3d4537cd6c1ad236f38f930fa825361c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58

The CBD for Botanists An introduction to the Convention on Biological Diversity for people working with botanical collections

What this presentation will cover • Introduction to the CBD • How the CBD operates • The CBD and botanical institutions • Practical implementation

Introduction

What is the CBD? • Result of Rio Earth Summit • A commitment to: – conserve biological diversity – use biological resources sustainably – share benefits fairly and equitably

What is unique about this treaty? • A framework for action • Decisions at the national level • Recognition that biodiversity is not equally distributed • Benefit-sharing

Parties to the CBD Party Non-Party

Scope of the CBD: What is biological diversity?

Importance of biodiversity
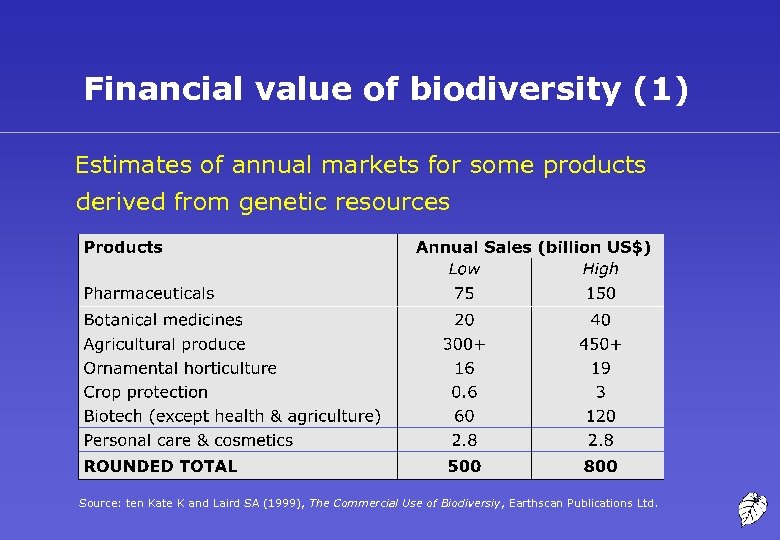
Financial value of biodiversity (1) Estimates of annual markets for some products derived from genetic resources Source: ten Kate K and Laird SA (1999), The Commercial Use of Biodiversiy, Earthscan Publications Ltd.

Financial value of biodiversity (2)

Threats to biodiversity • Habitat loss • Invasive alien species • Over-exploitation • Pollution and climate change

How does the CBD approach the challenge? (1) • Common concern of humankind • Sovereign rights • Countries responsible for conservation • Preventative and precautionary approach

How does the CBD approach the challenge? (2) • Ecosystem approach: – prioritises in situ conservation – backed up by ex situ conservation • Sustainable use

How the CBD operates

Bodies of the CBD • COP • SBSTTA • Secretariat • Ad-hoc working groups • Clearing House Mechanism

How is the CBD funded?

Thematic work programmes agricultural biodiversity of inland waters biodiversity of dry and subhumid lands forest biodiversity marine and coastal biodiversity mountain biodiversity

Cross-cutting issues plant conserv ation inva siv e al ien spe cies agricultural biodiversity of inland waters nal ditio dg tra owle kn e bio -s afe biodiversity of dry and subhumid lands ectual intell operty pr rights forest biodiversity marine and coastal biodiversity mountain biodiversity ty my ono ax t access to gene tic resourc es
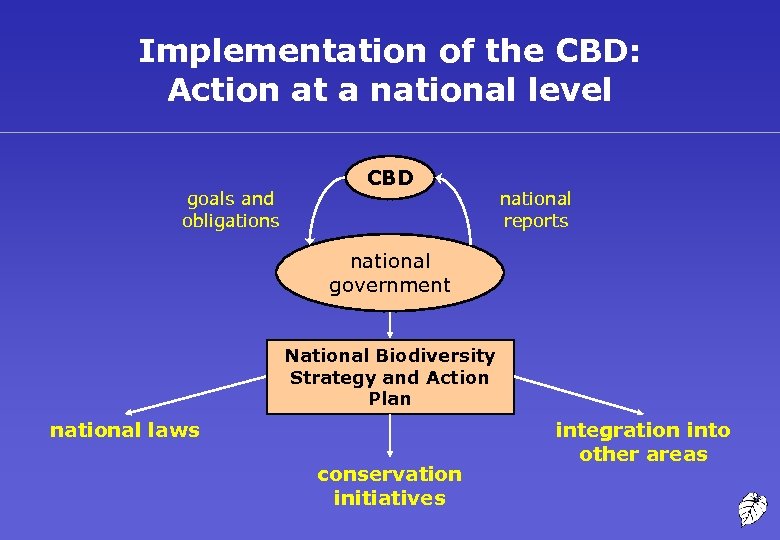
Implementation of the CBD: Action at a national level goals and obligations CBD national reports national government National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan national laws conservation initiatives integration into other areas
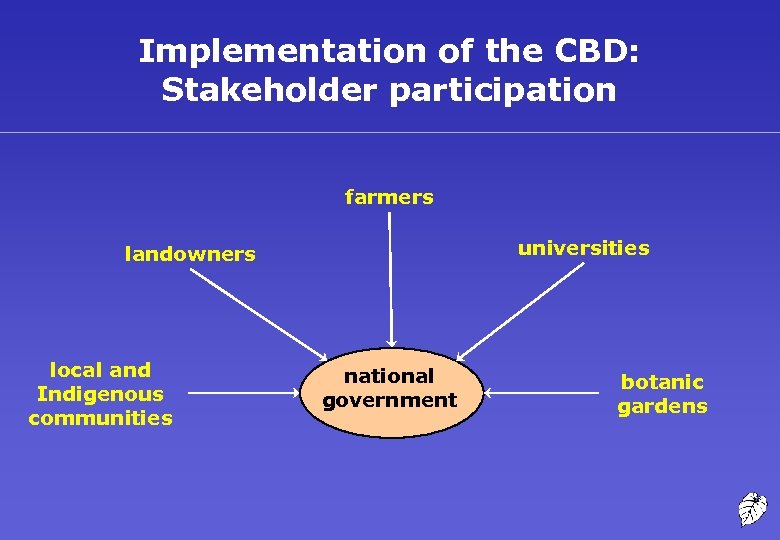
Implementation of the CBD: Stakeholder participation farmers universities landowners local and Indigenous communities national government botanic gardens

Botanical institutions

Botanical institutions support the CBD

Botanical institutions support the CBD 7 - identification & monitoring 8 - in-situ conservation 9 - ex-situ conservation 10 - sustainable use 12 - research & training 13 - public education & awareness 15 - access to genetic resources 16 - access to & transfer of technology 17 - exchange of information 18 - technical & scientific cooperation

Article 15: Access and benefitsharing - ‘the grand bargain’ • Follow national law • Prior informed consent • Mutually agreed terms • Benefit-sharing
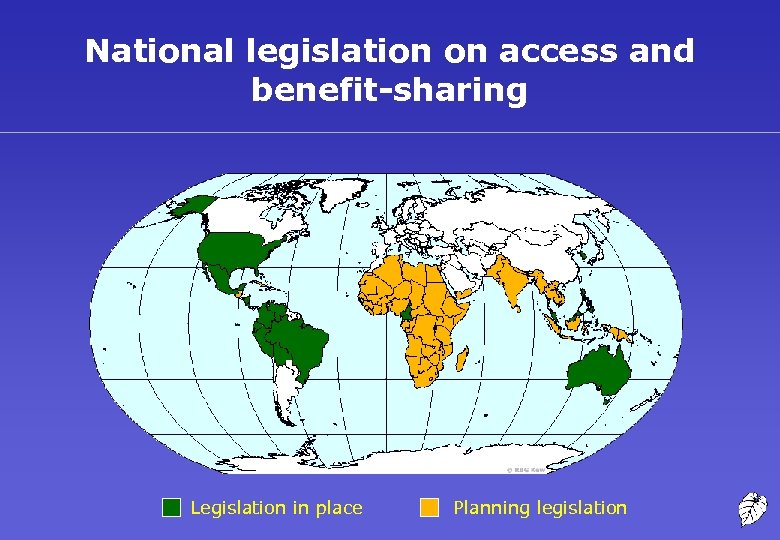
National legislation on access and benefit-sharing Legislation in place Planning legislation

Benefit-sharing • What kinds of benefits? • With whom should they be shared? • What is fair and equitable? • Bonn Guidelines

Pre-CBD collections • Article 15(3) – excludes pre-CBD collections

Commercialisation • Issues for institutions • What should institutions do? – define commercialisation – commercial use – commercial supply – commercialisation policy

Why is access and benefit-sharing important for botanists? • Exchange and access • Builds partnerships • Supports national implementation • Funding • Builds trust

Implementation

CBD-friendly work: Common challenges © Kate Davis

CBD-friendly work: Fieldwork (1) • Plan Ahead! – permission to collect – CITES permits – export & import permits – plant health • Work with local partners

CBD-friendly work: Fieldwork (2) • Prior Informed Consent – whose consent? – what information? – who can help?

CBD-friendly work: Fieldwork (3) • Agree terms – check terms on permits! • Keep written records – permits, letters, emails, notes
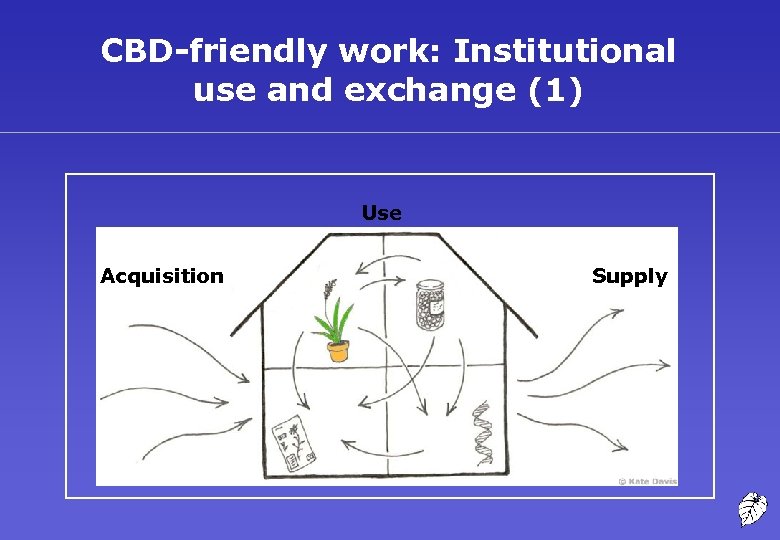
CBD-friendly work: Institutional use and exchange (1) Use Acquisition Supply

CBD-friendly work: Institutional use and exchange (2) • Acquire material legally • Use under same terms • Supply under same terms

CBD-friendly work: Institutional use and exchange (3) • Written agreements • Tracking • Internal procedures • Institutional CBD policy

CBD-friendly work: Benefit-sharing for botanists • For example… – joint fieldwork – joint research – access to information – capacity building – training and education – staff exchange – fees/royalties

CBD-friendly work: Plant sales • Right to sell? • What conditions? • What benefits?

Collective action • Stay informed and get involved! – work with stakeholders – work with government – work with botanic gardens

Further information on the CBD and National Focal Points The Secretariat of the CBD World Trade Centre 393 Saint Jacques, Suite 300 Montreal Québec Canada H 2 Y 1 N 9 CBD website: www. biodiv. org

Additional slides

Genetic resources • Any material of plant, animal, fungal, microbial or other origin containing functional units of heredity of actual or potential value • ‘Functional unit of heredity’ a matter for interpretation • May include herbarium specimens

Ecosystem services • Provide: –goods –ecosystem functions –aesthetic and cultural values • High global value • Cost of loss greatly exceeds benefits

Repatriation of information • Back to country of origin • Through exchange of information and access • Planning is vital!

The Bonn Guidelines · Guidance for governments and other stakeholders – responsibilities – negotiating access and benefitsharing – elements for agreements – benefit-sharing examples • Implications for collections © RBG Kew

Traditional Knowledge (1)

Traditional Knowledge (2) • National legislation • Indigenous Peoples’ declarations and codes of conduct • Professional codes of conduct • People’s Biodiversity Registers

Intellectual Property (1) · Types of IP include: – patents – copyright – plant breeders rights · IP and plants?

Intellectual Property (2) · Current issues – patents on life? – disclose sources? – IP and benefit-sharing • Implications for collections – agree, and track, benefitsharing terms

Global Taxonomy Initiative • The ‘taxonomic impediment’ • GTI supports: – taxonomic needs assessment – taxonomic information sharing – training – collaboration – National Focal Points

Global Strategy for Plant Conservation · 16 Targets for: – understanding and documenting plant diversity – conserving plant diversity – sustainable use – education – capacity building

Invasive alien species · Environmental and economic costs · ‘Guiding Principles’: – advice and goals • Role of horticulture
Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety • Promotes safe use of Living Modified Organisms (LMOs) • Procedure for governments on imports containing LMOs • Biosafety Clearing House • Relevance to botanical collections © Kate Davis

International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (1) • Multilateral system • Facilitated crop access • Sharing of financial benefits • Farmers’ rights

International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (2) • Facilitated access: – for food/feed purposes only – quickly, with minimal cost – standard MTA – recipients keep material available – no before/after date • Implications for collections

World Summit on Sustainable Development • WEHAB: water & sanitation, energy, health, agriculture, biodiversity • 3 main outcomes: – Plan of Implementation – Johannesburg Declaration – Type II initiatives • Implications for collections

Blank slide
3d4537cd6c1ad236f38f930fa825361c.ppt