cfcce04b46276d5a41b51bacbab5a53b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

The challenge of maternal and child nutrition globally: how can we contribute? Zulfiqar A. Bhutta Founding Chair Women & Child Health The Aga Khan University
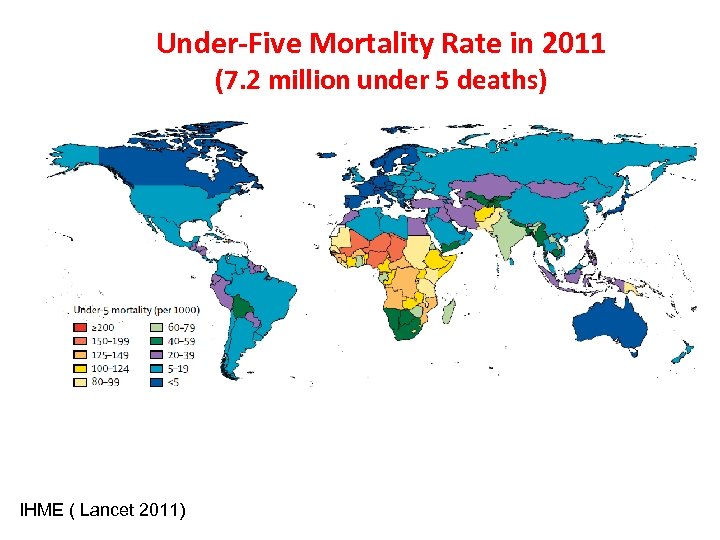

Under-Five Mortality Rate in 2011 (7. 2 million under 5 deaths) IHME ( Lancet 2011)
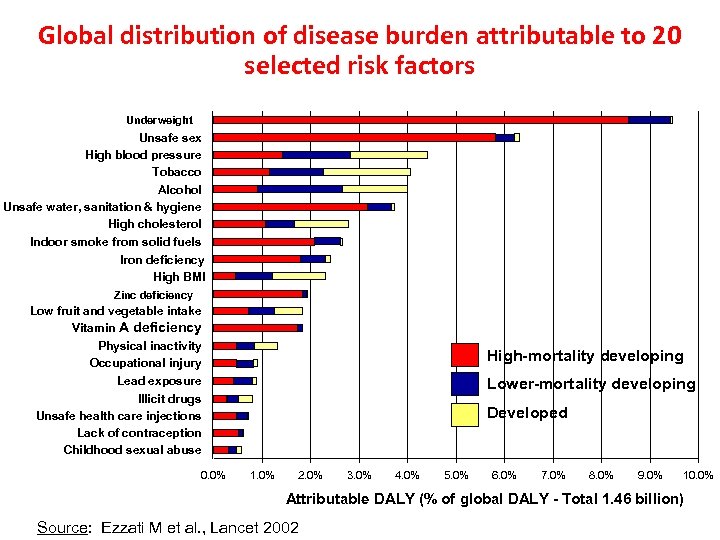
Global distribution of disease burden attributable to 20 selected risk factors Underweight Unsafe sex High blood pressure Tobacco Alcohol Unsafe water, sanitation & hygiene High cholesterol Indoor smoke from solid fuels Iron deficiency High BMI Zinc deficiency Low fruit and vegetable intake Vitamin A deficiency Physical inactivity Occupational injury Lead exposure High-mortality developing Lower-mortality developing Illicit drugs Unsafe health care injections Lack of contraception Childhood sexual abuse 0. 0% Developed 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. 0% 5. 0% 6. 0% 7. 0% 8. 0% 9. 0% 10. 0% Attributable DALY (% of global DALY - Total 1. 46 billion) Source: Ezzati M et al. , Lancet 2002
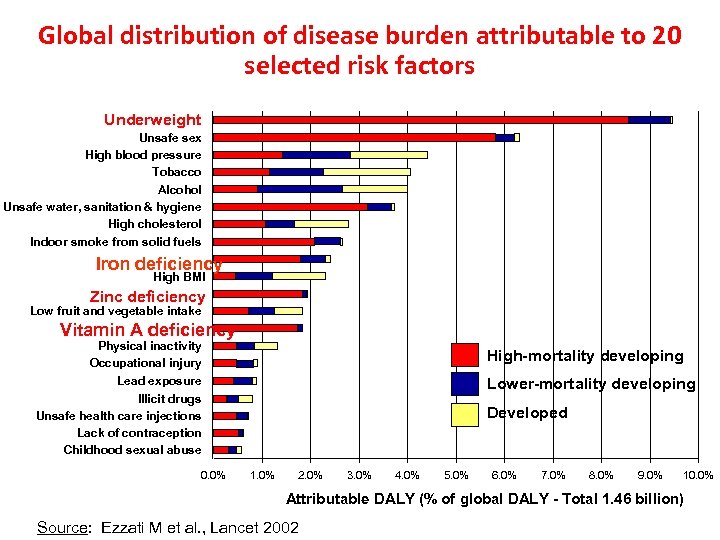
Global distribution of disease burden attributable to 20 selected risk factors Underweight Unsafe sex High blood pressure Tobacco Alcohol Unsafe water, sanitation & hygiene High cholesterol Indoor smoke from solid fuels Iron deficiency High BMI Zinc deficiency Low fruit and vegetable intake Vitamin A deficiency Physical inactivity Occupational injury Lead exposure High-mortality developing Lower-mortality developing Illicit drugs Unsafe health care injections Lack of contraception Childhood sexual abuse 0. 0% Developed 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. 0% 5. 0% 6. 0% 7. 0% 8. 0% 9. 0% 10. 0% Attributable DALY (% of global DALY - Total 1. 46 billion) Source: Ezzati M et al. , Lancet 2002
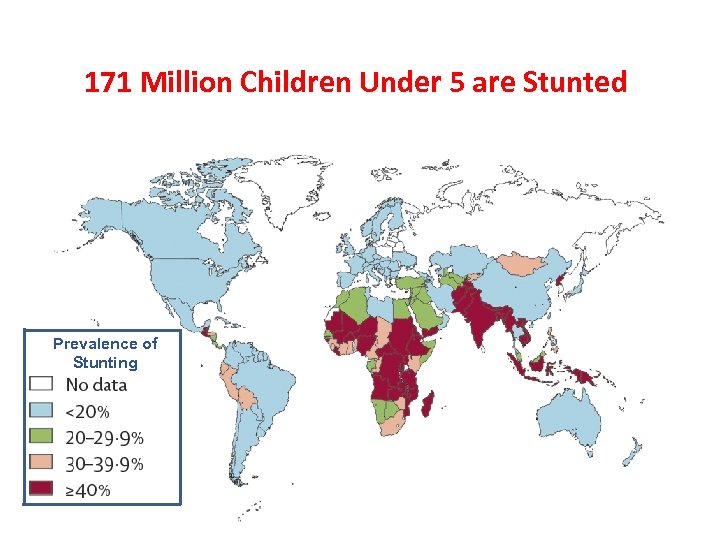
171 Million Children Under 5 are Stunted Prevalence of Stunting
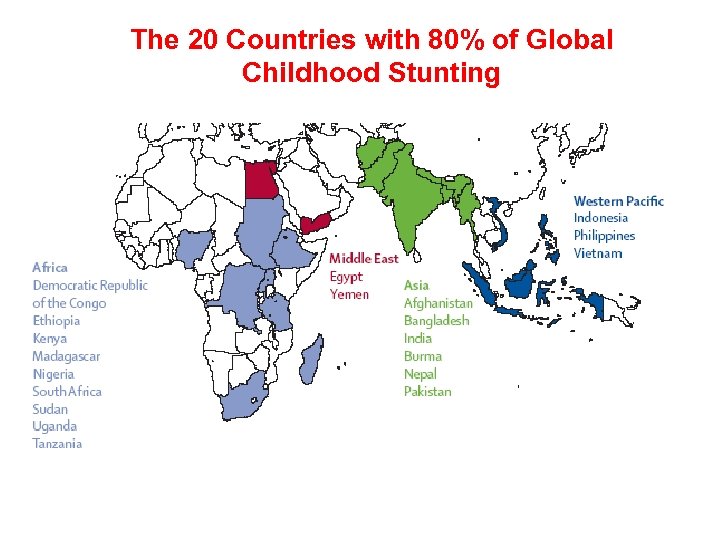
The 20 Countries with 80% of Global Childhood Stunting
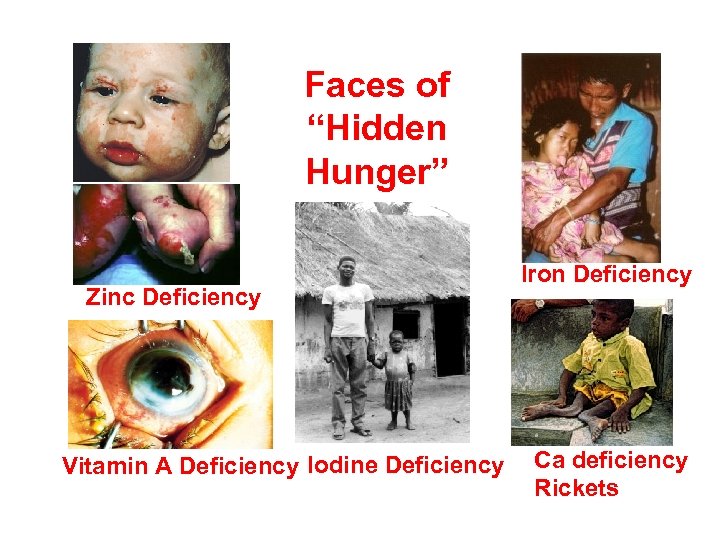
Faces of “Hidden Hunger” Zinc Deficiency Vitamin A Deficiency Iodine Deficiency Iron Deficiency Ca deficiency Rickets
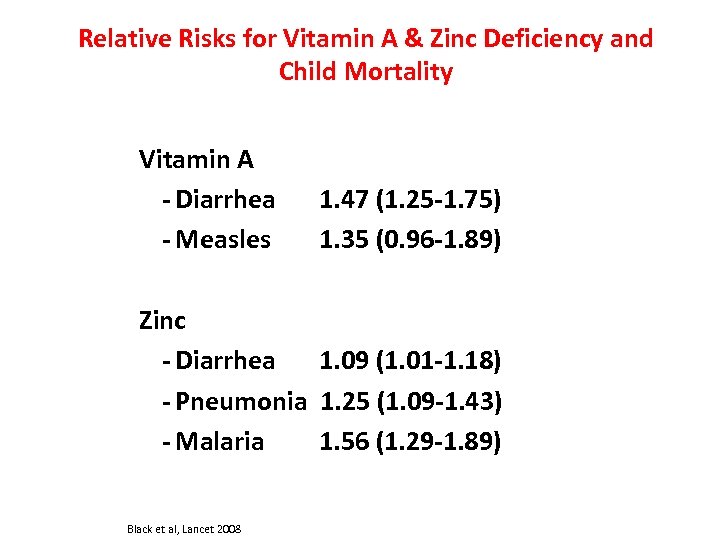
Relative Risks for Vitamin A & Zinc Deficiency and Child Mortality Vitamin A - Diarrhea - Measles 1. 47 (1. 25 -1. 75) 1. 35 (0. 96 -1. 89) Zinc - Diarrhea 1. 09 (1. 01 -1. 18) - Pneumonia 1. 25 (1. 09 -1. 43) - Malaria 1. 56 (1. 29 -1. 89) Black et al, Lancet 2008

Undernutrition Begins with the Mother Maternal undernutrition: underweight for height (low body mass index) Less visible micronutrient deficiencies May lead to health problems for the mother and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
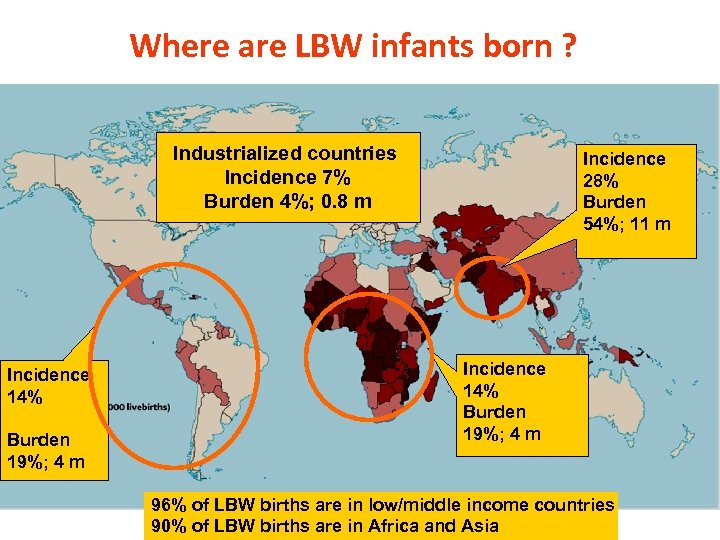
Where are LBW infants born ? Industrialized countries Incidence 7% Burden 4%; 0. 8 m Incidence 14% Burden 19%; 4 m Incidence 28% Burden 54%; 11 m Incidence 14% Burden 19%; 4 m 96% of LBW births are in low/middle income countries 90% of LBW births are in Africa and Asia

High Prevalence of IUGR, Stunting and Severe Wasting in Children Under 5 13 million babies are born each year with intrauterine growth restriction 171 million children are stunted; 32% of all children 55 million children are wasted; 19 million (35%) children severely affected
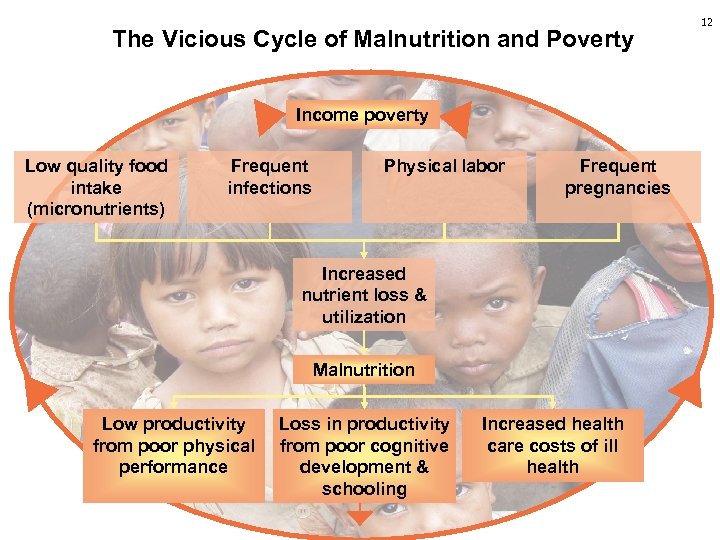
The Vicious Cycle of Malnutrition and Poverty Income poverty Low quality food intake (micronutrients) Frequent infections Physical labor Frequent pregnancies Increased nutrient loss & utilization Malnutrition Low productivity from poor physical performance Loss in productivity from poor cognitive development & schooling Increased health care costs of ill health 12
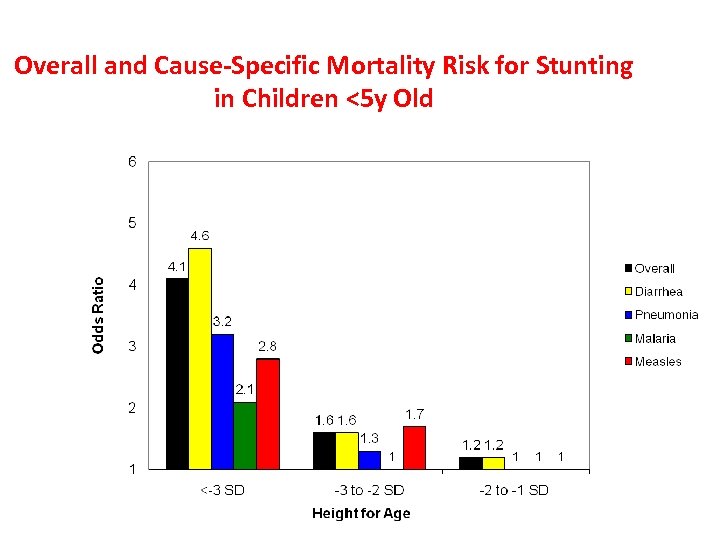
Overall and Cause-Specific Mortality Risk for Stunting in Children <5 y Old

The Burden of Maternal and Child Undernutrition IUGR, stunting and severe wasting together are responsible for 2. 2 million deaths and 91 million DALYS, 21% of the total for children under 5 Represents 7% of the total global disease burden for any age group, the highest for any risk factor for disease burden Together these risk factors are responsible for more than one-third—about 35%—of child deaths and 11% of the global total disease burden

Key Messages Global Burden of Undernutrition Together these risk factors are responsible for more than onethird—about 35%—of child deaths and 11% of the global total disease burden More than 3. 6 million mothers and children die each year as a result of undernutrition The very high mortality and disease burden resulting from these nutrition-related factors make a compelling case for the urgent implementation of proven interventions
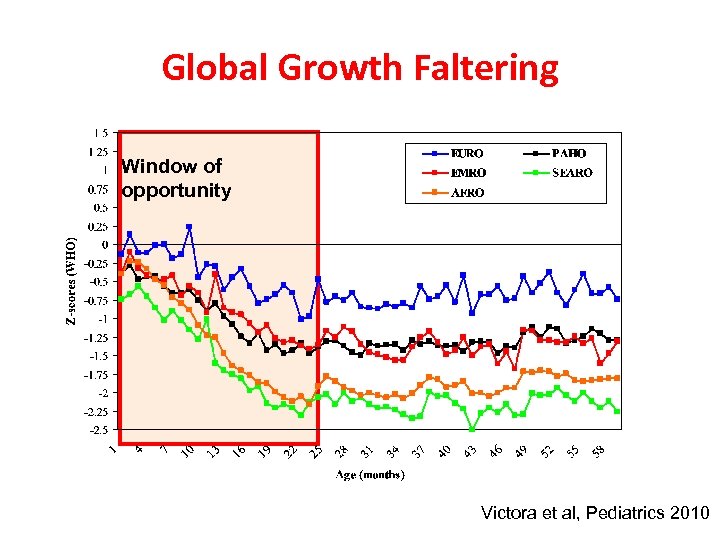
Global Growth Faltering Window of opportunity Victora et al, Pediatrics 2010

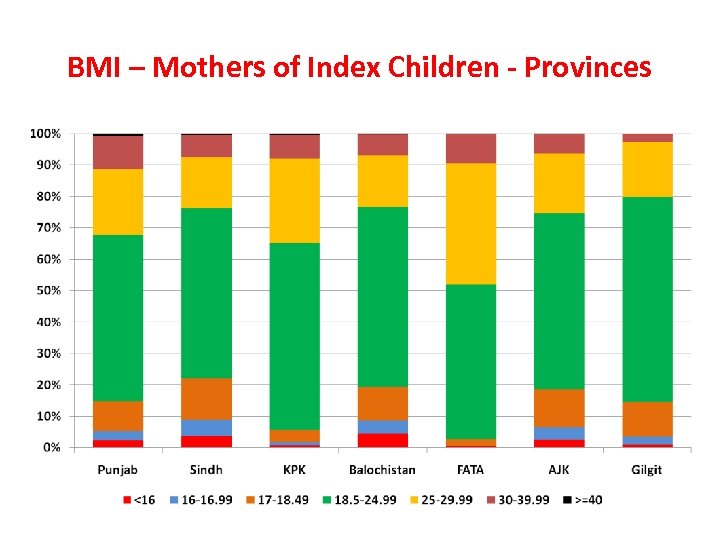
BMI – Mothers of Index Children - Provinces


The nature of poverty “ We think sometimes that poverty is only being hungry, naked and homeless. The poverty of being unwanted, unloved and uncared for is the greatest poverty. …” Mother Teresa
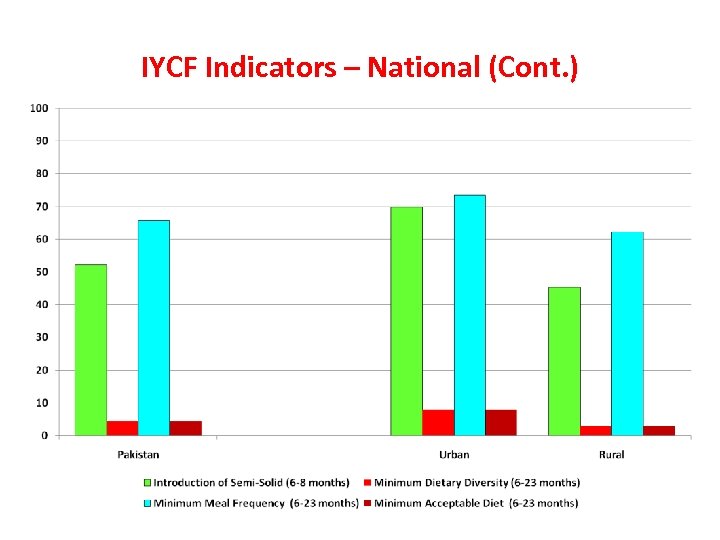
IYCF Indicators – National (Cont. )
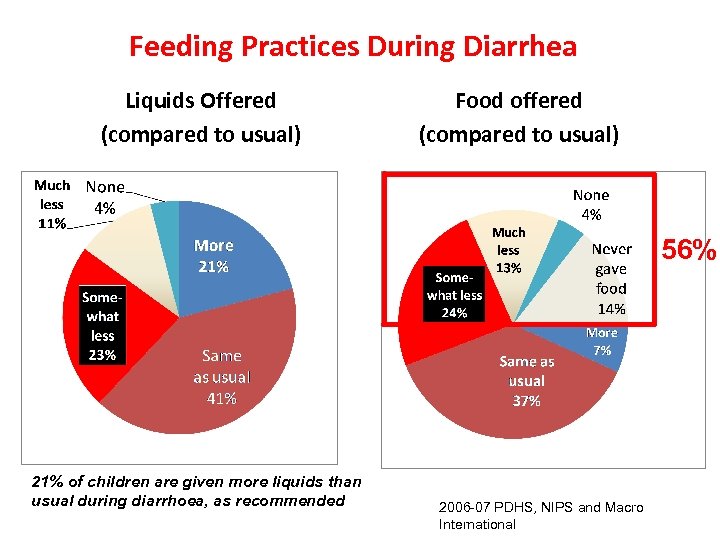
Feeding Practices During Diarrhea Liquids Offered (compared to usual) Food offered (compared to usual) 56% 21% of children are given more liquids than usual during diarrhoea, as recommended 2006 -07 PDHS, NIPS and Macro International


New sources of information • BMC Public Health Special issue on Li. ST interventions (March 2011) • Lancet Stillbirth series (March 2011) • Cochrane Library & 3 ie/DFID/BMGF reviews
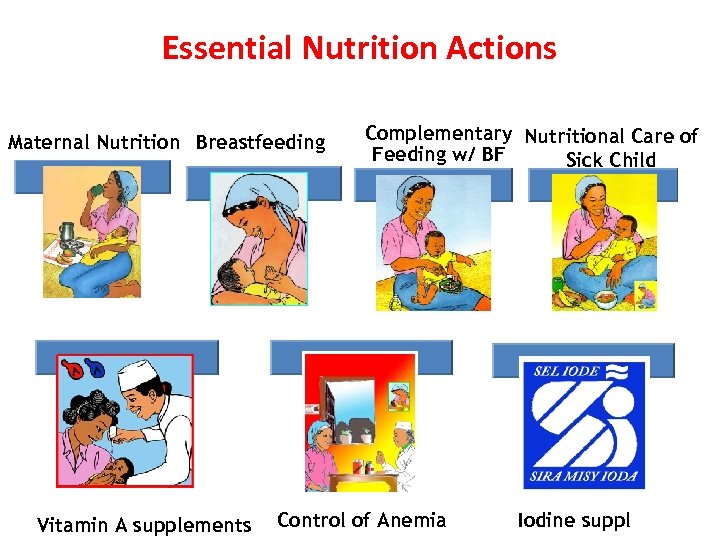
Essential Nutrition Actions Maternal Nutrition Breastfeeding Vitamin A supplements Complementary Nutritional Care of Feeding w/ BF Sick Child Control of Anemia Iodine suppl

Interventions with Sufficient Evidence to Implement in All Countries Maternal and Birth Outcomes • Iron folate supplementation • Maternal supplements of multiple micronutrients • Maternal iodine through iodization of salt • Maternal calcium supplementation • Interventions to reduce tobacco consumption or indoor air pollution Newborn Babies Infants and Children • Promotion of breastfeeding (individual and group counseling) • Behavior change communication for improved complementary feeding • Zinc supplementation • Zinc in management of diarrhea • Vitamin A fortification or supplementation • Universal salt iodization • Handwashing or hygiene interventions • Treatment of SAM

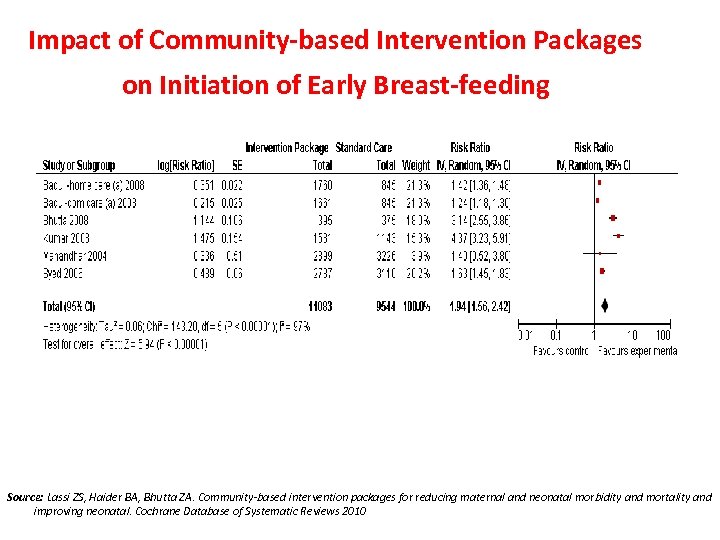
Impact of Community-based Intervention Packages on Initiation of Early Breast-feeding Source: Lassi ZS, Haider BA, Bhutta ZA. Community-based intervention packages for reducing maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality and improving neonatal. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010
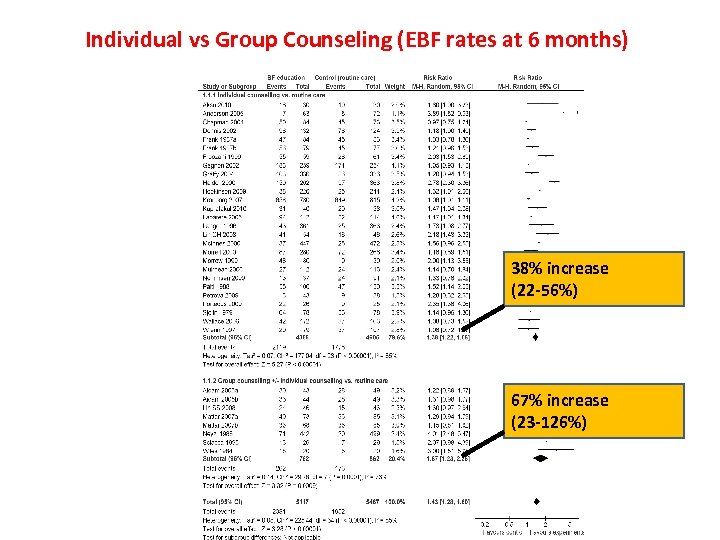
Individual vs Group Counseling (EBF rates at 6 months) 38% increase (22 -56%) 67% increase (23 -126%)

Interventions with Sufficient Evidence to Implement in Specific Situational Contexts Maternal and Birth Outcomes • Maternal supplements of balanced energy and protein • Maternal iodine supplements • Maternal deworming in pregnancy • Intermittent preventative treatment for malaria • Insecticide-treated bednets Newborn Babies Infants and Children • Neonatal vitamin A supplementation • Delayed cord clamping • Conditional cash transfer programs (with nutritional education) • Deworming • Iron fortification and supplementation programs • Insecticide-treated bednets

Local production of readyto-use therapeutic foods offers great promise

Who speaks for family planning? "Family planning is to maternal health what immunization is to child health" Khama Rogo (World Bank)

National Efforts Most countries with high levels of undernutrition are failing to reach undernourished mothers and children with effective interventions
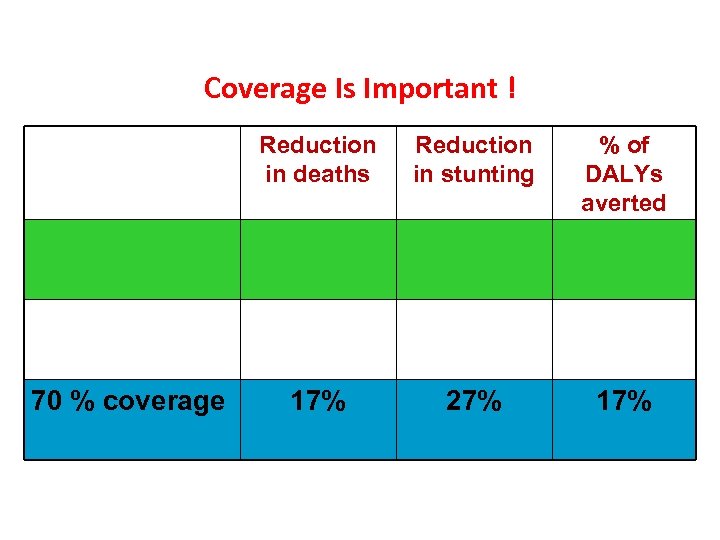
Coverage Is Important ! Reduction in deaths 70 % coverage Reduction in stunting % of DALYs averted 17% 27% 17%
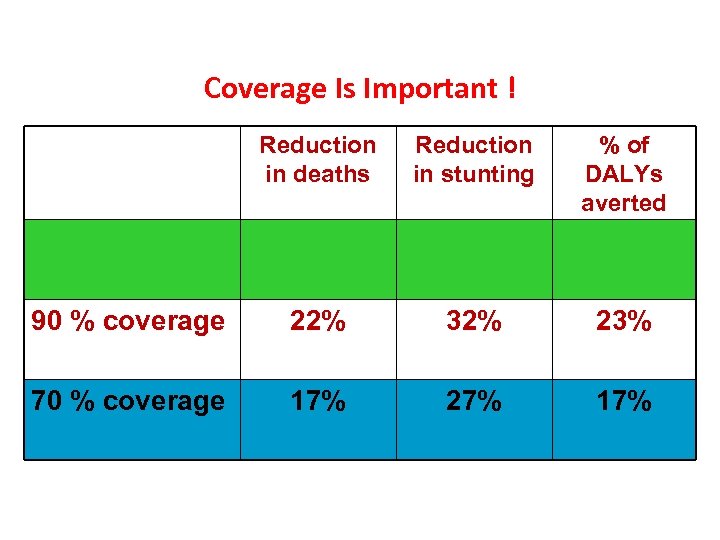
Coverage Is Important ! Reduction in deaths Reduction in stunting % of DALYs averted 90 % coverage 22% 32% 23% 70 % coverage 17% 27% 17%
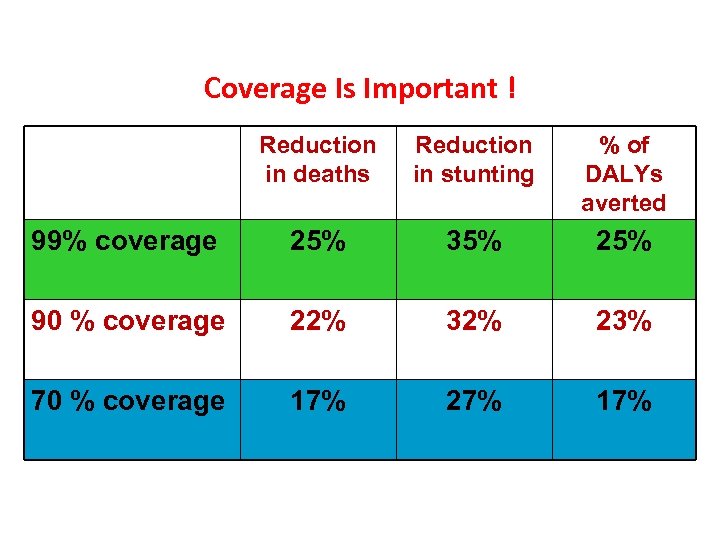
Coverage Is Important ! Reduction in deaths Reduction in stunting % of DALYs averted 99% coverage 25% 35% 25% 90 % coverage 22% 32% 23% 70 % coverage 17% 27% 17%
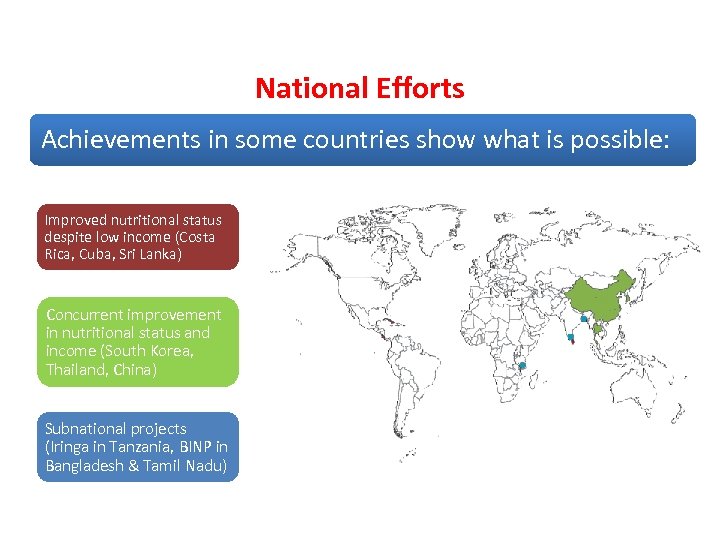
National Efforts Achievements in some countries show what is possible: Improved nutritional status despite low income (Costa Rica, Cuba, Sri Lanka) Concurrent improvement in nutritional status and income (South Korea, Thailand, China) Subnational projects (Iringa in Tanzania, BINP in Bangladesh & Tamil Nadu)

Priority Action Areas • Link maternal and infant nutrition • Scale up orphan interventions (Balanced Energy Protein supplementation for women of reproductive age, Complementary Feeding support in food insecure populations) • Community delivery platforms for nutrition • Link preconception care to nutrition – Adolescent nutrition – Folic acid fortification
cfcce04b46276d5a41b51bacbab5a53b.ppt