinian homelands Africa U. S. wanted pro-U. S. leaders
De-Colonization n n n n Liberation in countries controlled by Europeans Who would have power? ? ? Philippines, 1946 India, 1947 Middle East Israel in Palestinian homelands Africa U. S. wanted pro-U. S. leaders
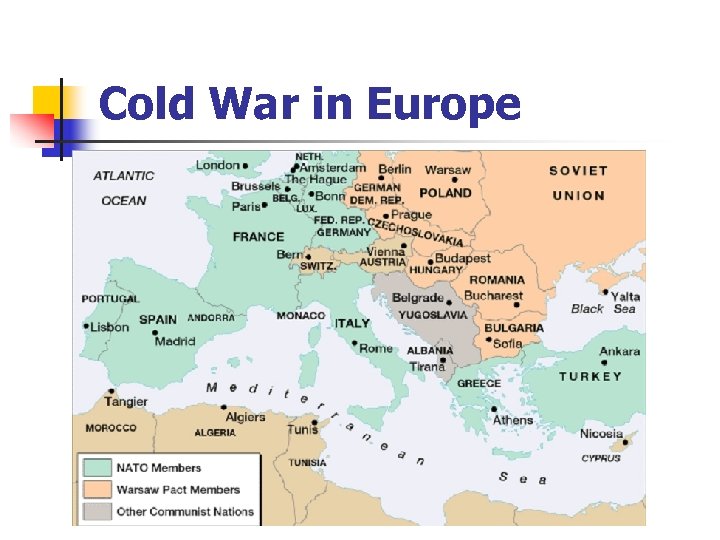 Cold War in Europe
Cold War in Europe
 Cold War Government n n n n National Security Council Document 68 (NSC-68) 1950 Massive military & global power Endless war National Security Acts, 1947 & 49 C. I. A Dept of Defense Pentagon
Cold War Government n n n n National Security Council Document 68 (NSC-68) 1950 Massive military & global power Endless war National Security Acts, 1947 & 49 C. I. A Dept of Defense Pentagon
 Cold War Institutions
Cold War Institutions
 China and the Cold War n n n n Japanese invasions U. S. economic interests Chinese Civil War Mao Zedong & the CCP won 1949: People’s Republic of China Nationalists retreated to Taiwan Agreement with USSR “Lost China”
China and the Cold War n n n n Japanese invasions U. S. economic interests Chinese Civil War Mao Zedong & the CCP won 1949: People’s Republic of China Nationalists retreated to Taiwan Agreement with USSR “Lost China”
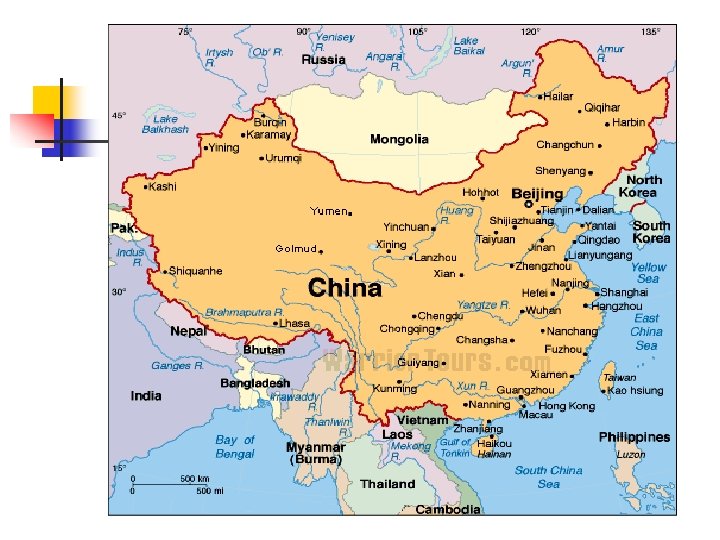
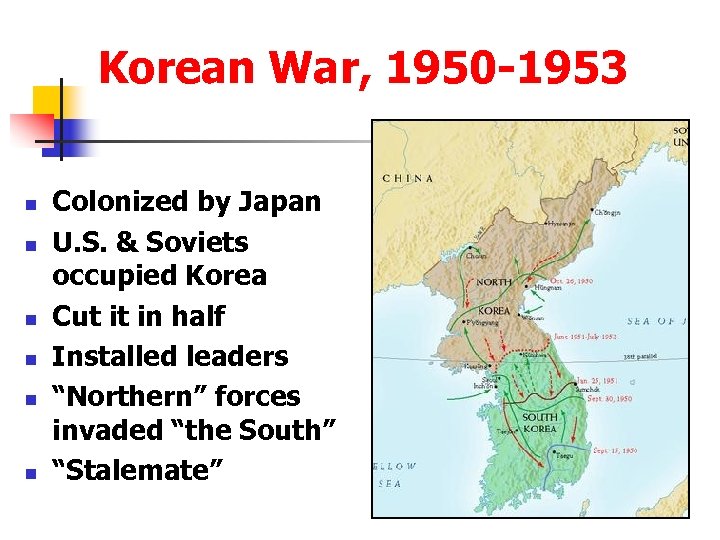 Korean War, 1950 -1953 n n n Colonized by Japan U. S. & Soviets occupied Korea Cut it in half Installed leaders “Northern” forces invaded “the South” “Stalemate”
Korean War, 1950 -1953 n n n Colonized by Japan U. S. & Soviets occupied Korea Cut it in half Installed leaders “Northern” forces invaded “the South” “Stalemate”
 American Involvement n n n Invaded Korea and pushed forces north Called a “police action” Assumed Moscow ordered invasion Mc. Arthur wanted to go north China sent in reinforcements Ended back at original dividing line
American Involvement n n n Invaded Korea and pushed forces north Called a “police action” Assumed Moscow ordered invasion Mc. Arthur wanted to go north China sent in reinforcements Ended back at original dividing line
 American Politics n n n C. W. ruined many of the gains of labor, progressivism, New Deal Demonized reformers and reform movements Polarized political debate Anti-Communist rhetoric polluted democracy Free Speech perceived as subversive
American Politics n n n C. W. ruined many of the gains of labor, progressivism, New Deal Demonized reformers and reform movements Polarized political debate Anti-Communist rhetoric polluted democracy Free Speech perceived as subversive
 Cold War Politics n n Taft-Hartley Act, 1947 G. I. Bill and FHA Racial Segregation & inequality continued Pledge of Allegiance
Cold War Politics n n Taft-Hartley Act, 1947 G. I. Bill and FHA Racial Segregation & inequality continued Pledge of Allegiance
 Second Red Scare n n n Joseph Mc. Carthy Life of anti-communism House Un-American Activities Committee Army-Mc. Carthy Hearings Hollywood Ten
Second Red Scare n n n Joseph Mc. Carthy Life of anti-communism House Un-American Activities Committee Army-Mc. Carthy Hearings Hollywood Ten
 Other Issues n n n Truman: loyalty oaths for federal workers 1952: Hydrogen bomb in U. S. Rosenbergs executed for allegations of selling atomic secrets
Other Issues n n n Truman: loyalty oaths for federal workers 1952: Hydrogen bomb in U. S. Rosenbergs executed for allegations of selling atomic secrets
 Cold War Culture n n n n America as victim Baby-boom and prosperity Conformity Fear and suspicion Sexual repression Distorted patriotism No political debate
Cold War Culture n n n n America as victim Baby-boom and prosperity Conformity Fear and suspicion Sexual repression Distorted patriotism No political debate
 Conclusions n n n n Endless War of ideology Struggle for global power Containment Atomic Arms Race Black and White World Cold War at Home Distorted American Politics Red Scare
Conclusions n n n n Endless War of ideology Struggle for global power Containment Atomic Arms Race Black and White World Cold War at Home Distorted American Politics Red Scare


