a2bbc423c04bf1f866946d04d891b1c8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 The CMS Muon System REFERENCES: Muon TDR, https: //twiki. cern. ch/twiki/bin/view/CMS/Muon. TDR PTDR 1, http: //cmsdoc. cern. ch/cms/cpt/tdr/ http: //www. physics. ohio-state. edu/~gilmore/talks/cms 101_muons. ppt http: //www. bo. infn. it/delphi/html/fln/cms-muon-system. pdf Chen Mingshui IHEP 2008. 12. 04 1
The CMS Muon System REFERENCES: Muon TDR, https: //twiki. cern. ch/twiki/bin/view/CMS/Muon. TDR PTDR 1, http: //cmsdoc. cern. ch/cms/cpt/tdr/ http: //www. physics. ohio-state. edu/~gilmore/talks/cms 101_muons. ppt http: //www. bo. infn. it/delphi/html/fln/cms-muon-system. pdf Chen Mingshui IHEP 2008. 12. 04 1
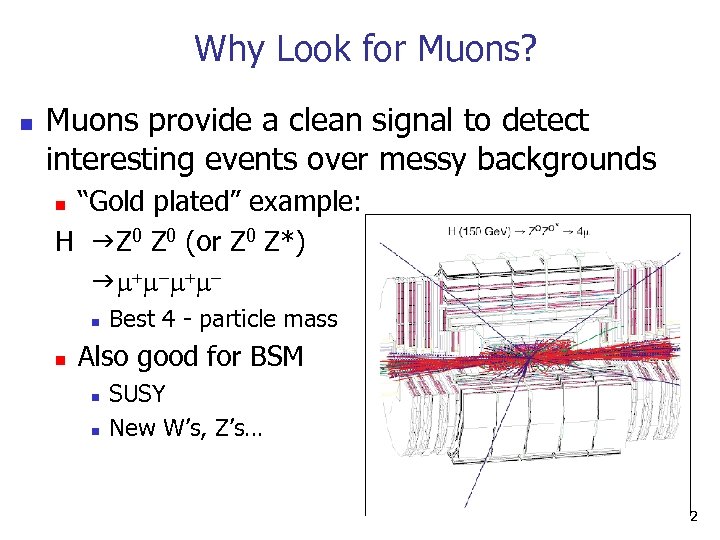 Why Look for Muons? n Muons provide a clean signal to detect interesting events over messy backgrounds “Gold plated” example: H g. Z 0 (or Z 0 Z*) g + - + n n n Best 4 - particle mass Also good for BSM n n SUSY New W’s, Z’s… 2
Why Look for Muons? n Muons provide a clean signal to detect interesting events over messy backgrounds “Gold plated” example: H g. Z 0 (or Z 0 Z*) g + - + n n n Best 4 - particle mass Also good for BSM n n SUSY New W’s, Z’s… 2
 Detector requirements 3
Detector requirements 3
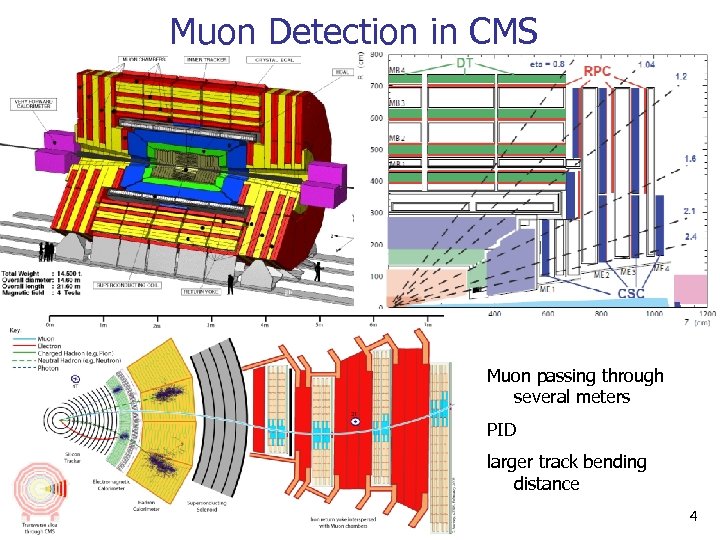 Muon Detection in CMS Muon passing through several meters PID larger track bending distance 4
Muon Detection in CMS Muon passing through several meters PID larger track bending distance 4
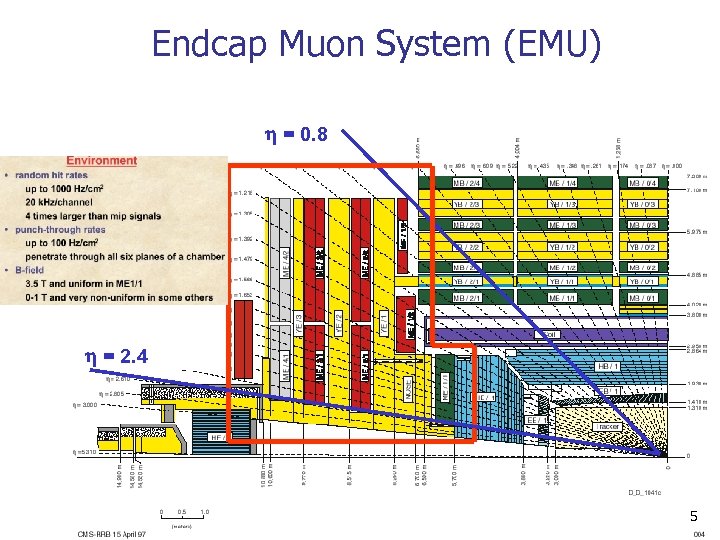 Endcap Muon System (EMU) h = 0. 8 h = 2. 4 5
Endcap Muon System (EMU) h = 0. 8 h = 2. 4 5
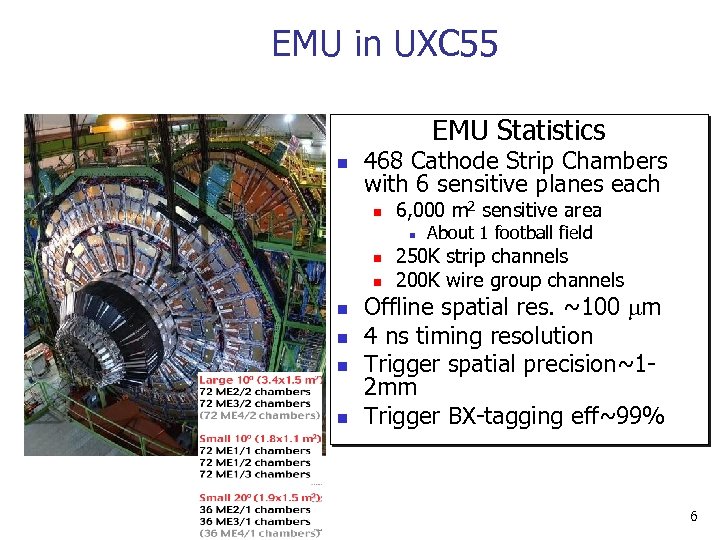 EMU in UXC 55 EMU Statistics n 468 Cathode Strip Chambers with 6 sensitive planes each n 6, 000 m 2 sensitive area n n n n About 1 football field 250 K strip channels 200 K wire group channels Offline spatial res. ~100 m 4 ns timing resolution Trigger spatial precision~12 mm Trigger BX-tagging eff~99% 6
EMU in UXC 55 EMU Statistics n 468 Cathode Strip Chambers with 6 sensitive planes each n 6, 000 m 2 sensitive area n n n n About 1 football field 250 K strip channels 200 K wire group channels Offline spatial res. ~100 m 4 ns timing resolution Trigger spatial precision~12 mm Trigger BX-tagging eff~99% 6
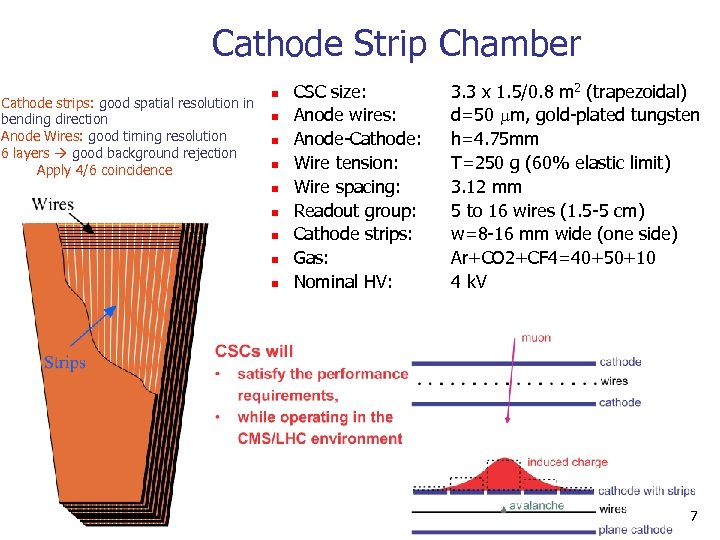 Cathode Strip Chamber Cathode strips: good spatial resolution in bending direction Anode Wires: good timing resolution 6 layers good background rejection Apply 4/6 coincidence n n n n n CSC size: Anode wires: Anode-Cathode: Wire tension: Wire spacing: Readout group: Cathode strips: Gas: Nominal HV: 3. 3 x 1. 5/0. 8 m 2 (trapezoidal) d=50 m, gold-plated tungsten h=4. 75 mm T=250 g (60% elastic limit) 3. 12 mm 5 to 16 wires (1. 5 -5 cm) w=8 -16 mm wide (one side) Ar+CO 2+CF 4=40+50+10 4 k. V 7
Cathode Strip Chamber Cathode strips: good spatial resolution in bending direction Anode Wires: good timing resolution 6 layers good background rejection Apply 4/6 coincidence n n n n n CSC size: Anode wires: Anode-Cathode: Wire tension: Wire spacing: Readout group: Cathode strips: Gas: Nominal HV: 3. 3 x 1. 5/0. 8 m 2 (trapezoidal) d=50 m, gold-plated tungsten h=4. 75 mm T=250 g (60% elastic limit) 3. 12 mm 5 to 16 wires (1. 5 -5 cm) w=8 -16 mm wide (one side) Ar+CO 2+CF 4=40+50+10 4 k. V 7
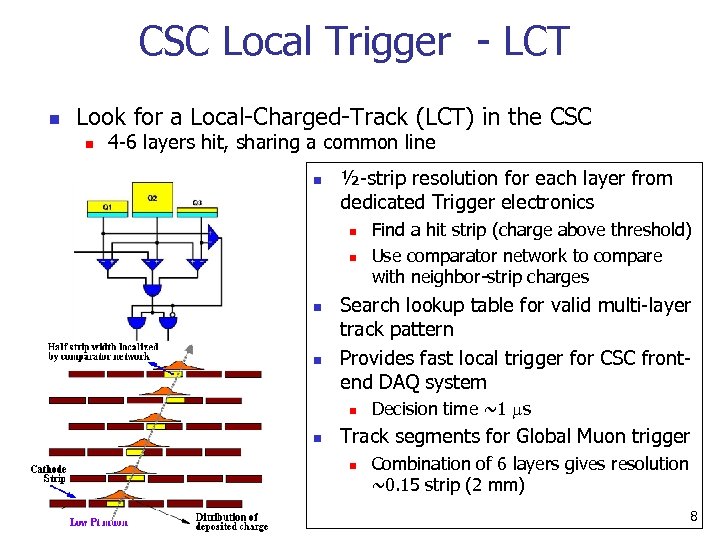 CSC Local Trigger - LCT n Look for a Local-Charged-Track (LCT) in the CSC n 4 -6 layers hit, sharing a common line n ½-strip resolution for each layer from dedicated Trigger electronics n n Search lookup table for valid multi-layer track pattern Provides fast local trigger for CSC frontend DAQ system n n Find a hit strip (charge above threshold) Use comparator network to compare with neighbor-strip charges Decision time ~1 s Track segments for Global Muon trigger n Combination of 6 layers gives resolution ~0. 15 strip (2 mm) 8
CSC Local Trigger - LCT n Look for a Local-Charged-Track (LCT) in the CSC n 4 -6 layers hit, sharing a common line n ½-strip resolution for each layer from dedicated Trigger electronics n n Search lookup table for valid multi-layer track pattern Provides fast local trigger for CSC frontend DAQ system n n Find a hit strip (charge above threshold) Use comparator network to compare with neighbor-strip charges Decision time ~1 s Track segments for Global Muon trigger n Combination of 6 layers gives resolution ~0. 15 strip (2 mm) 8
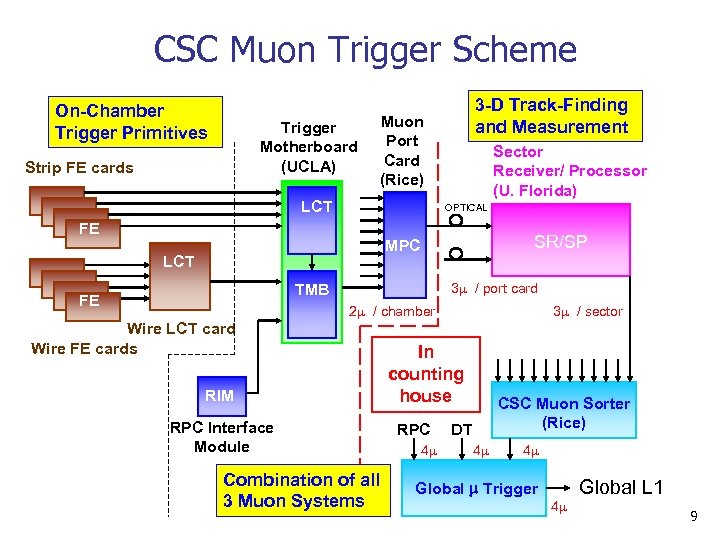 CSC Muon Trigger Scheme On-Chamber Trigger Primitives Trigger Motherboard (UCLA) Strip FE cards 3 -D Track-Finding and Measurement Muon Port Card (Rice) LCT Sector Receiver/ Processor (U. Florida) OPTICAL FE SR/SP MPC LCT 3 / port card TMB FE SP 2 / chamber Wire LCT card Wire FE cards RIM RPC Interface Module Combination of all 3 Muon Systems 3 / sector In counting house RPC 4 CSC Muon Sorter (Rice) DT 4 4 Global Trigger 4 Global L 1 9
CSC Muon Trigger Scheme On-Chamber Trigger Primitives Trigger Motherboard (UCLA) Strip FE cards 3 -D Track-Finding and Measurement Muon Port Card (Rice) LCT Sector Receiver/ Processor (U. Florida) OPTICAL FE SR/SP MPC LCT 3 / port card TMB FE SP 2 / chamber Wire LCT card Wire FE cards RIM RPC Interface Module Combination of all 3 Muon Systems 3 / sector In counting house RPC 4 CSC Muon Sorter (Rice) DT 4 4 Global Trigger 4 Global L 1 9
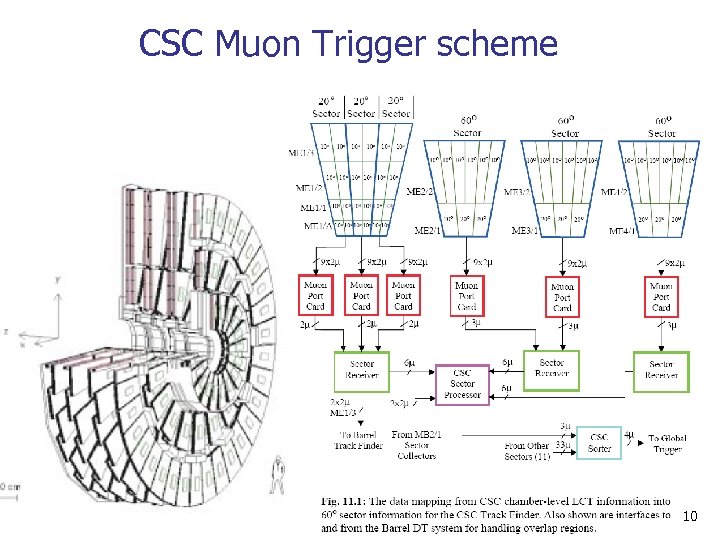 CSC Muon Trigger scheme 10
CSC Muon Trigger scheme 10
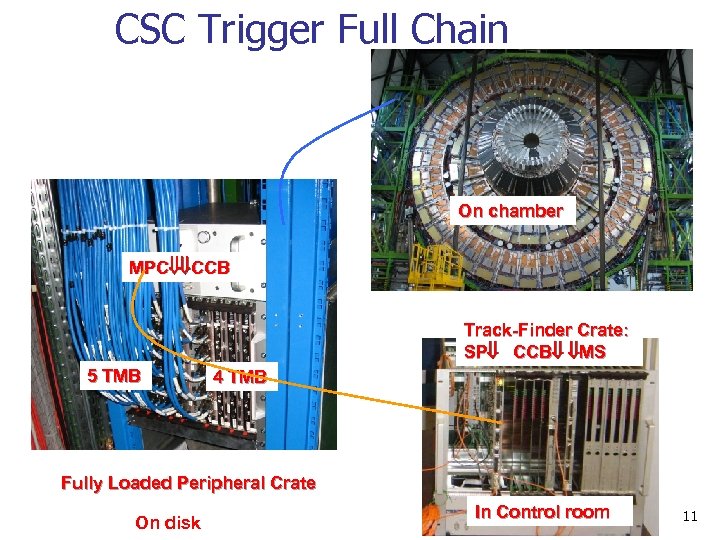 CSC Trigger Full Chain On chamber MPC CCB 5 TMB 4 TMB 5 TMB Track-Finder Crate: SP CCB MS 4 TMB Fully Loaded Peripheral Crate On disk In Control room 11
CSC Trigger Full Chain On chamber MPC CCB 5 TMB 4 TMB 5 TMB Track-Finder Crate: SP CCB MS 4 TMB Fully Loaded Peripheral Crate On disk In Control room 11
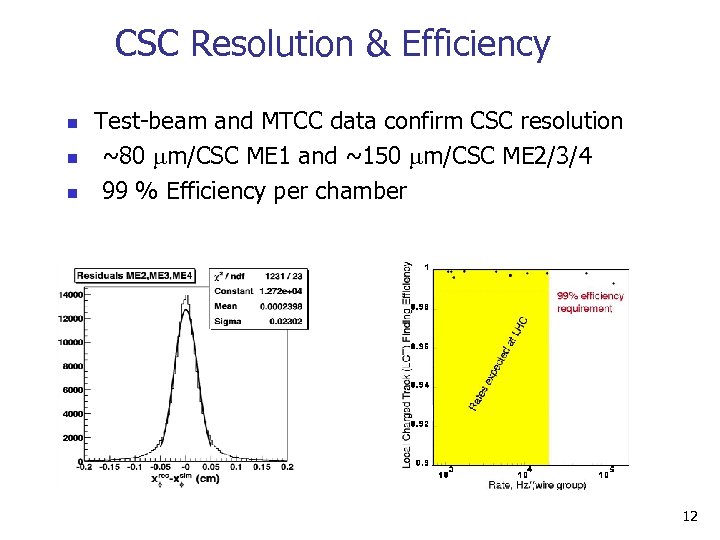 CSC Resolution & Efficiency n n n Test-beam and MTCC data confirm CSC resolution ~80 m/CSC ME 1 and ~150 m/CSC ME 2/3/4 99 % Efficiency per chamber MTCC ME 3/2 12
CSC Resolution & Efficiency n n n Test-beam and MTCC data confirm CSC resolution ~80 m/CSC ME 1 and ~150 m/CSC ME 2/3/4 99 % Efficiency per chamber MTCC ME 3/2 12
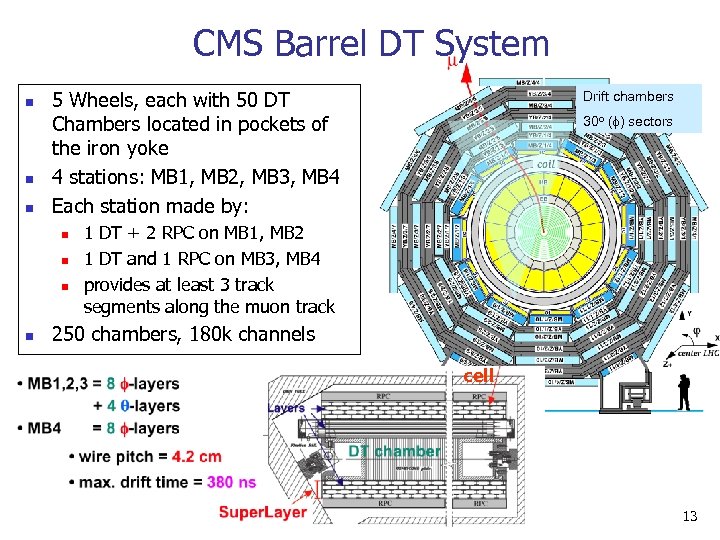 CMS Barrel DT System n n n 5 Wheels, each with 50 DT Chambers located in pockets of the iron yoke 4 stations: MB 1, MB 2, MB 3, MB 4 Each station made by: n n Drift chambers 30 o (f) sectors 1 DT + 2 RPC on MB 1, MB 2 1 DT and 1 RPC on MB 3, MB 4 provides at least 3 track segments along the muon track 250 chambers, 180 k channels cell 13
CMS Barrel DT System n n n 5 Wheels, each with 50 DT Chambers located in pockets of the iron yoke 4 stations: MB 1, MB 2, MB 3, MB 4 Each station made by: n n Drift chambers 30 o (f) sectors 1 DT + 2 RPC on MB 1, MB 2 1 DT and 1 RPC on MB 3, MB 4 provides at least 3 track segments along the muon track 250 chambers, 180 k channels cell 13
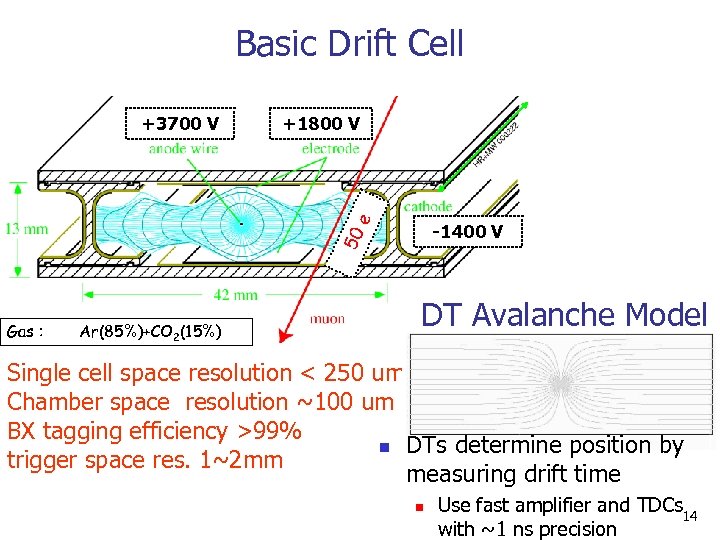 Basic Drift Cell +1800 V e +3700 V 50 -1400 V Gas : Ar(85%)+CO 2(15%) DT Avalanche Model Single cell space resolution < 250 um Chamber space resolution ~100 um BX tagging efficiency >99% n DTs determine position by trigger space res. 1~2 mm measuring drift time n Use fast amplifier and TDCs 14 with ~1 ns precision
Basic Drift Cell +1800 V e +3700 V 50 -1400 V Gas : Ar(85%)+CO 2(15%) DT Avalanche Model Single cell space resolution < 250 um Chamber space resolution ~100 um BX tagging efficiency >99% n DTs determine position by trigger space res. 1~2 mm measuring drift time n Use fast amplifier and TDCs 14 with ~1 ns precision
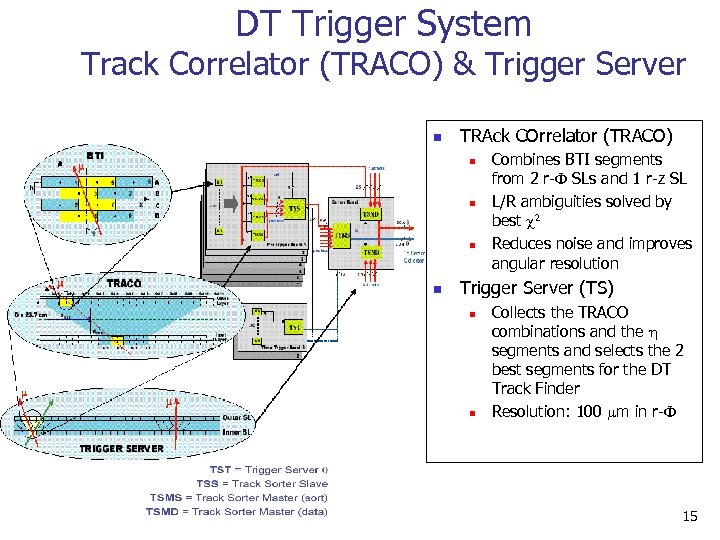 DT Trigger System Track Correlator (TRACO) & Trigger Server n TRAck COrrelator (TRACO) n n Combines BTI segments from 2 r-F SLs and 1 r-z SL L/R ambiguities solved by best c 2 Reduces noise and improves angular resolution Trigger Server (TS) n n Collects the TRACO combinations and the h segments and selects the 2 best segments for the DT Track Finder Resolution: 100 m in r-F 15
DT Trigger System Track Correlator (TRACO) & Trigger Server n TRAck COrrelator (TRACO) n n Combines BTI segments from 2 r-F SLs and 1 r-z SL L/R ambiguities solved by best c 2 Reduces noise and improves angular resolution Trigger Server (TS) n n Collects the TRACO combinations and the h segments and selects the 2 best segments for the DT Track Finder Resolution: 100 m in r-F 15
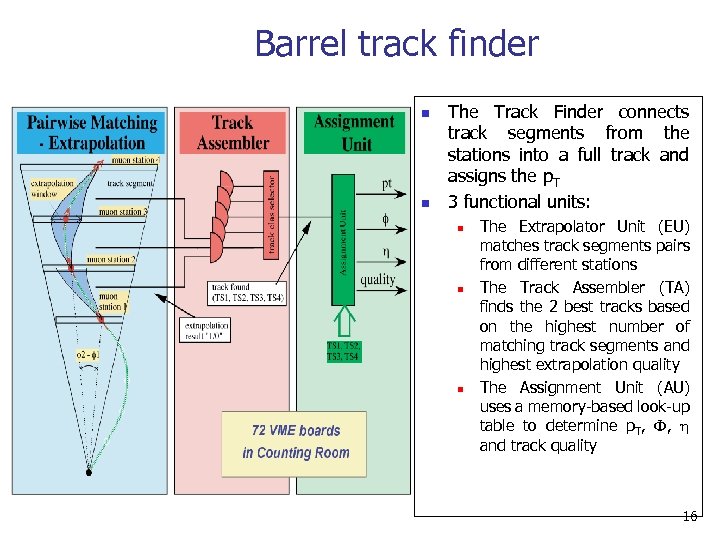 Barrel track finder n n The Track Finder connects track segments from the stations into a full track and assigns the p. T 3 functional units: n n n The Extrapolator Unit (EU) matches track segments pairs from different stations The Track Assembler (TA) finds the 2 best tracks based on the highest number of matching track segments and highest extrapolation quality The Assignment Unit (AU) uses a memory-based look-up table to determine p. T, F, h and track quality 16
Barrel track finder n n The Track Finder connects track segments from the stations into a full track and assigns the p. T 3 functional units: n n n The Extrapolator Unit (EU) matches track segments pairs from different stations The Track Assembler (TA) finds the 2 best tracks based on the highest number of matching track segments and highest extrapolation quality The Assignment Unit (AU) uses a memory-based look-up table to determine p. T, F, h and track quality 16
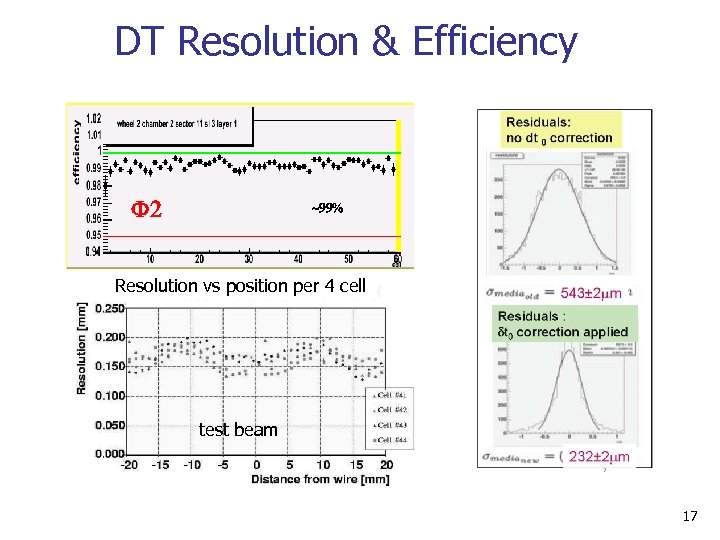 DT Resolution & Efficiency F 2 ~99% Resolution vs position per 4 cell test beam 17
DT Resolution & Efficiency F 2 ~99% Resolution vs position per 4 cell test beam 17
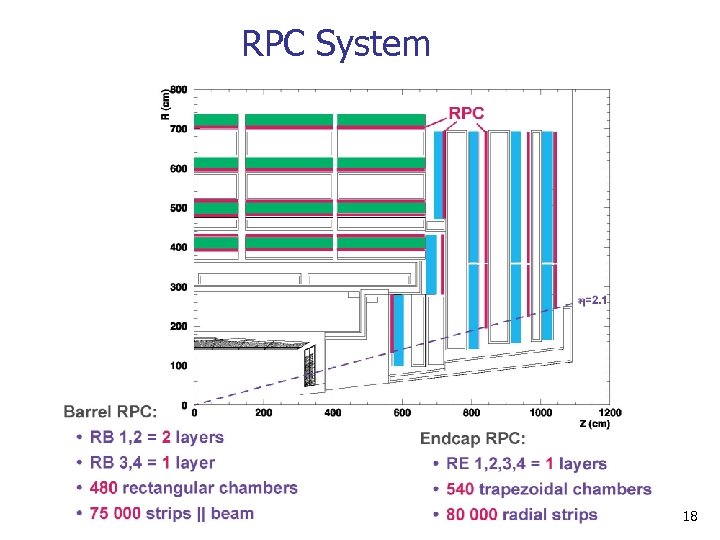 RPC System 18
RPC System 18
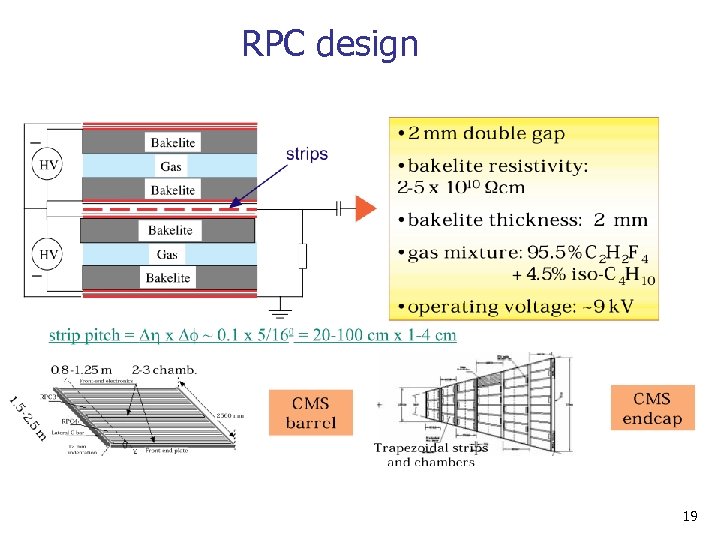 RPC design 19
RPC design 19
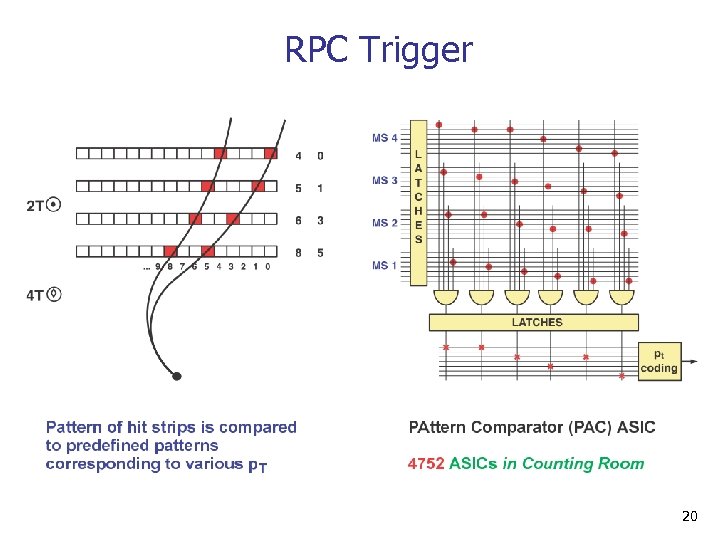 RPC Trigger 20
RPC Trigger 20
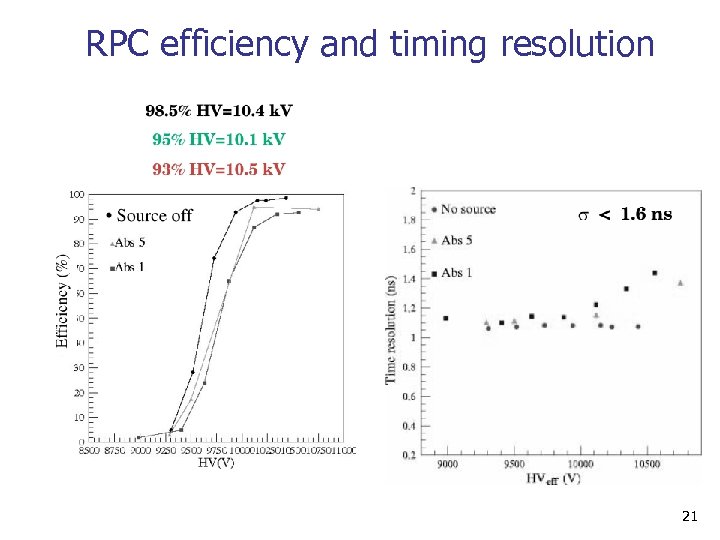 RPC efficiency and timing resolution 21
RPC efficiency and timing resolution 21
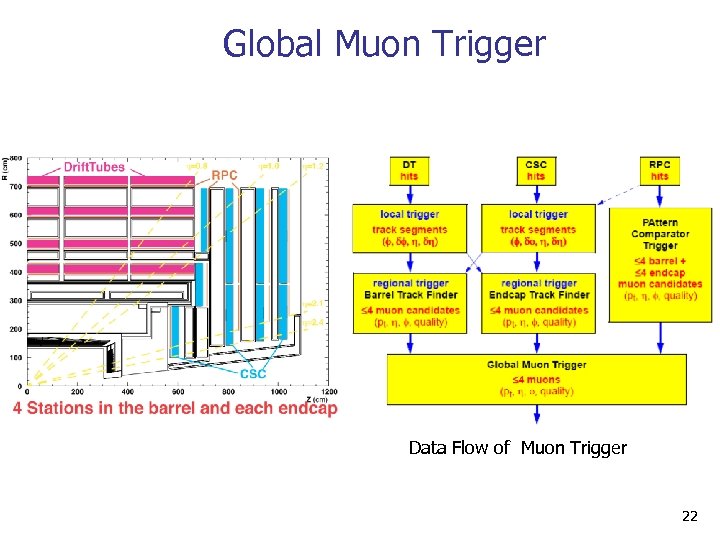 Global Muon Trigger Data Flow of Muon Trigger 22
Global Muon Trigger Data Flow of Muon Trigger 22
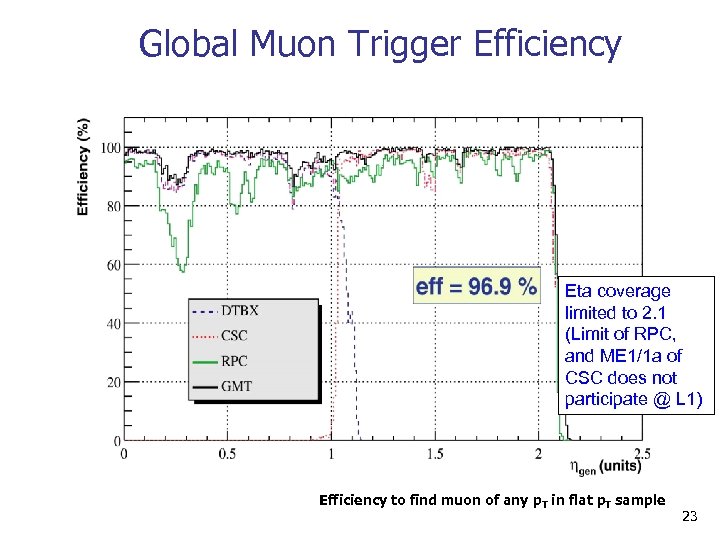 Global Muon Trigger Efficiency Eta coverage limited to 2. 1 (Limit of RPC, and ME 1/1 a of CSC does not participate @ L 1) Efficiency to find muon of any p. T in flat p. T sample 23
Global Muon Trigger Efficiency Eta coverage limited to 2. 1 (Limit of RPC, and ME 1/1 a of CSC does not participate @ L 1) Efficiency to find muon of any p. T in flat p. T sample 23
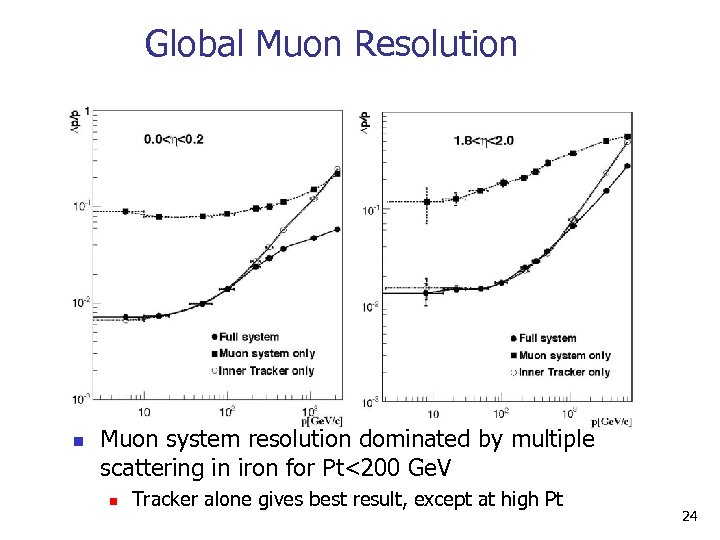 Global Muon Resolution n Muon system resolution dominated by multiple scattering in iron for Pt<200 Ge. V n Tracker alone gives best result, except at high Pt 24
Global Muon Resolution n Muon system resolution dominated by multiple scattering in iron for Pt<200 Ge. V n Tracker alone gives best result, except at high Pt 24
 Conclusion n A robust Muon Detection system is ready for CMS. n n n Efficient trigger, good resolution Already taken tons of Cosmic data Exciting physics discoveries are coming soon! 25
Conclusion n A robust Muon Detection system is ready for CMS. n n n Efficient trigger, good resolution Already taken tons of Cosmic data Exciting physics discoveries are coming soon! 25
 Back up 26
Back up 26
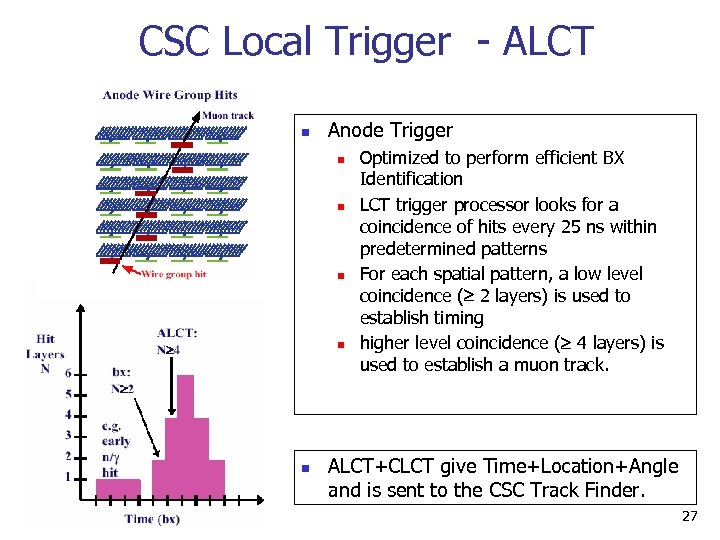 CSC Local Trigger - ALCT n Anode Trigger n n n Optimized to perform efficient BX Identification LCT trigger processor looks for a coincidence of hits every 25 ns within predetermined patterns For each spatial pattern, a low level coincidence ( 2 layers) is used to establish timing higher level coincidence ( 4 layers) is used to establish a muon track. ALCT+CLCT give Time+Location+Angle and is sent to the CSC Track Finder. 27
CSC Local Trigger - ALCT n Anode Trigger n n n Optimized to perform efficient BX Identification LCT trigger processor looks for a coincidence of hits every 25 ns within predetermined patterns For each spatial pattern, a low level coincidence ( 2 layers) is used to establish timing higher level coincidence ( 4 layers) is used to establish a muon track. ALCT+CLCT give Time+Location+Angle and is sent to the CSC Track Finder. 27
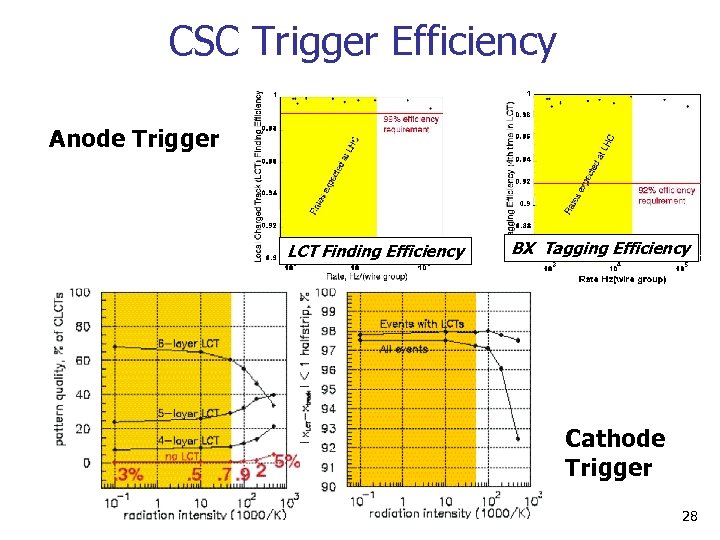 CSC Trigger Efficiency Anode Trigger LCT Finding Efficiency BX Tagging Efficiency Cathode Trigger 28
CSC Trigger Efficiency Anode Trigger LCT Finding Efficiency BX Tagging Efficiency Cathode Trigger 28
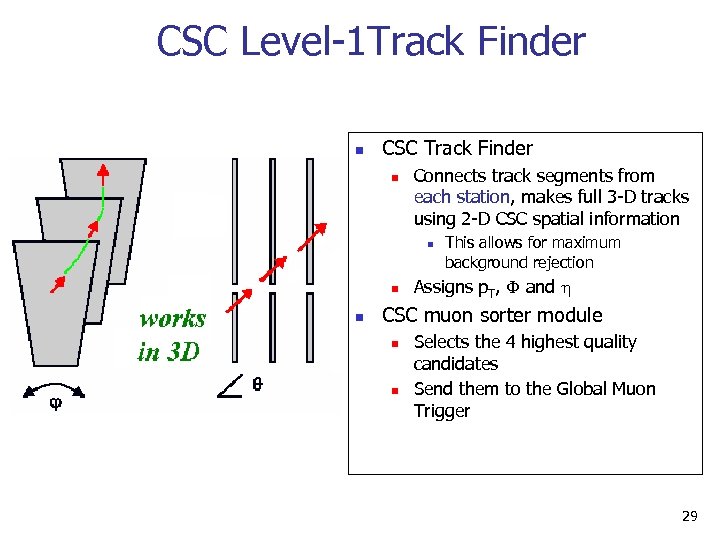 CSC Level-1 Track Finder n CSC Track Finder n Connects track segments from each station, makes full 3 -D tracks using 2 -D CSC spatial information n This allows for maximum background rejection Assigns p. T, F and h CSC muon sorter module n n Selects the 4 highest quality candidates Send them to the Global Muon Trigger 29
CSC Level-1 Track Finder n CSC Track Finder n Connects track segments from each station, makes full 3 -D tracks using 2 -D CSC spatial information n This allows for maximum background rejection Assigns p. T, F and h CSC muon sorter module n n Selects the 4 highest quality candidates Send them to the Global Muon Trigger 29
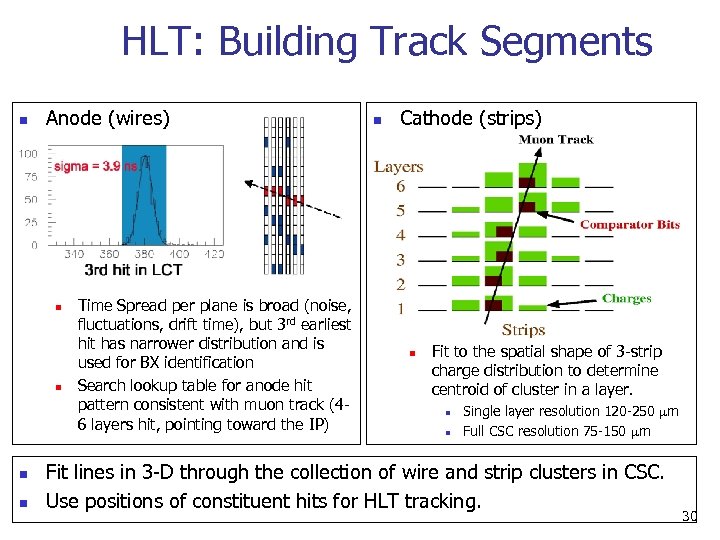 HLT: Building Track Segments n Anode (wires) n n Time Spread per plane is broad (noise, fluctuations, drift time), but 3 rd earliest hit has narrower distribution and is used for BX identification Search lookup table for anode hit pattern consistent with muon track (46 layers hit, pointing toward the IP) n Cathode (strips) n Fit to the spatial shape of 3 -strip charge distribution to determine centroid of cluster in a layer. n n Single layer resolution 120 -250 m Full CSC resolution 75 -150 m Fit lines in 3 -D through the collection of wire and strip clusters in CSC. Use positions of constituent hits for HLT tracking. 30
HLT: Building Track Segments n Anode (wires) n n Time Spread per plane is broad (noise, fluctuations, drift time), but 3 rd earliest hit has narrower distribution and is used for BX identification Search lookup table for anode hit pattern consistent with muon track (46 layers hit, pointing toward the IP) n Cathode (strips) n Fit to the spatial shape of 3 -strip charge distribution to determine centroid of cluster in a layer. n n Single layer resolution 120 -250 m Full CSC resolution 75 -150 m Fit lines in 3 -D through the collection of wire and strip clusters in CSC. Use positions of constituent hits for HLT tracking. 30
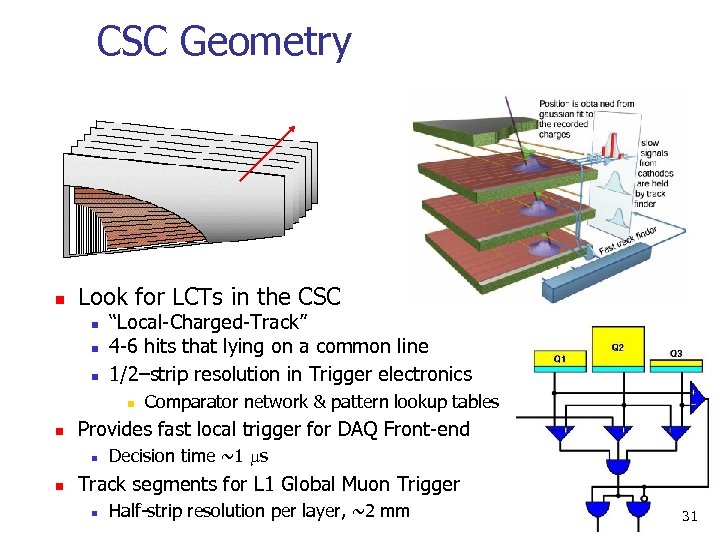 CSC Geometry n CSC Trivia n Look for Advantages: LCTs in the CSC n CSC size: 3. 3 x 1. 5/0. 8 m 2 (trapezoidal) n “Local-Charged-Track” n Close wire spacing gives fast response n Anode wires: d=50 m, gold-plated tungsten nn 4 -6 hits high rates Good for that lying on a common line n Anode-Cathode: h=4. 75 mm n 2 D 1/2–strip resolution in Trigger electronics n coordinate n n n Wire tension: T=250 g (60% elastic limit) Cathode strips: good spatial resolution in bending n Comparator network & pattern lookup tables Wire spacing: direction fast local 3. 12 mm DAQ Front-end Provides group: trigger for Readout 5 to 16 wires (1. 5 -5 cm) Anode Wires: good timing resolution n Decision time s Cathode strips: ~1 w=8 -16 mm wide (one side) 6 layers good background rejection Track segments for L 1 Global Muon Trigger Gas: Ar+CO 2+CF 4=40+50+10 n Apply 4/6 coincidence Nominal HV: resolution per layer, ~2 mm 4 k. V n Half-strip 31
CSC Geometry n CSC Trivia n Look for Advantages: LCTs in the CSC n CSC size: 3. 3 x 1. 5/0. 8 m 2 (trapezoidal) n “Local-Charged-Track” n Close wire spacing gives fast response n Anode wires: d=50 m, gold-plated tungsten nn 4 -6 hits high rates Good for that lying on a common line n Anode-Cathode: h=4. 75 mm n 2 D 1/2–strip resolution in Trigger electronics n coordinate n n n Wire tension: T=250 g (60% elastic limit) Cathode strips: good spatial resolution in bending n Comparator network & pattern lookup tables Wire spacing: direction fast local 3. 12 mm DAQ Front-end Provides group: trigger for Readout 5 to 16 wires (1. 5 -5 cm) Anode Wires: good timing resolution n Decision time s Cathode strips: ~1 w=8 -16 mm wide (one side) 6 layers good background rejection Track segments for L 1 Global Muon Trigger Gas: Ar+CO 2+CF 4=40+50+10 n Apply 4/6 coincidence Nominal HV: resolution per layer, ~2 mm 4 k. V n Half-strip 31
 CSC Reliability optimization n Careful choice of design parameters n large gas gap (~10 mm): n n thick wires (50 m): n n harder to break wide wire spacing (~3. 2 mm) n n lower chances of wire snapping low wire tension (60% of elastic limit) n n harder to break, better grip with solder and epoxy wires are soldered and glued n n panel size & flatness requirements are available from industry electrostatic stability over 1. 2 m (longest span) Simple design optimized for mass production n n automated where possible low number of parts 32
CSC Reliability optimization n Careful choice of design parameters n large gas gap (~10 mm): n n thick wires (50 m): n n harder to break wide wire spacing (~3. 2 mm) n n lower chances of wire snapping low wire tension (60% of elastic limit) n n harder to break, better grip with solder and epoxy wires are soldered and glued n n panel size & flatness requirements are available from industry electrostatic stability over 1. 2 m (longest span) Simple design optimized for mass production n n automated where possible low number of parts 32
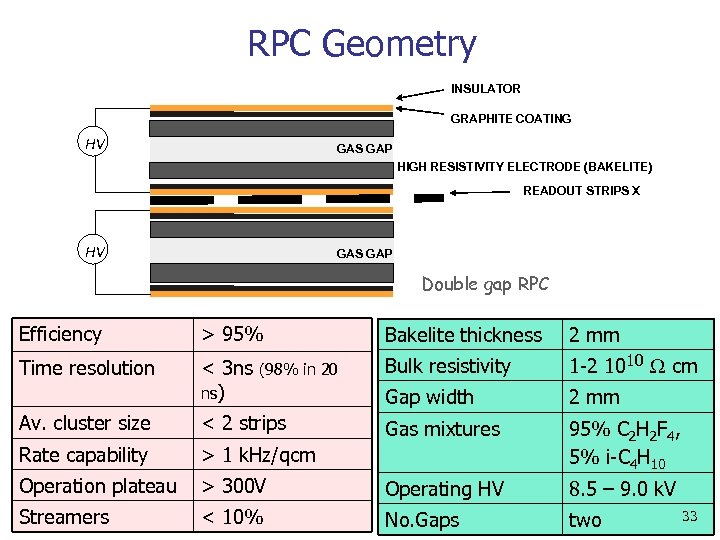 RPC Geometry INSULATOR GRAPHITE COATING HV GAS GAP HIGH RESISTIVITY ELECTRODE (BAKELITE) READOUT STRIPS X HV GAS GAP Double gap RPC Efficiency > 95% Bakelite thickness 2 mm Time resolution < 3 ns ns) Bulk resistivity 1 -2 1010 W cm Gap width 2 mm Gas mixtures 95% C 2 H 2 F 4, 5% i-C 4 H 10 (98% in 20 Av. cluster size < 2 strips Rate capability > 1 k. Hz/qcm Operation plateau > 300 V Operating HV 8. 5 – 9. 0 k. V Streamers < 10% No. Gaps two 33
RPC Geometry INSULATOR GRAPHITE COATING HV GAS GAP HIGH RESISTIVITY ELECTRODE (BAKELITE) READOUT STRIPS X HV GAS GAP Double gap RPC Efficiency > 95% Bakelite thickness 2 mm Time resolution < 3 ns ns) Bulk resistivity 1 -2 1010 W cm Gap width 2 mm Gas mixtures 95% C 2 H 2 F 4, 5% i-C 4 H 10 (98% in 20 Av. cluster size < 2 strips Rate capability > 1 k. Hz/qcm Operation plateau > 300 V Operating HV 8. 5 – 9. 0 k. V Streamers < 10% No. Gaps two 33


