f76804d0dc893fd2642c4a11d212e458.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 …… The Classical Theory of International Trade
…… The Classical Theory of International Trade
 The Classical Theory of International Trade Adam Smith; John Stuart Mills; James Torrens; David Ricardo (Ricardian Theory)
The Classical Theory of International Trade Adam Smith; John Stuart Mills; James Torrens; David Ricardo (Ricardian Theory)
 Key Questions… • Why do nations trade? • What determines in which good(s) they trade?
Key Questions… • Why do nations trade? • What determines in which good(s) they trade?
 Model Assumptions Factors are immobile between countries No barriers to trade Exports pay for imports Labor is the only factor of production Constant return to scale in production
Model Assumptions Factors are immobile between countries No barriers to trade Exports pay for imports Labor is the only factor of production Constant return to scale in production
 Absolute Advantage Adam Smith (1776) For various reasons, including differences in technology and climate, countries differ in their abilities to produce different goods Some are more productive than others
Absolute Advantage Adam Smith (1776) For various reasons, including differences in technology and climate, countries differ in their abilities to produce different goods Some are more productive than others
 Definition: A country is said to have Absolute Advantage in the production of one good if it produces that good using smaller (lower) amount of productive inputs than is possible anywhere else in the world
Definition: A country is said to have Absolute Advantage in the production of one good if it produces that good using smaller (lower) amount of productive inputs than is possible anywhere else in the world
 Implication 1. World output would expand if countries specialize in the production of a good in which they have Absolute Advantage (highest relative productivity)
Implication 1. World output would expand if countries specialize in the production of a good in which they have Absolute Advantage (highest relative productivity)
 Implication 2. Each good will be cheaper if produced in the country that has Absolute Advantage The above two are possible only if there is free international trade
Implication 2. Each good will be cheaper if produced in the country that has Absolute Advantage The above two are possible only if there is free international trade
 Absolute Advantage ___________________ 2 countries : USA and France 2 Goods : Beer and Wine 1 Factor : Labor Each country has 2 units of labor
Absolute Advantage ___________________ 2 countries : USA and France 2 Goods : Beer and Wine 1 Factor : Labor Each country has 2 units of labor
 Suppose One-Person Day of Labor Produces Beer Wine USA 60 20 France 20 40
Suppose One-Person Day of Labor Produces Beer Wine USA 60 20 France 20 40
 Which Country has AA to Produce Beer? Beer Wine USA 60 20 France 20 40
Which Country has AA to Produce Beer? Beer Wine USA 60 20 France 20 40
 Which Country has AA to Produce Wine? Beer Wine USA 60 20 France 20 40
Which Country has AA to Produce Wine? Beer Wine USA 60 20 France 20 40
 Specialization (Complete) Beer Wine 120 80
Specialization (Complete) Beer Wine 120 80
 Why Nations Trade? Some Answers Nations trade because trade allows them to specialize in the production of the good in which they have absolute advantage Specialization increases world output
Why Nations Trade? Some Answers Nations trade because trade allows them to specialize in the production of the good in which they have absolute advantage Specialization increases world output
 Why Nations Trade? Answer Nations trade because trade allows them to get a product at a lower cost than if it is produced at home…. Free international trade allows nations to consume at a point outside their PPF
Why Nations Trade? Answer Nations trade because trade allows them to get a product at a lower cost than if it is produced at home…. Free international trade allows nations to consume at a point outside their PPF
 What determines which goods … The relative amount of productive factors that a nation uses to produce a good Productivity (efficiency) of factors…
What determines which goods … The relative amount of productive factors that a nation uses to produce a good Productivity (efficiency) of factors…
 Direction of Trade…. A country should specialize in the production of a good in which it has AA. EXPORT the surplus output (of the good in which it has AA) in exchange for the IMPORT of the good in which it has Absolute disadvantage
Direction of Trade…. A country should specialize in the production of a good in which it has AA. EXPORT the surplus output (of the good in which it has AA) in exchange for the IMPORT of the good in which it has Absolute disadvantage
 However, the world is not…
However, the world is not…
 Suppose One-Person Day of Labor Produces Beer Wine USA 60 20 France 20 10
Suppose One-Person Day of Labor Produces Beer Wine USA 60 20 France 20 10
 Puzzles ……. Which country has AA? Which good should the U. S. Produce and Export? Which good should France Produce and Export? Is there a possibility for international trade between the US and France? If so, on what basis?
Puzzles ……. Which country has AA? Which good should the U. S. Produce and Export? Which good should France Produce and Export? Is there a possibility for international trade between the US and France? If so, on what basis?
 Comparative Advantage A country has comparative advantage in the production of a good if it has a lower pre-trade relative price than is found elsewhere In other words….
Comparative Advantage A country has comparative advantage in the production of a good if it has a lower pre-trade relative price than is found elsewhere In other words….
 Comparative Advantage A country has comparative advantage in the production of a good in which it has the lowest opportunity cost than is found elsewhere
Comparative Advantage A country has comparative advantage in the production of a good in which it has the lowest opportunity cost than is found elsewhere
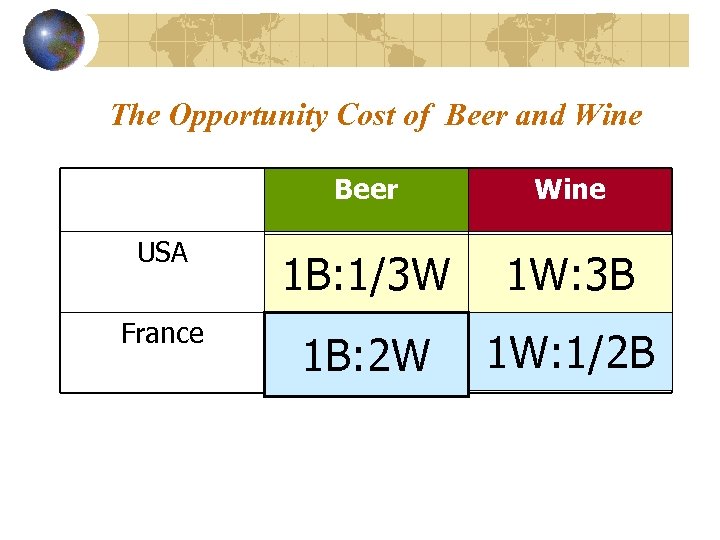 The Opportunity Cost of Beer and Wine Beer Wine USA 1 B: 1/3 W 1 W: 3 B France 1 B: 2 W 1 W: 1/2 B
The Opportunity Cost of Beer and Wine Beer Wine USA 1 B: 1/3 W 1 W: 3 B France 1 B: 2 W 1 W: 1/2 B
 Where is it Cheaper to Produce… Beer Wine USA 1 B: 1/3 W 1 W: 3 B France 1 B: 2 W 1 W: 1/2 B
Where is it Cheaper to Produce… Beer Wine USA 1 B: 1/3 W 1 W: 3 B France 1 B: 2 W 1 W: 1/2 B
 Puzzles Solved Which country has AA? US has AA in both Goods Which good should the US Produce? US has CA in the production of Beer…
Puzzles Solved Which country has AA? US has AA in both Goods Which good should the US Produce? US has CA in the production of Beer…
 Puzzles Solved Which good should France Produce? France has CA in the production of Wine Is there a possibility for international trade between the US and France? If so, on what basis? Yes, on the basis of CA.
Puzzles Solved Which good should France Produce? France has CA in the production of Wine Is there a possibility for international trade between the US and France? If so, on what basis? Yes, on the basis of CA.
 Direction of Trade… Each country should specialize in the production of a good in which it has comparative advantage and then EXPORT the excess of the production of that good in exchange for the IMPORT of the other good (in which it has comparative disadvantage)
Direction of Trade… Each country should specialize in the production of a good in which it has comparative advantage and then EXPORT the excess of the production of that good in exchange for the IMPORT of the other good (in which it has comparative disadvantage)
 Implications… It is NOT necessary for a country to have absolute advantage in the production of any good for that country to be able to participate in international trade…
Implications… It is NOT necessary for a country to have absolute advantage in the production of any good for that country to be able to participate in international trade…
 Implications… The basis for international trade (specialization and export) is comparative advantage not absolute advantage…. Differences in the comparative cost of production (Opportunity cost)
Implications… The basis for international trade (specialization and export) is comparative advantage not absolute advantage…. Differences in the comparative cost of production (Opportunity cost)
 Implications… Complete specialization is possible in the production of a good in which each country has comparative advantage…
Implications… Complete specialization is possible in the production of a good in which each country has comparative advantage…
 Implications… The volume of trade flow between countries that have different productivity or opportunity cost will be large. Large volume of trade flows between the North (developed countries) and the South ( developing countries will take place)….
Implications… The volume of trade flow between countries that have different productivity or opportunity cost will be large. Large volume of trade flows between the North (developed countries) and the South ( developing countries will take place)….
 Implications… With specialization and international trade, world output would increase and the trading partners will benefit. …The actual benefit of each trading partner, however, will depend on their respective Terms of Trade (TOT)…. the ratio of the price of exports to the price of imports.
Implications… With specialization and international trade, world output would increase and the trading partners will benefit. …The actual benefit of each trading partner, however, will depend on their respective Terms of Trade (TOT)…. the ratio of the price of exports to the price of imports.
 Implications… With international trade, there will be one world price (price equalization)… …. the world price of an internationally traded good will lie some where between the autarky prices of the two countries (trading partners).
Implications… With international trade, there will be one world price (price equalization)… …. the world price of an internationally traded good will lie some where between the autarky prices of the two countries (trading partners).
 …… Does the classical theory of international trade explain the current world trade pattern very well? What are the limitations of the Classical theory of International Trade?
…… Does the classical theory of international trade explain the current world trade pattern very well? What are the limitations of the Classical theory of International Trade?


