5711ff89ad0fc575008a3cd386724594.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

The Cereal Box Problem By Narineh Movsessian

Random or Chance Outcomes S How much precipitation is expected next year in the Kansas wheat belt? S How many people in your town are expected to get the flu this winter? S How much of an increase is expected in the value of a particular stock in the next two weeks?

“Predicting” the Future l l l Suppose each cereal box has one of 6 different colored pens. Orange Yellow Blue Pink Red Green Assume chances of getting any of the 6 colored pens are equal. How many boxes of cereal would you expect to have to buy to get a complete set of all six colored pens?

Method One Conduct an experiment. S Go on a shopping trip and repeatedly buy cereal boxes until you get a pen of each color. S This ends one shopping trip. S Repeat this process. S

Results of One Shopping Trip Shopping Orange Yellow Blue Trip 1 /// / // Pink Red /////// # of Green Boxes //// 21 We see that we bought 21 boxes of cereal before we had a complete set.

Method Two S S S Use a six sided die as a physical model for buying cereal boxes. Randomly let 1=orange 2=yellow 3=blue 4=pink 5=red 6=green One toss of the die will correspond to the purchase of one box.
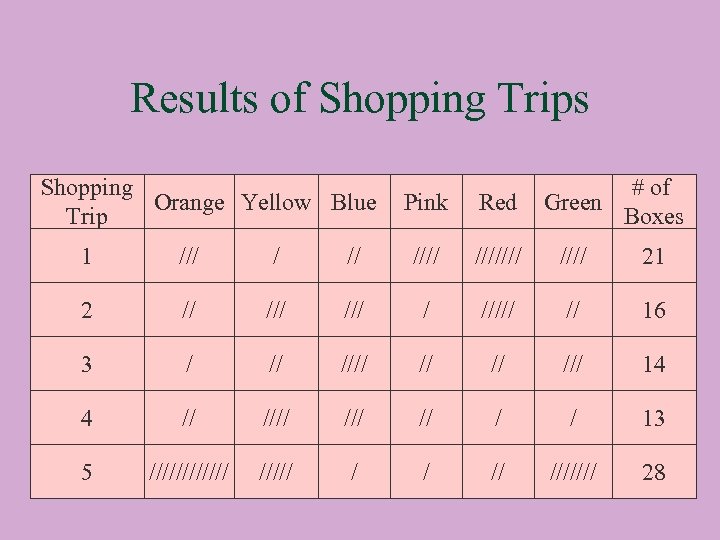
Results of Shopping Trips Shopping Orange Yellow Blue Trip Pink Red # of Green Boxes 1 /// /////// 21 2 // ///// // 16 3 / // /// 14 4 // /// // / / 13 5 ////// / / // /////// 28
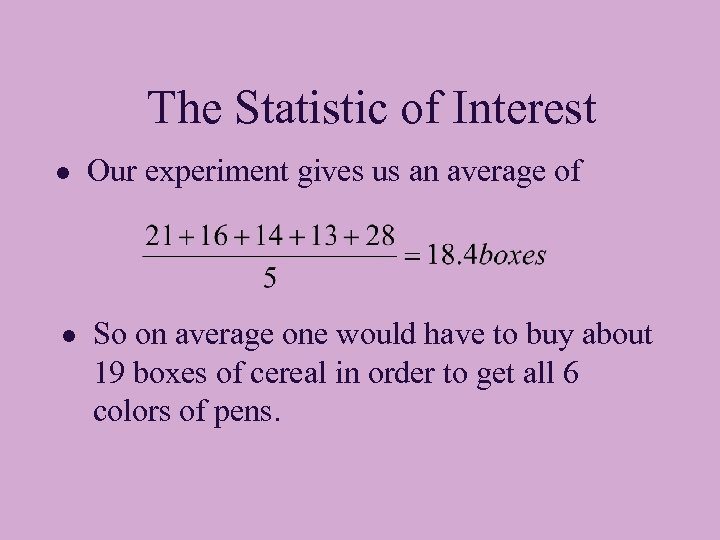
The Statistic of Interest l Our experiment gives us an average of l So on average one would have to buy about 19 boxes of cereal in order to get all 6 colors of pens.

Method Three S S S Using computer generated random numbers to simulate the experiment. The actual expected value was found using method three over a large number of trials, about 10, 000. The actual average is 14. 7.
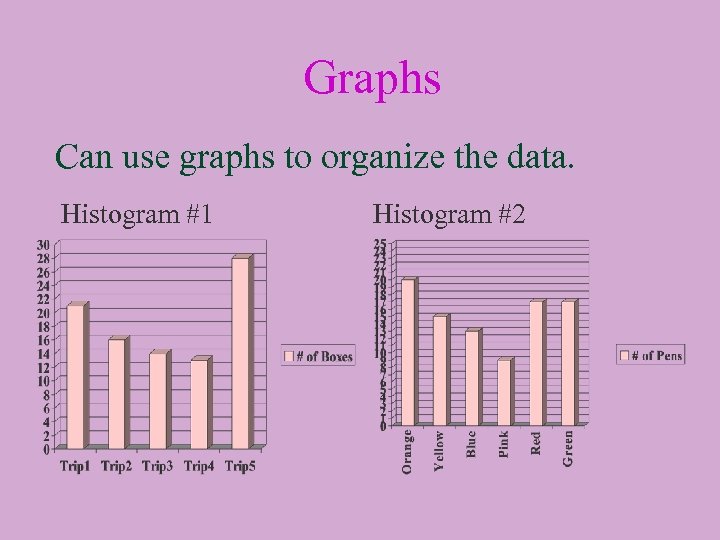
Graphs Can use graphs to organize the data. Histogram #1 Histogram #2

5711ff89ad0fc575008a3cd386724594.ppt