4b07a7c597dac4da95509aad1cdf87cb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 The CCSDS Cislunar Communications Architecture Keith Scott The MITRE Corporation CCSDS Meeting January 2007
The CCSDS Cislunar Communications Architecture Keith Scott The MITRE Corporation CCSDS Meeting January 2007
 Agenda • CCSDS Cislunar Space Internetworking Working Group Scope and Charter • Current Mission Architecture • Future Mission Scenarios • Networked Communications • Terrestrial Interoperability
Agenda • CCSDS Cislunar Space Internetworking Working Group Scope and Charter • Current Mission Architecture • Future Mission Scenarios • Networked Communications • Terrestrial Interoperability
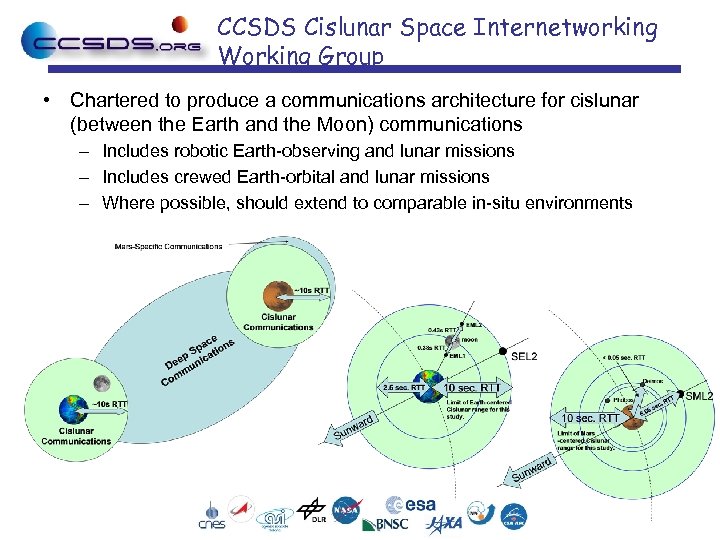 CCSDS Cislunar Space Internetworking Working Group • Chartered to produce a communications architecture for cislunar (between the Earth and the Moon) communications – Includes robotic Earth-observing and lunar missions – Includes crewed Earth-orbital and lunar missions – Where possible, should extend to comparable in-situ environments
CCSDS Cislunar Space Internetworking Working Group • Chartered to produce a communications architecture for cislunar (between the Earth and the Moon) communications – Includes robotic Earth-observing and lunar missions – Includes crewed Earth-orbital and lunar missions – Where possible, should extend to comparable in-situ environments
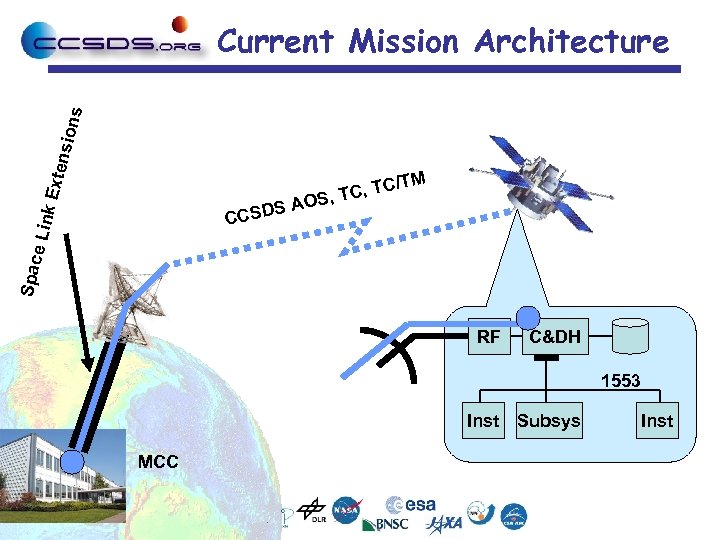 k Ex tens ions Current Mission Architecture AO Spac e Lin S CCSD /TM C, TC S, T RF C&DH 1553 Inst MCC Subsys Inst
k Ex tens ions Current Mission Architecture AO Spac e Lin S CCSD /TM C, TC S, T RF C&DH 1553 Inst MCC Subsys Inst
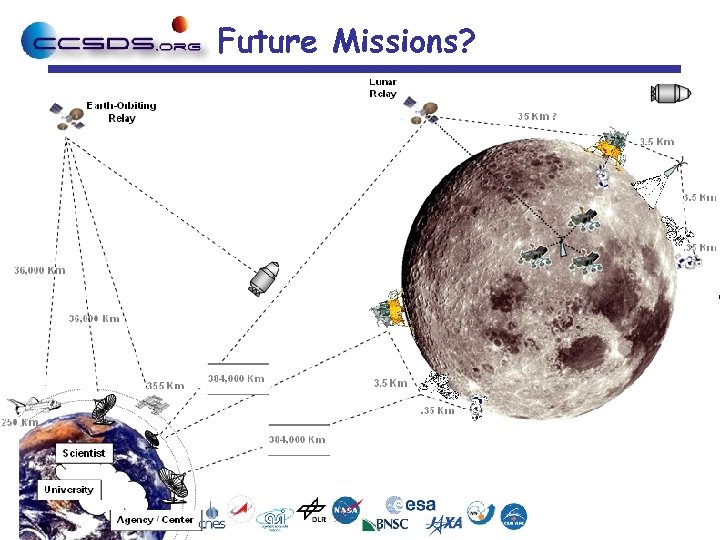 Future Missions?
Future Missions?
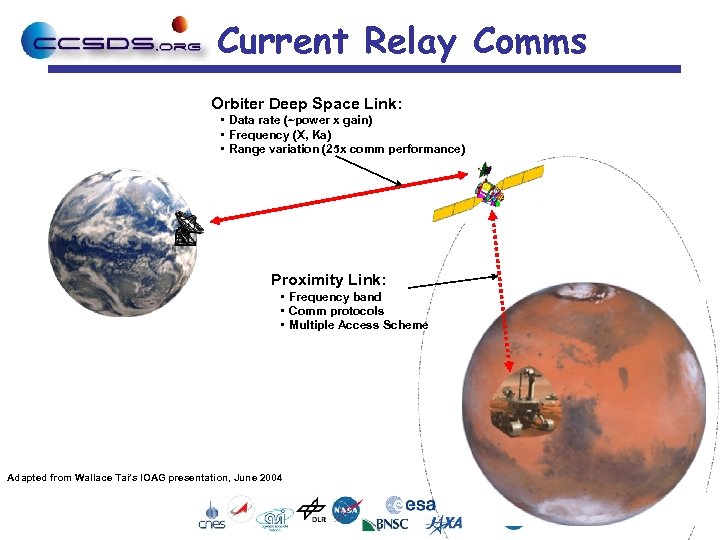 Current Relay Comms Orbiter Deep Space Link: • Data rate (~power x gain) • Frequency (X, Ka) • Range variation (25 x comm performance) Proximity Link: • Frequency band • Comm protocols • Multiple Access Scheme Adapted from Wallace Tai’s IOAG presentation, June 2004
Current Relay Comms Orbiter Deep Space Link: • Data rate (~power x gain) • Frequency (X, Ka) • Range variation (25 x comm performance) Proximity Link: • Frequency band • Comm protocols • Multiple Access Scheme Adapted from Wallace Tai’s IOAG presentation, June 2004
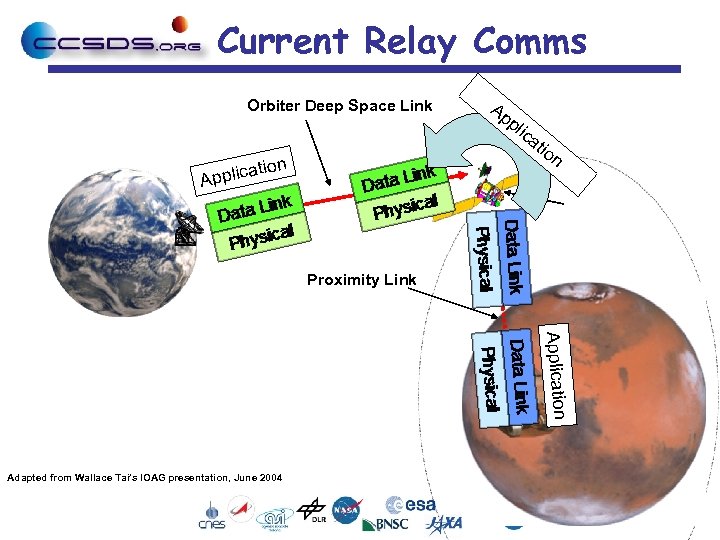 Current Relay Comms Orbiter Deep Space Link on plicati Ap Ap pl ica tio n Proximity Link Application Adapted from Wallace Tai’s IOAG presentation, June 2004
Current Relay Comms Orbiter Deep Space Link on plicati Ap Ap pl ica tio n Proximity Link Application Adapted from Wallace Tai’s IOAG presentation, June 2004
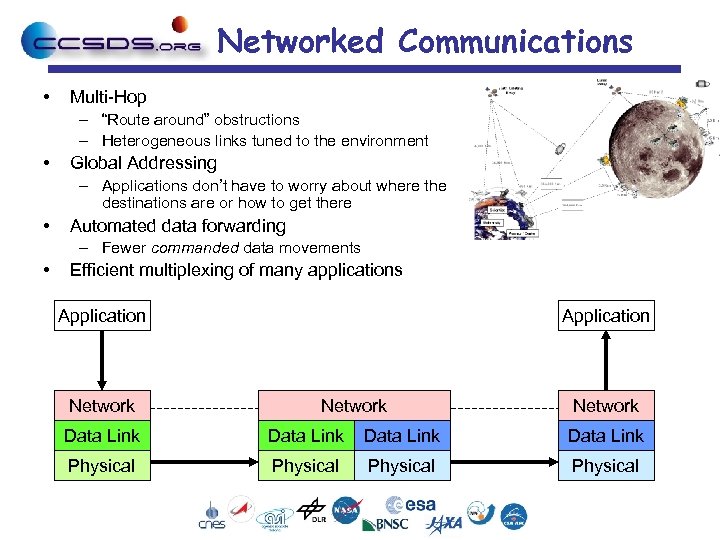 Networked Communications • Multi-Hop – “Route around” obstructions – Heterogeneous links tuned to the environment • Global Addressing – Applications don’t have to worry about where the destinations are or how to get there • Automated data forwarding – Fewer commanded data movements • Efficient multiplexing of many applications Application Network Data Link Physical
Networked Communications • Multi-Hop – “Route around” obstructions – Heterogeneous links tuned to the environment • Global Addressing – Applications don’t have to worry about where the destinations are or how to get there • Automated data forwarding – Fewer commanded data movements • Efficient multiplexing of many applications Application Network Data Link Physical
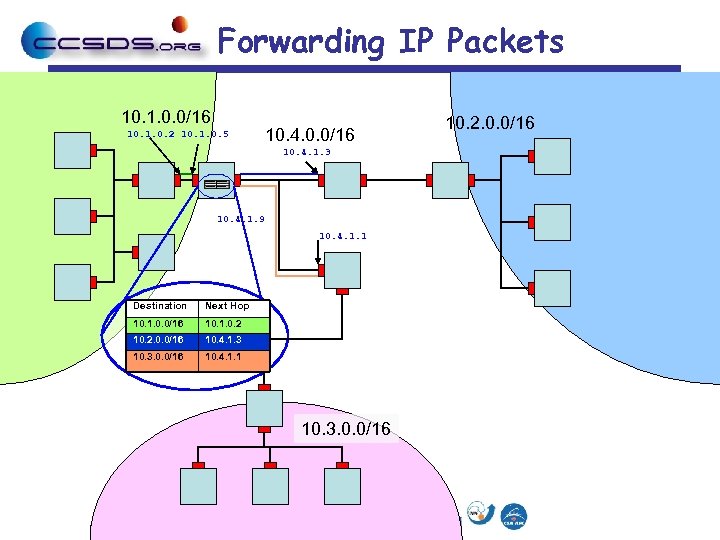 Forwarding IP Packets 10. 1. 0. 0/16 10. 1. 0. 2 10. 1. 0. 5 10. 4. 0. 0/16 10. 4. 1. 3 10. 4. 1. 9 10. 4. 1. 1 Destination Next Hop 10. 1. 0. 0/16 10. 1. 0. 2 10. 2. 0. 0/16 10. 4. 1. 3 10. 3. 0. 0/16 10. 4. 1. 1 10. 3. 0. 0/16 10. 2. 0. 0/16
Forwarding IP Packets 10. 1. 0. 0/16 10. 1. 0. 2 10. 1. 0. 5 10. 4. 0. 0/16 10. 4. 1. 3 10. 4. 1. 9 10. 4. 1. 1 Destination Next Hop 10. 1. 0. 0/16 10. 1. 0. 2 10. 2. 0. 0/16 10. 4. 1. 3 10. 3. 0. 0/16 10. 4. 1. 1 10. 3. 0. 0/16 10. 2. 0. 0/16
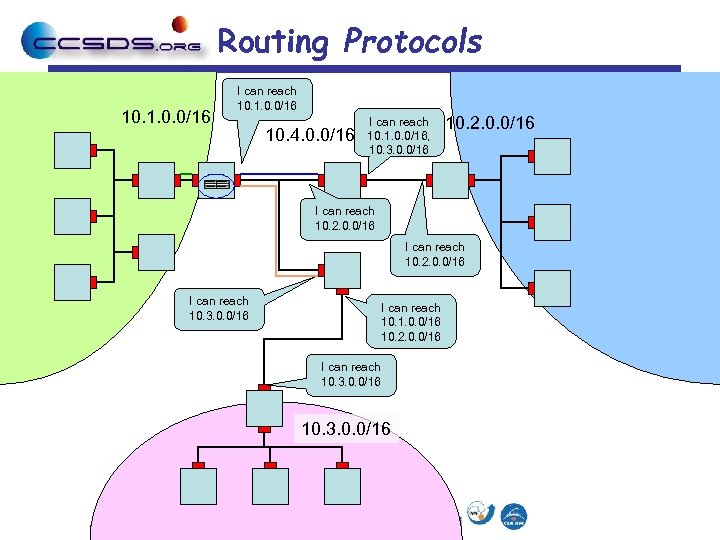 Routing Protocols 10. 1. 0. 0/16 I can reach 10. 1. 0. 0/16 10. 4. 0. 0/16 I can reach 10. 1. 0. 0/16, 10. 3. 0. 0/16 10. 2. 0. 0/16 I can reach 10. 3. 0. 0/16 I can reach 10. 1. 0. 0/16 10. 2. 0. 0/16 I can reach 10. 3. 0. 0/16
Routing Protocols 10. 1. 0. 0/16 I can reach 10. 1. 0. 0/16 10. 4. 0. 0/16 I can reach 10. 1. 0. 0/16, 10. 3. 0. 0/16 10. 2. 0. 0/16 I can reach 10. 3. 0. 0/16 I can reach 10. 1. 0. 0/16 10. 2. 0. 0/16 I can reach 10. 3. 0. 0/16
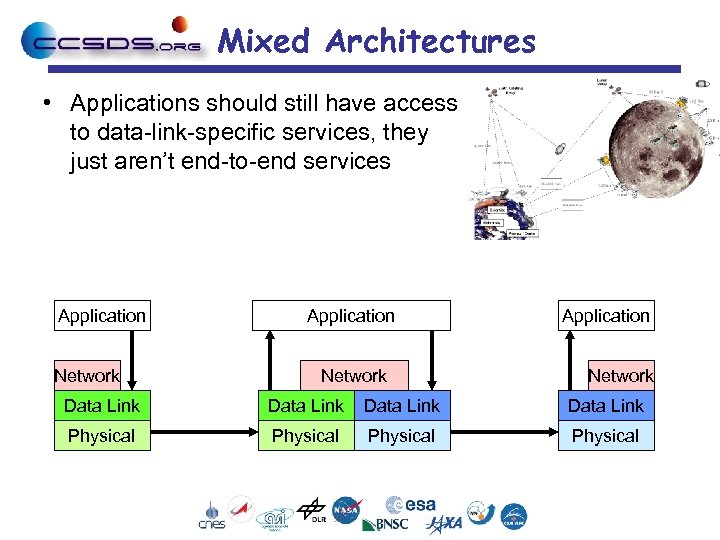 Mixed Architectures • Applications should still have access to data-link-specific services, they just aren’t end-to-end services Application Network Data Link Physical
Mixed Architectures • Applications should still have access to data-link-specific services, they just aren’t end-to-end services Application Network Data Link Physical
 Which Network Layer? • Choices include – – – IP ATM IPX Apple. Talk … • Advantages of IP – NOT connection-oriented (don’t need end-to-end signaling to set up path) – Wide availability of implementations / hardware • Including small implementations suitable for flight software – Interoperability with ground infrastructure • Simplifies testing / verification
Which Network Layer? • Choices include – – – IP ATM IPX Apple. Talk … • Advantages of IP – NOT connection-oriented (don’t need end-to-end signaling to set up path) – Wide availability of implementations / hardware • Including small implementations suitable for flight software – Interoperability with ground infrastructure • Simplifies testing / verification
 Other Topics in Green Book • • Quality of Service Security Emergency Commanding Overlay Communications
Other Topics in Green Book • • Quality of Service Security Emergency Commanding Overlay Communications
 Terrestrial Data Transport • What support is needed in the ground infrastructure to support IP-based missions? • Spacecraft built by Agency. A that uses IP networking using Agency. B’s ground station – Several options, depending on ground station capabilities and inter-agency connectivity characteristics • Space Link Extensions return-all-frames and return-channel-frames services being prototyped now by NASA, ESA, JAXA • Direct routed IP from the ground station – What changes would this require at ground stations? – What are the constraints on inter-agency connections (security, Qo. S)? • Tunnel IP datagrams from ground station to mission operations – What changes would this require at ground stations? – What are the constraints on inter-agency connections (security, Qo. S)?
Terrestrial Data Transport • What support is needed in the ground infrastructure to support IP-based missions? • Spacecraft built by Agency. A that uses IP networking using Agency. B’s ground station – Several options, depending on ground station capabilities and inter-agency connectivity characteristics • Space Link Extensions return-all-frames and return-channel-frames services being prototyped now by NASA, ESA, JAXA • Direct routed IP from the ground station – What changes would this require at ground stations? – What are the constraints on inter-agency connections (security, Qo. S)? • Tunnel IP datagrams from ground station to mission operations – What changes would this require at ground stations? – What are the constraints on inter-agency connections (security, Qo. S)?
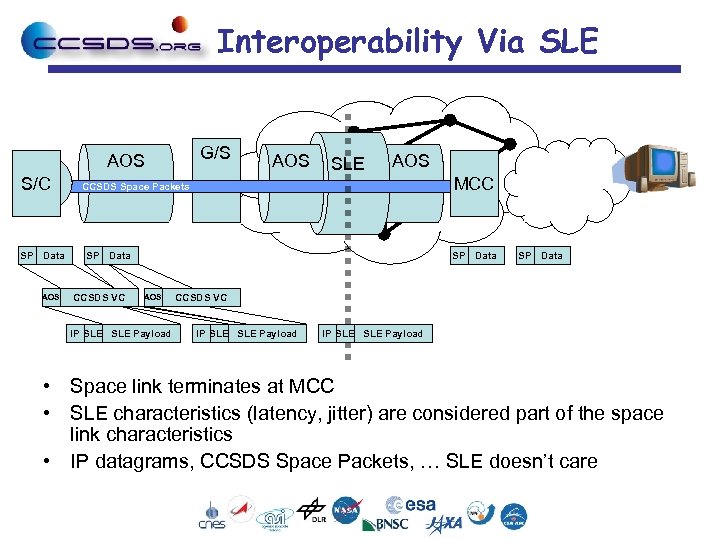 Interoperability Via SLE G/S AOS S/C SP Data AOS SLE AOS CCSDS Space Packets SP Data CCSDS VC MCC SP Data AOS IP SLE Payload SP Data CCSDS VC IP SLE SLE Payload • Space link terminates at MCC • SLE characteristics (latency, jitter) are considered part of the space link characteristics • IP datagrams, CCSDS Space Packets, … SLE doesn’t care
Interoperability Via SLE G/S AOS S/C SP Data AOS SLE AOS CCSDS Space Packets SP Data CCSDS VC MCC SP Data AOS IP SLE Payload SP Data CCSDS VC IP SLE SLE Payload • Space link terminates at MCC • SLE characteristics (latency, jitter) are considered part of the space link characteristics • IP datagrams, CCSDS Space Packets, … SLE doesn’t care
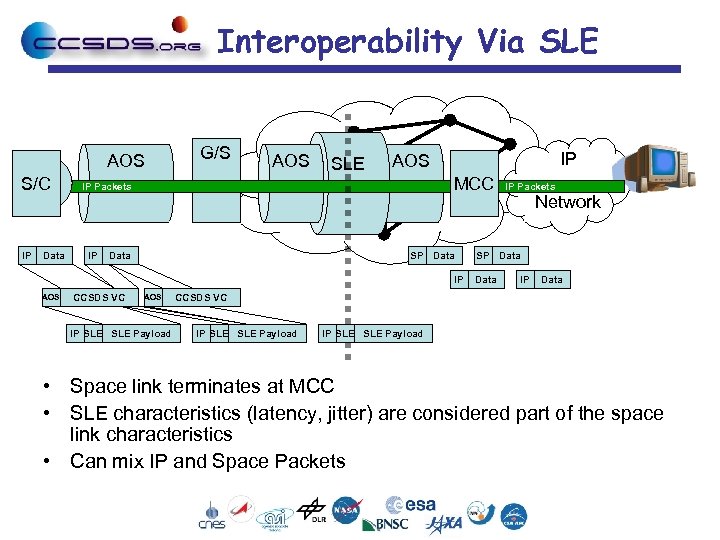 Interoperability Via SLE AOS S/C IP Data G/S AOS SLE MCC IP Packets IP Data IP AOS SP Data IP AOS CCSDS VC AOS IP SLE Payload IP Packets Network SP Data IP Data CCSDS VC IP SLE SLE Payload • Space link terminates at MCC • SLE characteristics (latency, jitter) are considered part of the space link characteristics • Can mix IP and Space Packets
Interoperability Via SLE AOS S/C IP Data G/S AOS SLE MCC IP Packets IP Data IP AOS SP Data IP AOS CCSDS VC AOS IP SLE Payload IP Packets Network SP Data IP Data CCSDS VC IP SLE SLE Payload • Space link terminates at MCC • SLE characteristics (latency, jitter) are considered part of the space link characteristics • Can mix IP and Space Packets
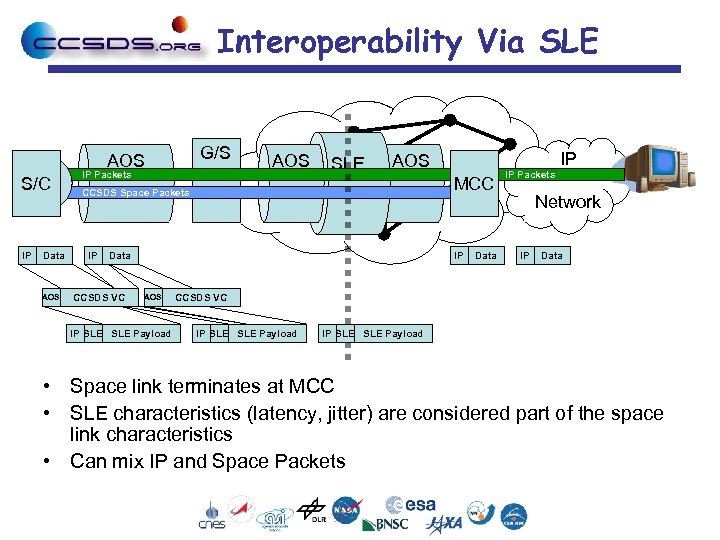 Interoperability Via SLE G/S AOS S/C IP Data AOS IP Packets AOS SLE AOS CCSDS Space Packets IP Data CCSDS VC MCC IP AOS IP SLE Payload Data IP Packets IP Network IP Data CCSDS VC IP SLE SLE Payload • Space link terminates at MCC • SLE characteristics (latency, jitter) are considered part of the space link characteristics • Can mix IP and Space Packets
Interoperability Via SLE G/S AOS S/C IP Data AOS IP Packets AOS SLE AOS CCSDS Space Packets IP Data CCSDS VC MCC IP AOS IP SLE Payload Data IP Packets IP Network IP Data CCSDS VC IP SLE SLE Payload • Space link terminates at MCC • SLE characteristics (latency, jitter) are considered part of the space link characteristics • Can mix IP and Space Packets
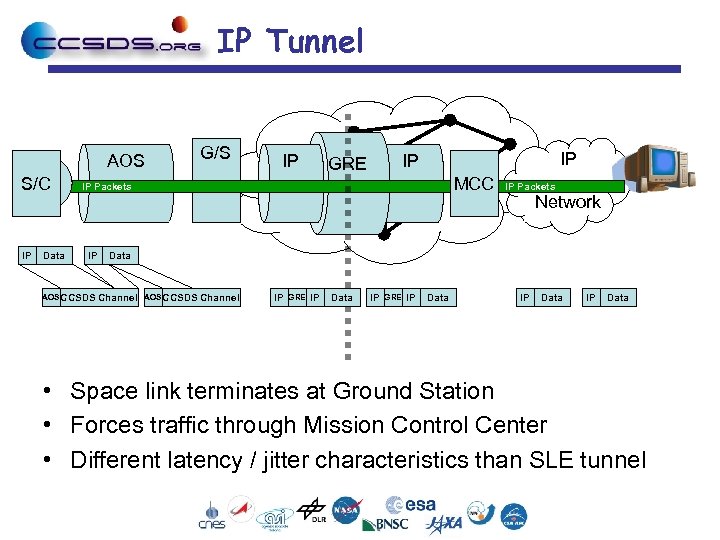 IP Tunnel AOS S/C IP Data G/S IP IP IP GRE MCC IP Packets IP AOS CCSDS IP Packets Network Data Channel AOS CCSDS Channel IP GRE IP Data • Space link terminates at Ground Station • Forces traffic through Mission Control Center • Different latency / jitter characteristics than SLE tunnel
IP Tunnel AOS S/C IP Data G/S IP IP IP GRE MCC IP Packets IP AOS CCSDS IP Packets Network Data Channel AOS CCSDS Channel IP GRE IP Data • Space link terminates at Ground Station • Forces traffic through Mission Control Center • Different latency / jitter characteristics than SLE tunnel
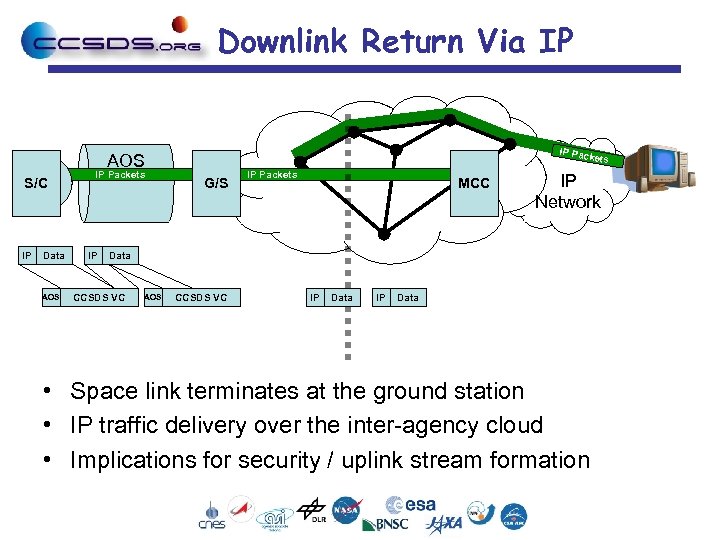 Downlink Return Via IP IP Pac kets AOS S/C IP Data AOS IP Packets IP G/S IP Packets MCC IP Network Data CCSDS VC AOS CCSDS VC IP Data • Space link terminates at the ground station • IP traffic delivery over the inter-agency cloud • Implications for security / uplink stream formation
Downlink Return Via IP IP Pac kets AOS S/C IP Data AOS IP Packets IP G/S IP Packets MCC IP Network Data CCSDS VC AOS CCSDS VC IP Data • Space link terminates at the ground station • IP traffic delivery over the inter-agency cloud • Implications for security / uplink stream formation
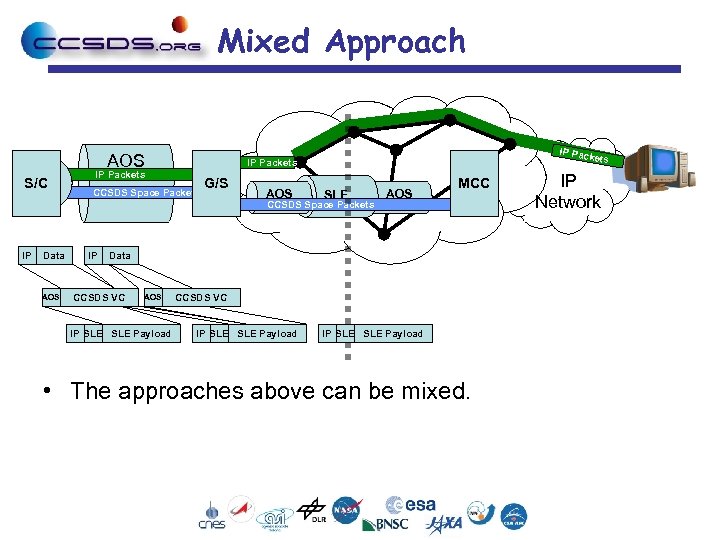 Mixed Approach AOS S/C IP Pac kets IP Packets CCSDS Space Packets G/S AOS SLE CCSDS Space Packets IP Data AOS IP AOS MCC Data CCSDS VC AOS IP SLE Payload CCSDS VC IP SLE SLE Payload • The approaches above can be mixed. IP Network
Mixed Approach AOS S/C IP Pac kets IP Packets CCSDS Space Packets G/S AOS SLE CCSDS Space Packets IP Data AOS IP AOS MCC Data CCSDS VC AOS IP SLE Payload CCSDS VC IP SLE SLE Payload • The approaches above can be mixed. IP Network
 Conclusions • A network layer unifies possibly heterogeneous data links • Automated data forwarding simplifies operations over what we do now or might do using current protocols • An IP-based system leverages commercial technologies and can leverage the terrestrial infrastructure • An IP-based infrastructure can handle the range of data types we currently envision and has shown flexibility in the past • The technical issues with an IP infrastructure in space are addressable • It’s possible to mix-and-match new routing components alongside traditional operations in the same spacecraft and terrestrial systems
Conclusions • A network layer unifies possibly heterogeneous data links • Automated data forwarding simplifies operations over what we do now or might do using current protocols • An IP-based system leverages commercial technologies and can leverage the terrestrial infrastructure • An IP-based infrastructure can handle the range of data types we currently envision and has shown flexibility in the past • The technical issues with an IP infrastructure in space are addressable • It’s possible to mix-and-match new routing components alongside traditional operations in the same spacecraft and terrestrial systems
 Status • Green book (architecture) done and about to be submitted to CESG for review (final editing completed last week) • Starting first Recommendation dealing with ‘simple’ IPbased spacecraft operations – Focus on terrestrial interoperability
Status • Green book (architecture) done and about to be submitted to CESG for review (final editing completed last week) • Starting first Recommendation dealing with ‘simple’ IPbased spacecraft operations – Focus on terrestrial interoperability
 Questions?
Questions?


