3321e30ec71a728905e577b8dca746bc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 99
 The Civil War 1850 -1865
The Civil War 1850 -1865
 Preparing for War Objectives ► Explain how the ceded land of Mexico led to debates in congress. ► Explain the Compromise of 1850 and the Kansas-Nebraska Act. ► Describe the political views of John C. Calhoun and Daniel Webster. ► Analyze the rise of Lincoln and the election of 1860.
Preparing for War Objectives ► Explain how the ceded land of Mexico led to debates in congress. ► Explain the Compromise of 1850 and the Kansas-Nebraska Act. ► Describe the political views of John C. Calhoun and Daniel Webster. ► Analyze the rise of Lincoln and the election of 1860.
 Slavery in the U. S. ► Existed for more than 200 years ► At one time in every colony ► 1790 – 90% of slaves were in the south ► Missouri Compromise 1820 had banned slavery in most of the new terr. in the north ► 1850 California applied for statehood – balance was about to change
Slavery in the U. S. ► Existed for more than 200 years ► At one time in every colony ► 1790 – 90% of slaves were in the south ► Missouri Compromise 1820 had banned slavery in most of the new terr. in the north ► 1850 California applied for statehood – balance was about to change
 Controversy of New Land The US added 500, 000 sq miles of land ceded by Mexico after the Mexican War ► Would the new states that would form from this land ban slavery or allow it? ► Three distinct groups developed. ► 1. 2. 3. Some wanted the land to be free Some wanted to allow slavery Others wanted Popular sovereignty to rule
Controversy of New Land The US added 500, 000 sq miles of land ceded by Mexico after the Mexican War ► Would the new states that would form from this land ban slavery or allow it? ► Three distinct groups developed. ► 1. 2. 3. Some wanted the land to be free Some wanted to allow slavery Others wanted Popular sovereignty to rule
 The Debate ► Senator Henry Clay introduced a Compromise in 1850, when California applied for statehood. ► Daniel Webster (Mass) for the compromise v. John C. Calhoun (SC) against ► After the death of Calhoun and President Taylor. The senate passed the Clay’s Resolution.
The Debate ► Senator Henry Clay introduced a Compromise in 1850, when California applied for statehood. ► Daniel Webster (Mass) for the compromise v. John C. Calhoun (SC) against ► After the death of Calhoun and President Taylor. The senate passed the Clay’s Resolution.
 Daniel Webster ► 1782 -1852 ► Senator from Mass. ► Leading Whig during Antebellum period ► Promoted Nationalism, preserving the Union, Abolition. ► Ran for President three times.
Daniel Webster ► 1782 -1852 ► Senator from Mass. ► Leading Whig during Antebellum period ► Promoted Nationalism, preserving the Union, Abolition. ► Ran for President three times.
 John C. Calhoun ► 1782 -1850 ► Leading politician from South Carolina during Antebellum ► Promoted States rights, nullification, and slavery ► Vice President under JQ Adams and Jackson
John C. Calhoun ► 1782 -1850 ► Leading politician from South Carolina during Antebellum ► Promoted States rights, nullification, and slavery ► Vice President under JQ Adams and Jackson
 Compromise of 1850 ► The compromise was a relief, but each side disliked certain aspects California would enter as a free state 2. Fugitive Slave Act was made much more strict 3. Utah and New Mexico terr could decide for themselves about slavery (popular Sovereignty) 1.
Compromise of 1850 ► The compromise was a relief, but each side disliked certain aspects California would enter as a free state 2. Fugitive Slave Act was made much more strict 3. Utah and New Mexico terr could decide for themselves about slavery (popular Sovereignty) 1.
 Henry Clay takes the floor in the Senate. Fillmore presides while Calhoun and Webster look on.
Henry Clay takes the floor in the Senate. Fillmore presides while Calhoun and Webster look on.
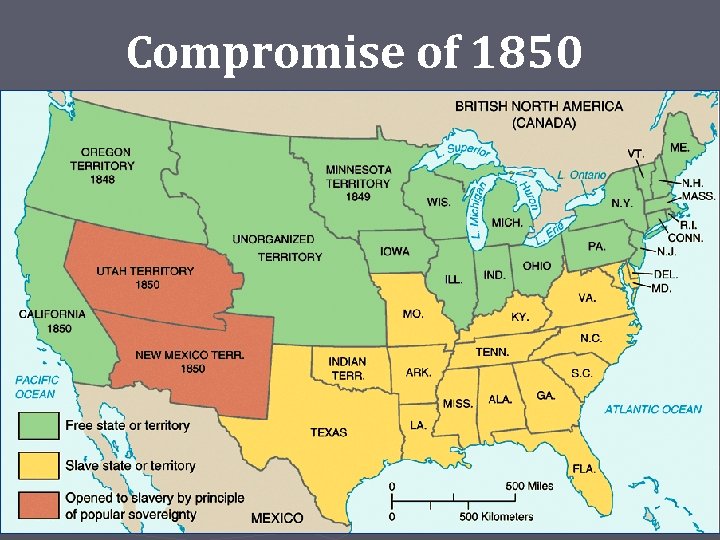 Compromise of 1850
Compromise of 1850
 Harriet Beecher Stowe ► 1811 -1896 ► Wrote “Uncle Toms Cabin” in 1852 ► Depicted slave life as horrible ► Reenergized Abolition in the North and anger toward South
Harriet Beecher Stowe ► 1811 -1896 ► Wrote “Uncle Toms Cabin” in 1852 ► Depicted slave life as horrible ► Reenergized Abolition in the North and anger toward South
 Kansas-Nebraska Act ► Introduced by Stephen Douglas (senator from Illinois) ► Repealed Missouri Compromise allowing popular sovereignty in Nebraska and Kansas Terr. ► Many Abolitionist were outraged ► This was all over a railroad to the Pacific
Kansas-Nebraska Act ► Introduced by Stephen Douglas (senator from Illinois) ► Repealed Missouri Compromise allowing popular sovereignty in Nebraska and Kansas Terr. ► Many Abolitionist were outraged ► This was all over a railroad to the Pacific
 Shifts in Politics ► Many Northerners quit the Democratic Party after many Southern Democrats supported the Kansas-Nebraska Act ► The Whig party were also split over the issue of slavery: Conscience Whigs v. Cotton Whigs. ► After the deaths of Clay and Webster the Whig party fell.
Shifts in Politics ► Many Northerners quit the Democratic Party after many Southern Democrats supported the Kansas-Nebraska Act ► The Whig party were also split over the issue of slavery: Conscience Whigs v. Cotton Whigs. ► After the deaths of Clay and Webster the Whig party fell.
 Republican Party Born ► 1854 – Abolitionist, “Free Soilers”, Conscience Whigs and Northern Democrats joined forces and formed the Republican Party ► The main goal of the Republican Party was to defeat the Southern Democrats— descended from Jackson, and get rid of slavery ► One Whig who joined the party during this time was a man by the name of Lincoln
Republican Party Born ► 1854 – Abolitionist, “Free Soilers”, Conscience Whigs and Northern Democrats joined forces and formed the Republican Party ► The main goal of the Republican Party was to defeat the Southern Democrats— descended from Jackson, and get rid of slavery ► One Whig who joined the party during this time was a man by the name of Lincoln
 The “Know Nothings” revived ► Many Republicans worked with the American Party or “Know Nothings” to get candidate elected. ► The Know Nothings were the Nativist Party or Anti-Immigration ► Even though many Republicans didn’t agree with the Know Nothings they wanted to defeat the Jacksonian Democrats
The “Know Nothings” revived ► Many Republicans worked with the American Party or “Know Nothings” to get candidate elected. ► The Know Nothings were the Nativist Party or Anti-Immigration ► Even though many Republicans didn’t agree with the Know Nothings they wanted to defeat the Jacksonian Democrats
 Bleeding Kansas ► May, 1856 - Struggle over slavery erupted in a civil war inside of Kansas ► By Sept 1856 – Federal Troops ended the war. ► Fighting however, continued in the form of a guerrilla warfare ► Deepened the split in Congress over Slavery
Bleeding Kansas ► May, 1856 - Struggle over slavery erupted in a civil war inside of Kansas ► By Sept 1856 – Federal Troops ended the war. ► Fighting however, continued in the form of a guerrilla warfare ► Deepened the split in Congress over Slavery
 Election of 1856 ► Democratic Party chose James Buchanan, a former Senator from Penn. ► Republican Party chose John Fremont who helped seize Cal. During Mexican War ► Buchanan won because of large number of immigrants going against “Know Nothings” and because some Republican were viewed as extremist on issue of slavery (John Brown)
Election of 1856 ► Democratic Party chose James Buchanan, a former Senator from Penn. ► Republican Party chose John Fremont who helped seize Cal. During Mexican War ► Buchanan won because of large number of immigrants going against “Know Nothings” and because some Republican were viewed as extremist on issue of slavery (John Brown)
 James Buchanan 1791 -1868 15 th President Dem. Life long bachelor (possible homosexual) ► Buchanan's opinion was that secession was illegal, but that going to war to stop it was also illegal; hence, he remained inactive. ► His handling of the crisis preceding the Civil War has led to his consistent ranking by historians as one of the worst Presidents, and frequently the worst, in American history ► ► ►
James Buchanan 1791 -1868 15 th President Dem. Life long bachelor (possible homosexual) ► Buchanan's opinion was that secession was illegal, but that going to war to stop it was also illegal; hence, he remained inactive. ► His handling of the crisis preceding the Civil War has led to his consistent ranking by historians as one of the worst Presidents, and frequently the worst, in American history ► ► ►
 Dred-Scott Decision ► A slave Dred Scott sued for his freedom ► He lived on land that became free so he said he should be free ► 1857 The supreme court ruled against Scott stating the rights of property holders over human rights ► The court also ruled that slaves could be transported anywhere and remain slaves ► South happy/North angry
Dred-Scott Decision ► A slave Dred Scott sued for his freedom ► He lived on land that became free so he said he should be free ► 1857 The supreme court ruled against Scott stating the rights of property holders over human rights ► The court also ruled that slaves could be transported anywhere and remain slaves ► South happy/North angry
 John Brown’s Raid ► Brown wanted to take action to free slaves and set up a free colony in Appalachian Mts. ► He led a raid on a US arsenal at Harpers Ferry, Virginia. ---He was finance by leading abolitionist ► Robert E. Lee and the Marines surrounded and captured Brown and executed him ► Many and the North praised what Brown had done; Southern fears rose.
John Brown’s Raid ► Brown wanted to take action to free slaves and set up a free colony in Appalachian Mts. ► He led a raid on a US arsenal at Harpers Ferry, Virginia. ---He was finance by leading abolitionist ► Robert E. Lee and the Marines surrounded and captured Brown and executed him ► Many and the North praised what Brown had done; Southern fears rose.
 John Brown 1800 -1859 ► led the Pottawatomie Massacre in 1856 in Bleeding Kansas and made his name in the unsuccessful raid at Harpers Ferry in 1859 ► He was tried for treason against the state of Virginia, the murder of five proslavery Southerners, and inciting a slave insurrection and was subsequently hanged ► Major figure in increasing tensions in Civil War ►
John Brown 1800 -1859 ► led the Pottawatomie Massacre in 1856 in Bleeding Kansas and made his name in the unsuccessful raid at Harpers Ferry in 1859 ► He was tried for treason against the state of Virginia, the murder of five proslavery Southerners, and inciting a slave insurrection and was subsequently hanged ► Major figure in increasing tensions in Civil War ►
 Lincoln-Douglas Debates ► The Lincoln–Douglas Debates of 1858 were a series of seven debates between Abraham Lincoln, the Republican candidate, and the incumbent Stephen A. Douglas, a Democrat, for an Illinois seat in the United States Senate ► After losing the election for Senator in Illinois, Lincoln edited the texts of all the debates and had them published in a book. The widespread coverage of the original debates and the subsequent popularity of the book led eventually to Lincoln's nomination for President of the United States by the 1860 Republican National Convention in Chicago.
Lincoln-Douglas Debates ► The Lincoln–Douglas Debates of 1858 were a series of seven debates between Abraham Lincoln, the Republican candidate, and the incumbent Stephen A. Douglas, a Democrat, for an Illinois seat in the United States Senate ► After losing the election for Senator in Illinois, Lincoln edited the texts of all the debates and had them published in a book. The widespread coverage of the original debates and the subsequent popularity of the book led eventually to Lincoln's nomination for President of the United States by the 1860 Republican National Convention in Chicago.
 Stephen A. Douglas ► 1813 -1861 ► Politician Illinois ► Constructed the Kansas-Nebraska Act ► Lost to Lincoln during the election of 1860.
Stephen A. Douglas ► 1813 -1861 ► Politician Illinois ► Constructed the Kansas-Nebraska Act ► Lost to Lincoln during the election of 1860.
 Abraham Lincoln ► 1809 -1865 ► Illinois politician ► 16 th President ► Preserved Union during Civil War ► Emancipation Proclamation – ending slavery
Abraham Lincoln ► 1809 -1865 ► Illinois politician ► 16 th President ► Preserved Union during Civil War ► Emancipation Proclamation – ending slavery
 Election of 1860 1. 2. 3. 4. Southern Democrats – John C. Breckenridge (Pro Slavery) Northern Democrats – Stephen Douglas (Popular Sovereignty) Republican – Abraham Lincoln (Anti-Slavery) Constitutional Union Party – John Bell (Senator Tenn. )
Election of 1860 1. 2. 3. 4. Southern Democrats – John C. Breckenridge (Pro Slavery) Northern Democrats – Stephen Douglas (Popular Sovereignty) Republican – Abraham Lincoln (Anti-Slavery) Constitutional Union Party – John Bell (Senator Tenn. )
 Election of 1860 ► North – Lincoln v. Douglas ► South – Breckinridge v. Bell (Lincoln didn’t even appear on the ballot in the south) ► Lincoln won the North, Bell and Breckinridge split the south ► The split allowed Lincoln to win with less than 40% of popular vote
Election of 1860 ► North – Lincoln v. Douglas ► South – Breckinridge v. Bell (Lincoln didn’t even appear on the ballot in the south) ► Lincoln won the North, Bell and Breckinridge split the south ► The split allowed Lincoln to win with less than 40% of popular vote
 1860 Election: A Nation Coming Apart? !
1860 Election: A Nation Coming Apart? !
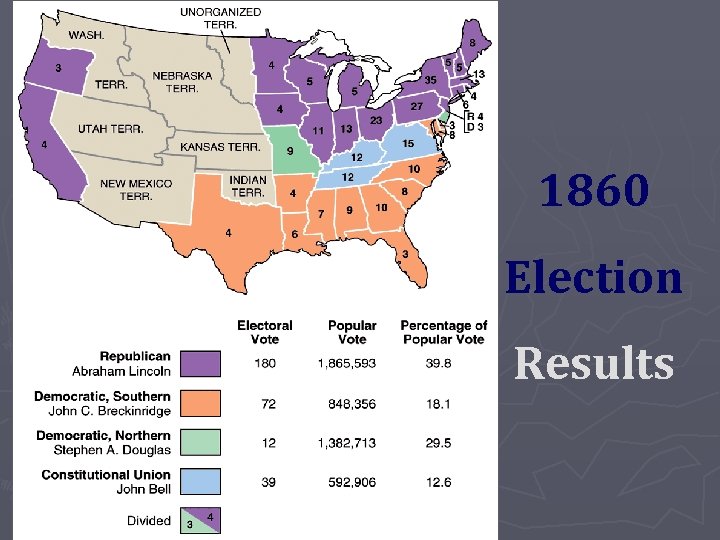 1860 Election Results
1860 Election Results
 New President ► Abraham Lincoln is elected President of the Untied States. During the election, he had spoken out strongly against the spread of slavery and hoped that one day it would end.
New President ► Abraham Lincoln is elected President of the Untied States. During the election, he had spoken out strongly against the spread of slavery and hoped that one day it would end.
 Civil War Objectives ► Describe the Union and Confederate goals and strategies for the war. ► Explain the significant battles of the Civil War. ► Analyze how the Emancipation Proclamation affected the war and the US. ► Discuss why the Union was victorious.
Civil War Objectives ► Describe the Union and Confederate goals and strategies for the war. ► Explain the significant battles of the Civil War. ► Analyze how the Emancipation Proclamation affected the war and the US. ► Discuss why the Union was victorious.
 Secession! ► Nov. 13 1860 – South Carolina Secedes – with Declaration of Independence from US ► Many southern states followed example § Mississippi – Jan. 9 1861 § Florida - Jan 10 1861 § Alabama – Jan 11 1861 § Georgia, Louisiana and Texas – Feb. 1 1861 § Virginia, Tennesse, Arkansas, and N. Carolina threatened to secede if Fed gov. tried to stop any state.
Secession! ► Nov. 13 1860 – South Carolina Secedes – with Declaration of Independence from US ► Many southern states followed example § Mississippi – Jan. 9 1861 § Florida - Jan 10 1861 § Alabama – Jan 11 1861 § Georgia, Louisiana and Texas – Feb. 1 1861 § Virginia, Tennesse, Arkansas, and N. Carolina threatened to secede if Fed gov. tried to stop any state.
 Major Reasons for Succession 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Compromise of 1850 Uncle Toms Cabin (1852) Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854) Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858) Raids of John Brown (1859) Election of Lincoln as President (1860)
Major Reasons for Succession 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Compromise of 1850 Uncle Toms Cabin (1852) Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854) Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858) Raids of John Brown (1859) Election of Lincoln as President (1860)
 Forming the Confederacy ► Delegates from seceded states met in Montgomery, Alabama in Feb 1861 ► Choose Jefferson Davis as President ► Drafted Constitution similar to Articles of Confederation ► They named new Nation the Confederate States of America (Confederacy)
Forming the Confederacy ► Delegates from seceded states met in Montgomery, Alabama in Feb 1861 ► Choose Jefferson Davis as President ► Drafted Constitution similar to Articles of Confederation ► They named new Nation the Confederate States of America (Confederacy)
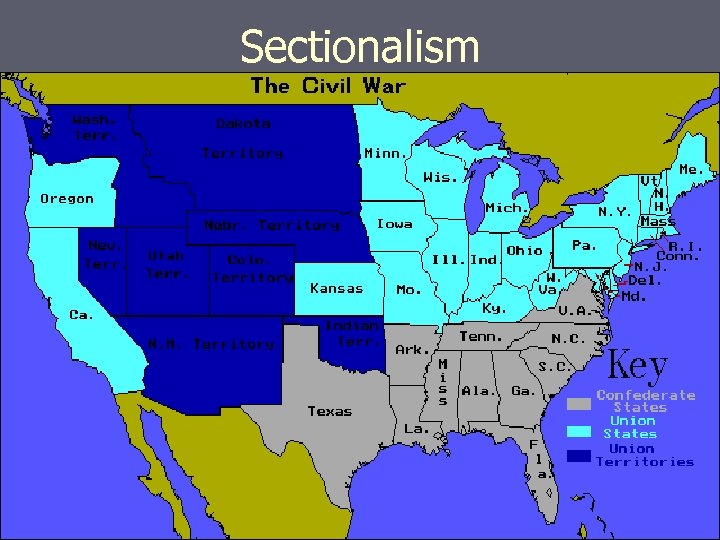 Sectionalism
Sectionalism
 The Fall of Fort Sumter ► S. Carolina - April 12, 1861 – first fighting ► Fort Sumter was controlled by Union. Davis called on the fort to surrender, as many other forts did in S. Carolina. ► Lincoln pledged to only send nonmilitary aid ► Jefferson decided to attack ► April 12, Confederate artillery began firing ► April 14, the US flag was replaced with a Confederate flag
The Fall of Fort Sumter ► S. Carolina - April 12, 1861 – first fighting ► Fort Sumter was controlled by Union. Davis called on the fort to surrender, as many other forts did in S. Carolina. ► Lincoln pledged to only send nonmilitary aid ► Jefferson decided to attack ► April 12, Confederate artillery began firing ► April 14, the US flag was replaced with a Confederate flag
 The war begins - the firing on Fort Sumter
The war begins - the firing on Fort Sumter
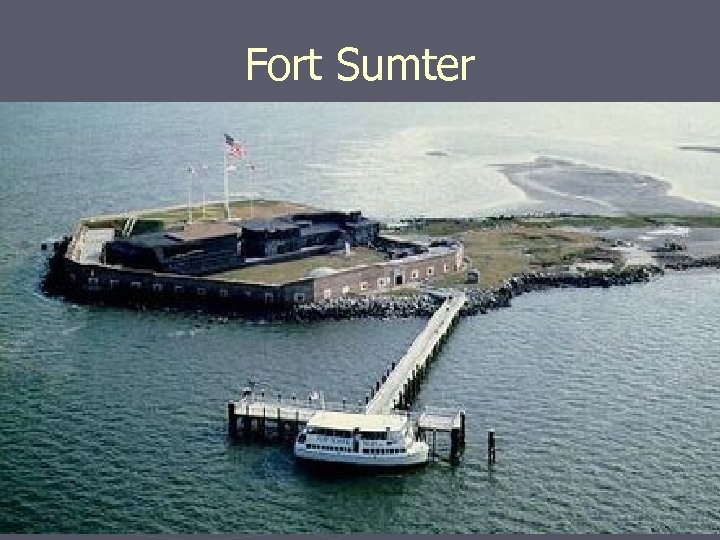 Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter

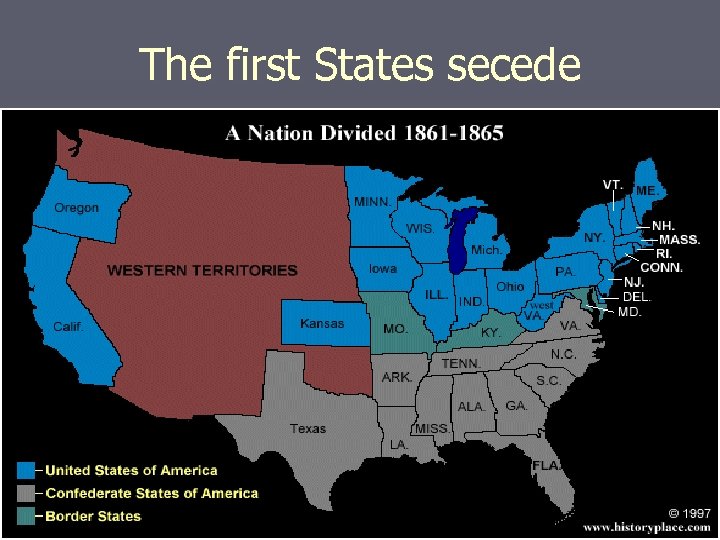 The first States secede
The first States secede
 Rush to War ► In response to the fall of Fort Sumter, Lincoln called for 75, 000 volunteers to serve for 90 days to put down rebellion ► Forced other southern states to secede including Arkansas ► Border states – Delaware, Kentucky, Maryland, and Missouri (both sides fought)
Rush to War ► In response to the fall of Fort Sumter, Lincoln called for 75, 000 volunteers to serve for 90 days to put down rebellion ► Forced other southern states to secede including Arkansas ► Border states – Delaware, Kentucky, Maryland, and Missouri (both sides fought)
 Strategies ► North § Developed by General Winfield Scott § Blockade South’s Ports § Ships down Miss. River to divide Confederacy § Many disapproved of plan—taking too long ► South § Cotton Diplomacy – to convince France and Britain to help § Defensive Strategy
Strategies ► North § Developed by General Winfield Scott § Blockade South’s Ports § Ships down Miss. River to divide Confederacy § Many disapproved of plan—taking too long ► South § Cotton Diplomacy – to convince France and Britain to help § Defensive Strategy
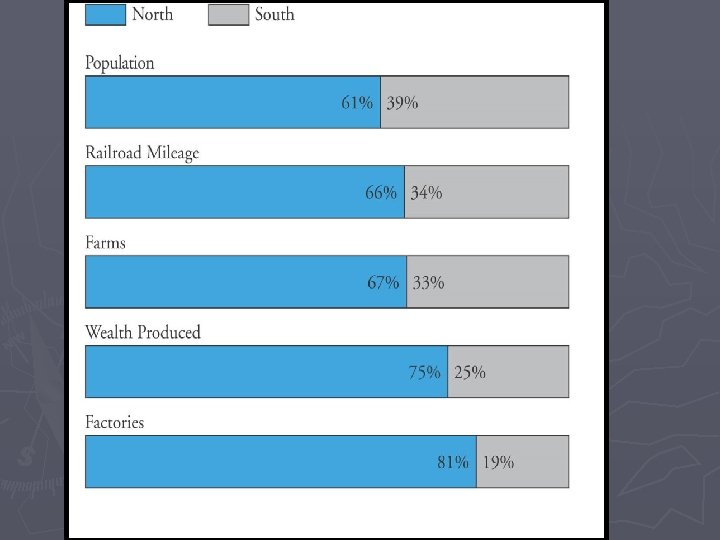
 Advantages ► North § Double the population § Double the railroads § Five times as many factories ► South § Better leaders § Defending is easier than attacking § Fighting for their cause (passion)
Advantages ► North § Double the population § Double the railroads § Five times as many factories ► South § Better leaders § Defending is easier than attacking § Fighting for their cause (passion)
 Confederate Union
Confederate Union
 Major Battles 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. First Battle of Bull Run 1861 Manassas, Virginia Confederate Victory Shiloh 1862 Tennessee Union Victory Second Battle of Bull Run 1862 Virginia Confederate Victory Antietam 1862 Maryland Union Victory Vicksburg 1863 Mississippi Union Victory Gettysburg 1863 Pennsylvania Union Victory Petersburg 1864 -1865 Petersburg, Virginia Union Victory
Major Battles 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. First Battle of Bull Run 1861 Manassas, Virginia Confederate Victory Shiloh 1862 Tennessee Union Victory Second Battle of Bull Run 1862 Virginia Confederate Victory Antietam 1862 Maryland Union Victory Vicksburg 1863 Mississippi Union Victory Gettysburg 1863 Pennsylvania Union Victory Petersburg 1864 -1865 Petersburg, Virginia Union Victory
 Civil War Technology http: //www. old-picture. com/civil-war/Artillery-Civil-War-001. htm
Civil War Technology http: //www. old-picture. com/civil-war/Artillery-Civil-War-001. htm
 Telegraph http: //w 1 tp. com/perkcol. htm
Telegraph http: //w 1 tp. com/perkcol. htm
 http: //www. sonofthesouth. net/leefoundation/civil-war/1863/january/telegraph. htm
http: //www. sonofthesouth. net/leefoundation/civil-war/1863/january/telegraph. htm
 Telegraph wagon http: //www. civilwarhome. com/telegraph. htm
Telegraph wagon http: //www. civilwarhome. com/telegraph. htm
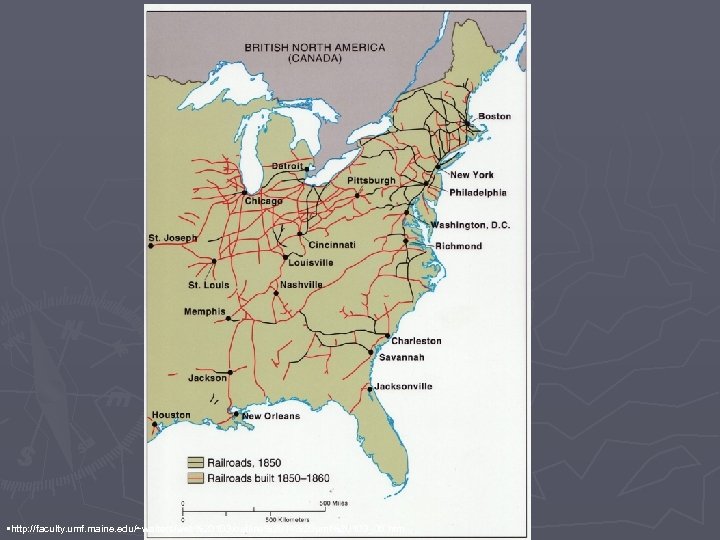
 Railroads http: //updatecenter. britannica. com/art? assembly. Id=8341&type=A
Railroads http: //updatecenter. britannica. com/art? assembly. Id=8341&type=A
 http: //www. old-picture. com/civil-war/Soldiers-railroad-cannon-small. htm
http: //www. old-picture. com/civil-war/Soldiers-railroad-cannon-small. htm
 • http: //faculty. umf. maine. edu/~walters/web%20103/outline%2014%20 umf%20103_06. htm
• http: //faculty. umf. maine. edu/~walters/web%20103/outline%2014%20 umf%20103_06. htm
 http: //www. anselm. edu/academic/history/hdubrulle/Warand. Revolution
http: //www. anselm. edu/academic/history/hdubrulle/Warand. Revolution
 Rifled musket http: //www. marstar. ca/gf-armisport/Armi. Sport-Civil-War-US-rifles. shtm
Rifled musket http: //www. marstar. ca/gf-armisport/Armi. Sport-Civil-War-US-rifles. shtm
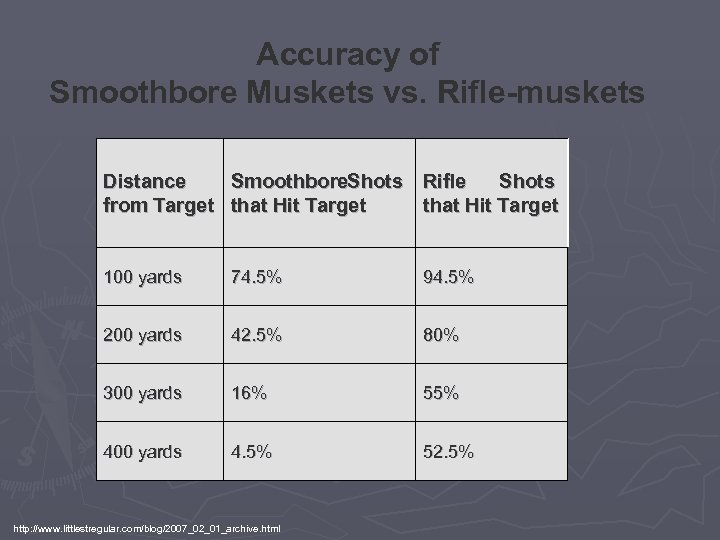 Accuracy of Smoothbore Muskets vs. Rifle-muskets Distance from Target Smoothbore. Shots Rifle Shots that Hit Target 100 yards 74. 5% 94. 5% 200 yards 42. 5% 80% 300 yards 16% 55% 400 yards 4. 5% 52. 5% http: //www. littlestregular. com/blog/2007_02_01_archive. html
Accuracy of Smoothbore Muskets vs. Rifle-muskets Distance from Target Smoothbore. Shots Rifle Shots that Hit Target 100 yards 74. 5% 94. 5% 200 yards 42. 5% 80% 300 yards 16% 55% 400 yards 4. 5% 52. 5% http: //www. littlestregular. com/blog/2007_02_01_archive. html
 Rifled Cannon The Whitworth designed cannon could fire a shell over 6 miles. http: //www. andrewspages. dial. pipex. com
Rifled Cannon The Whitworth designed cannon could fire a shell over 6 miles. http: //www. andrewspages. dial. pipex. com
 Repeating rifles http: //www. au. af. mil/au/awcgate/gabrmetz/gabr 001 b. htm
Repeating rifles http: //www. au. af. mil/au/awcgate/gabrmetz/gabr 001 b. htm
 Hand grenades/rockets http: //grenadelauncher. com/
Hand grenades/rockets http: //grenadelauncher. com/
 Ironclads/gunboats http: //www. flickr. com/photos/
Ironclads/gunboats http: //www. flickr. com/photos/
 Iron clad (plated) boats
Iron clad (plated) boats
 Submarines http: //news. webshots. com/photo/1195793651015913979 Kyvk. EV
Submarines http: //news. webshots. com/photo/1195793651015913979 Kyvk. EV
 http: //www. sonofthesouth. net/leefoundation/civil-war/1861/november/submarine. htm
http: //www. sonofthesouth. net/leefoundation/civil-war/1861/november/submarine. htm
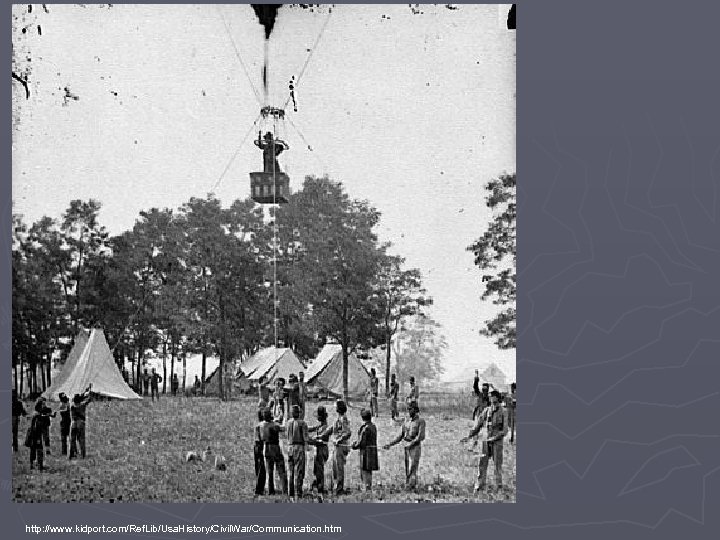
 Balloons http: //www. sonofthesouth. net/leefoundation/civil-war/1861/october/civil-war-balloons. htm
Balloons http: //www. sonofthesouth. net/leefoundation/civil-war/1861/october/civil-war-balloons. htm
 http: //www. old-picture. com/civil-war/Professor-military-Virginia-balloon. htm
http: //www. old-picture. com/civil-war/Professor-military-Virginia-balloon. htm
 http: //www. kidport. com/Ref. Lib/Usa. History/Civil. War/Communication. htm
http: //www. kidport. com/Ref. Lib/Usa. History/Civil. War/Communication. htm
 Photography http: //howardlanham. tripod. com/photography. html
Photography http: //howardlanham. tripod. com/photography. html
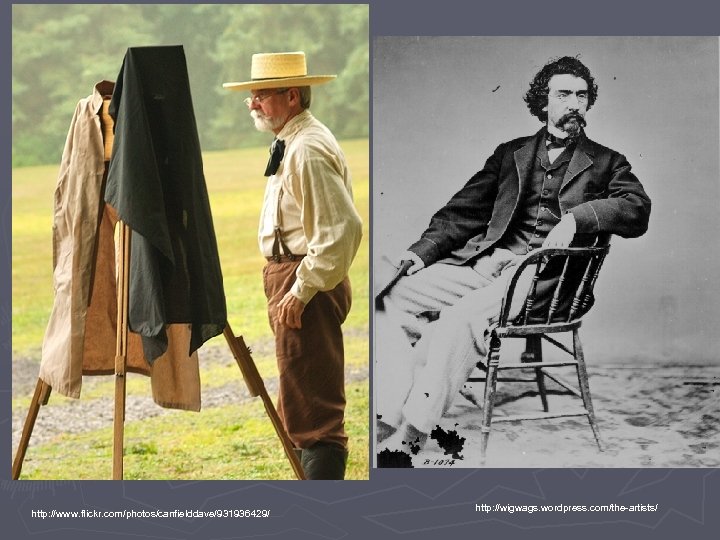 http: //www. flickr. com/photos/canfielddave/931936429/ http: //wigwags. wordpress. com/the-artists/
http: //www. flickr. com/photos/canfielddave/931936429/ http: //wigwags. wordpress. com/the-artists/
 http: //www. rbhayes. org/hayes/civilwar/display. asp? id=362&subj=civilwar http: //www. littlestregular. com/blog/labels/civil%20 war%20 photographs. html
http: //www. rbhayes. org/hayes/civilwar/display. asp? id=362&subj=civilwar http: //www. littlestregular. com/blog/labels/civil%20 war%20 photographs. html
 http: //www. sonofthesouth. net/leefoundation/antietam-dead. htm
http: //www. sonofthesouth. net/leefoundation/antietam-dead. htm
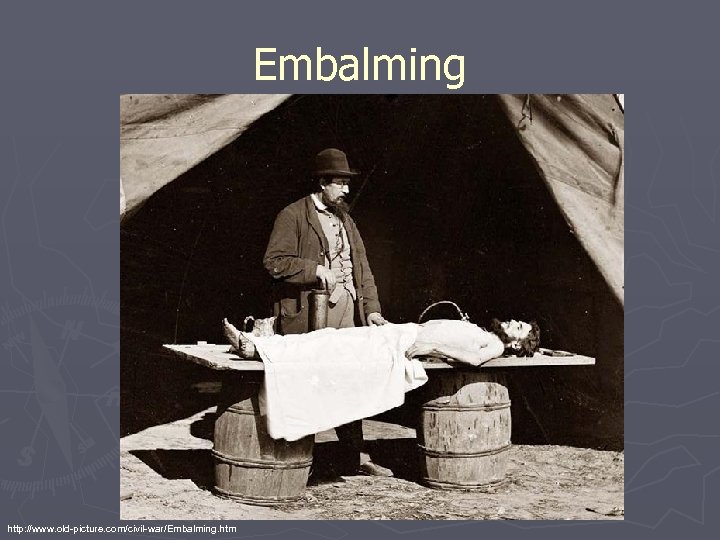 Embalming http: //www. old-picture. com/civil-war/Embalming. htm
Embalming http: //www. old-picture. com/civil-war/Embalming. htm
 Emancipation Proclamation ► Jan 1, 1863 – Freed slaves in all areas in rebellion to the Union. ► Lincoln hoped this would weaken south ► Mixed reactions ► Abolitionist were angered it didn’t free all slaves ► Some in north were scared about competition for jobs ► Encouraged emancipated slaves to join war
Emancipation Proclamation ► Jan 1, 1863 – Freed slaves in all areas in rebellion to the Union. ► Lincoln hoped this would weaken south ► Mixed reactions ► Abolitionist were angered it didn’t free all slaves ► Some in north were scared about competition for jobs ► Encouraged emancipated slaves to join war
 It freed the slaves only in states that have seceded from the Union. It did not free slaves in border states.
It freed the slaves only in states that have seceded from the Union. It did not free slaves in border states.
 African Americans the Military ►After the Emancipation William Carney Proclamation blacks began to join the Union Army ►Initially they were only used for manual labor ►Eventually, Blacks saw live combat ► 54 th regiment out of Massachusetts
African Americans the Military ►After the Emancipation William Carney Proclamation blacks began to join the Union Army ►Initially they were only used for manual labor ►Eventually, Blacks saw live combat ► 54 th regiment out of Massachusetts
 African Americans in the Civil War ► About 10 % of the Union forces were made up of African Americans after the Emancipation Proclamation ► Their valor on the field of battle proved their worth.
African Americans in the Civil War ► About 10 % of the Union forces were made up of African Americans after the Emancipation Proclamation ► Their valor on the field of battle proved their worth.
 Clara Barton ► teacher, nurse and humanitarian ► Organized “Red Cross” during the Civil War to distribute supplies to wounded soldiers
Clara Barton ► teacher, nurse and humanitarian ► Organized “Red Cross” during the Civil War to distribute supplies to wounded soldiers
 Battle of Bull Run ► General Thomas Jackson stopped Union advance – “Stone Wall Jackson” ► Union troops began to fall back ► Ended hopes for a quick victory for the Union
Battle of Bull Run ► General Thomas Jackson stopped Union advance – “Stone Wall Jackson” ► Union troops began to fall back ► Ended hopes for a quick victory for the Union

 Military historians consider Jackson to be one of the most gifted tactical commanders in United States history. He excelled at the First Battle of Bull Run (where he received his famous nickname "Stonewall"), Second Bull Run, Antietam, and Fredericksburg.
Military historians consider Jackson to be one of the most gifted tactical commanders in United States history. He excelled at the First Battle of Bull Run (where he received his famous nickname "Stonewall"), Second Bull Run, Antietam, and Fredericksburg.
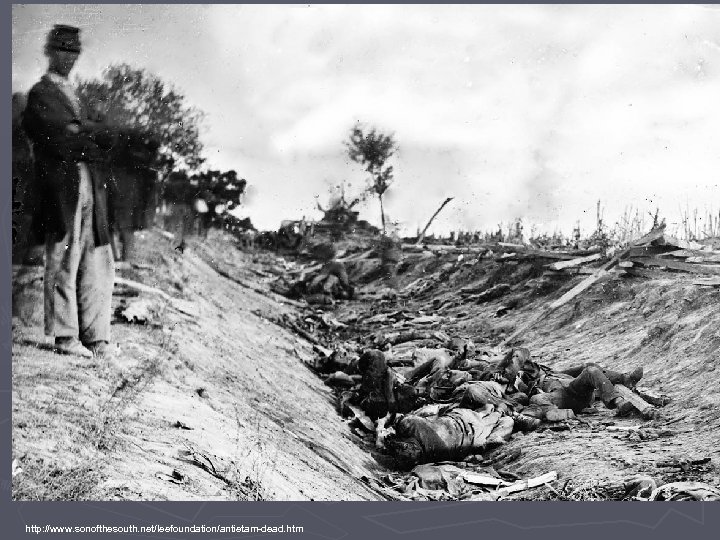
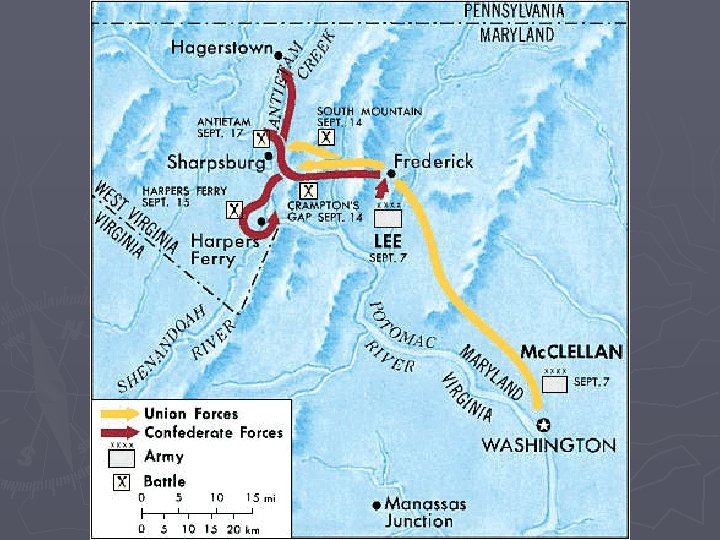
 Battle of Antietam ► Sept. 1862 – 70, 000 Union v. 40, 000 Con. ► Maryland ► Bloodiest single day battle of the Civil War and in American History ► 23, 000 Union and Confederacy died ► Union Victory
Battle of Antietam ► Sept. 1862 – 70, 000 Union v. 40, 000 Con. ► Maryland ► Bloodiest single day battle of the Civil War and in American History ► 23, 000 Union and Confederacy died ► Union Victory

 Confederate Dead
Confederate Dead
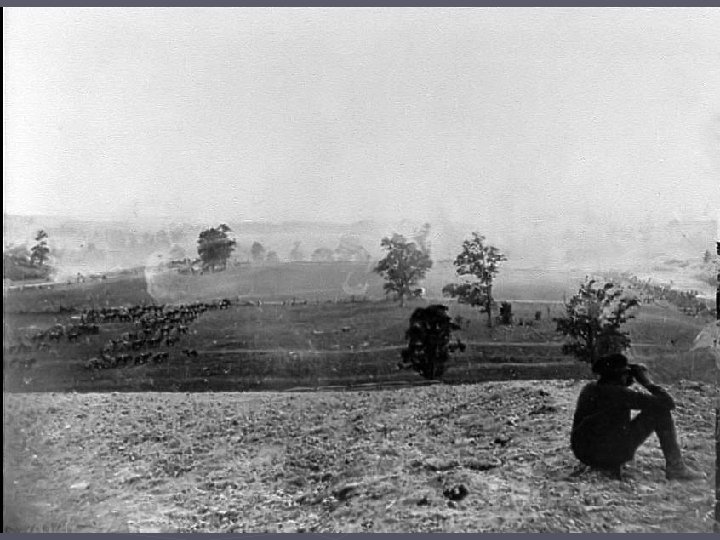
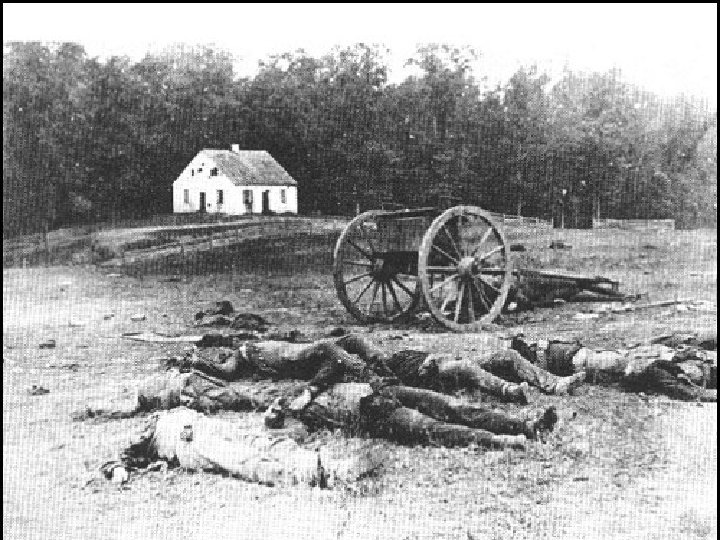




 Battle of Gettysburg ► Gettysburg, Penn – June 24, 1863 ► Three day campaign ► Confederates push back Union troops at first, but overextend ► Union troops eventually win the battle ► Confederate – 28, 000 KIA ► Union – 23, 000 ► Lincoln Address – create cemetery and remind country why we are fighting
Battle of Gettysburg ► Gettysburg, Penn – June 24, 1863 ► Three day campaign ► Confederates push back Union troops at first, but overextend ► Union troops eventually win the battle ► Confederate – 28, 000 KIA ► Union – 23, 000 ► Lincoln Address – create cemetery and remind country why we are fighting
 Gettysburg – turning point ►Gettysburg is the largest battle in the history of the Western hemisphere. ►Over 100, 000 people died in 3 days. ►It was the last time the South invaded the North.
Gettysburg – turning point ►Gettysburg is the largest battle in the history of the Western hemisphere. ►Over 100, 000 people died in 3 days. ►It was the last time the South invaded the North.


 Gettysburg Address - 1863
Gettysburg Address - 1863
 Gettysburg Address ► That from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion -- that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain -- that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom -- and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth. Abe Lincoln
Gettysburg Address ► That from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion -- that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain -- that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom -- and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth. Abe Lincoln
 General William Sherman (Union) ► Invaded Georgia and captured Atlanta 1864 ► Sherman began is famous “march” to the Atlantic Ocean ► Slaughtering/burning a 50 mile wide across the heart of Georgia ► Captured Savannah and entered South Carolina, then headed North ► Reinforced Grant in Richmond, Virginia
General William Sherman (Union) ► Invaded Georgia and captured Atlanta 1864 ► Sherman began is famous “march” to the Atlantic Ocean ► Slaughtering/burning a 50 mile wide across the heart of Georgia ► Captured Savannah and entered South Carolina, then headed North ► Reinforced Grant in Richmond, Virginia
 General William Sherman
General William Sherman
 Fall of Richmond ► Richmond, Virginia ► Grants army attacks from the North ► Sherman’s army attacks from the South ► Confederates flee city as Union troops enters ► Grant blocked Lee’s escape ► Lee surrenders at Appomattox Court House, Virginia. April 1865
Fall of Richmond ► Richmond, Virginia ► Grants army attacks from the North ► Sherman’s army attacks from the South ► Confederates flee city as Union troops enters ► Grant blocked Lee’s escape ► Lee surrenders at Appomattox Court House, Virginia. April 1865
 Over 618, 000 military deaths during Civil War.
Over 618, 000 military deaths during Civil War.
 After four bloody years of civil war, the South was defeated.
After four bloody years of civil war, the South was defeated.
 Lee surrendering to Grant at APPOMATTOX COURT HOUSE April, 1865
Lee surrendering to Grant at APPOMATTOX COURT HOUSE April, 1865
 Causes/Effects of Civil War ► Causes § Conflicts over Slavery § Lincolns Election § Secession of South § Attack on Fort Sumter ► Effects § End of Slavery § More than 600, 000 deaths § Physical and economic devastation of the South
Causes/Effects of Civil War ► Causes § Conflicts over Slavery § Lincolns Election § Secession of South § Attack on Fort Sumter ► Effects § End of Slavery § More than 600, 000 deaths § Physical and economic devastation of the South


