6844eaf2062426bd5f4a43eed37a70a2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 The Civil War Social Studies Lesson Power Point Laura G. Sarah T. Sheena S. ED 639
The Civil War Social Studies Lesson Power Point Laura G. Sarah T. Sheena S. ED 639
 The Civil War- Factors Leading Up to the War § 8 th grade American History
The Civil War- Factors Leading Up to the War § 8 th grade American History
 Objectives § At the completion of this lesson, students will be able to: § recognize the political, economic, geographic, and social factors that influenced the outbreak of war § Identify and define the major events/acts
Objectives § At the completion of this lesson, students will be able to: § recognize the political, economic, geographic, and social factors that influenced the outbreak of war § Identify and define the major events/acts
 Materials § § § Textbook Atlas Handouts-maps, court materials, political cartoons § Colored pencils § Note-taking materials
Materials § § § Textbook Atlas Handouts-maps, court materials, political cartoons § Colored pencils § Note-taking materials
 Useful Websites The History Place Civilwar. com American Civil War The American Civil War Page
Useful Websites The History Place Civilwar. com American Civil War The American Civil War Page
 Economic Issues § Tariffs, Tariffs § A tariff is a tax paid on imports § Hurt South because it raised the price of goods that they had to buy; Protected North because they could make their own goods and made it easier to compete with foreign goods § South was paying almost 87% of tariff revenue while abolitionists were attacking their way of life. § How would this make you feel? § Tariff of Abomination-1828, was revised in 1833 under threat of secession
Economic Issues § Tariffs, Tariffs § A tariff is a tax paid on imports § Hurt South because it raised the price of goods that they had to buy; Protected North because they could make their own goods and made it easier to compete with foreign goods § South was paying almost 87% of tariff revenue while abolitionists were attacking their way of life. § How would this make you feel? § Tariff of Abomination-1828, was revised in 1833 under threat of secession
 Secession and Nullification § Idea 1 st appeared during War of 1812 when New Englanders were upset with the war § The 1828 Tariff was viewed as unfair and threatening to the South § VP John C. Calhoun wrote “The South Carolina Exposition and Protest” advocating the right to nullify federal laws –South Carolina followed his advice § Andrew Jackson managed to avoid a war during the Nullification Crisis by allowing a reduced tariff to be passed § Key issue was about states’ rights
Secession and Nullification § Idea 1 st appeared during War of 1812 when New Englanders were upset with the war § The 1828 Tariff was viewed as unfair and threatening to the South § VP John C. Calhoun wrote “The South Carolina Exposition and Protest” advocating the right to nullify federal laws –South Carolina followed his advice § Andrew Jackson managed to avoid a war during the Nullification Crisis by allowing a reduced tariff to be passed § Key issue was about states’ rights
 The Issue of Slavery and Expansion § The Constitution failed to end slavery § It gave South an advantage in House and the Presidency with the 3/5 clause § Cotton Gin (by Eli Whitney) revived the importance of cotton and therefore slavery § Slavery was an important aspect to the Southern economy- cash crops/plantations § Only 26% of whites in South owned slaves, yet slaves were 1/3 -1/2 of the population § Why would non-slave holders support slavery?
The Issue of Slavery and Expansion § The Constitution failed to end slavery § It gave South an advantage in House and the Presidency with the 3/5 clause § Cotton Gin (by Eli Whitney) revived the importance of cotton and therefore slavery § Slavery was an important aspect to the Southern economy- cash crops/plantations § Only 26% of whites in South owned slaves, yet slaves were 1/3 -1/2 of the population § Why would non-slave holders support slavery?
 Abolition § The religious revivals of the 1820’s made ABOLITIONISM an important issue § Believed slavery was evil; wanted to abolish slavery. Used publications (The Liberator), petitions, and more extreme measures to end slavery. § Others: § Free-soilers- wanted to only limit the expansion of slavery § Colonialists- wanted to end slavery and return them back to Africa; advocated by Monroe, Lincoln, and many other politicians and Northerners § What present day country is a result of this idea?
Abolition § The religious revivals of the 1820’s made ABOLITIONISM an important issue § Believed slavery was evil; wanted to abolish slavery. Used publications (The Liberator), petitions, and more extreme measures to end slavery. § Others: § Free-soilers- wanted to only limit the expansion of slavery § Colonialists- wanted to end slavery and return them back to Africa; advocated by Monroe, Lincoln, and many other politicians and Northerners § What present day country is a result of this idea?
 Frederick Douglass § Runaway Slave § Joined abolitionist movement; was anti-colonization § Was hired by William Lloyd Garrison as a speaker; became world famous § Also supported equal political rights for women § May 1845, 5, 000 copies of his book Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave were published § 1847 published own paper North Star in Rochester, NY § During Civil War, served as advisor to Lincoln § What made Douglass so famous and so controversial?
Frederick Douglass § Runaway Slave § Joined abolitionist movement; was anti-colonization § Was hired by William Lloyd Garrison as a speaker; became world famous § Also supported equal political rights for women § May 1845, 5, 000 copies of his book Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave were published § 1847 published own paper North Star in Rochester, NY § During Civil War, served as advisor to Lincoln § What made Douglass so famous and so controversial?
 The Missouri Compromise • Created by Henry Clay • Admitted Missouri as a slave state (1821), Maine as a free state (1820); Kept the balance; Created free/slave line at 36’ 30°N in hopes of resolving future issues • Western expansion was the desire and fear of both sides • New states would create an imbalance in Congress • Made the imbalance of states and slavery a major issue in the political arena
The Missouri Compromise • Created by Henry Clay • Admitted Missouri as a slave state (1821), Maine as a free state (1820); Kept the balance; Created free/slave line at 36’ 30°N in hopes of resolving future issues • Western expansion was the desire and fear of both sides • New states would create an imbalance in Congress • Made the imbalance of states and slavery a major issue in the political arena
 The Compromise of 1850 § Collection of 5 compromises created by Henry Clay as a way to keep the Union together following the acquisition of territory from the Mexican War § Texas would relinquish the disputed land (for $10 million to pay off its debt to Mexico) § NM, NV, UT, & AZ would be added without mentioning slavery § Slave trade would be abolished in DC (slavery would still be legal) § California would be a free state § Fugitive Slave Law would be enacted
The Compromise of 1850 § Collection of 5 compromises created by Henry Clay as a way to keep the Union together following the acquisition of territory from the Mexican War § Texas would relinquish the disputed land (for $10 million to pay off its debt to Mexico) § NM, NV, UT, & AZ would be added without mentioning slavery § Slave trade would be abolished in DC (slavery would still be legal) § California would be a free state § Fugitive Slave Law would be enacted
 Compromise of 1850 § Kept the Union together for another decade, but… § The Fugitive Slave Law was the most controversial of the acts § It required citizens to aid in the recovery of fugitive slaves and denied fugitives to a trial by jury § Abolitionists resolved to end slavery immediately
Compromise of 1850 § Kept the Union together for another decade, but… § The Fugitive Slave Law was the most controversial of the acts § It required citizens to aid in the recovery of fugitive slaves and denied fugitives to a trial by jury § Abolitionists resolved to end slavery immediately
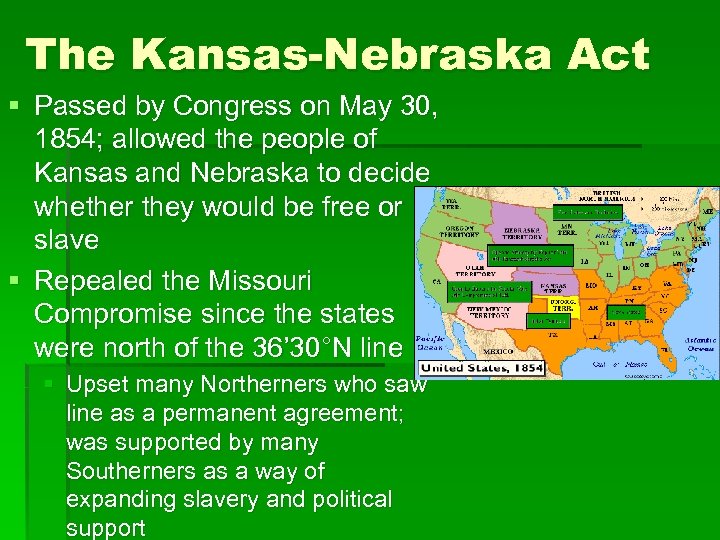 The Kansas-Nebraska Act § Passed by Congress on May 30, 1854; allowed the people of Kansas and Nebraska to decide whether they would be free or slave § Repealed the Missouri Compromise since the states were north of the 36’ 30°N line § Upset many Northerners who saw line as a permanent agreement; was supported by many Southerners as a way of expanding slavery and political support
The Kansas-Nebraska Act § Passed by Congress on May 30, 1854; allowed the people of Kansas and Nebraska to decide whether they would be free or slave § Repealed the Missouri Compromise since the states were north of the 36’ 30°N line § Upset many Northerners who saw line as a permanent agreement; was supported by many Southerners as a way of expanding slavery and political support
 § § Aftermath of K-N Act: Bloody Kansas Both pro- and anti-slavery settlers rushed to Kansas to affect the vote Pro-slavery won out, but the election was seen as fraudulent; another anti-slavery election was held- Result? 2 legislatures! Violence erupted, led by John Brown President Pierce sent troops to stop the violence; another election was held, but it too was charged with fraud and Congress refused to recognize Kansas as a state (until 1861 as a free state)
§ § Aftermath of K-N Act: Bloody Kansas Both pro- and anti-slavery settlers rushed to Kansas to affect the vote Pro-slavery won out, but the election was seen as fraudulent; another anti-slavery election was held- Result? 2 legislatures! Violence erupted, led by John Brown President Pierce sent troops to stop the violence; another election was held, but it too was charged with fraud and Congress refused to recognize Kansas as a state (until 1861 as a free state)
 John Brown • Raised in North by deeply religious, radical abolitionists • Met Frederick Douglas in 1847 • Waged a war against those who supported slavery in Kansas • On Oct. 16, 1859, he led 21 other men on an assault against Harper’s Ferry, a federal arsenal. • Was put down by Federal troops led by Lee • He was tried of treason and executed • Seen as a martyr for the abolitionist cause and a major threat to Southerners (and many Northerners) • List some reasons why both Southerners and Northerners would be opposed to abolition.
John Brown • Raised in North by deeply religious, radical abolitionists • Met Frederick Douglas in 1847 • Waged a war against those who supported slavery in Kansas • On Oct. 16, 1859, he led 21 other men on an assault against Harper’s Ferry, a federal arsenal. • Was put down by Federal troops led by Lee • He was tried of treason and executed • Seen as a martyr for the abolitionist cause and a major threat to Southerners (and many Northerners) • List some reasons why both Southerners and Northerners would be opposed to abolition.
 Dred-Scott Decision-1857 § Dred Scott was a slave who lived in Illinois and Wisconsin (free states), then was moved back to Missouri (a slave state) § He appealed to the Supreme Court in hopes to gain his freedom § Court ruled that Scott was black, therefore not a citizen and had no right to sue and should be treated as property § This ruling incited abolitionists; however, Douglass believed the decision would bring to light the issue of slavery and its eventual downfall
Dred-Scott Decision-1857 § Dred Scott was a slave who lived in Illinois and Wisconsin (free states), then was moved back to Missouri (a slave state) § He appealed to the Supreme Court in hopes to gain his freedom § Court ruled that Scott was black, therefore not a citizen and had no right to sue and should be treated as property § This ruling incited abolitionists; however, Douglass believed the decision would bring to light the issue of slavery and its eventual downfall
 Student Activities § 1. Write a persuasive letter for war from the viewpoint of a Southerner or a Northerner § 1 -2 pages in length § Use at least 3 of the discussed factors to create your argument
Student Activities § 1. Write a persuasive letter for war from the viewpoint of a Southerner or a Northerner § 1 -2 pages in length § Use at least 3 of the discussed factors to create your argument
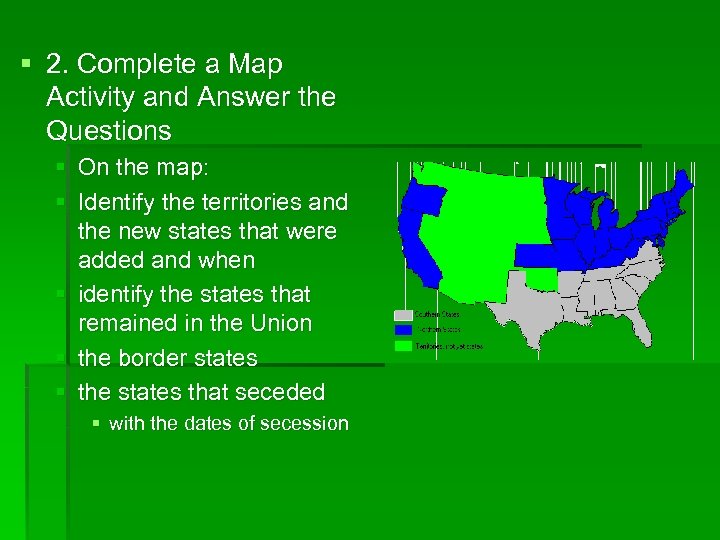 § 2. Complete a Map Activity and Answer the Questions § On the map: § Identify the territories and the new states that were added and when § identify the states that remained in the Union § the border states § the states that seceded § with the dates of secession
§ 2. Complete a Map Activity and Answer the Questions § On the map: § Identify the territories and the new states that were added and when § identify the states that remained in the Union § the border states § the states that seceded § with the dates of secession
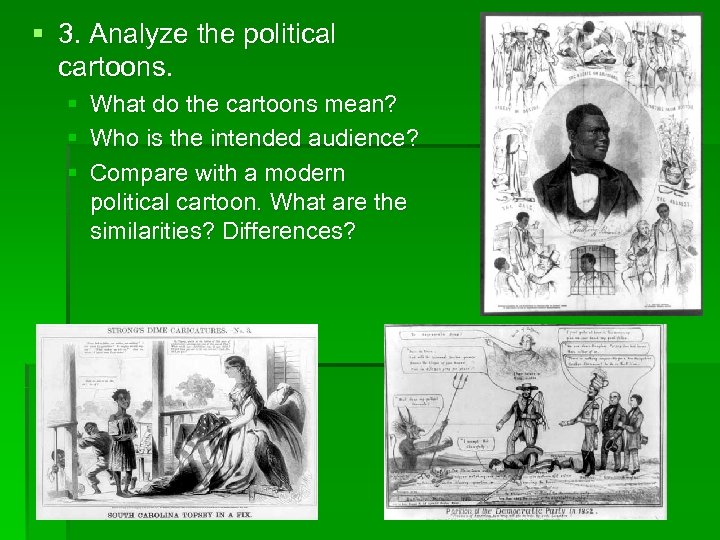 § 3. Analyze the political cartoons. § § § What do the cartoons mean? Who is the intended audience? Compare with a modern political cartoon. What are the similarities? Differences?
§ 3. Analyze the political cartoons. § § § What do the cartoons mean? Who is the intended audience? Compare with a modern political cartoon. What are the similarities? Differences?
 § 4. Divide into 2 groups, 1 a defense team and 1 a prosecuting team. Recreate the trial of Dred Scott using the arguments of the historical players and original arguments.
§ 4. Divide into 2 groups, 1 a defense team and 1 a prosecuting team. Recreate the trial of Dred Scott using the arguments of the historical players and original arguments.
 § 5. Create a timeline of events that helped lead to the eruption of the Civil War in 1861.
§ 5. Create a timeline of events that helped lead to the eruption of the Civil War in 1861.


