cba7f2def3ae8aef49ff80a04f11d079.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 The Challenges to Implementing an AMR System in the Middle East Presented By: Maha Chalouhi Chalhoub NEEDS Near East Engineering and Development Services Date: February 1, 2005
The Challenges to Implementing an AMR System in the Middle East Presented By: Maha Chalouhi Chalhoub NEEDS Near East Engineering and Development Services Date: February 1, 2005
 February 1, 2005 Table of Content • • Energy Status in the Middle East AMR Enterprise Solution AMR Challenges in the Area AMR Potential 2
February 1, 2005 Table of Content • • Energy Status in the Middle East AMR Enterprise Solution AMR Challenges in the Area AMR Potential 2
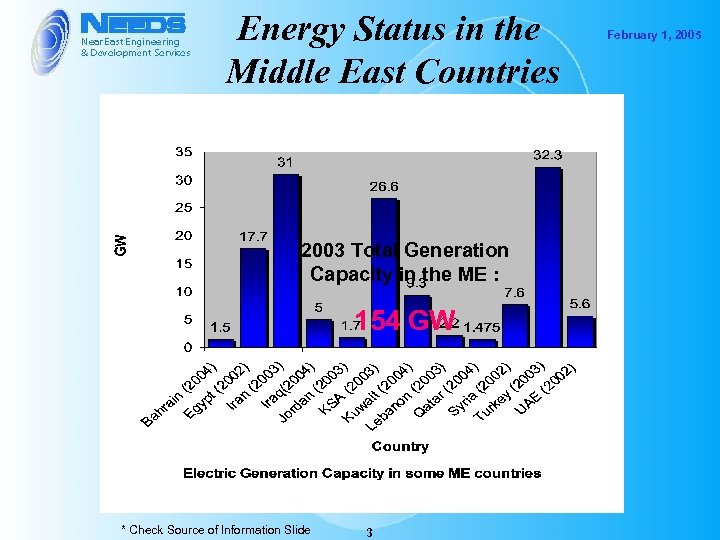 Energy Status in the Middle East Countries 2003 Total Generation Capacity in the ME : 154 GW * Check Source of Information Slide 3 February 1, 2005
Energy Status in the Middle East Countries 2003 Total Generation Capacity in the ME : 154 GW * Check Source of Information Slide 3 February 1, 2005
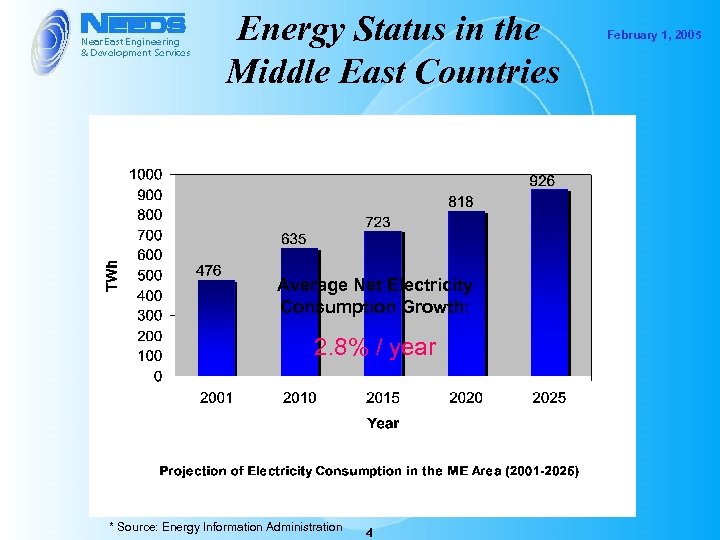 Energy Status in the Middle East Countries Average Net Electricity Consumption Growth: 2. 8% / year * Source: Energy Information Administration 4 February 1, 2005
Energy Status in the Middle East Countries Average Net Electricity Consumption Growth: 2. 8% / year * Source: Energy Information Administration 4 February 1, 2005
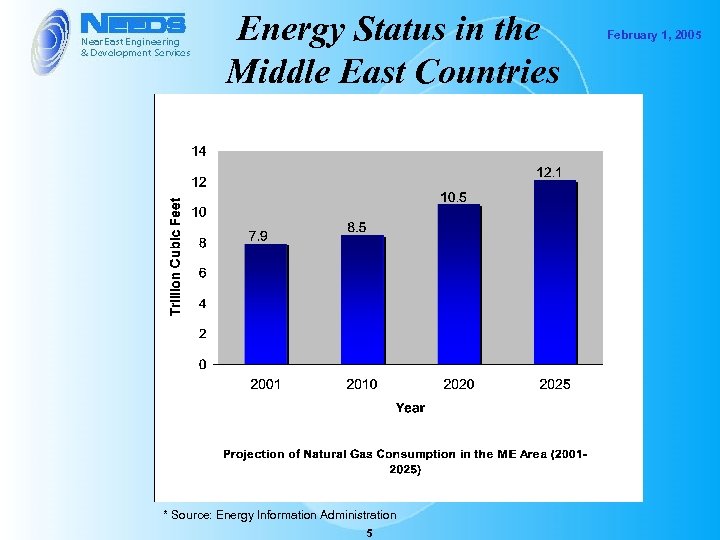 Energy Status in the Middle East Countries * Source: Energy Information Administration 5 February 1, 2005
Energy Status in the Middle East Countries * Source: Energy Information Administration 5 February 1, 2005
 Energy Status in the Middle East Countries February 1, 2005 Facts in the Middle East: - Saudi Arabia has 25% of proven oil reserve, UAE 10%, Kuwait 8%. - 2004 KSA oil exports revenues > 100 billion $ - 2001: ME produced 32% of crude oil world production - The largest reserve of natural gas is in ME: 3 rd in Qatar, 5 th in UAE: ME holds 35% of world’s estimated reserve in gas - 2004 GDP Growth: UAE: 4%, Bahrain/Jordan: 4. 6%, Qatar: 4. 7%, KSA: 6. 1%. - Dubai: the Model of the New 21 st Century City: Internet City, Children’s City, Festivity City, Knowledge Village 6
Energy Status in the Middle East Countries February 1, 2005 Facts in the Middle East: - Saudi Arabia has 25% of proven oil reserve, UAE 10%, Kuwait 8%. - 2004 KSA oil exports revenues > 100 billion $ - 2001: ME produced 32% of crude oil world production - The largest reserve of natural gas is in ME: 3 rd in Qatar, 5 th in UAE: ME holds 35% of world’s estimated reserve in gas - 2004 GDP Growth: UAE: 4%, Bahrain/Jordan: 4. 6%, Qatar: 4. 7%, KSA: 6. 1%. - Dubai: the Model of the New 21 st Century City: Internet City, Children’s City, Festivity City, Knowledge Village 6
 Energy Status in the Middle East Countries February 1, 2005 Maturity of Various Business Lines Economic / Industrial Boom Population Growth Great Potential Business Market Area 7
Energy Status in the Middle East Countries February 1, 2005 Maturity of Various Business Lines Economic / Industrial Boom Population Growth Great Potential Business Market Area 7
 Energy Status in the Middle East Countries February 1, 2005 HOWEVER… - Electricity Prices differs from lowest prices (Qatar, Saudi, UAE, Syria) to the highest prices in the world (Lebanon, Jordan) - Losses are stamped by non-technical losses like electricity theft that may reach 24% of production - Electricity Demand may exceed sometimes electricity supply leading some ME countries to import electricity from neighbors to avoid black-out - Many ME Power Sectors are State-Owned: No competition. * Check Source of Information Slide 8
Energy Status in the Middle East Countries February 1, 2005 HOWEVER… - Electricity Prices differs from lowest prices (Qatar, Saudi, UAE, Syria) to the highest prices in the world (Lebanon, Jordan) - Losses are stamped by non-technical losses like electricity theft that may reach 24% of production - Electricity Demand may exceed sometimes electricity supply leading some ME countries to import electricity from neighbors to avoid black-out - Many ME Power Sectors are State-Owned: No competition. * Check Source of Information Slide 8
 Energy Status in the Middle East Countries February 1, 2005 Quality of Service not matching Quality of Life High Rate of Non-Technical Losses Operation Deficiency Great Potential for Customer Services Improvement 9
Energy Status in the Middle East Countries February 1, 2005 Quality of Service not matching Quality of Life High Rate of Non-Technical Losses Operation Deficiency Great Potential for Customer Services Improvement 9
 Energy Status in the Middle East Countries February 1, 2005 Transformations in Middle East Power Sector: - Qatar: 2000: Privatization: Asset of MEW → QEWC 2001: Ras Laffan IWPP - Bahrain: In 2004: First contract for IPP / Consideration of Privatization of entire electricity sector - UAE: In 1998: ADWED → ADWEA / 2 nd IPP in Gulf area - Jordan: Deregulation distribution and generation power network -In 2002, grid linking project: Egypt, Jordan, Syria and others 10
Energy Status in the Middle East Countries February 1, 2005 Transformations in Middle East Power Sector: - Qatar: 2000: Privatization: Asset of MEW → QEWC 2001: Ras Laffan IWPP - Bahrain: In 2004: First contract for IPP / Consideration of Privatization of entire electricity sector - UAE: In 1998: ADWED → ADWEA / 2 nd IPP in Gulf area - Jordan: Deregulation distribution and generation power network -In 2002, grid linking project: Egypt, Jordan, Syria and others 10
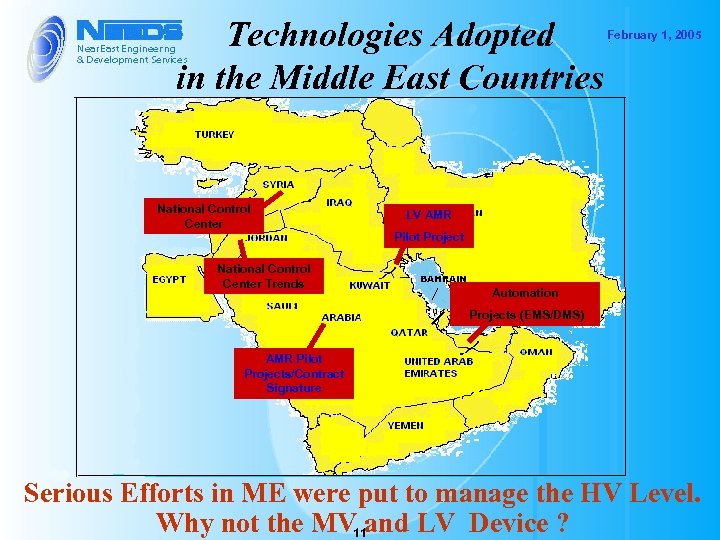 Technologies Adopted in the Middle East Countries National Control Center Trends February 1, 2005 LV AMR Pilot Project BAHRAIN Automation Projects (EMS/DMS) AMR Pilot Projects/Contract Signature Serious Efforts in ME were put to manage the HV Level. Why not the MV 11 and LV Device ?
Technologies Adopted in the Middle East Countries National Control Center Trends February 1, 2005 LV AMR Pilot Project BAHRAIN Automation Projects (EMS/DMS) AMR Pilot Projects/Contract Signature Serious Efforts in ME were put to manage the HV Level. Why not the MV 11 and LV Device ?
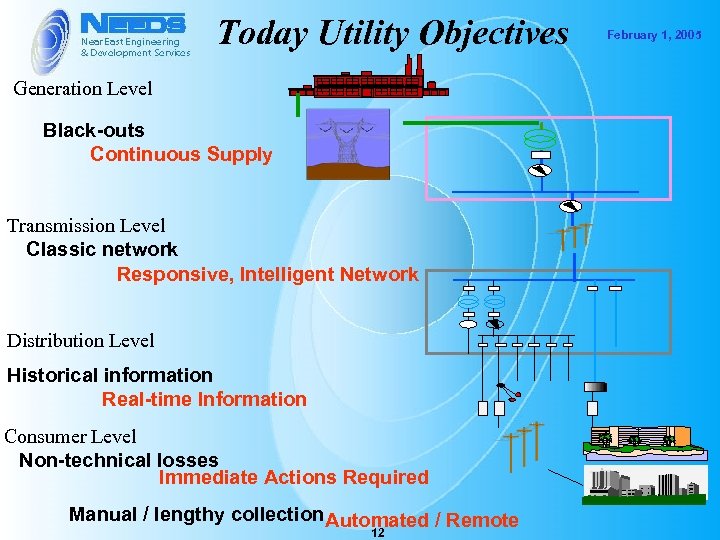 Today Utility Objectives Generation Level Black-outs Continuous Supply Transmission Level Classic network Responsive, Intelligent Network Distribution Level Historical information Real-time Information Consumer Level Non-technical losses Immediate Actions Required Manual / lengthy collection Automated / Remote 12 February 1, 2005
Today Utility Objectives Generation Level Black-outs Continuous Supply Transmission Level Classic network Responsive, Intelligent Network Distribution Level Historical information Real-time Information Consumer Level Non-technical losses Immediate Actions Required Manual / lengthy collection Automated / Remote 12 February 1, 2005
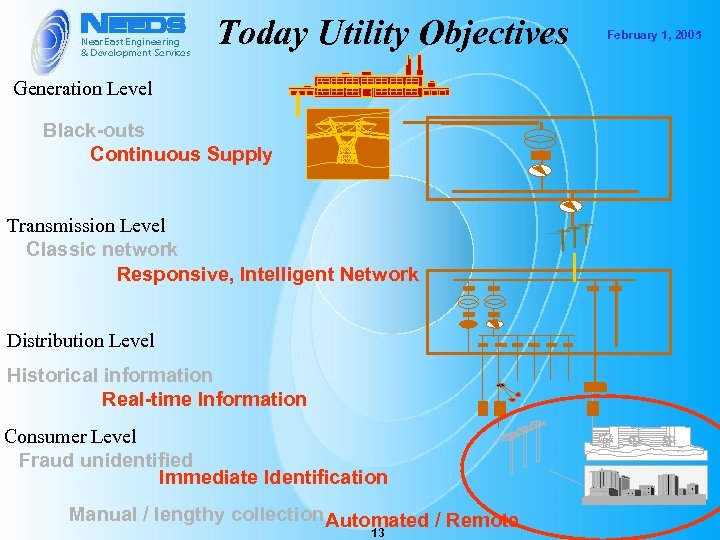 Today Utility Objectives Generation Level Black-outs Continuous Supply Transmission Level Classic network Responsive, Intelligent Network Distribution Level Historical information Real-time Information Consumer Level Fraud unidentified Immediate Identification Manual / lengthy collection Automated / Remote 13 February 1, 2005
Today Utility Objectives Generation Level Black-outs Continuous Supply Transmission Level Classic network Responsive, Intelligent Network Distribution Level Historical information Real-time Information Consumer Level Fraud unidentified Immediate Identification Manual / lengthy collection Automated / Remote 13 February 1, 2005
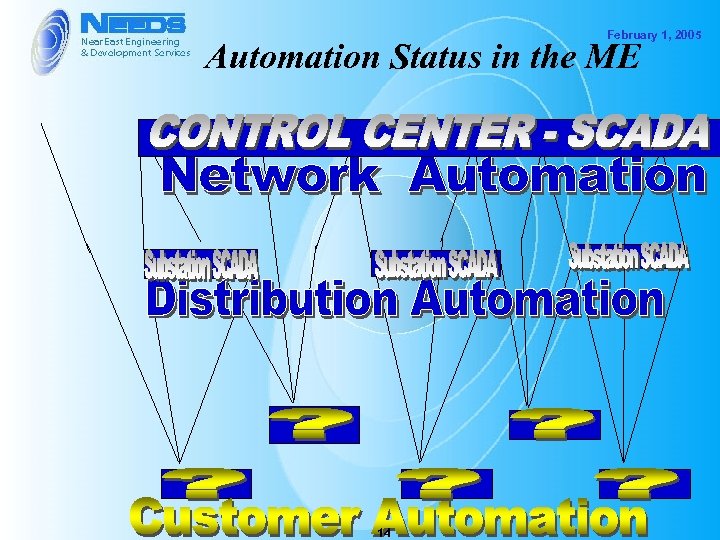 February 1, 2005 Automation Status in the ME 14
February 1, 2005 Automation Status in the ME 14
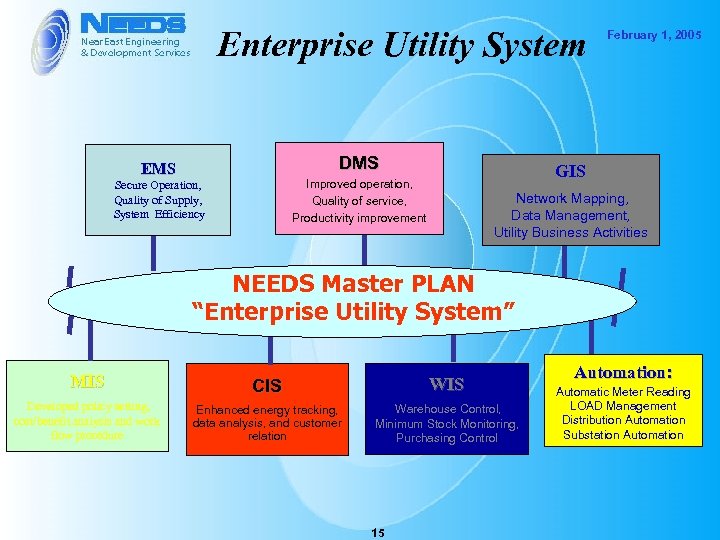 Enterprise Utility System DMS EMS GIS Improved operation, Quality of service, Productivity improvement Secure Operation, Quality of Supply, System Efficiency February 1, 2005 Network Mapping, Data Management, Utility Business Activities NEEDS Master PLAN “Enterprise Utility System” MIS CIS WIS Developed policy setting, cost/benefit analysis and work flow procedure Enhanced energy tracking, data analysis, and customer relation Warehouse Control, Minimum Stock Monitoring, Purchasing Control 15 Automation: Automatic Meter Reading LOAD Management Distribution Automation Substation Automation
Enterprise Utility System DMS EMS GIS Improved operation, Quality of service, Productivity improvement Secure Operation, Quality of Supply, System Efficiency February 1, 2005 Network Mapping, Data Management, Utility Business Activities NEEDS Master PLAN “Enterprise Utility System” MIS CIS WIS Developed policy setting, cost/benefit analysis and work flow procedure Enhanced energy tracking, data analysis, and customer relation Warehouse Control, Minimum Stock Monitoring, Purchasing Control 15 Automation: Automatic Meter Reading LOAD Management Distribution Automation Substation Automation
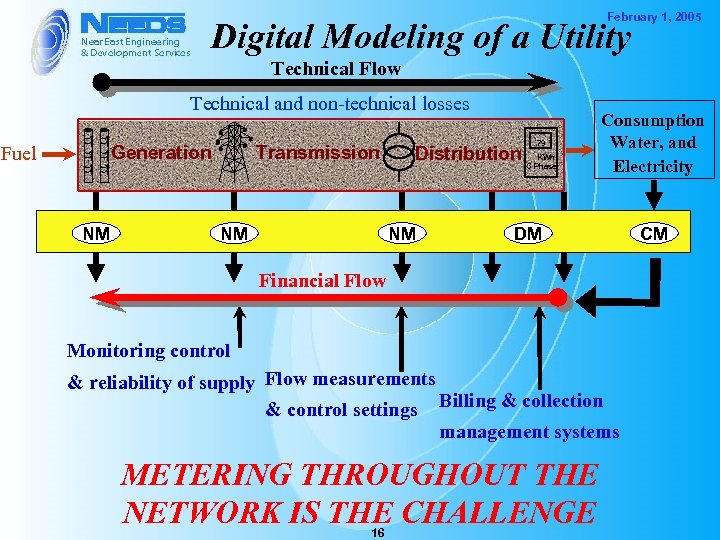 February 1, 2005 Digital Modeling of a Utility Technical Flow Technical and non-technical losses Generation Fuel NM Transmission NM Distribution NM 79 KWh 3 Phase Consumption Water, and Electricity DM Financial Flow Monitoring control & reliability of supply Flow measurements & control settings Billing & collection management systems METERING THROUGHOUT THE NETWORK IS THE CHALLENGE 16 CM
February 1, 2005 Digital Modeling of a Utility Technical Flow Technical and non-technical losses Generation Fuel NM Transmission NM Distribution NM 79 KWh 3 Phase Consumption Water, and Electricity DM Financial Flow Monitoring control & reliability of supply Flow measurements & control settings Billing & collection management systems METERING THROUGHOUT THE NETWORK IS THE CHALLENGE 16 CM
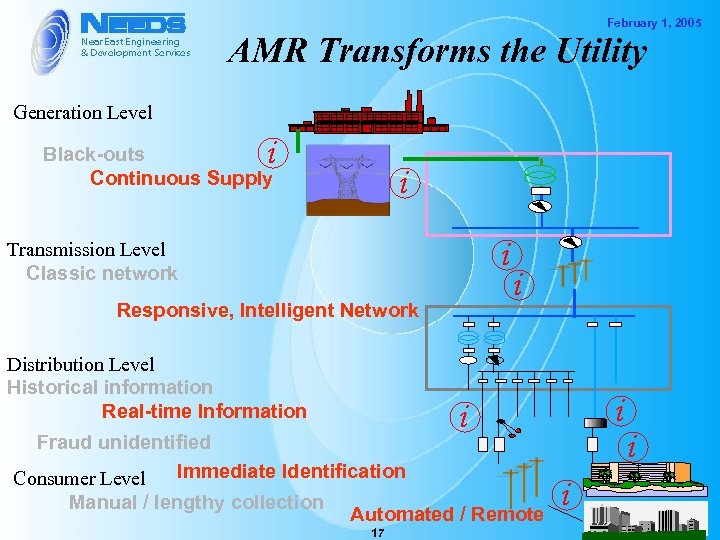 February 1, 2005 AMR Transforms the Utility Generation Level i Black-outs Continuous Supply i i Transmission Level Classic network Responsive, Intelligent Network Distribution Level Historical information Real-time Information Fraud unidentified Immediate Identification Consumer Level Manual / lengthy collection i Automated / Remote 17 i i
February 1, 2005 AMR Transforms the Utility Generation Level i Black-outs Continuous Supply i i Transmission Level Classic network Responsive, Intelligent Network Distribution Level Historical information Real-time Information Fraud unidentified Immediate Identification Consumer Level Manual / lengthy collection i Automated / Remote 17 i i
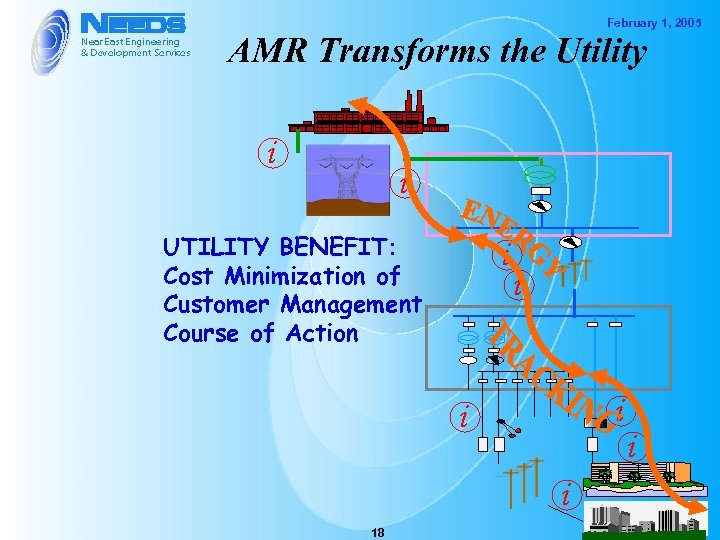 February 1, 2005 AMR Transforms the Utility i i UTILITY BENEFIT: Cost Minimization of Customer Management Course of Action i i i 18 i
February 1, 2005 AMR Transforms the Utility i i UTILITY BENEFIT: Cost Minimization of Customer Management Course of Action i i i 18 i
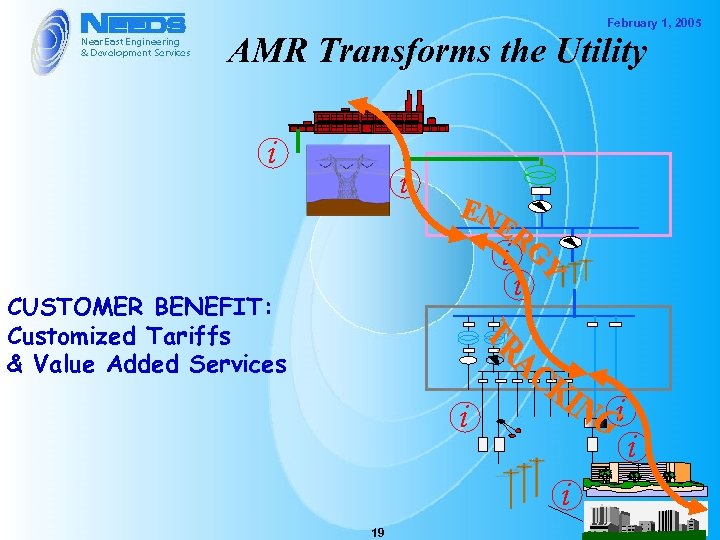 February 1, 2005 AMR Transforms the Utility i i i CUSTOMER BENEFIT: Customized Tariffs & Value Added Services i i 19 i
February 1, 2005 AMR Transforms the Utility i i i CUSTOMER BENEFIT: Customized Tariffs & Value Added Services i i 19 i
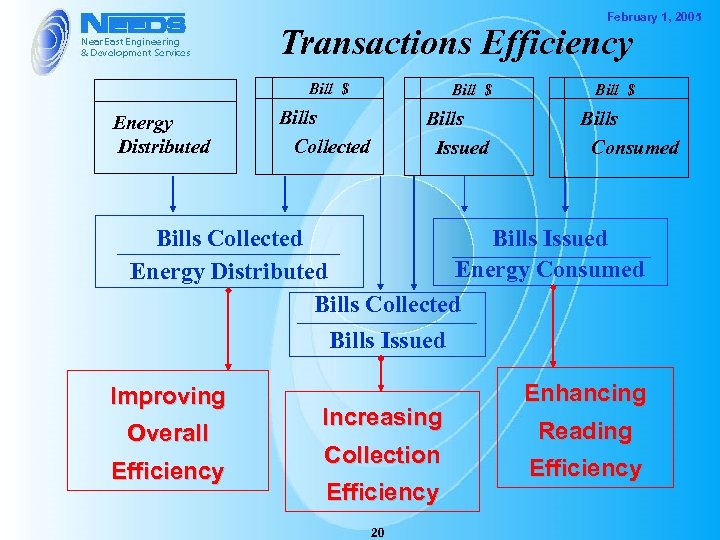 February 1, 2005 Transactions Efficiency Bill $ Energy Distributed Bill $ Bills Collected Bills Issued Bill $ Bills Consumed Bills Collected Bills Issued Energy Consumed Energy Distributed Bills Collected Bills Issued Improving Overall Efficiency Increasing Collection Efficiency 20 Enhancing Reading Efficiency
February 1, 2005 Transactions Efficiency Bill $ Energy Distributed Bill $ Bills Collected Bills Issued Bill $ Bills Consumed Bills Collected Bills Issued Energy Consumed Energy Distributed Bills Collected Bills Issued Improving Overall Efficiency Increasing Collection Efficiency 20 Enhancing Reading Efficiency
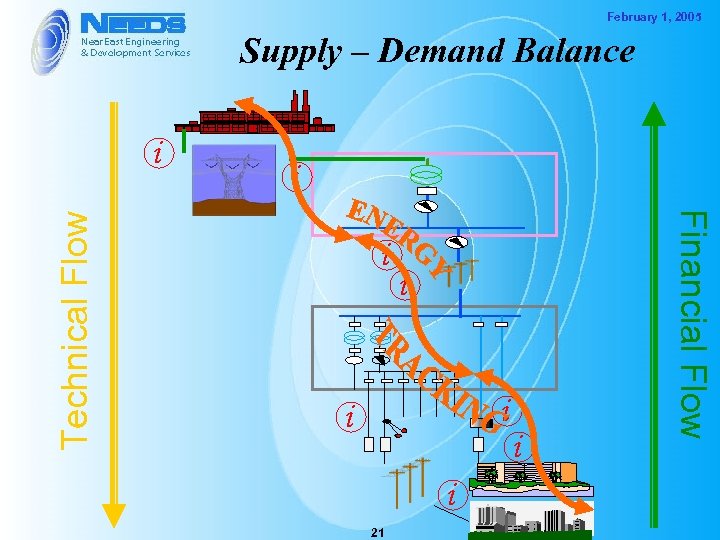 February 1, 2005 Supply – Demand Balance i i i 21 i Financial Flow Technical Flow i
February 1, 2005 Supply – Demand Balance i i i 21 i Financial Flow Technical Flow i
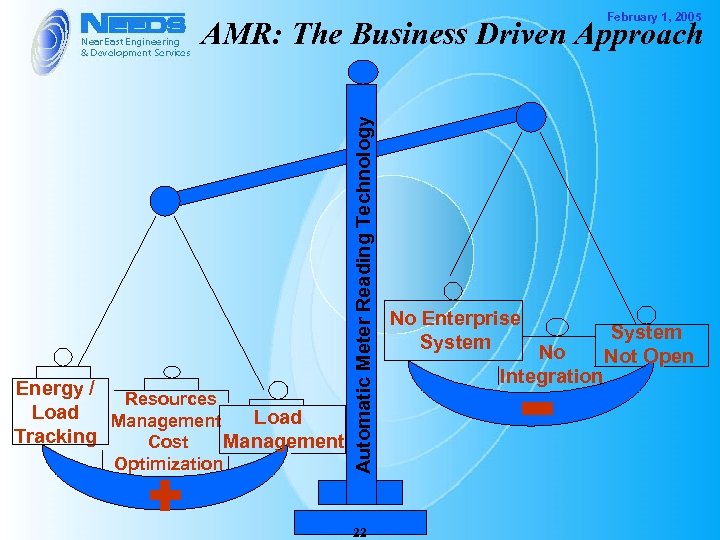 February 1, 2005 Energy / Resources Load Management Tracking Management Cost Optimization Automatic Meter Reading Technology AMR: The Business Driven Approach 22 No Enterprise System No Integration System Not Open
February 1, 2005 Energy / Resources Load Management Tracking Management Cost Optimization Automatic Meter Reading Technology AMR: The Business Driven Approach 22 No Enterprise System No Integration System Not Open
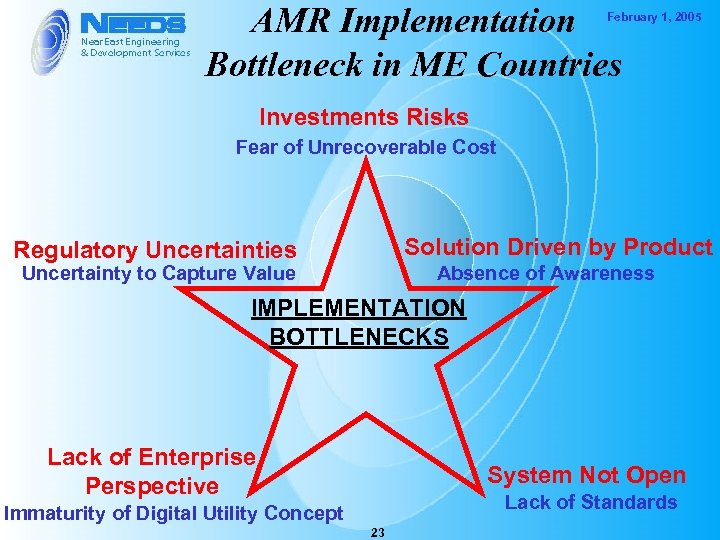 AMR Implementation Bottleneck in ME Countries February 1, 2005 Investments Risks Fear of Unrecoverable Cost Solution Driven by Product Regulatory Uncertainties Uncertainty to Capture Value Absence of Awareness IMPLEMENTATION BOTTLENECKS Lack of Enterprise Perspective System Not Open Lack of Standards Immaturity of Digital Utility Concept 23
AMR Implementation Bottleneck in ME Countries February 1, 2005 Investments Risks Fear of Unrecoverable Cost Solution Driven by Product Regulatory Uncertainties Uncertainty to Capture Value Absence of Awareness IMPLEMENTATION BOTTLENECKS Lack of Enterprise Perspective System Not Open Lack of Standards Immaturity of Digital Utility Concept 23
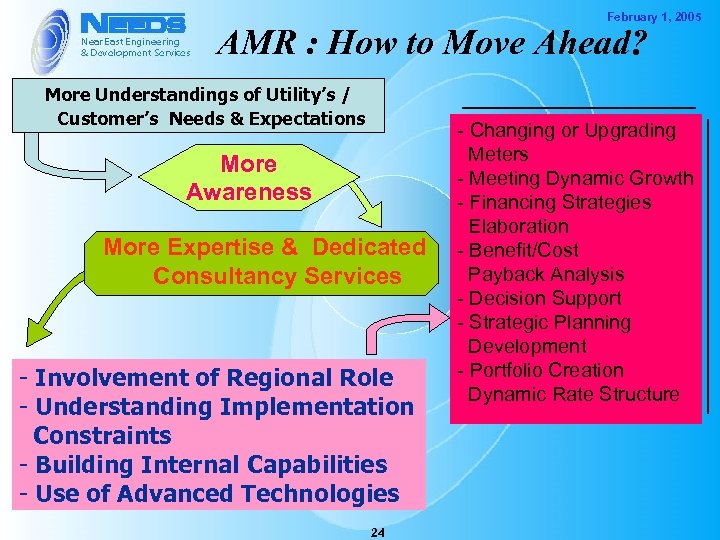 February 1, 2005 AMR : How to Move Ahead? More Understandings of Utility’s / Customer’s Needs & Expectations More Awareness More Expertise & Dedicated Consultancy Services - Involvement of Regional Role - Understanding Implementation Constraints - Building Internal Capabilities - Use of Advanced Technologies 24 - Changing or Upgrading Meters - Meeting Dynamic Growth - Financing Strategies Elaboration - Benefit/Cost Payback Analysis - Decision Support - Strategic Planning Development - Portfolio Creation Dynamic Rate Structure
February 1, 2005 AMR : How to Move Ahead? More Understandings of Utility’s / Customer’s Needs & Expectations More Awareness More Expertise & Dedicated Consultancy Services - Involvement of Regional Role - Understanding Implementation Constraints - Building Internal Capabilities - Use of Advanced Technologies 24 - Changing or Upgrading Meters - Meeting Dynamic Growth - Financing Strategies Elaboration - Benefit/Cost Payback Analysis - Decision Support - Strategic Planning Development - Portfolio Creation Dynamic Rate Structure
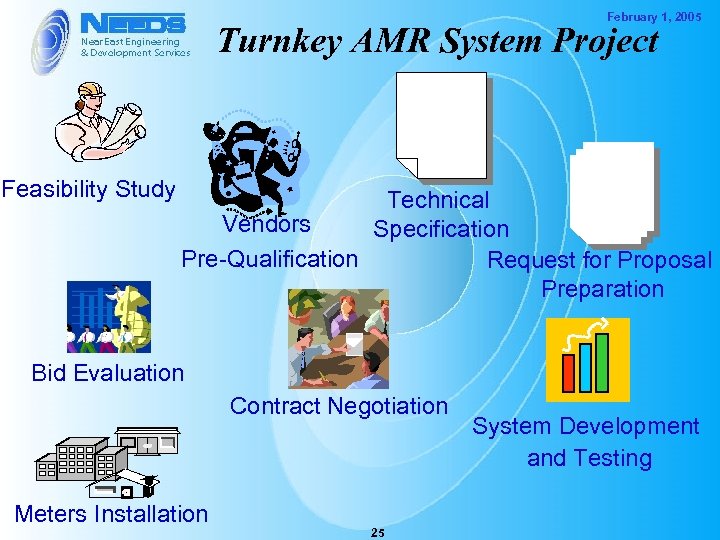 February 1, 2005 Turnkey AMR System Project Feasibility Study Technical Vendors Specification Pre-Qualification Request for Proposal Preparation Bid Evaluation Contract Negotiation Meters Installation 25 System Development and Testing
February 1, 2005 Turnkey AMR System Project Feasibility Study Technical Vendors Specification Pre-Qualification Request for Proposal Preparation Bid Evaluation Contract Negotiation Meters Installation 25 System Development and Testing
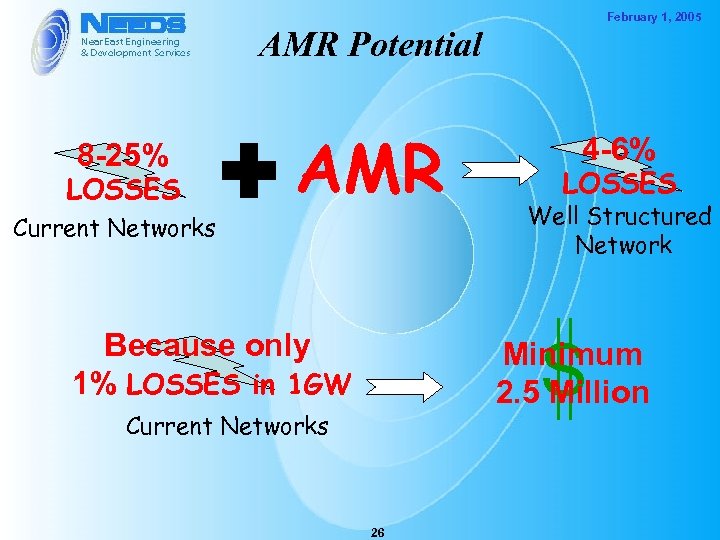 February 1, 2005 AMR Potential 8 -25% LOSSES Current Networks AMR Because only 1% LOSSES in 1 GW 4 -6% LOSSES Well Structured Network S Minimum 2. 5 Million Current Networks 26
February 1, 2005 AMR Potential 8 -25% LOSSES Current Networks AMR Because only 1% LOSSES in 1 GW 4 -6% LOSSES Well Structured Network S Minimum 2. 5 Million Current Networks 26
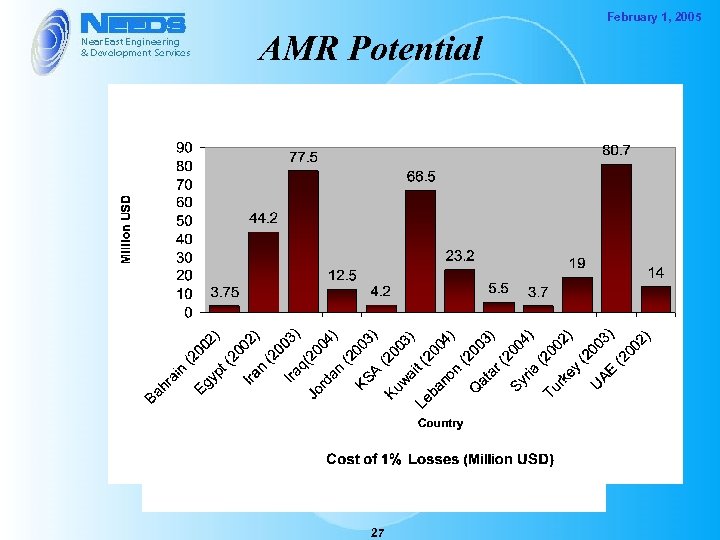 February 1, 2005 AMR Potential 27
February 1, 2005 AMR Potential 27
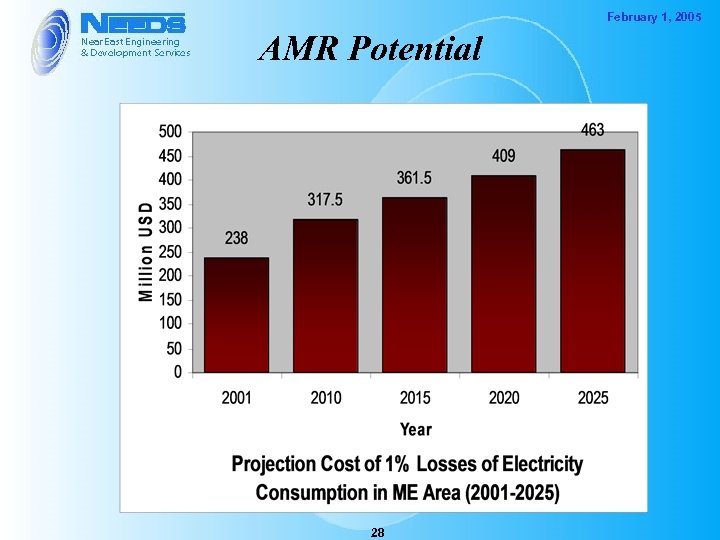 February 1, 2005 AMR Potential 28
February 1, 2005 AMR Potential 28
 Source of Information February 1, 2005 • Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) • Abu Dhabi Electricity and Water Authority (ADWEA) • Energy Information Administration • The World Bank • The United Nations Stats • The Saudi Arabia Information Resource • Emiri Diwan - Qatar
Source of Information February 1, 2005 • Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) • Abu Dhabi Electricity and Water Authority (ADWEA) • Energy Information Administration • The World Bank • The United Nations Stats • The Saudi Arabia Information Resource • Emiri Diwan - Qatar
 THANK YOU For More Reference: Paper ‘Transforming the Utility Business Environment’ / Metering International / Issue 4 Contact Address: info@needs. com. lb
THANK YOU For More Reference: Paper ‘Transforming the Utility Business Environment’ / Metering International / Issue 4 Contact Address: info@needs. com. lb


