528c33288937ce26eb20c3288ace4da0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71
 The Cognitive Perspective: Memory
The Cognitive Perspective: Memory


 Write down you three clearest memories
Write down you three clearest memories
 What is memory? • Memory is what reminds you on Friday what you should have done on the previous Monday!!
What is memory? • Memory is what reminds you on Friday what you should have done on the previous Monday!!
 What is memory The more I study, The more I know; The more I know, The more I forget; The more I forget, The less I know, So why study? The more I lecture, The more you know; The more you know, The more you forget; The more you forget, The less you know, So why should I lecture?
What is memory The more I study, The more I know; The more I know, The more I forget; The more I forget, The less I know, So why study? The more I lecture, The more you know; The more you know, The more you forget; The more you forget, The less you know, So why should I lecture?
 A little experiment • Remember the following words
A little experiment • Remember the following words
 • BEE • SEE • PEA • TREE • GLEE • KEY
• BEE • SEE • PEA • TREE • GLEE • KEY
 Read these, no need to remember • SHE • KNEE • FREE • THREE • TEA • PLEA
Read these, no need to remember • SHE • KNEE • FREE • THREE • TEA • PLEA
 RECALL THE WORDS ON THE FIRST LIST
RECALL THE WORDS ON THE FIRST LIST
 What about • SHE • KNEE • FREE • THREE • TEA • PLEA Are replaced by • ESKIMO • BUFFALO • TELEPHONE • VIOLIN • PENCIL • WINTER
What about • SHE • KNEE • FREE • THREE • TEA • PLEA Are replaced by • ESKIMO • BUFFALO • TELEPHONE • VIOLIN • PENCIL • WINTER
 Short-term Memory • • acoustic code rehearsal serial exhaustive retrieval forgetting is due to interference (replacement) or decay
Short-term Memory • • acoustic code rehearsal serial exhaustive retrieval forgetting is due to interference (replacement) or decay
 Short-term Memory • Storage: – limited storage : 7± 2 items, chunking Working Memory What you can articulate in 2. 5 s
Short-term Memory • Storage: – limited storage : 7± 2 items, chunking Working Memory What you can articulate in 2. 5 s
 Pioneers in memory • James (1890) • First US psychologist • Wrote the monumental Principles in Psychology PRIMARY MEMORY • Immediate, present effortless • SECONDARY MEMORY • Unconscious - permanent • Genuine Past • Requires effort
Pioneers in memory • James (1890) • First US psychologist • Wrote the monumental Principles in Psychology PRIMARY MEMORY • Immediate, present effortless • SECONDARY MEMORY • Unconscious - permanent • Genuine Past • Requires effort
 Pioneers in memory Hermann Ebbinghaus 1885 • Nonsense syllables • Clusters of three letters: • KED, MOZ • Read list, covered it, recited • Repeat • Discovered he gradually improved • Flaws of design?
Pioneers in memory Hermann Ebbinghaus 1885 • Nonsense syllables • Clusters of three letters: • KED, MOZ • Read list, covered it, recited • Repeat • Discovered he gradually improved • Flaws of design?
 Pioneers in memory Hermann Ebbinghaus 1885 • Associationist • Short term and long term memory
Pioneers in memory Hermann Ebbinghaus 1885 • Associationist • Short term and long term memory
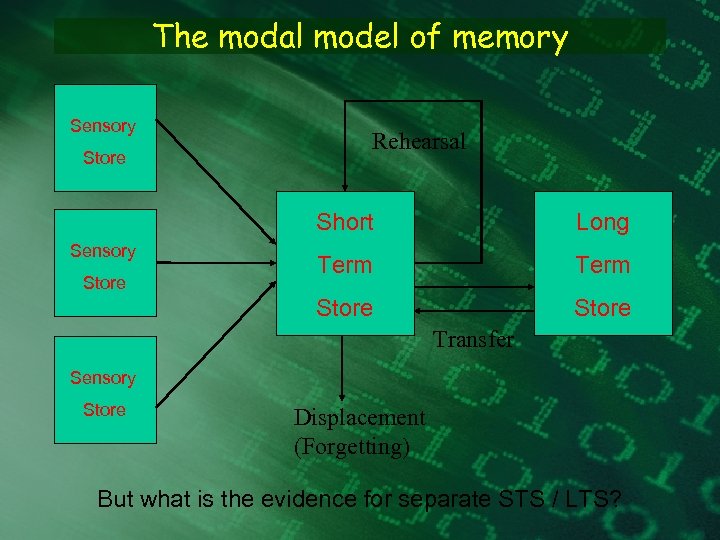 The modal model of memory Sensory Store Rehearsal Short Store Term Store Sensory Long Store Transfer Sensory Store Displacement (Forgetting) But what is the evidence for separate STS / LTS?
The modal model of memory Sensory Store Rehearsal Short Store Term Store Sensory Long Store Transfer Sensory Store Displacement (Forgetting) But what is the evidence for separate STS / LTS?
 Evidence for STS / LTS distinction Converging evidence appeared to support the STS / LTS distinction as proposed by the modal model: • Capacity differences - STS = limited / LTS = unlimited • Encoding differences - STS = phonological / LTS = semantic • Serial Position Curves - STS = Recency / LTS = Primacy + Asym • Forgetting - STS = trace decay / LTS = interference • Neuropsych Evidence - HM = intact STS, impaired LTS KF = intact LTS, impaired STS BUT - psychology is never simple. . .
Evidence for STS / LTS distinction Converging evidence appeared to support the STS / LTS distinction as proposed by the modal model: • Capacity differences - STS = limited / LTS = unlimited • Encoding differences - STS = phonological / LTS = semantic • Serial Position Curves - STS = Recency / LTS = Primacy + Asym • Forgetting - STS = trace decay / LTS = interference • Neuropsych Evidence - HM = intact STS, impaired LTS KF = intact LTS, impaired STS BUT - psychology is never simple. . .
 Case studies • • HM Milner (1996) Epileptic Antergrade amenesia Reread newspaper Time for 15 seconds Memento • KF • Shallice an Warrington (1970) • Motorcycle accident • STM impaired • LTM good--even after the accident
Case studies • • HM Milner (1996) Epileptic Antergrade amenesia Reread newspaper Time for 15 seconds Memento • KF • Shallice an Warrington (1970) • Motorcycle accident • STM impaired • LTM good--even after the accident
 Problems for STS / LTS distinction • Encoding differences - How do we comprehend text / learn language / remember faces? • SPCs - Recency effects after 20 sec distraction following each item (Tzeng, 1973). Long term recency (Baddeley & Hitch, 1977) constant ratio rule ( t / T) (Glenberg et al, 1980). • Forgetting - Interference effects in STS (e. g. Release from Proactive Interference - RPI) • NP Evidence - Why is HM able to encode information in LTS if the STS is a critical bottleneck? The modal model provided the first systematic attempt to account for the structures and processes which comprise the memory system But by the end of the 1960 s there were several well established findings that it was unable to account for.
Problems for STS / LTS distinction • Encoding differences - How do we comprehend text / learn language / remember faces? • SPCs - Recency effects after 20 sec distraction following each item (Tzeng, 1973). Long term recency (Baddeley & Hitch, 1977) constant ratio rule ( t / T) (Glenberg et al, 1980). • Forgetting - Interference effects in STS (e. g. Release from Proactive Interference - RPI) • NP Evidence - Why is HM able to encode information in LTS if the STS is a critical bottleneck? The modal model provided the first systematic attempt to account for the structures and processes which comprise the memory system But by the end of the 1960 s there were several well established findings that it was unable to account for.
 Magic number 7 • 7 Plus or minus 2 • George Miller (1956) • STM can hold between 5 and 9 chunks of items • Brown and Peterson technique (1959) • Three letter in a Trigram • Count back ward in threes from 176 aloud
Magic number 7 • 7 Plus or minus 2 • George Miller (1956) • STM can hold between 5 and 9 chunks of items • Brown and Peterson technique (1959) • Three letter in a Trigram • Count back ward in threes from 176 aloud
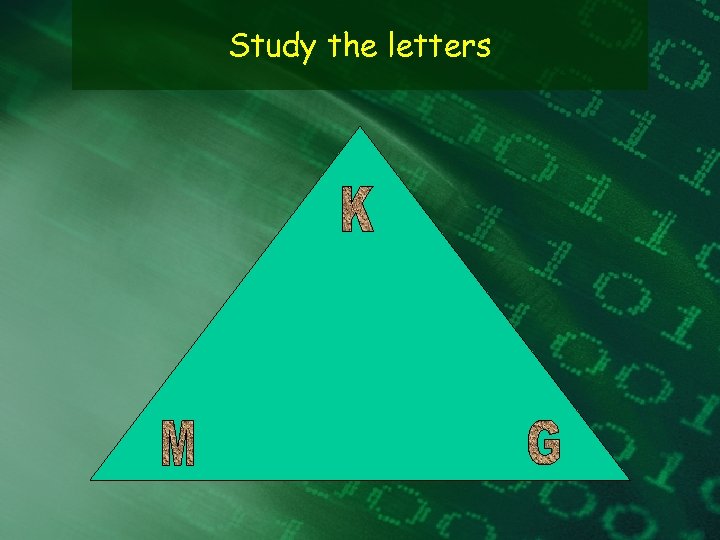 Study the letters
Study the letters
 Count Backwards by three aloud 176
Count Backwards by three aloud 176
 Study the letters
Study the letters
 Count Backwards by three aloud 176
Count Backwards by three aloud 176
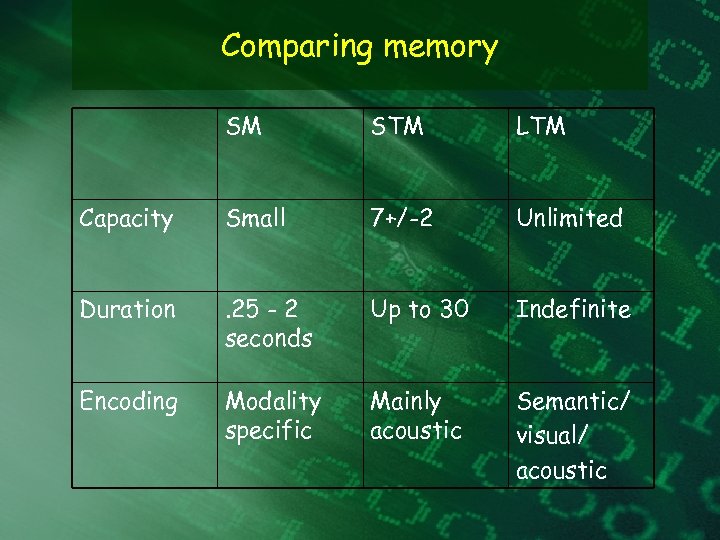 Comparing memory SM STM LTM Capacity Small 7+/-2 Unlimited Duration . 25 - 2 seconds Up to 30 Indefinite Encoding Modality specific Mainly acoustic Semantic/ visual/ acoustic
Comparing memory SM STM LTM Capacity Small 7+/-2 Unlimited Duration . 25 - 2 seconds Up to 30 Indefinite Encoding Modality specific Mainly acoustic Semantic/ visual/ acoustic
 Sensory Processing • Short-term sensory memory – iconic, echoic, and kinesthetic memory – Sperling’s experiment
Sensory Processing • Short-term sensory memory – iconic, echoic, and kinesthetic memory – Sperling’s experiment
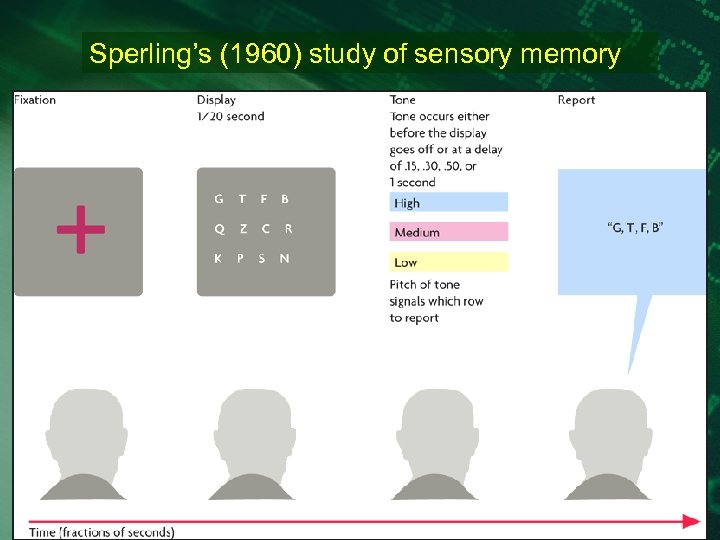 Sperling’s (1960) study of sensory memory
Sperling’s (1960) study of sensory memory
 Whole report procedure • Pay attention to the following matrix
Whole report procedure • Pay attention to the following matrix
 N K J A F Z +P M T W X U
N K J A F Z +P M T W X U
 Task • Try to recall as many letters as possible.
Task • Try to recall as many letters as possible.
 Partial report • Report the letters in the row indicated by the arrow.
Partial report • Report the letters in the row indicated by the arrow.
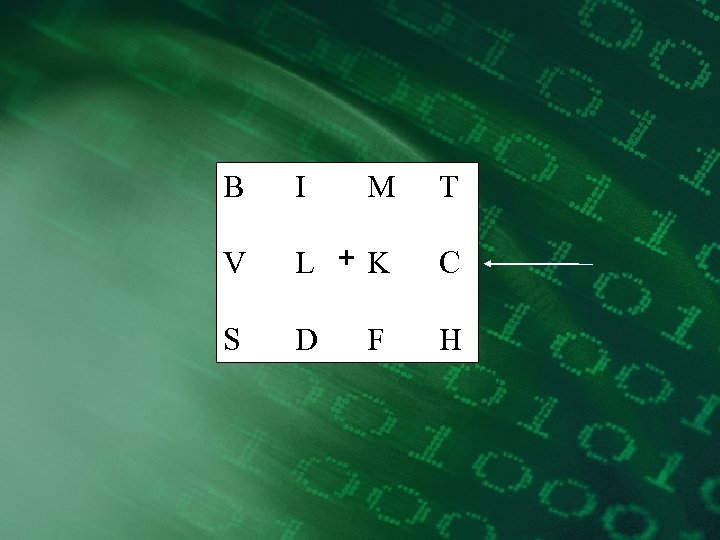 B I M T V L +K C S D H F
B I M T V L +K C S D H F
 Independent variables • Delay between matrix and cue
Independent variables • Delay between matrix and cue
 Sperling’s Experiment • whole report : 4 -5 items • partial report : 9 items – delay cue : 0 ms - 9 items 150 ms - 7 items 250 ms - 6 items 1000 ms - 4 -5 items
Sperling’s Experiment • whole report : 4 -5 items • partial report : 9 items – delay cue : 0 ms - 9 items 150 ms - 7 items 250 ms - 6 items 1000 ms - 4 -5 items
 Short-term sensory memory (C’d) • preattentive: large capacity, parallel processing • veridical : much physical information of the stimulus is preserved • rapid decay
Short-term sensory memory (C’d) • preattentive: large capacity, parallel processing • veridical : much physical information of the stimulus is preserved • rapid decay

 • Write down as many as you can remember
• Write down as many as you can remember

 Story telling • Make up a story for each and every item • The sillier the better.
Story telling • Make up a story for each and every item • The sillier the better.

 • Write down as many as you can remember
• Write down as many as you can remember

 Wander around the house • Put each item in a part of the house. • Imagine your house, from the moment you enter it. • Pick ten distinct places • Go progressively from one to the next. • Simonides
Wander around the house • Put each item in a part of the house. • Imagine your house, from the moment you enter it. • Pick ten distinct places • Go progressively from one to the next. • Simonides

 • Write down as many as you can remember
• Write down as many as you can remember

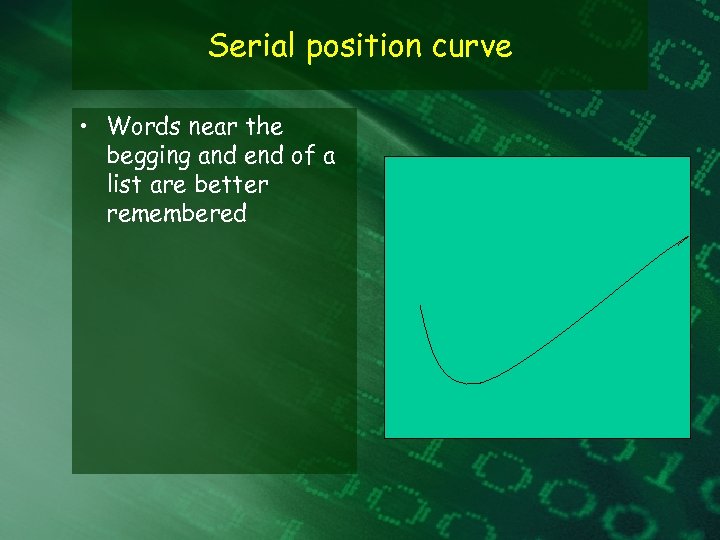 Serial position curve • Words near the begging and end of a list are better remembered
Serial position curve • Words near the begging and end of a list are better remembered
 Coding in STM • • Activity 3 Two lists Two groups Counterbalancing
Coding in STM • • Activity 3 Two lists Two groups Counterbalancing
 Write in order they appear (Conrad 1964)
Write in order they appear (Conrad 1964)
 Tulving (1972) • Semantic memory • Episodic memory • Procedural memory
Tulving (1972) • Semantic memory • Episodic memory • Procedural memory
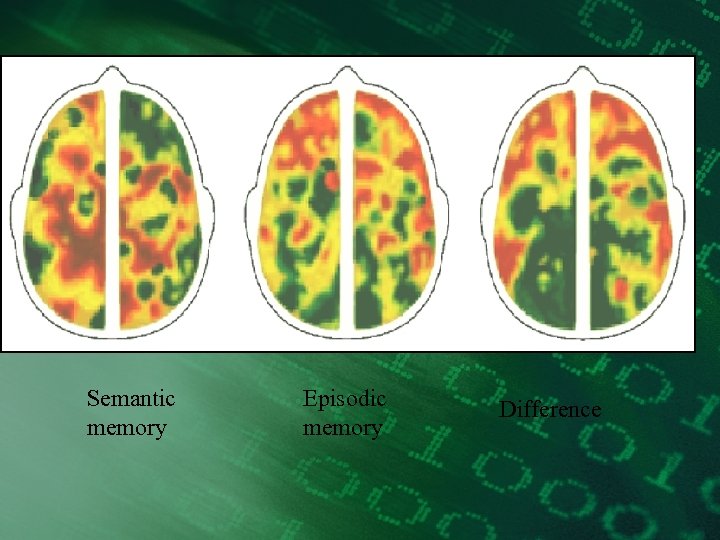 Semantic memory Episodic memory Difference
Semantic memory Episodic memory Difference
 June 23, 2004 • Describe as much as you can remember that day
June 23, 2004 • Describe as much as you can remember that day
 September 11, 2001 • Describe as much as you can remember that day
September 11, 2001 • Describe as much as you can remember that day
 Flashbulb memory • • Brown and Kulik (1977): 1) Where they were 2) what they were doing 3) person who gave them the news 4) How they felt about it 5) how Others felt about it 6) the aftermath
Flashbulb memory • • Brown and Kulik (1977): 1) Where they were 2) what they were doing 3) person who gave them the news 4) How they felt about it 5) how Others felt about it 6) the aftermath
 Your three clearest memories • • Rubin and Kozin (1984) Injury Love affairs Emotionally explosive How often rehersed Was there surprise Was it a national event?
Your three clearest memories • • Rubin and Kozin (1984) Injury Love affairs Emotionally explosive How often rehersed Was there surprise Was it a national event?
 Perceptual Encoding A A A
Perceptual Encoding A A A
 Perceptual Encoding • detection, recognition (LTM), identification, or categorization • Mental representation
Perceptual Encoding • detection, recognition (LTM), identification, or categorization • Mental representation
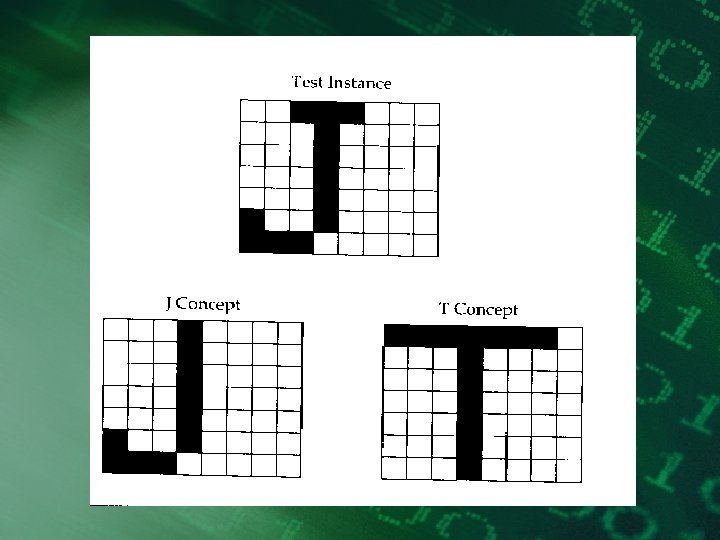
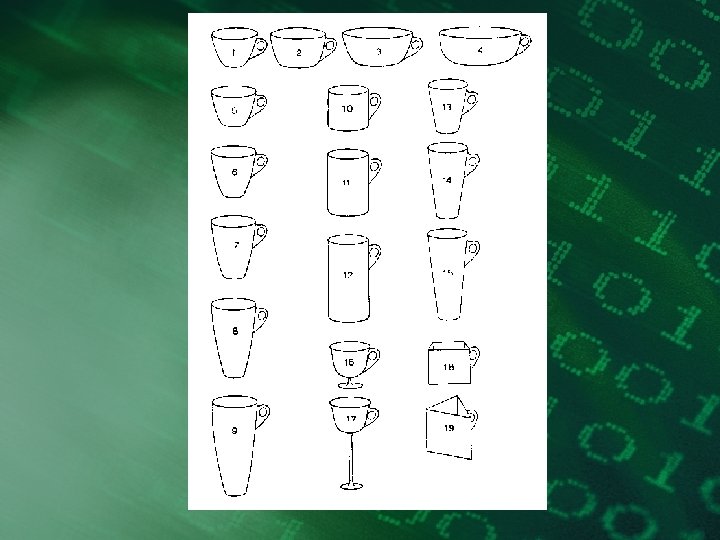

 Long-term memory • • permanent unlimited capacity forgetting - due to retrieval failure coded by meaning, hierarchy, semantic network, etc.
Long-term memory • • permanent unlimited capacity forgetting - due to retrieval failure coded by meaning, hierarchy, semantic network, etc.
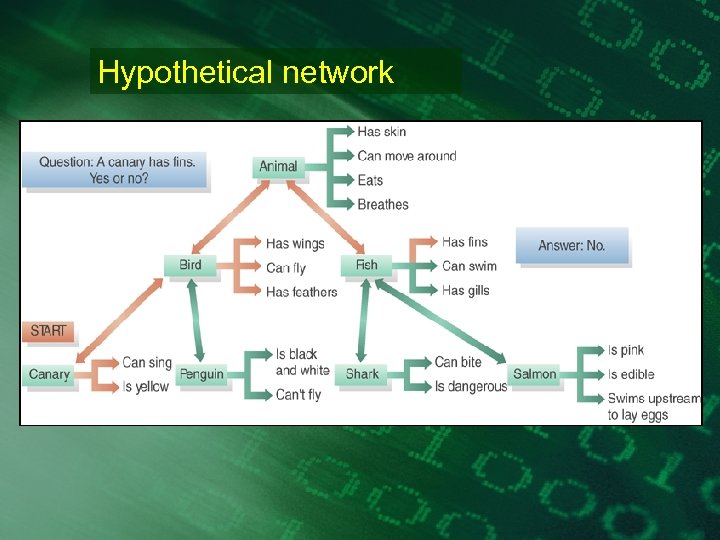 Hypothetical network
Hypothetical network
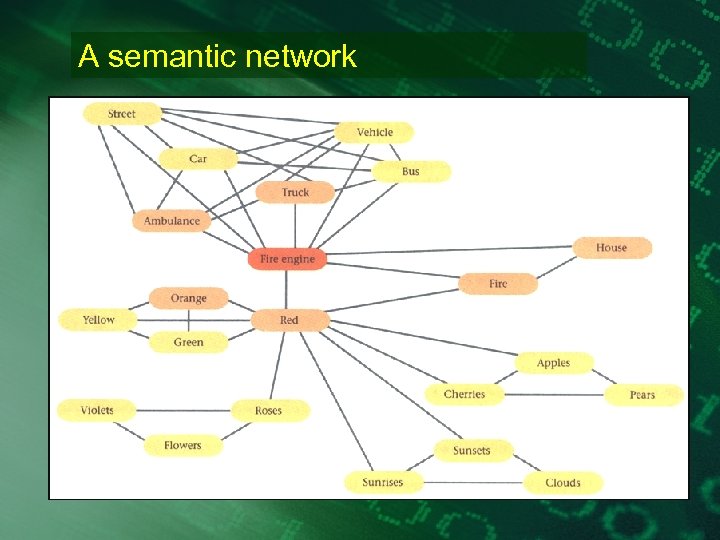 A semantic network
A semantic network

 Slide from Dr. Joe Lau
Slide from Dr. Joe Lau
 Slide from Dr. Joe Lau
Slide from Dr. Joe Lau
 How does science work? • Example of working memory
How does science work? • Example of working memory
 Working Memory (Baddeley, 1975) Experiment 1 • Stimulus: Monosyllable & 5 -syllable words • • • (sum, hate vs. university, organization) IVs: 1) Number of syllables (1 vs. 5) 2) Number of words per sequence (4, 5, 6, 7, 8) Presentation: 1. 5 s/word, auditory Result: more sequences of monosyllable words recalled.
Working Memory (Baddeley, 1975) Experiment 1 • Stimulus: Monosyllable & 5 -syllable words • • • (sum, hate vs. university, organization) IVs: 1) Number of syllables (1 vs. 5) 2) Number of words per sequence (4, 5, 6, 7, 8) Presentation: 1. 5 s/word, auditory Result: more sequences of monosyllable words recalled.
 Working Memory (Baddeley, 1975) Experiment 6 • Stimulus: Words of with 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 syllables • • (zinc, carbon, calcium, uranium, aluminum) – – Presentation: 50 lists of 5 words, 2 s/word S read the words as quickly as possible Result: Ss recall what they could read in 1. 8 s
Working Memory (Baddeley, 1975) Experiment 6 • Stimulus: Words of with 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 syllables • • (zinc, carbon, calcium, uranium, aluminum) – – Presentation: 50 lists of 5 words, 2 s/word S read the words as quickly as possible Result: Ss recall what they could read in 1. 8 s
 Working Memory • Articulatory loop for storage: capacity is what you can say in 2. 5 s, acoustic code • Central executive: for computation and decision making • Visuospatial pad: for storing and processing of nonverbal information.
Working Memory • Articulatory loop for storage: capacity is what you can say in 2. 5 s, acoustic code • Central executive: for computation and decision making • Visuospatial pad: for storing and processing of nonverbal information.


