4de85ba1fa39b8a8fd10e2614ea2bf87.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 81

 THE CATALAN LANGUAGE TODAY: AN INTRODUCTION TO SOME ASPECTS
THE CATALAN LANGUAGE TODAY: AN INTRODUCTION TO SOME ASPECTS

 INSTRUCTIONS To see the next slide: – Press
INSTRUCTIONS To see the next slide: – Press
 CREDITS & ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Author: David Casals Andreu Coordinator: Conxa Planas Assistants: Anna Grau Francesc González Sílvia Catasús Meritxell Planas Translation: Escola d’Idiomes Moderns Design: CASS Photography: Giles Plowden Web edition: Eduard Sosa Power. Point technical advice: Genís Pérez Financial support for this product was received from the Commission for Universities and Research, of the Ministry of Innovation, Universities and Enterprise, of the Government of Catalonia. The total or partial reproduction of this work is any form prohibited without the expressed written consent of the holders of the copyright. © Linguistic Services of the University of Barcelona. This electronic product is part of the Interc@t project, the language program for participants on university exchanges and students for other areas. Institutional coordination of the Interc@t project: Language Policy Office at the Commission for Universities and Research. The project was supported by: Comissionat per a Universitats i Recerca, Serveis Lingüístics (UB), Servei de Llengües (UAB), Servei de Llengües i Terminologia (UPC), Gabinet Lingüístic (UPF), Servei de Llengües Modernes (Ud. G), Servei de Llengua i Terminologia (Ud. L), Servei Lingüístic (URV), Unitat de Llengua (UOC), Universitat Ramon Llull.
CREDITS & ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Author: David Casals Andreu Coordinator: Conxa Planas Assistants: Anna Grau Francesc González Sílvia Catasús Meritxell Planas Translation: Escola d’Idiomes Moderns Design: CASS Photography: Giles Plowden Web edition: Eduard Sosa Power. Point technical advice: Genís Pérez Financial support for this product was received from the Commission for Universities and Research, of the Ministry of Innovation, Universities and Enterprise, of the Government of Catalonia. The total or partial reproduction of this work is any form prohibited without the expressed written consent of the holders of the copyright. © Linguistic Services of the University of Barcelona. This electronic product is part of the Interc@t project, the language program for participants on university exchanges and students for other areas. Institutional coordination of the Interc@t project: Language Policy Office at the Commission for Universities and Research. The project was supported by: Comissionat per a Universitats i Recerca, Serveis Lingüístics (UB), Servei de Llengües (UAB), Servei de Llengües i Terminologia (UPC), Gabinet Lingüístic (UPF), Servei de Llengües Modernes (Ud. G), Servei de Llengua i Terminologia (Ud. L), Servei Lingüístic (URV), Unitat de Llengua (UOC), Universitat Ramon Llull.
 PREFACE Lingcat is a multimedia presentation that describes the situation of the Catalan language today. It aims to answer exchange students’ questions on sociolinguistic issues in Catalonia and the Catalanspeaking areas, with particular emphasis on the university context. Lingcat is a useful source of information for those who want to find out more about the language, either before they come to Catalonia, or shortly after their arrival. The materials compiled here have been used for many years in the introductory sessions that the University of Barcelona runs for students from abroad. Lingcat is part of Intercat, the language program organized by the Catalan universities for these students. Unlike other multimedia packages available, Lingcat provides a step by step introduction specifically for exchange students, focusing on aspects of the Catalan language and its uses in the social situations that they are likely to encounter. Lingcat is divided into eight sections: “Introduction”, “Catalan and Europe”, Sociolinguistics”, “ Linguistic proficiency”, “Catalan in the mass media”, “Catalan in the universities”, “Other information resources” and “Opportunities to learn Catalan”. Here students will find:
PREFACE Lingcat is a multimedia presentation that describes the situation of the Catalan language today. It aims to answer exchange students’ questions on sociolinguistic issues in Catalonia and the Catalanspeaking areas, with particular emphasis on the university context. Lingcat is a useful source of information for those who want to find out more about the language, either before they come to Catalonia, or shortly after their arrival. The materials compiled here have been used for many years in the introductory sessions that the University of Barcelona runs for students from abroad. Lingcat is part of Intercat, the language program organized by the Catalan universities for these students. Unlike other multimedia packages available, Lingcat provides a step by step introduction specifically for exchange students, focusing on aspects of the Catalan language and its uses in the social situations that they are likely to encounter. Lingcat is divided into eight sections: “Introduction”, “Catalan and Europe”, Sociolinguistics”, “ Linguistic proficiency”, “Catalan in the mass media”, “Catalan in the universities”, “Other information resources” and “Opportunities to learn Catalan”. Here students will find:
 PREFACE — A description of the state of bilingualism in Catalonia, showing that not all Catalans are totally proficient in the two languages, and that Catalan is under-represented in certain areas, for example the mass media. — A discussion of the concept of minority language that sees Catalan placed on an equal footing with other European languages such as Danish and Finnish. — A brief description of the language: where it is spoken, who speaks it, its dialects, its history, its current use and status. — A description of language policies implemented by the universities and the support offered to enable exchange students to integrate in university life.
PREFACE — A description of the state of bilingualism in Catalonia, showing that not all Catalans are totally proficient in the two languages, and that Catalan is under-represented in certain areas, for example the mass media. — A discussion of the concept of minority language that sees Catalan placed on an equal footing with other European languages such as Danish and Finnish. — A brief description of the language: where it is spoken, who speaks it, its dialects, its history, its current use and status. — A description of language policies implemented by the universities and the support offered to enable exchange students to integrate in university life.
 INTRODUCTION 1 CATALAN AND EUROPE 2 SOCIOLINGUISTICS 3 LINGUISTIC PROFICIENCY 4 CATALAN IN THE MASS MEDIA 5 CATALAN IN THE UNIVERSITIES 6 OTHER INFORMATION RESOURCES 7 OPPORTUNITIES TO LEARN CATALAN 8
INTRODUCTION 1 CATALAN AND EUROPE 2 SOCIOLINGUISTICS 3 LINGUISTIC PROFICIENCY 4 CATALAN IN THE MASS MEDIA 5 CATALAN IN THE UNIVERSITIES 6 OTHER INFORMATION RESOURCES 7 OPPORTUNITIES TO LEARN CATALAN 8
 INTRODUCTION Aspects of the history and present situation of the Catalan language 1
INTRODUCTION Aspects of the history and present situation of the Catalan language 1
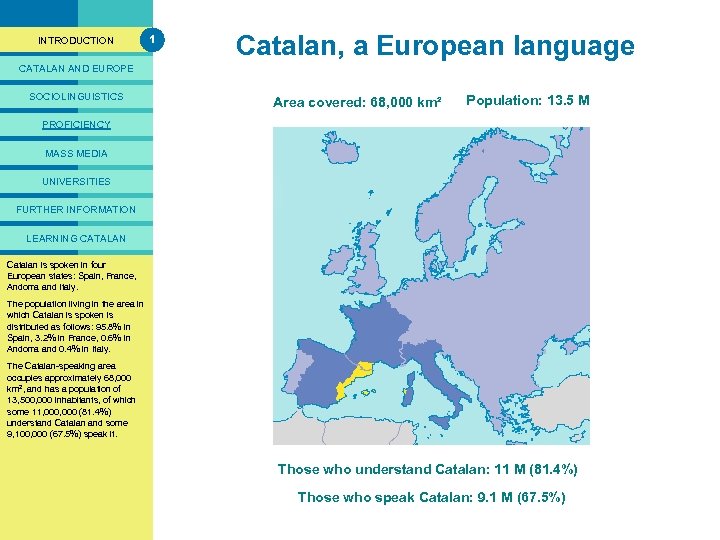 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 Catalan, a European language CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS Area covered: 68, 000 km² Population: 13. 5 M PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Catalan is spoken in four European states: Spain, France, Andorra and Italy. The population living in the area in which Catalan is spoken is distributed as follows: 95. 8% in Spain, 3. 2% in France, 0. 6% in Andorra and 0. 4% in Italy. The Catalan-speaking area occupies approximately 68, 000 km 2, and has a population of 13, 500, 000 inhabitants, of which some 11, 000 (81. 4%) understand Catalan and some 9, 100, 000 (67. 5%) speak it. Those who understand Catalan: 11 M (81. 4%) Those who speak Catalan: 9. 1 M (67. 5%)
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 Catalan, a European language CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS Area covered: 68, 000 km² Population: 13. 5 M PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Catalan is spoken in four European states: Spain, France, Andorra and Italy. The population living in the area in which Catalan is spoken is distributed as follows: 95. 8% in Spain, 3. 2% in France, 0. 6% in Andorra and 0. 4% in Italy. The Catalan-speaking area occupies approximately 68, 000 km 2, and has a population of 13, 500, 000 inhabitants, of which some 11, 000 (81. 4%) understand Catalan and some 9, 100, 000 (67. 5%) speak it. Those who understand Catalan: 11 M (81. 4%) Those who speak Catalan: 9. 1 M (67. 5%)
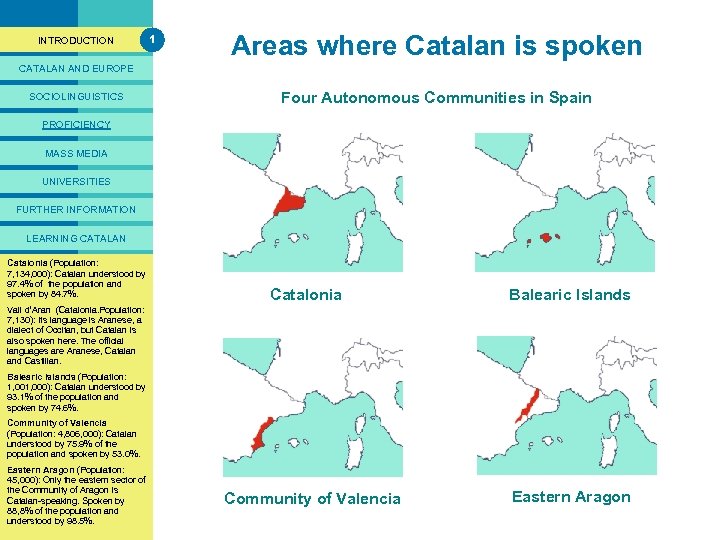 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 Areas where Catalan is spoken CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS Four Autonomous Communities in Spain PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Catalonia (Population: Catalan is spoken in four 7, 134, 000): Catalan understood by Autonomous Communities. 97. 4% of the population and Catalan-speakers comprise the spoken by 84. 7%. second largest language group in Spain. Vall d’Aran (Catalonia. Population: 7, 130): Its language is Aranese, a Estimates. Occitan, but Catalan is dialect of suggest that one in every six people in. The official also spoken here. Spain speaks Catalan and one in every four lives languages are Aranese, Catalan in one of the territories of the and Castilian. Catalan-speaking area ( 27. 5% of Balearic Islands (Population: the Spanish Catalan understood by 1, 000): population). Catalonia Balearic Islands 93. 1% of the population and spoken by 74. 6%. Community of Valencia (Population: 4, 806, 000): Catalan understood by 75. 9% of the population and spoken by 53. 0%. Eastern Aragon (Population: 45, 000): Only the eastern sector of the Community of Aragon is Catalan-speaking. Spoken by 88, 8% of the population and understood by 98. 5%. Community of Valencia Eastern Aragon
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 Areas where Catalan is spoken CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS Four Autonomous Communities in Spain PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Catalonia (Population: Catalan is spoken in four 7, 134, 000): Catalan understood by Autonomous Communities. 97. 4% of the population and Catalan-speakers comprise the spoken by 84. 7%. second largest language group in Spain. Vall d’Aran (Catalonia. Population: 7, 130): Its language is Aranese, a Estimates. Occitan, but Catalan is dialect of suggest that one in every six people in. The official also spoken here. Spain speaks Catalan and one in every four lives languages are Aranese, Catalan in one of the territories of the and Castilian. Catalan-speaking area ( 27. 5% of Balearic Islands (Population: the Spanish Catalan understood by 1, 000): population). Catalonia Balearic Islands 93. 1% of the population and spoken by 74. 6%. Community of Valencia (Population: 4, 806, 000): Catalan understood by 75. 9% of the population and spoken by 53. 0%. Eastern Aragon (Population: 45, 000): Only the eastern sector of the Community of Aragon is Catalan-speaking. Spoken by 88, 8% of the population and understood by 98. 5%. Community of Valencia Eastern Aragon
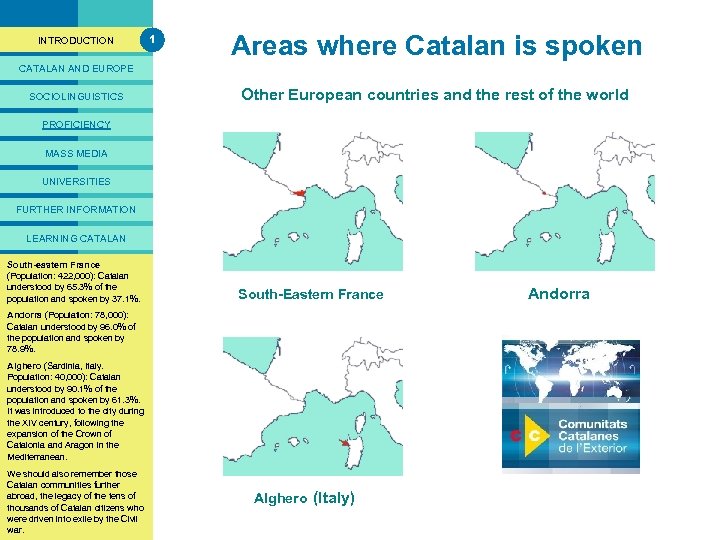 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 Areas where Catalan is spoken CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS Other European countries and the rest of the world PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN South-eastern France (Population: 422, 000): Catalan understood by 65. 3% of the population and spoken by 37. 1%. South-Eastern France Andorra (Population: 78, 000): Catalan understood by 96. 0% of the population and spoken by 78. 9%. Alghero (Sardinia, Italy. Population: 40, 000): Catalan understood by 90. 1% of the population and spoken by 61. 3%. It was introduced to the city during the XIV century, following the expansion of the Crown of Catalonia and Aragon in the Mediterranean. We should also remember those Catalan communities further abroad, the legacy of the tens of thousands of Catalan citizens who were driven into exile by the Civil war. Alghero (Italy) Andorra
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 Areas where Catalan is spoken CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS Other European countries and the rest of the world PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN South-eastern France (Population: 422, 000): Catalan understood by 65. 3% of the population and spoken by 37. 1%. South-Eastern France Andorra (Population: 78, 000): Catalan understood by 96. 0% of the population and spoken by 78. 9%. Alghero (Sardinia, Italy. Population: 40, 000): Catalan understood by 90. 1% of the population and spoken by 61. 3%. It was introduced to the city during the XIV century, following the expansion of the Crown of Catalonia and Aragon in the Mediterranean. We should also remember those Catalan communities further abroad, the legacy of the tens of thousands of Catalan citizens who were driven into exile by the Civil war. Alghero (Italy) Andorra
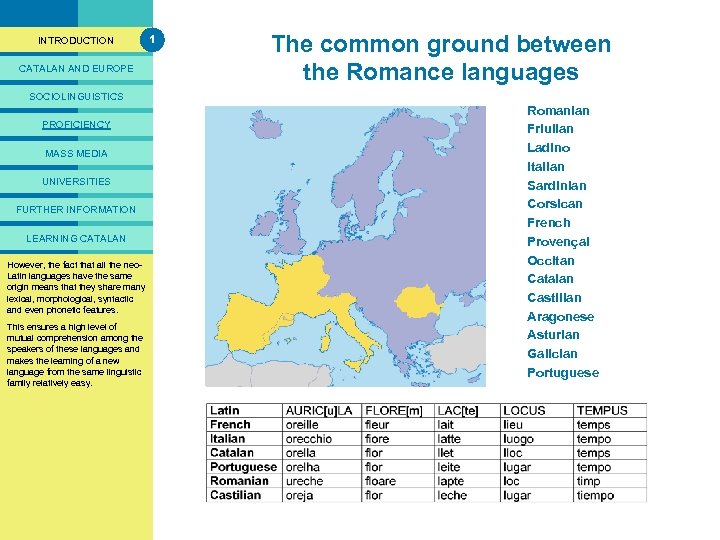 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE 1 The common ground between Romance languages Catalan, a Romance language the Romance common origin) (evolution from a languages SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN However, a Romance These languages vary all the neo. Catalan is the fact that language, Latin languages have group of considerably due thatthe same and so belongs toto a range of origin means include the influence factors which that they share many languages derived from Latin; lexical, morphological, syntactic of the pre-Romance languages more specifically, it belongs to the and even each of features. spoken branch of these westernin phoneticthe territories before Romanization, the languages. This ensures a high level of influence of other languages with mutual Romance languages are Severalcomprehension among the which they have had contact speakers of these languages and spoken internationally, such as during their history and their own makes the learning of French Castilian, Portuguese, a new and intralinguistic evolution. language Italian. from the same linguistic family relatively describes the The table below easy. This family also includes main differences in phonetic languages such as Occitan, evolution between each of these Provençal, Corsican and languages starting from the same Aragonese. Some of these are Latin word. falling into disuse and are being replaced by majority languages. Romanian Friulian Ladino Italian Sardinian Corsican French Provençal Occitan Catalan Castilian Aragonese Asturian Galician Portuguese
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE 1 The common ground between Romance languages Catalan, a Romance language the Romance common origin) (evolution from a languages SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN However, a Romance These languages vary all the neo. Catalan is the fact that language, Latin languages have group of considerably due thatthe same and so belongs toto a range of origin means include the influence factors which that they share many languages derived from Latin; lexical, morphological, syntactic of the pre-Romance languages more specifically, it belongs to the and even each of features. spoken branch of these westernin phoneticthe territories before Romanization, the languages. This ensures a high level of influence of other languages with mutual Romance languages are Severalcomprehension among the which they have had contact speakers of these languages and spoken internationally, such as during their history and their own makes the learning of French Castilian, Portuguese, a new and intralinguistic evolution. language Italian. from the same linguistic family relatively describes the The table below easy. This family also includes main differences in phonetic languages such as Occitan, evolution between each of these Provençal, Corsican and languages starting from the same Aragonese. Some of these are Latin word. falling into disuse and are being replaced by majority languages. Romanian Friulian Ladino Italian Sardinian Corsican French Provençal Occitan Catalan Castilian Aragonese Asturian Galician Portuguese
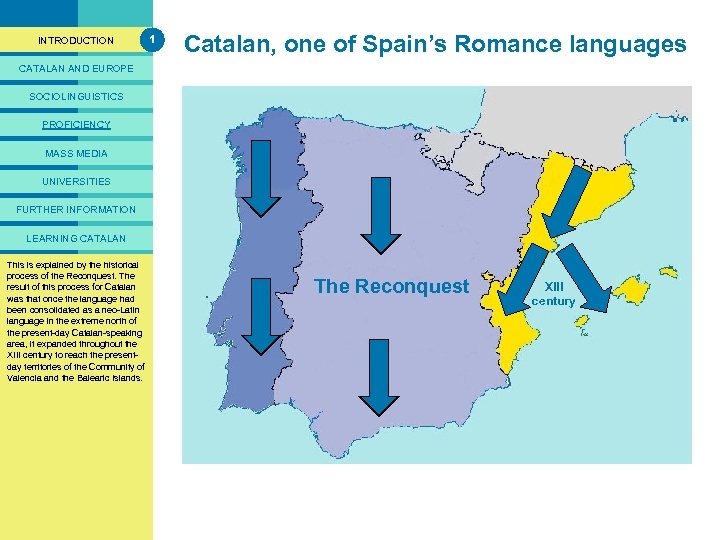 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 Catalan, one of Spain’s Romance languages CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Catalan is one of by the This is explained the Romance All the language areas ofare only In historical terms, there historical languagesoriginareas of Latin process of of the Iberian Romance the in the Iberian three language. Reconquest. The Peninsular. Galician, for Catalan result in this process Portuguese Peninsula run from Peninsular: origin of the Iberian north to south. and Castilian are other neo-Latin was that Galician-Portuguese and Castilian, once the language had languages of the Peninsular. been consolidated as a neo-Latin Catalan. language in the extreme north of Basque is not related to this the present-day Catalan-speaking Iberian family of languages and area, it expanded throughout the research has not yet determined XIII century to reach the presentwhether it is related to other day territories of the Community of European languages. Valencia and the Balearic Islands. The Reconquest XIII century
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 Catalan, one of Spain’s Romance languages CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Catalan is one of by the This is explained the Romance All the language areas ofare only In historical terms, there historical languagesoriginareas of Latin process of of the Iberian Romance the in the Iberian three language. Reconquest. The Peninsular. Galician, for Catalan result in this process Portuguese Peninsula run from Peninsular: origin of the Iberian north to south. and Castilian are other neo-Latin was that Galician-Portuguese and Castilian, once the language had languages of the Peninsular. been consolidated as a neo-Latin Catalan. language in the extreme north of Basque is not related to this the present-day Catalan-speaking Iberian family of languages and area, it expanded throughout the research has not yet determined XIII century to reach the presentwhether it is related to other day territories of the Community of European languages. Valencia and the Balearic Islands. The Reconquest XIII century
 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 Catalan: origins of the language CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS 3 PROFICIENCY 1 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The first known texts to be written Catalan developed between the wholly in Catalan date a result VIII and X centuries asfrom the of end of the XII century. One of the evolution in the Vulgar Latin these spoken translation of a being was the in the northern parts fragment of a code of Visigothic of the present-day Catalan. Law, Liber iudiciorum (1), and the speaking area. other was the Homilies d’Organyà As a language, it originated in the (2), the first text originally written counties of the Spanish March, in Catalan to be conserved. which formed part of the Later, in the XIII century and the Carolingian Empire. beginning of the XIV century, It was not, however, until the XIV Ramon Llull (3) wrote his body of century that the present-day work, which is a synthesis of all territorial boundaries of the philosophical and scientific Catalan language were finally thought of the age. At the end of made permanent. the XV century, Joanot Martorell wrote Tirant lo Blanc (4), considered to be the first modern novel in world literature. 2 4 3
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 Catalan: origins of the language CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS 3 PROFICIENCY 1 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The first known texts to be written Catalan developed between the wholly in Catalan date a result VIII and X centuries asfrom the of end of the XII century. One of the evolution in the Vulgar Latin these spoken translation of a being was the in the northern parts fragment of a code of Visigothic of the present-day Catalan. Law, Liber iudiciorum (1), and the speaking area. other was the Homilies d’Organyà As a language, it originated in the (2), the first text originally written counties of the Spanish March, in Catalan to be conserved. which formed part of the Later, in the XIII century and the Carolingian Empire. beginning of the XIV century, It was not, however, until the XIV Ramon Llull (3) wrote his body of century that the present-day work, which is a synthesis of all territorial boundaries of the philosophical and scientific Catalan language were finally thought of the age. At the end of made permanent. the XV century, Joanot Martorell wrote Tirant lo Blanc (4), considered to be the first modern novel in world literature. 2 4 3
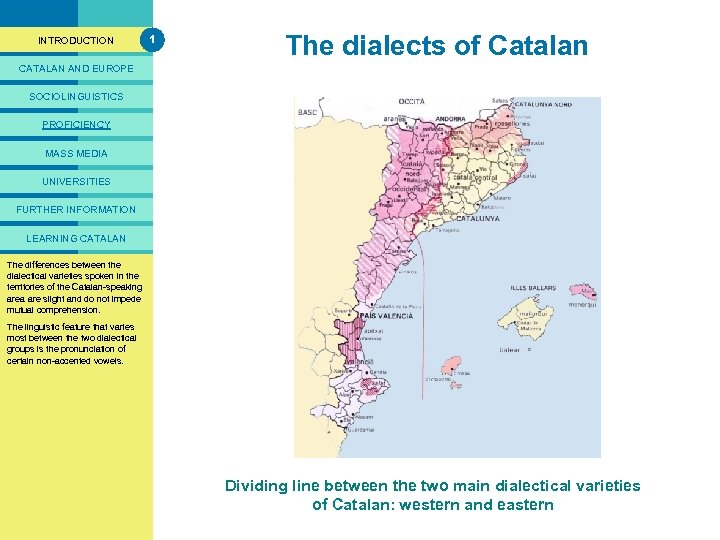 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 The dialects of Catalan CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN territory in quite clearly The map shows between the that differenceswhich Catalan is spoken is divided into seven two dialectical varieties spoken in the dividing line between the different administrative areas. territories of of Catalan-speaking main groups thedialects is area are to either do not impede unrelatedslight and territorial Although Catalan is made up of mutual comprehension. divisions between the states in different dialects, no one Catalanwhich Catalan is spoken, or to the speaking territory is uniformly The linguistic feature that varies divisions between the characterised by just one of these. most between the two dialectical Autonomous Communities of groups is the pronunciation of Valencian is the official name Spain. certain non-accented vowels. given to the Catalan language in the Community of Valencia. (1) The language spoken in the Catalan comarca or district of the Vall d’Aran is Aranese, a dialect of Occitan. The territory in which Catalan is spoken Dividing linedivided into seven different areas varieties is between the two main dialectical of Catalan: western and eastern
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION 1 The dialects of Catalan CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN territory in quite clearly The map shows between the that differenceswhich Catalan is spoken is divided into seven two dialectical varieties spoken in the dividing line between the different administrative areas. territories of of Catalan-speaking main groups thedialects is area are to either do not impede unrelatedslight and territorial Although Catalan is made up of mutual comprehension. divisions between the states in different dialects, no one Catalanwhich Catalan is spoken, or to the speaking territory is uniformly The linguistic feature that varies divisions between the characterised by just one of these. most between the two dialectical Autonomous Communities of groups is the pronunciation of Valencian is the official name Spain. certain non-accented vowels. given to the Catalan language in the Community of Valencia. (1) The language spoken in the Catalan comarca or district of the Vall d’Aran is Aranese, a dialect of Occitan. The territory in which Catalan is spoken Dividing linedivided into seven different areas varieties is between the two main dialectical of Catalan: western and eastern
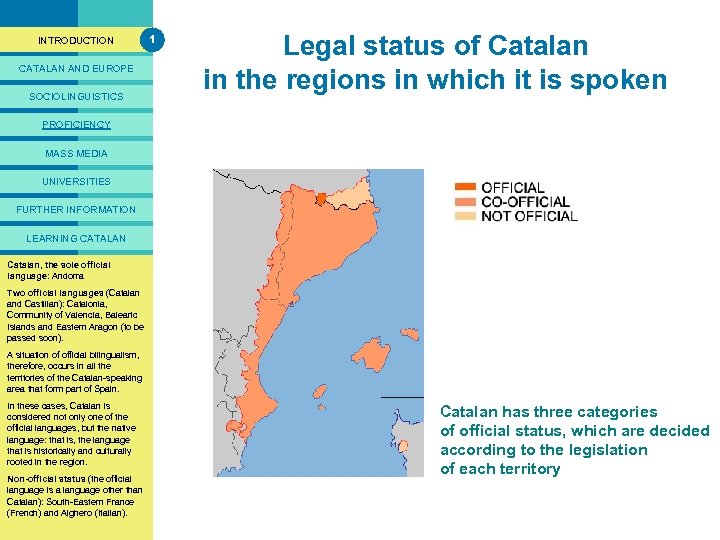 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS 1 Legal status of Catalan in the regions in which it is spoken PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Catalan, the sole official The fact that a language is spoken language: Andorra in a territory or that it is the mother tongue of all or of the majority of Two official languages (Catalan the population is no guarantee that and Castilian): Catalonia, this language will be recognised Community of Valencia, Balearic as an official language. The status Islands and Eastern Aragon (to be of Catalan in the countries in passed soon). which it is spoken varies according A the legislation governing to situation of official bilingualism, therefore, occurs in the state in language matters in all the territories question: of the Catalan-speaking area that form part of Spain. Catalan as the official language: In these cases, the sole official when Catalan is considered not only one of the language in a territory. official languages, but the native Two official languages: when language: that is, the language Catalan is the official language in that is historically and culturally a territory, but another language rooted in the region. also has official status. Non-official status (the official Non-official status: when the language is a language other than official language is a language Catalan): South-Eastern France other than Catalan. (French) and Alghero (Italian). Catalan has three categories of official status, which are decided according to the legislation of each territory
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS 1 Legal status of Catalan in the regions in which it is spoken PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Catalan, the sole official The fact that a language is spoken language: Andorra in a territory or that it is the mother tongue of all or of the majority of Two official languages (Catalan the population is no guarantee that and Castilian): Catalonia, this language will be recognised Community of Valencia, Balearic as an official language. The status Islands and Eastern Aragon (to be of Catalan in the countries in passed soon). which it is spoken varies according A the legislation governing to situation of official bilingualism, therefore, occurs in the state in language matters in all the territories question: of the Catalan-speaking area that form part of Spain. Catalan as the official language: In these cases, the sole official when Catalan is considered not only one of the language in a territory. official languages, but the native Two official languages: when language: that is, the language Catalan is the official language in that is historically and culturally a territory, but another language rooted in the region. also has official status. Non-official status (the official Non-official status: when the language is a language other than official language is a language Catalan): South-Eastern France other than Catalan. (French) and Alghero (Italian). Catalan has three categories of official status, which are decided according to the legislation of each territory
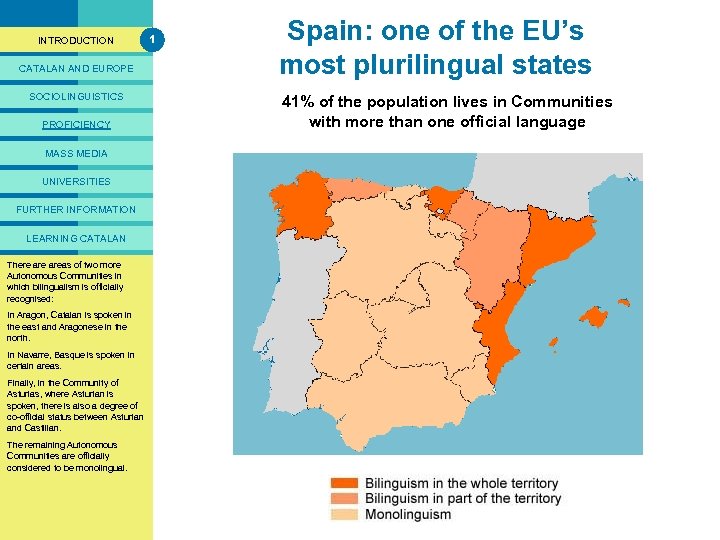 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN There areas two more The legal status of the Spanish Autonomous Communities State’s multilingualism was in which bilingualism is officially established in the 1978 Spanish recognised: Constitution, in the statutes of autonomy for the Autonomous In Aragon, Catalan is spoken in Communities where more than the east and Aragonese in the one language is spoken and in the north. Linguistic Policy Acts passed by In Navarre, Basque is Catalonia, these Communities (inspoken in certain and 1998). in 1983 areas. Finally, in the Community of In the State, 41% of the population Asturias, where Asturian is lives in territories with two official spoken, there is in every four languages. One also a degree of co-official status between Asturian Spaniards (27. 5%) lives in a and Castilian. Community in which Catalan is the official language. The remaining Autonomous Communities are officially In the Communities of Galicia and considered Country (where the Basque to be monolingual. Galician and Basque are spoken) the official languages are those of the territory and Castilian. 1 Spain: one of the EU’s most plurilingual states 41% of the population lives in Communities with more than one official language
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN There areas two more The legal status of the Spanish Autonomous Communities State’s multilingualism was in which bilingualism is officially established in the 1978 Spanish recognised: Constitution, in the statutes of autonomy for the Autonomous In Aragon, Catalan is spoken in Communities where more than the east and Aragonese in the one language is spoken and in the north. Linguistic Policy Acts passed by In Navarre, Basque is Catalonia, these Communities (inspoken in certain and 1998). in 1983 areas. Finally, in the Community of In the State, 41% of the population Asturias, where Asturian is lives in territories with two official spoken, there is in every four languages. One also a degree of co-official status between Asturian Spaniards (27. 5%) lives in a and Castilian. Community in which Catalan is the official language. The remaining Autonomous Communities are officially In the Communities of Galicia and considered Country (where the Basque to be monolingual. Galician and Basque are spoken) the official languages are those of the territory and Castilian. 1 Spain: one of the EU’s most plurilingual states 41% of the population lives in Communities with more than one official language
 CATALAN AND EUROPE Perspectives for Catalan inside the construction of Europe 2
CATALAN AND EUROPE Perspectives for Catalan inside the construction of Europe 2
 PRESENTACIÓ The process of the construction of Europe INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE 2 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN In this section, we shall is a the The European continentstudy the reflect on opportunity that the process possible implications and cultures. mosaic of languages of the of European number of languages process ofintegration represents Indeed, thethe construction of for designing future as this Europe amounts to official will spoken in the a new considerably multilinguistic number of official affect the model, beyond the more thanofficial recognition of official state languages. minority languages, meaning state languages limited to small areas or, simply, languages without a state. and regional or lesser-used languages
PRESENTACIÓ The process of the construction of Europe INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE 2 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN In this section, we shall is a the The European continentstudy the reflect on opportunity that the process possible implications and cultures. mosaic of languages of the of European number of languages process ofintegration represents Indeed, thethe construction of for designing future as this Europe amounts to official will spoken in the a new considerably multilinguistic number of official affect the model, beyond the more thanofficial recognition of official state languages. minority languages, meaning state languages limited to small areas or, simply, languages without a state. and regional or lesser-used languages
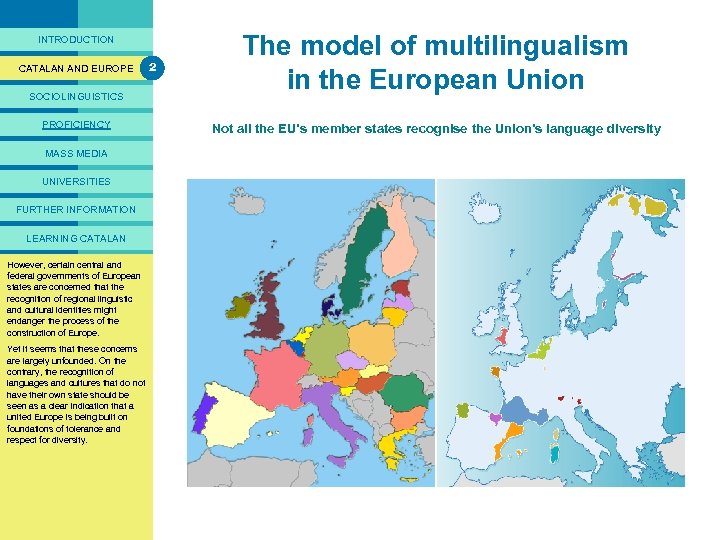 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN While being fully engaged in the However, certain central and construction of Europe, European federal governments of the member states of the that are also states are concerned EU the defending their own national recognition of regional linguistic identity, though not bymight and cultural identities adopting a “nationalistic” stance, in the worst endanger the process of the sense of the of Europe. construction word. The it seems that these state Yet defence of distinct concerns identities, therefore, shouldthe are largely unfounded. On not constitutethe recognition of to contrary, any impediment seeking the common roots of allnot languages and cultures that do Europeansown state should be have their and a shared cultural inheritance. seen as a clear indication that a united Europe is being built on Provided that it is undertaken foundations of tolerance and democratically, defending one’s respect for diversity. identity, language and culture is a right that all peoples of the world should have. 2 The model of multilingualism in the European Union Not all the EU’s member states recognise the Union’s language diversity The European Union is multilingual
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN While being fully engaged in the However, certain central and construction of Europe, European federal governments of the member states of the that are also states are concerned EU the defending their own national recognition of regional linguistic identity, though not bymight and cultural identities adopting a “nationalistic” stance, in the worst endanger the process of the sense of the of Europe. construction word. The it seems that these state Yet defence of distinct concerns identities, therefore, shouldthe are largely unfounded. On not constitutethe recognition of to contrary, any impediment seeking the common roots of allnot languages and cultures that do Europeansown state should be have their and a shared cultural inheritance. seen as a clear indication that a united Europe is being built on Provided that it is undertaken foundations of tolerance and democratically, defending one’s respect for diversity. identity, language and culture is a right that all peoples of the world should have. 2 The model of multilingualism in the European Union Not all the EU’s member states recognise the Union’s language diversity The European Union is multilingual
 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 2 The model of multilingualism in the European Union The European Union is multilingual MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Today 27 European states form the EU. There are 23 official languages in the Union – that is, the official languages of all its member states. Since 2005 Catalan, which ranks as the fourteenth most spoken language in the EU, has received semi-official status. This status means that treaties and basic texts produced by the EU are translated into Catalan and it upholds the right to be attended in Catalan in the offices of this institution in the territories of the Catalan-speaking area. However, Catalan does not have the same status as the state languages which, as well as being truly official languages of the EU, are also its working languages. Catalan and the 23 official languages of the European Union (January 2007)
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 2 The model of multilingualism in the European Union The European Union is multilingual MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Today 27 European states form the EU. There are 23 official languages in the Union – that is, the official languages of all its member states. Since 2005 Catalan, which ranks as the fourteenth most spoken language in the EU, has received semi-official status. This status means that treaties and basic texts produced by the EU are translated into Catalan and it upholds the right to be attended in Catalan in the offices of this institution in the territories of the Catalan-speaking area. However, Catalan does not have the same status as the state languages which, as well as being truly official languages of the EU, are also its working languages. Catalan and the 23 official languages of the European Union (January 2007)
 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 2 The model of multilingualism in the European Union Most member states of the European Union are also multilingual MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN As can be seen in the map and in the table, the present model of multilingualism does not reflect the linguistic and cultural reality of many of the member states. In the 27 member states of the EU, around 45 regional languages are spoken. There already more than 50 million people whose mother tongue is different to that of the official state language. What is more, some of these languages can hardly be considered minority languages as they are spoken by more European citizens than some of the official EU languages. This is the case of Catalan. Number of speakers of some regional languages of the EU
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 2 The model of multilingualism in the European Union Most member states of the European Union are also multilingual MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN As can be seen in the map and in the table, the present model of multilingualism does not reflect the linguistic and cultural reality of many of the member states. In the 27 member states of the EU, around 45 regional languages are spoken. There already more than 50 million people whose mother tongue is different to that of the official state language. What is more, some of these languages can hardly be considered minority languages as they are spoken by more European citizens than some of the official EU languages. This is the case of Catalan. Number of speakers of some regional languages of the EU
 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The philosophy defended byis A further essential measure the Furthermore, measures which the states in the of a European introduction construction of favour the recognition of linguistic Europe, based on tolerance and dimension in the educational and cultural diversity complement respect for diversity, should in systems of all the countries those others which aim to also be seen promote at regional level. order to to Europe’s common strengthen apply common European heritage. values and to eliminate It would therefore be appropriate those stereotypical images of to grant official status to any For example, the implementation certain cultures that can provoke language spoken in any area ofto of language learning programs misunderstandings. the member states and, between facilitate understanding particularly, to those languages The introduction of a linguistic speakers of the same. European that already have this status in the dimension in education should family, such as the speakers of territory in which they are spoken. also create a common awareness Romance, Anglo-Germanic, and among the people Slav languages. of the European Union of what it means to be European. 2 The need for changes in our understanding of multilingualism
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The philosophy defended byis A further essential measure the Furthermore, measures which the states in the of a European introduction construction of favour the recognition of linguistic Europe, based on tolerance and dimension in the educational and cultural diversity complement respect for diversity, should in systems of all the countries those others which aim to also be seen promote at regional level. order to to Europe’s common strengthen apply common European heritage. values and to eliminate It would therefore be appropriate those stereotypical images of to grant official status to any For example, the implementation certain cultures that can provoke language spoken in any area ofto of language learning programs misunderstandings. the member states and, between facilitate understanding particularly, to those languages The introduction of a linguistic speakers of the same. European that already have this status in the dimension in education should family, such as the speakers of territory in which they are spoken. also create a common awareness Romance, Anglo-Germanic, and among the people Slav languages. of the European Union of what it means to be European. 2 The need for changes in our understanding of multilingualism
 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE 2 The need for changes in our understanding and management of multilingualism SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY The linguistic diversity of the new citizens should also be taken into account MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN So far we and the other Catalan. We will need to consider the Catalonia have spoken ofconcepts linguistic diversity, of such as areas that the speaking diversity of form part languagesno exception to this multilingualism cultures that have Spain are and interculturality historically been related to the EU which, as well as representing process and are hosts to large a territories. However, in the new approach to the description of numbers of immigrants from European Union. The numberin Europe today, are essential of outside the EU. today, and even more inresidents in Catalonia achieving any process of union. foreign the EU of tomorrow, languages 12. 2% of the comprises from outside population In short, the languages and European continent will become according to the figures published cultures of Europe are those of all extremely important: these are the for 2006. European citizens. languages of immigrants. The Iberian Peninsula has, after Immigration has come to typify all, strong historical and cultural modern societies. It would seem links with the southern shores of right to protect and promote the Mediterranean and South languages of the immigrants. America. Illustrative of this are the approximately 2 million Germans of Turkish and Kurdish origin and the more than 4 million Maghrebis and sub-Saharians that live in France. Moroccans Equatorians Colombians Bolivians Argentineans Chinese Pakistanis
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE 2 The need for changes in our understanding and management of multilingualism SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY The linguistic diversity of the new citizens should also be taken into account MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN So far we and the other Catalan. We will need to consider the Catalonia have spoken ofconcepts linguistic diversity, of such as areas that the speaking diversity of form part languagesno exception to this multilingualism cultures that have Spain are and interculturality historically been related to the EU which, as well as representing process and are hosts to large a territories. However, in the new approach to the description of numbers of immigrants from European Union. The numberin Europe today, are essential of outside the EU. today, and even more inresidents in Catalonia achieving any process of union. foreign the EU of tomorrow, languages 12. 2% of the comprises from outside population In short, the languages and European continent will become according to the figures published cultures of Europe are those of all extremely important: these are the for 2006. European citizens. languages of immigrants. The Iberian Peninsula has, after Immigration has come to typify all, strong historical and cultural modern societies. It would seem links with the southern shores of right to protect and promote the Mediterranean and South languages of the immigrants. America. Illustrative of this are the approximately 2 million Germans of Turkish and Kurdish origin and the more than 4 million Maghrebis and sub-Saharians that live in France. Moroccans Equatorians Colombians Bolivians Argentineans Chinese Pakistanis
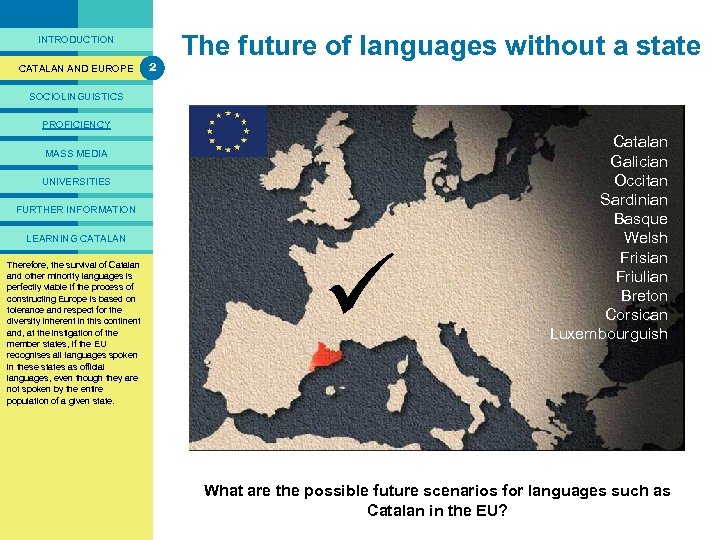 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE 2 The future of languages without a state SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN In short, in the survival do not Therefore, this section On the other hand, to remain If all the member stateswe. Catalan Were this situation the of have examined minority languages is and other some the chances construction of Europe spokennot grant all the languagespossible unchanged, thenof the should of implicationsboundaries official ofthe that to process perfectly representviable ifthe survival within theirstateless languages survival ofa threattheprocess of construction the. Europe based have constructing Europe is than of any then of Abovecontinue status, language. is more all, on to such as Catalan. EU will might for the future viability ofthe tolerance Europe should redress Europe’s recognise and respect for the doubtful. only one official regional languages and linguistic diversity per member continent situation caused in this cultures. languageinherentby thestate (with and, at of instigation of Finland, policiesthepast Belgium, in the exception ofcenturiesthesome By way of summary, the following member states, nation of the European if the EUMalta). Ireland, Luxemburg andstates, observations might be made: recognises all certain languages which granted languages spoken in these states as minority nothing more thanofficial status, languages, even entirely replace or even sought tothough they are not spoken by the entire them with other languages. population of a given state. Catalan Galician Occitan Sardinian Basque Welsh Frisian Friulian Breton Corsican Luxembourguish What are the possible future scenarios for languages such as Catalan in the EU?
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE 2 The future of languages without a state SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN In short, in the survival do not Therefore, this section On the other hand, to remain If all the member stateswe. Catalan Were this situation the of have examined minority languages is and other some the chances construction of Europe spokennot grant all the languagespossible unchanged, thenof the should of implicationsboundaries official ofthe that to process perfectly representviable ifthe survival within theirstateless languages survival ofa threattheprocess of construction the. Europe based have constructing Europe is than of any then of Abovecontinue status, language. is more all, on to such as Catalan. EU will might for the future viability ofthe tolerance Europe should redress Europe’s recognise and respect for the doubtful. only one official regional languages and linguistic diversity per member continent situation caused in this cultures. languageinherentby thestate (with and, at of instigation of Finland, policiesthepast Belgium, in the exception ofcenturiesthesome By way of summary, the following member states, nation of the European if the EUMalta). Ireland, Luxemburg andstates, observations might be made: recognises all certain languages which granted languages spoken in these states as minority nothing more thanofficial status, languages, even entirely replace or even sought tothough they are not spoken by the entire them with other languages. population of a given state. Catalan Galician Occitan Sardinian Basque Welsh Frisian Friulian Breton Corsican Luxembourguish What are the possible future scenarios for languages such as Catalan in the EU?
 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN We have seen that the linguistic At the same time, in all likelihood, and. EU will have to restrict Union is the cultural mosaic of the its made up of many more pieces– number of working languages thanis, the number of languages that we might have thought just by looking at its member states. used in documents produced by the EU and also spoken or used in It would seem right to continue to simultaneous translation. consider all the official languages of the member states as of The EU’s current model official languages in the EU. multilingualism will have to be redefined in the near future. 2 The model of multilingualism in the European Union
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN We have seen that the linguistic At the same time, in all likelihood, and. EU will have to restrict Union is the cultural mosaic of the its made up of many more pieces– number of working languages thanis, the number of languages that we might have thought just by looking at its member states. used in documents produced by the EU and also spoken or used in It would seem right to continue to simultaneous translation. consider all the official languages of the member states as of The EU’s current model official languages in the EU. multilingualism will have to be redefined in the near future. 2 The model of multilingualism in the European Union
 THE SOCIOLINGUISTIC SITUATION Contact between languages in Catalonia 3
THE SOCIOLINGUISTIC SITUATION Contact between languages in Catalonia 3
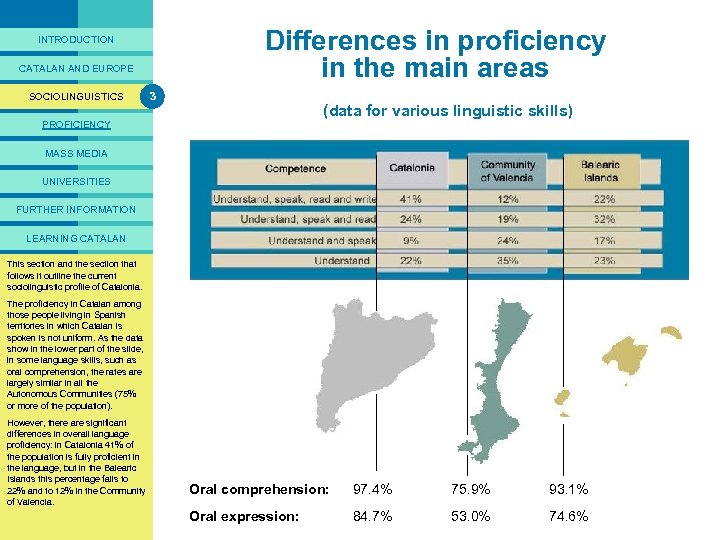 PRESENTACIÓ Differences in proficiency in the main areas INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS 3 (data for various linguistic skills) PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN This section and the section that follows it outline the current sociolinguistic profile of Catalonia. The proficiency in Catalan among those people living in Spanish territories in which Catalan is spoken is not uniform. As the data show in the lower part of the slide, in some language skills, such as oral comprehension, the rates are largely similar in all the Autonomous Communities (75% or more of the population). However, there are significant differences in overall language proficiency: in Catalonia 41% of the population is fully proficient in the language, but in the Balearic Islands this percentage falls to 22% and to 12% in the Community of Valencia. Oral comprehension: 97. 4% 75. 9% 93. 1% Oral expression: 84. 7% 53. 0% 74. 6%
PRESENTACIÓ Differences in proficiency in the main areas INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS 3 (data for various linguistic skills) PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN This section and the section that follows it outline the current sociolinguistic profile of Catalonia. The proficiency in Catalan among those people living in Spanish territories in which Catalan is spoken is not uniform. As the data show in the lower part of the slide, in some language skills, such as oral comprehension, the rates are largely similar in all the Autonomous Communities (75% or more of the population). However, there are significant differences in overall language proficiency: in Catalonia 41% of the population is fully proficient in the language, but in the Balearic Islands this percentage falls to 22% and to 12% in the Community of Valencia. Oral comprehension: 97. 4% 75. 9% 93. 1% Oral expression: 84. 7% 53. 0% 74. 6%
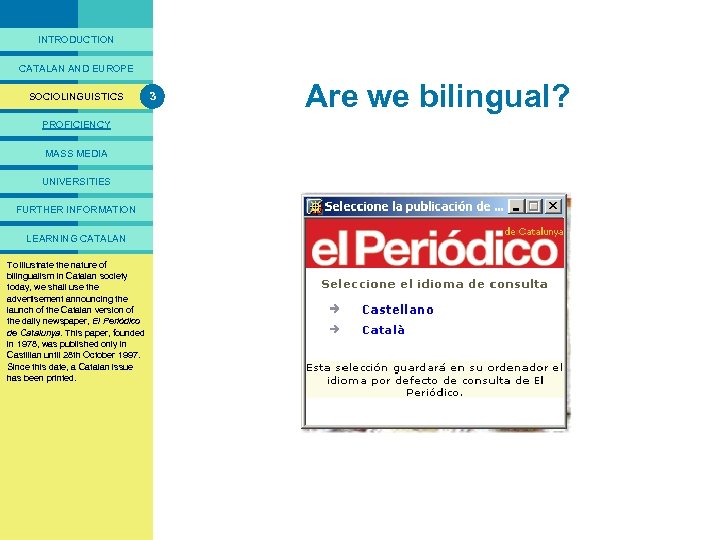 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Because of simplyand of To illustrate 1990 considering Rather than the nature the In fact, as represents study Cataloniain an overallthe arrival language competenceis by far 1 the bilingualism of approximately this figure, in Catalan society in Catalonia with what would Communityhowever, what thisbe shown wevary from outside today, population: the section sets out to region million to shall use some million highestimmigrants do is to 6 to region owing Catalans in terms on advertisement the 2006 that describe the EU, the toyear significant people. for the announcing the differencesalready increased to launch of in proficiency; to their languagesociolinguistic figure hadthe Catalan version of indicators (proficiency in. Periódico the daily whether or El the examine newspaper, not Catalan over 7 million. language and the use of the de Catalunya. truly considered society can be This paper, founded language), our assessment of the in 1978, bilingual. was published only in Catalan language will be based Castilian until 28 th October 1997. solely this date, a Catalan issue Since Catalonia. has been printed. 3 What are we like? Are we bilingual?
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Because of simplyand of To illustrate 1990 considering Rather than the nature the In fact, as represents study Cataloniain an overallthe arrival language competenceis by far 1 the bilingualism of approximately this figure, in Catalan society in Catalonia with what would Communityhowever, what thisbe shown wevary from outside today, population: the section sets out to region million to shall use some million highestimmigrants do is to 6 to region owing Catalans in terms on advertisement the 2006 that describe the EU, the toyear significant people. for the announcing the differencesalready increased to launch of in proficiency; to their languagesociolinguistic figure hadthe Catalan version of indicators (proficiency in. Periódico the daily whether or El the examine newspaper, not Catalan over 7 million. language and the use of the de Catalunya. truly considered society can be This paper, founded language), our assessment of the in 1978, bilingual. was published only in Catalan language will be based Castilian until 28 th October 1997. solely this date, a Catalan issue Since Catalonia. has been printed. 3 What are we like? Are we bilingual?
 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION The way we are “We are bilingual” CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS 3 “Catalan society is bilingual. ” PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN language of the advertising This firstthe notion that Catalonia means that Catalonia is Indeed, behind in theory and The idea of bilingualism that Catalan: thewhere only this El of independently to show that is a country historical two the agency presents inlanguage campaign was of their mother this territory. newspaper ona tongue, all the languages coexist is itself the advertisement is based printed in Periódico, a inhabitants of Catalonia was theto simplification able truth. following hypothesis: understand, Catalonia, are ofadapting to the One of the characteristics of speak, read and write in the two country’s sociolinguistic reality and present-day University of In six/seven million society is the All 2005, the Catalans are languages. so, since 1997, the paper’s widespread the two official Barcelona Study Group on proficient in phenomenon of readers have been able to choose contact between two which an In the section below, languages: Threatened Languages Catalan languages of Catalonia: held the language they prefer to read it Catalan and Castilian. proficiency examines which testified exhibition the and Castilian. language to the in. of the inhabitants of Catalonia, we fact that between 250 and 300 This iswhen present-day Catalan Thus, the idea that the shall seelanguages are presently different that this adaptation did Nevertheless, this premise is not advertising campaign’s being “Tal society is described as slogan altogether true. changes in the spoken to any not leadin Catalonia. com som”the descriptionare) bilingual, (the way we refers nature of the product itself. attemptsthe express. language more to to individual proficiency of its citizens (and, by extension, to the whole of society) than to territorial questions of the language Community, as it would do if our country of study were Belgium or Switzerland. One newspaper, two languages “One society, two languages. ” Is the whole of Catalan society bilingual?
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION The way we are “We are bilingual” CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS 3 “Catalan society is bilingual. ” PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN language of the advertising This firstthe notion that Catalonia means that Catalonia is Indeed, behind in theory and The idea of bilingualism that Catalan: thewhere only this El of independently to show that is a country historical two the agency presents inlanguage campaign was of their mother this territory. newspaper ona tongue, all the languages coexist is itself the advertisement is based printed in Periódico, a inhabitants of Catalonia was theto simplification able truth. following hypothesis: understand, Catalonia, are ofadapting to the One of the characteristics of speak, read and write in the two country’s sociolinguistic reality and present-day University of In six/seven million society is the All 2005, the Catalans are languages. so, since 1997, the paper’s widespread the two official Barcelona Study Group on proficient in phenomenon of readers have been able to choose contact between two which an In the section below, languages: Threatened Languages Catalan languages of Catalonia: held the language they prefer to read it Catalan and Castilian. proficiency examines which testified exhibition the and Castilian. language to the in. of the inhabitants of Catalonia, we fact that between 250 and 300 This iswhen present-day Catalan Thus, the idea that the shall seelanguages are presently different that this adaptation did Nevertheless, this premise is not advertising campaign’s being “Tal society is described as slogan altogether true. changes in the spoken to any not leadin Catalonia. com som”the descriptionare) bilingual, (the way we refers nature of the product itself. attemptsthe express. language more to to individual proficiency of its citizens (and, by extension, to the whole of society) than to territorial questions of the language Community, as it would do if our country of study were Belgium or Switzerland. One newspaper, two languages “One society, two languages. ” Is the whole of Catalan society bilingual?
 LINGUISTIC PROFICIENCY Knowledge of Catalan and Castilian in Catalonia 4
LINGUISTIC PROFICIENCY Knowledge of Catalan and Castilian in Catalonia 4
 PRESENTACIÓ Is Catalan society bilingual? INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN This exhibition on today section the knowledge in In Catalan societylanguagesof The data on examine themore languages live the Catalan was proof is many than twoand Castilianof drawn Catalonia proficiencythatside-by. Catalans. The data describing the from side. the Spanish Population and different languages are spoken distribution of theof 2001. Housing Census proficiency of here. It can therefore be argued that the Catalan and Castilian across the Since that year, the number of language contact that occurs in different language skills of foreign people who be more Catalonia today canhave come to listening and reading live in Catalonia has in terms of accurately described doubled or in comprehension, and speaking and some areas even tripled so that multilingualism than bilingualism. writing. foreign citizens presently account However, here we will only Models of theory always simplify for more than 12% of the Catalan describe the interrelationship the truth. The data should population. between Catalan and Castilian. therefore be interpreted more as a As yet there are no detailed general tendency or the major statistics to describe the language trend of Catalan society, or certain knowledge of this sector of subgroups, rather than an exact Catalan society. portrait of the language proficiency EU immigrants of each person. aside, the majority of recent newcomers to Catalonia have come from Morocco. They are followed, at some distance, by Ecuadorians, Colombians, Bolivians, Argentineans, Chinese and Pakistanis. 4
PRESENTACIÓ Is Catalan society bilingual? INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN This exhibition on today section the knowledge in In Catalan societylanguagesof The data on examine themore languages live the Catalan was proof is many than twoand Castilianof drawn Catalonia proficiencythatside-by. Catalans. The data describing the from side. the Spanish Population and different languages are spoken distribution of theof 2001. Housing Census proficiency of here. It can therefore be argued that the Catalan and Castilian across the Since that year, the number of language contact that occurs in different language skills of foreign people who be more Catalonia today canhave come to listening and reading live in Catalonia has in terms of accurately described doubled or in comprehension, and speaking and some areas even tripled so that multilingualism than bilingualism. writing. foreign citizens presently account However, here we will only Models of theory always simplify for more than 12% of the Catalan describe the interrelationship the truth. The data should population. between Catalan and Castilian. therefore be interpreted more as a As yet there are no detailed general tendency or the major statistics to describe the language trend of Catalan society, or certain knowledge of this sector of subgroups, rather than an exact Catalan society. portrait of the language proficiency EU immigrants of each person. aside, the majority of recent newcomers to Catalonia have come from Morocco. They are followed, at some distance, by Ecuadorians, Colombians, Bolivians, Argentineans, Chinese and Pakistanis. 4
 PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Castilian INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Spanish Population Census, 2001 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION Oral comprehension Oral expression Written comprehension Written expression LEARNING CATALAN When the to the state census According 2011 census is published, in Spain in 2001, conducted these percentages will almost certainly their mother independently ofdiffer because of the effects of recent immigration: tongue, virtually all the inhabitants many immigrants do not know of Spain (and, by extension, of Castilian on arriving in Spain. Catalonia) are proficient in Castilian, which means that they can understand, speak, read and write in this language. A knowledge of Castilian has been guaranteed for all the Spanish population. All generations of Spaniards have learnt Castilian at school. In fact, according to these figures, only 3% of all Spaniards can neither read nor write in Castilian. This percentage corresponds to the official figures for literacy in the 2001 census.
PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Castilian INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Spanish Population Census, 2001 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION Oral comprehension Oral expression Written comprehension Written expression LEARNING CATALAN When the to the state census According 2011 census is published, in Spain in 2001, conducted these percentages will almost certainly their mother independently ofdiffer because of the effects of recent immigration: tongue, virtually all the inhabitants many immigrants do not know of Spain (and, by extension, of Castilian on arriving in Spain. Catalonia) are proficient in Castilian, which means that they can understand, speak, read and write in this language. A knowledge of Castilian has been guaranteed for all the Spanish population. All generations of Spaniards have learnt Castilian at school. In fact, according to these figures, only 3% of all Spaniards can neither read nor write in Castilian. This percentage corresponds to the official figures for literacy in the 2001 census.
 PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Catalan Population Census, 2001 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The data for Catalan has been taken from the 2001 Census for Catalonia. 94. 5% of the Catalan population claims to understand spoken Catalan, while 74. 5% claims to speak the language. Oral comprehension Oral expression
PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Catalan Population Census, 2001 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The data for Catalan has been taken from the 2001 Census for Catalonia. 94. 5% of the Catalan population claims to understand spoken Catalan, while 74. 5% claims to speak the language. Oral comprehension Oral expression
 PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Catalan Population Census, 2001 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN However, the percentages for the skills that are acquired principally at school (reading comprehension and written expression) are much lower, particularly for writing: 49. 8% of Catalan citizens claim that they have inadequate writing skills. Written comprehension Written expression
PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Catalan Population Census, 2001 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN However, the percentages for the skills that are acquired principally at school (reading comprehension and written expression) are much lower, particularly for writing: 49. 8% of Catalan citizens claim that they have inadequate writing skills. Written comprehension Written expression
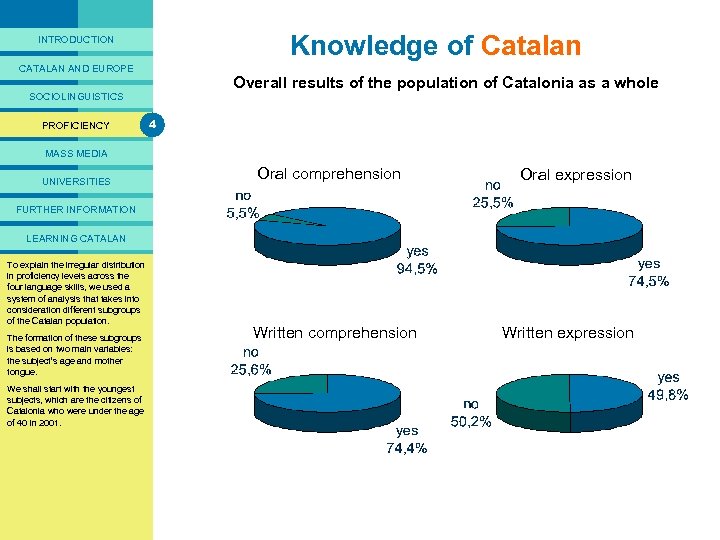 PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Overall results of the population of Catalonia as a whole SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES Oral comprehension Oral expression FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN To explain data for Catalan as a Taking the irregular distribution in proficiency levels across be whole, two conclusions can the four language skills, we used a drawn. system of analysis that takes into The first is that the proficiency of consideration different subgroups the citizens of Catalonia in the of the Catalan population. Catalan language is considerably The formation of these subgroups lower than their proficiency in is based Castilian. on two main variables: the subject’s age and mother The other finding is that the level tongue. of proficiency in Catalan differs We shall start with the youngest greatly depending on the language subjects, which While virtually of skill concerned. are the citizensall Catalonia who were under the age the Catalan population of 40 in 2001. understands spoken Catalan, one in every four says they are unable to speak Catalan and half of the population claims not to be able to write it. Written comprehension Written expression
PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Overall results of the population of Catalonia as a whole SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES Oral comprehension Oral expression FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN To explain data for Catalan as a Taking the irregular distribution in proficiency levels across be whole, two conclusions can the four language skills, we used a drawn. system of analysis that takes into The first is that the proficiency of consideration different subgroups the citizens of Catalonia in the of the Catalan population. Catalan language is considerably The formation of these subgroups lower than their proficiency in is based Castilian. on two main variables: the subject’s age and mother The other finding is that the level tongue. of proficiency in Catalan differs We shall start with the youngest greatly depending on the language subjects, which While virtually of skill concerned. are the citizensall Catalonia who were under the age the Catalan population of 40 in 2001. understands spoken Catalan, one in every four says they are unable to speak Catalan and half of the population claims not to be able to write it. Written comprehension Written expression
 PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Under the age of 40 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 (especially all those between the ages of 16 and 40) MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Oral comprehension = Today in Catalonia, Catalan is Independently of their mother the main language of instruction in tongue, all Catalans under the age compulsory education. According of 40 can understand, speak, read to data for the 1999 -2000 school and write in Catalan. year, 88. 9% of primary schools The language proficiency in and 51. 2% of secondary schools Catalan among the younger taught all classes in Catalan (with generations can be accounted for the exception, in both cases, of by the fact that they received their the subjects of Castilian Language schooling after the end of General and Literature and foreign Franco’s dictatorship. During the languages). military dictatorship, the use of In part due to the predominance of Catalan was prohibited and the mother tongue in politically persecuted. infancy, during the first Catalan was Consequently, few years of not schooling some schoolgoers taught in schools, nor was it used demonstrate greater competence as the language of instruction. in Catalan while others have in With the return of democracya greater mastery of Castilian. Spain (1976), Catalan was However, in Catalonia as of introducedwhen at the age a 16 schoolgoers reach in end compulsory subjectthe both of compulsory secondary education. primary and education, no student can claim not to understand either language. Oral expression Written comprehension Written expression All the members of this subgroup are linguistically proficient
PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Under the age of 40 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 (especially all those between the ages of 16 and 40) MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Oral comprehension = Today in Catalonia, Catalan is Independently of their mother the main language of instruction in tongue, all Catalans under the age compulsory education. According of 40 can understand, speak, read to data for the 1999 -2000 school and write in Catalan. year, 88. 9% of primary schools The language proficiency in and 51. 2% of secondary schools Catalan among the younger taught all classes in Catalan (with generations can be accounted for the exception, in both cases, of by the fact that they received their the subjects of Castilian Language schooling after the end of General and Literature and foreign Franco’s dictatorship. During the languages). military dictatorship, the use of In part due to the predominance of Catalan was prohibited and the mother tongue in politically persecuted. infancy, during the first Catalan was Consequently, few years of not schooling some schoolgoers taught in schools, nor was it used demonstrate greater competence as the language of instruction. in Catalan while others have in With the return of democracya greater mastery of Castilian. Spain (1976), Catalan was However, in Catalonia as of introducedwhen at the age a 16 schoolgoers reach in end compulsory subjectthe both of compulsory secondary education. primary and education, no student can claim not to understand either language. Oral expression Written comprehension Written expression All the members of this subgroup are linguistically proficient
 PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Over the age of 40 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY Catalan speakers 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Only those that have chosen to study in schools for adults can write in Catalan, not having had the opportunity to do so in compulsory education. Oral comprehension = The data for the population over the age of 40 is presented in two subgroups, according to the mother tongue of each subject. All the Catalan speakers (with Catalan as their mother tongue) can understand Catalan and speak it as it is the first language they learnt. In contrast, not all the members of this subgroup read in this language as a matter of course and a large number are not competent writers of Catalan. Oral expression Written comprehension Written expression Not all the members of this subgroup are linguistically proficient
PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Over the age of 40 SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY Catalan speakers 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Only those that have chosen to study in schools for adults can write in Catalan, not having had the opportunity to do so in compulsory education. Oral comprehension = The data for the population over the age of 40 is presented in two subgroups, according to the mother tongue of each subject. All the Catalan speakers (with Catalan as their mother tongue) can understand Catalan and speak it as it is the first language they learnt. In contrast, not all the members of this subgroup read in this language as a matter of course and a large number are not competent writers of Catalan. Oral expression Written comprehension Written expression Not all the members of this subgroup are linguistically proficient
 PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Over the age of 40 SOCIOLINGUISTICS COMPETÈNCIA PROFICIENCY Catalan speakers Castilian speakers 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Thus, the main of Catalans over Most Castilian speakers of the A large number difference between the two are Castilian speakers older generation in their relative 40 who groups iscan neither read ability to in Catalan because, nor write speak Catalan. On (with Castilian as their mother like arriving were either most the other Catalonia, of Catalonia, tongue) ininhabitantsborn outside members or are the children of they did not this migrant subgroup Catalonia of have the opportunity did not Catalan to learnwho were. additional people make theat school. effort required to speak a new language, However, in 2001 (the year in Between 1950 and 1970, more because during Franco’s regime which million migrants came to than a the data for this study was the use of Catalan was forbidden. gathered) all the members of Catalonia from other parts of this In short, for what to movements subgroup claimedwere largely Spain. The migratorybe able to historical reasons, the migrants understand Catalan because they during these two decades were to did been born speak Catalan hadnot great demographic effect. have a learn to in Catalonia, or because they had livedmotivation little in In 1975, for example, 38% of the to do so: was not needed and, Cataloniaitfor more than thirty or Catalan population was of migrant above all, they ran a risk by forty years. origin. In 1996, the migrants and choosing to speak a prohibited Furthermore, the similarities their children born in Catalonia language. between Catalan and Castilian accounted for 41% of the Catalan make the former much easier to population. understand for those who can speak the latter. Oral comprehension Oral expression Written comprehension Written expression
PRESENTACIÓ Knowledge of Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Over the age of 40 SOCIOLINGUISTICS COMPETÈNCIA PROFICIENCY Catalan speakers Castilian speakers 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Thus, the main of Catalans over Most Castilian speakers of the A large number difference between the two are Castilian speakers older generation in their relative 40 who groups iscan neither read ability to in Catalan because, nor write speak Catalan. On (with Castilian as their mother like arriving were either most the other Catalonia, of Catalonia, tongue) ininhabitantsborn outside members or are the children of they did not this migrant subgroup Catalonia of have the opportunity did not Catalan to learnwho were. additional people make theat school. effort required to speak a new language, However, in 2001 (the year in Between 1950 and 1970, more because during Franco’s regime which million migrants came to than a the data for this study was the use of Catalan was forbidden. gathered) all the members of Catalonia from other parts of this In short, for what to movements subgroup claimedwere largely Spain. The migratorybe able to historical reasons, the migrants understand Catalan because they during these two decades were to did been born speak Catalan hadnot great demographic effect. have a learn to in Catalonia, or because they had livedmotivation little in In 1975, for example, 38% of the to do so: was not needed and, Cataloniaitfor more than thirty or Catalan population was of migrant above all, they ran a risk by forty years. origin. In 1996, the migrants and choosing to speak a prohibited Furthermore, the similarities their children born in Catalonia language. between Catalan and Castilian accounted for 41% of the Catalan make the former much easier to population. understand for those who can speak the latter. Oral comprehension Oral expression Written comprehension Written expression
 PRESENTACIÓ Are all sectors of the population of Catalonia bilingual? INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES Population under 40 YES ? FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN the case of of change If terms then the. Castilian and But this is likely language in aged Inthe teachingof topopulation the over 40, continues to be more Catalan it might the future, given thatwell population proficiency, can Catalonia be accurate to speak of a situation compulsory in school, and under 40 is fully bilingual. bearing considered a bilingual society? of asymmetrical bilingualism. in mind that there are constant For the time being, the answer opportunities to use the two On the one to be no. would seemhand, most Catalan languages, the Catalan speakers are virtually bilingual; if demographic pyramid shows us they are not, it is because, that in fifty years’ time the entire bizarrely, not all can read or write population of Catalonia should be in their own language, their mother proficient in Catalan and Castilian. tongue. On the other hand, the Castilian speakers are virtually monolingual as they have fairly serious shortcomings in three of the skills in Catalan: reading, writing and speaking. Population over 40 Catalan speakers NO ? CAST CAT Population over 40 Castilian speakers CAST CAST CAT CAT NO ?
PRESENTACIÓ Are all sectors of the population of Catalonia bilingual? INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES Population under 40 YES ? FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN the case of of change If terms then the. Castilian and But this is likely language in aged Inthe teachingof topopulation the over 40, continues to be more Catalan it might the future, given thatwell population proficiency, can Catalonia be accurate to speak of a situation compulsory in school, and under 40 is fully bilingual. bearing considered a bilingual society? of asymmetrical bilingualism. in mind that there are constant For the time being, the answer opportunities to use the two On the one to be no. would seemhand, most Catalan languages, the Catalan speakers are virtually bilingual; if demographic pyramid shows us they are not, it is because, that in fifty years’ time the entire bizarrely, not all can read or write population of Catalonia should be in their own language, their mother proficient in Catalan and Castilian. tongue. On the other hand, the Castilian speakers are virtually monolingual as they have fairly serious shortcomings in three of the skills in Catalan: reading, writing and speaking. Population over 40 Catalan speakers NO ? CAST CAT Population over 40 Castilian speakers CAST CAST CAT CAT NO ?
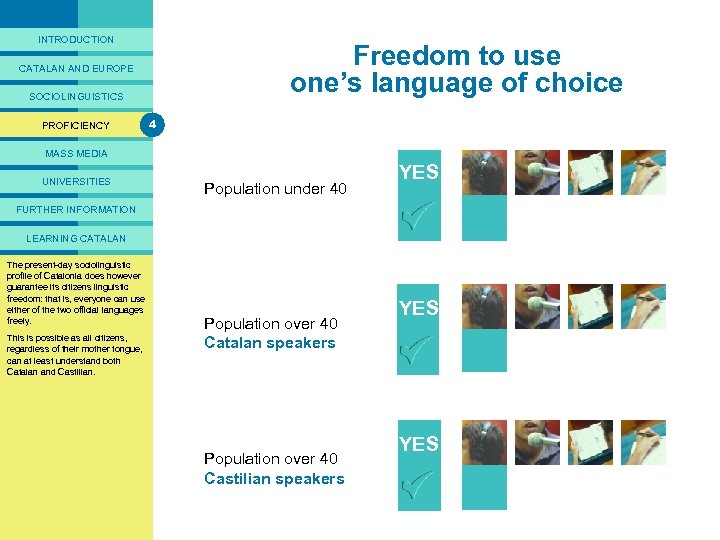 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION Freedom to use one’s language of choice CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES Population under 40 YES SÍ FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The present-day sociolinguistic profile of Catalonia does however guarantee its citizens linguistic freedom: that is, everyone can use either of the two official languages freely. This is possible as all citizens, regardless of their mother tongue, can at least understand both Catalan and Castilian. Population over 40 Catalan speakers Population over 40 Castilian speakers YES NO YES CAST CAT
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION Freedom to use one’s language of choice CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY 4 MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES Population under 40 YES SÍ FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The present-day sociolinguistic profile of Catalonia does however guarantee its citizens linguistic freedom: that is, everyone can use either of the two official languages freely. This is possible as all citizens, regardless of their mother tongue, can at least understand both Catalan and Castilian. Population over 40 Catalan speakers Population over 40 Castilian speakers YES NO YES CAST CAT
 CATALAN IN THE MASS MEDIA The language’s presence in the mass media and in culture 5
CATALAN IN THE MASS MEDIA The language’s presence in the mass media and in culture 5
 PRESENTACIÓ The way we are INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Asitssecond idea conspicuous In Undoubtedly, above, one of the The example, the related to might own natural market, for Fordiscussed though, what essential of Catalan themost of the example, Catalan finds itself in in part best that the advertising bilingualismexplain in absence of absence conditions for Catalan society tocompetition withbilingual constant certain fields, Catalan inbe in the advertisement agency uses is due to the mass media considered is that all Catalanshypothesis that Castilian, a language the be particularly in the should has was based onthe mass media, are restrictions placed on that use of proficient in theirright to choose great demographic and, more the effects of globalisation. in Catalonia the use of marketing Catalan in this field and the two officiallanguage toof Catalonia. power. which languages use at all times generally, to the political There are few real opportunities is guaranteed. persecution suffered by the for minority languages in global Despite the challenges Catalan language from authoritarian relations. What’s more, in the This is the secondition the faces in establishing itself as regimes at various periods in the internationalisation of political, the predominant language in that which, in theory, ensures the mass recent history of Catalonia, dating economic, social andcan are media of Catalonia, cultural citizens of Cataloniatherechoose back more than 250 years. exchange in they prefer. world, examples, both modern the languageourin the media and languages likesector, where it in the cultural Catalan find In this next section, we shall look increasingly difficult toas Castilian Catalan is as present find fields in at the mass media, an area in which they can continue to be or even more so. which the aim mentioned above predominant, even in The slides that follow present has not been fully achieved. the communicative situations inside percentage use of Catalan in their own territory. various sectors of the media. The web pages of these sectors can be visited by clicking on the corresponding logotype. “Can “Is Catalan choose which we always You choose represented? ” language to use? ”
PRESENTACIÓ The way we are INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Asitssecond idea conspicuous In Undoubtedly, above, one of the The example, the related to might own natural market, for Fordiscussed though, what essential of Catalan themost of the example, Catalan finds itself in in part best that the advertising bilingualismexplain in absence of absence conditions for Catalan society tocompetition withbilingual constant certain fields, Catalan inbe in the advertisement agency uses is due to the mass media considered is that all Catalanshypothesis that Castilian, a language the be particularly in the should has was based onthe mass media, are restrictions placed on that use of proficient in theirright to choose great demographic and, more the effects of globalisation. in Catalonia the use of marketing Catalan in this field and the two officiallanguage toof Catalonia. power. which languages use at all times generally, to the political There are few real opportunities is guaranteed. persecution suffered by the for minority languages in global Despite the challenges Catalan language from authoritarian relations. What’s more, in the This is the secondition the faces in establishing itself as regimes at various periods in the internationalisation of political, the predominant language in that which, in theory, ensures the mass recent history of Catalonia, dating economic, social andcan are media of Catalonia, cultural citizens of Cataloniatherechoose back more than 250 years. exchange in they prefer. world, examples, both modern the languageourin the media and languages likesector, where it in the cultural Catalan find In this next section, we shall look increasingly difficult toas Castilian Catalan is as present find fields in at the mass media, an area in which they can continue to be or even more so. which the aim mentioned above predominant, even in The slides that follow present has not been fully achieved. the communicative situations inside percentage use of Catalan in their own territory. various sectors of the media. The web pages of these sectors can be visited by clicking on the corresponding logotype. “Can “Is Catalan choose which we always You choose represented? ” language to use? ”
 PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in the press INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Language Policy Report SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The presence of Catalan in the general-information paying newspapers, together with those offering sports and financial information, comes to 19. 2%. Three newspapers (Avui, El Periódico and El Punt), one sports paper (El 9 esportiu de Catalunya) and one weekly news magazine (El Temps) are on sale in most parts of the Catalan-speaking area. The remaining Catalan publications are local papers. The circulation of Catalan press publications amounts to 36% of total volume of newspapers and magazines in Catalonia. 36%
PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in the press INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Language Policy Report SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The presence of Catalan in the general-information paying newspapers, together with those offering sports and financial information, comes to 19. 2%. Three newspapers (Avui, El Periódico and El Punt), one sports paper (El 9 esportiu de Catalunya) and one weekly news magazine (El Temps) are on sale in most parts of the Catalan-speaking area. The remaining Catalan publications are local papers. The circulation of Catalan press publications amounts to 36% of total volume of newspapers and magazines in Catalonia. 36%
 PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in television broadcasting INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS Data from the Language Policy Report PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The channels that broadcast Of the television programs in the Catalan-speaking area 30% broadcast in Catalonia, do soare in either entirely or mostly in Catalan. These throughout the Catalan. Today, are TV 3, Canal 33 -K 3 and 3 -24 (owned by the Government speaking area, ten television of Catalonia), Canal 9 and both channels can be received, Punt Dos (owned by the Valencian public and private (not including Government), IB 3 TV). cable and satellite (owned by the Balearic Government), and BTV, However, their ownership is not a Td 8 and Canal. CatalàTV factor determining whether they (broadcast in Barcelona). choose to broadcast in Castilian or The state Catalan. broadcasters, however, schedule programs almost entirely in Castilian: TVE 1 and TVE 2 (Spain’s state broadcasting corporation) and Antena 3, Tele 5, Cuatro and La Sexta (private companies). 30%
PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in television broadcasting INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS Data from the Language Policy Report PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The channels that broadcast Of the television programs in the Catalan-speaking area 30% broadcast in Catalonia, do soare in either entirely or mostly in Catalan. These throughout the Catalan. Today, are TV 3, Canal 33 -K 3 and 3 -24 (owned by the Government speaking area, ten television of Catalonia), Canal 9 and both channels can be received, Punt Dos (owned by the Valencian public and private (not including Government), IB 3 TV). cable and satellite (owned by the Balearic Government), and BTV, However, their ownership is not a Td 8 and Canal. CatalàTV factor determining whether they (broadcast in Barcelona). choose to broadcast in Castilian or The state Catalan. broadcasters, however, schedule programs almost entirely in Castilian: TVE 1 and TVE 2 (Spain’s state broadcasting corporation) and Antena 3, Tele 5, Cuatro and La Sexta (private companies). 30%
 PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in radio broadcasting INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Language Policy Report SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN On the radio, more than 50% of broadcasts are in Catalan. The four stations belonging to the Government of Catalonia (Catalunya Ràdio, i. Cat fm, Catalunya Música and Catalunya Informació) broadcast entirely in Catalan. There are two more public stations that also broadcast in Catalan: COM Ràdio and Ràdio 4. The local stations mainly use Catalan, as do about half the private stations (such as Ona Catalana, RAC 1 and Flash FM). +50%
PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in radio broadcasting INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Language Policy Report SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN On the radio, more than 50% of broadcasts are in Catalan. The four stations belonging to the Government of Catalonia (Catalunya Ràdio, i. Cat fm, Catalunya Música and Catalunya Informació) broadcast entirely in Catalan. There are two more public stations that also broadcast in Catalan: COM Ràdio and Ràdio 4. The local stations mainly use Catalan, as do about half the private stations (such as Ona Catalana, RAC 1 and Flash FM). +50%
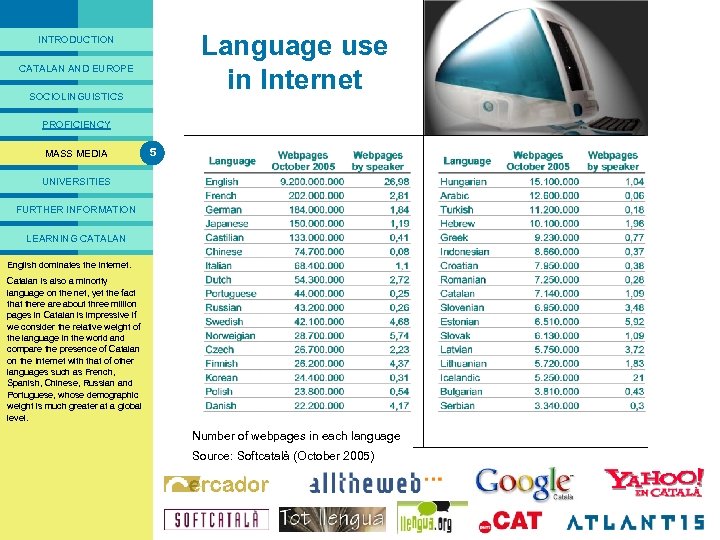 PRESENTACIÓ Language use in Internet INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN English dominates the Internet. Catalan is also a minority language on the net, yet the fact that there about three million pages in Catalan is impressive if we consider the relative weight of the language in the world and compare the presence of Catalan on the Internet with that of other languages such as French, Spanish, Chinese, Russian and Portuguese, whose demographic weight is much greater at a global level. Number of webpages in each language Source: Softcatalà (October 2005)
PRESENTACIÓ Language use in Internet INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN English dominates the Internet. Catalan is also a minority language on the net, yet the fact that there about three million pages in Catalan is impressive if we consider the relative weight of the language in the world and compare the presence of Catalan on the Internet with that of other languages such as French, Spanish, Chinese, Russian and Portuguese, whose demographic weight is much greater at a global level. Number of webpages in each language Source: Softcatalà (October 2005)
 PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in the cinema INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Language Policy Report SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION 5 2% LEARNING CATALAN Films in Spain (both those shown on television and those screened in the cinema) are nearly always dubbed. In most cases the films can only be seen in Castilian. Only in the major cities, such as Barcelona, is there a sizeable offer of foreign language films. Films dubbed into Catalan are few and far between: just 2% of films shown in Catalonia are screened in Catalan. Thus, Catalans have little choice of language when going to the cinema. If you wish to up-date this page just click on the link: Page update!
PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in the cinema INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Language Policy Report SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION 5 2% LEARNING CATALAN Films in Spain (both those shown on television and those screened in the cinema) are nearly always dubbed. In most cases the films can only be seen in Castilian. Only in the major cities, such as Barcelona, is there a sizeable offer of foreign language films. Films dubbed into Catalan are few and far between: just 2% of films shown in Catalonia are screened in Catalan. Thus, Catalans have little choice of language when going to the cinema. If you wish to up-date this page just click on the link: Page update!
 PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in theatre INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Language Policy Report SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN 63% The theatre is the only cultural sector in which Catalan is predominant. Approximately 62. 6% of performances in Barcelona are given in this language. La Fura dels Baus Plays drawn from Catalan literature, as well as those taken from world literature, are normally staged in Catalan. Among the plays performed in Castilian in Catalonia, most are works originally written in that language and therefore also performed in it. Els Comediants El Tricicle
PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in theatre INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE Data from the Language Policy Report SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN 63% The theatre is the only cultural sector in which Catalan is predominant. Approximately 62. 6% of performances in Barcelona are given in this language. La Fura dels Baus Plays drawn from Catalan literature, as well as those taken from world literature, are normally staged in Catalan. Among the plays performed in Castilian in Catalonia, most are works originally written in that language and therefore also performed in it. Els Comediants El Tricicle
 PRESENTACIÓ Catalan in publishing INTRODUCTION Data from the Language Policy Report CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES 5 30% FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Although the percentage of publications in Catalan in 2003 was still small, representing 30. 2% of all published titles, 18% of copies produced and 17% of total turnover, the absolute figures were encouraging: 8, 386 new titles were published in Catalan in 2003 (including books written in this language and translations). The average print-run is approximately 2, 000 copies, reaching 100, 000 in a few cases. These figures are relatively high if we consider that Catalan is a language of limited demographic (and, therefore, market) force. According to figures published by UNESCO, Catalan ranks as the fifteenth language in the world in terms of its volume of publishing. 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 4, 327 4, 838 4, 965 5, 806 5, 905 5, 281 5, 793 6, 061 6, 844 7, 306 7, 261 7, 795 8, 015 8, 183 8, 386 Number of books published each year Catalan is the 15 th most published language in the world (UNESCO)
PRESENTACIÓ Catalan in publishing INTRODUCTION Data from the Language Policy Report CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES 5 30% FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Although the percentage of publications in Catalan in 2003 was still small, representing 30. 2% of all published titles, 18% of copies produced and 17% of total turnover, the absolute figures were encouraging: 8, 386 new titles were published in Catalan in 2003 (including books written in this language and translations). The average print-run is approximately 2, 000 copies, reaching 100, 000 in a few cases. These figures are relatively high if we consider that Catalan is a language of limited demographic (and, therefore, market) force. According to figures published by UNESCO, Catalan ranks as the fifteenth language in the world in terms of its volume of publishing. 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 4, 327 4, 838 4, 965 5, 806 5, 905 5, 281 5, 793 6, 061 6, 844 7, 306 7, 261 7, 795 8, 015 8, 183 8, 386 Number of books published each year Catalan is the 15 th most published language in the world (UNESCO)
 PRESENTACIÓ Translations from Catalan into other languages INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Moreover, Catalan ranks as the 22 nd most translated language in the world, again according to UNESCO. This slide shows just some of the translations into other languages of works by leading authors of Catalan literature: the poet Salvador Espriu, the novelist Mercè Rodoreda, author of La plaça del diamant (translated into sixteen languages), and more contemporary authors such as Sergi Pàmies, Carme Riera and Quim Monzó. It should be remembered that Catalan literature has a history dating back many centuries. At the end of the XV century, Joanot Martorell wrote Tirant lo Blanc, considered the first modern novel in world literature. Catalan is the 22 ndtranslations from Catalan into otherworld (UNESCO) Information on most translated language in the languages: www. llull. cat/llull/biblioteca/trac. jsp? idioma=en
PRESENTACIÓ Translations from Catalan into other languages INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA 5 UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Moreover, Catalan ranks as the 22 nd most translated language in the world, again according to UNESCO. This slide shows just some of the translations into other languages of works by leading authors of Catalan literature: the poet Salvador Espriu, the novelist Mercè Rodoreda, author of La plaça del diamant (translated into sixteen languages), and more contemporary authors such as Sergi Pàmies, Carme Riera and Quim Monzó. It should be remembered that Catalan literature has a history dating back many centuries. At the end of the XV century, Joanot Martorell wrote Tirant lo Blanc, considered the first modern novel in world literature. Catalan is the 22 ndtranslations from Catalan into otherworld (UNESCO) Information on most translated language in the languages: www. llull. cat/llull/biblioteca/trac. jsp? idioma=en
 CATALAN IN THE UNIVERSITIES Catalan in the universities of Catalonia 6
CATALAN IN THE UNIVERSITIES Catalan in the universities of Catalonia 6
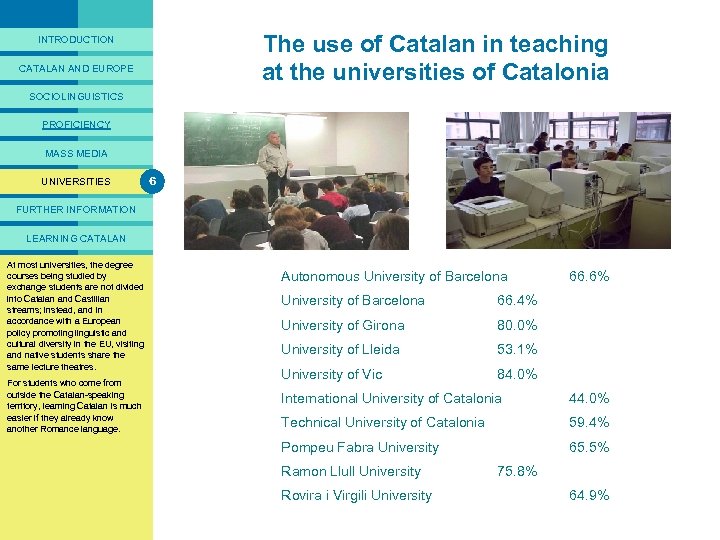 PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in teaching at the universities of Catalonia INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES 6 FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN At most and Castilian are the two Catalan universities, the degree courses being studied by official languages of tertiary exchange education. students are not divided into Catalan and Castilian Data drawn from the academic streams; instead, and in year 2004 -2005 indicates that accordance with a European about two thirds of all university policy promoting linguistic and lectures and seminars are cultural diversity in the EU, visiting conducted in Catalan. and native students share the The policy of the Catalan same lecture theatres. universities is not, however, to For students who come from divide students into groups outside the Catalan-speaking according to their language of territory, learning Catalan is much study. Because of this, students easier if they already know on exchange programs share another Romance language. lecture theatres with local students. Autonomous University of Barcelona 66. 4% University of Girona 80. 0% University of Lleida 53. 1% University of Vic 66. 6% 84. 0% International University of Catalonia 44. 0% Technical University of Catalonia 59. 4% Pompeu Fabra University 65. 5% Ramon Llull University Rovira i Virgili University 75. 8% 64. 9%
PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in teaching at the universities of Catalonia INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES 6 FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN At most and Castilian are the two Catalan universities, the degree courses being studied by official languages of tertiary exchange education. students are not divided into Catalan and Castilian Data drawn from the academic streams; instead, and in year 2004 -2005 indicates that accordance with a European about two thirds of all university policy promoting linguistic and lectures and seminars are cultural diversity in the EU, visiting conducted in Catalan. and native students share the The policy of the Catalan same lecture theatres. universities is not, however, to For students who come from divide students into groups outside the Catalan-speaking according to their language of territory, learning Catalan is much study. Because of this, students easier if they already know on exchange programs share another Romance language. lecture theatres with local students. Autonomous University of Barcelona 66. 4% University of Girona 80. 0% University of Lleida 53. 1% University of Vic 66. 6% 84. 0% International University of Catalonia 44. 0% Technical University of Catalonia 59. 4% Pompeu Fabra University 65. 5% Ramon Llull University Rovira i Virgili University 75. 8% 64. 9%
 PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in teaching at the universities of Catalonia INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Differences in the percentage of lectures given in Catalan are not only to be found from one university to another but also between the faculties within universities. Lecturers choose one of the two official languages in which they wish to give their lectures. The language of instruction for each university subject is made public and is published as a matter of course in student handbooks and guides. By clicking on the logotype of each university, information can be obtained about the percentage of teaching conducted in either language at each of the faculties. 6
PRESENTACIÓ The use of Catalan in teaching at the universities of Catalonia INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Differences in the percentage of lectures given in Catalan are not only to be found from one university to another but also between the faculties within universities. Lecturers choose one of the two official languages in which they wish to give their lectures. The language of instruction for each university subject is made public and is published as a matter of course in student handbooks and guides. By clicking on the logotype of each university, information can be obtained about the percentage of teaching conducted in either language at each of the faculties. 6
 PRESENTACIÓ Multimedia system for exchange students INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES 6 FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Backed by all the students To help exchange. Catalan adapt universities, the language to life in Catalonia and its support program for exchange students academic institutions, the has its own of Catalonia have universities Internet portal: Intercat. agreed to provide a language support program. The portal is a multimedia system built by the universities’ language Given that Catalan is the language units widely used in the of the most under the directionteaching Ministry of Innovation, Universities at the universities of Catalonia, the and Enterprise of the to ensure aim of this program is. Government of Catalonia. It no handicap to the that this poses was designed with the idea that exchange students. could begin to study Catalan and learn the language, thanks to a range of distance learning methods, while still at their home university and before leaving to study in Catalonia. http: //intercat. cesca. es/eng/
PRESENTACIÓ Multimedia system for exchange students INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES 6 FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Backed by all the students To help exchange. Catalan adapt universities, the language to life in Catalonia and its support program for exchange students academic institutions, the has its own of Catalonia have universities Internet portal: Intercat. agreed to provide a language support program. The portal is a multimedia system built by the universities’ language Given that Catalan is the language units widely used in the of the most under the directionteaching Ministry of Innovation, Universities at the universities of Catalonia, the and Enterprise of the to ensure aim of this program is. Government of Catalonia. It no handicap to the that this poses was designed with the idea that exchange students. could begin to study Catalan and learn the language, thanks to a range of distance learning methods, while still at their home university and before leaving to study in Catalonia. http: //intercat. cesca. es/eng/
 OTHER INFORMATION RESOURCES Web links for Catalan 7
OTHER INFORMATION RESOURCES Web links for Catalan 7
 PRESENTACIÓ Information provided by universities INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION MORE INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Most of the universities have web pages detailing the languages used in their teaching. Click on the images in the web pages to open information windows about the languages of instruction and the facilities available for learning Catalan. These pages also contain FAQs posed by exchange students before coming to Catalonia, and also an e-mail facility where students’ questions can be answered personally. Barcelona University Centre (BCU) and the Inter-University Board of Catalonia (CIC) also provide information on questions related to language. 7
PRESENTACIÓ Information provided by universities INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION MORE INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Most of the universities have web pages detailing the languages used in their teaching. Click on the images in the web pages to open information windows about the languages of instruction and the facilities available for learning Catalan. These pages also contain FAQs posed by exchange students before coming to Catalonia, and also an e-mail facility where students’ questions can be answered personally. Barcelona University Centre (BCU) and the Inter-University Board of Catalonia (CIC) also provide information on questions related to language. 7
 PRESENTACIÓ Information provided by universities Index INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY Barcelona University Centre. MASS MEDIA Barcelona and the surrounding area Studying at the Universities of Catalonia. UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION MORE INFORMATION Government of Catalonia; City Council of Barcelona; universities of 7 Government of Catalonia Catalan at the University of Barcelona. Information for incoming exchange students. University of Barcelona LEARNING CATALAN You can use this selection of links as a list of university webpages or shortlist of useful information resources for the Catalan language. Information foreign students. Where are you from? Autonomous University of Barcelona Technical University of Catalonia Did you know that in Catalonia we also speak Catalan? Pompeu Fabra University Languages at the Rovira i Virgili University Catalan at the University of Lleida Modern Languages Service. University of Girona
PRESENTACIÓ Information provided by universities Index INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY Barcelona University Centre. MASS MEDIA Barcelona and the surrounding area Studying at the Universities of Catalonia. UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION MORE INFORMATION Government of Catalonia; City Council of Barcelona; universities of 7 Government of Catalonia Catalan at the University of Barcelona. Information for incoming exchange students. University of Barcelona LEARNING CATALAN You can use this selection of links as a list of university webpages or shortlist of useful information resources for the Catalan language. Information foreign students. Where are you from? Autonomous University of Barcelona Technical University of Catalonia Did you know that in Catalonia we also speak Catalan? Pompeu Fabra University Languages at the Rovira i Virgili University Catalan at the University of Lleida Modern Languages Service. University of Girona
 PRESENTACIÓ General information on the Catalan language INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION MORE INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN By clicking on the link image, access can be gained to other webs containing general information about the Catalan language. 7
PRESENTACIÓ General information on the Catalan language INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION MORE INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN By clicking on the link image, access can be gained to other webs containing general information about the Catalan language. 7
 PRESENTACIÓ Guides to enjoy your stay INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION MORE INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The Cultural Routes offered by the Language Resource Program and ‘ 30 tips‘ guide book introduce visiting students in Catalonia to the various habits and customs of Catalan society. 7
PRESENTACIÓ Guides to enjoy your stay INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION MORE INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The Cultural Routes offered by the Language Resource Program and ‘ 30 tips‘ guide book introduce visiting students in Catalonia to the various habits and customs of Catalan society. 7
 PRESENTACIÓ Guides to Barcelona and to Catalan culture INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION MORE INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Do you know Barcelona? and bcn. youth are guides to Barcelona and to Catalan culture aimed at visitors that have just arrived in the city or who are planning to stay here in the near future. 7
PRESENTACIÓ Guides to Barcelona and to Catalan culture INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION MORE INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Do you know Barcelona? and bcn. youth are guides to Barcelona and to Catalan culture aimed at visitors that have just arrived in the city or who are planning to stay here in the near future. 7
 OPPORTUNITIES TO LEARN CATALAN Catalan language learning resources 8
OPPORTUNITIES TO LEARN CATALAN Catalan language learning resources 8
 PRESENTACIÓ Courses taught at the universities of Catalonia INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN All Catalan universities offer visiting students either free or subsidised Catalan language instruction to facilitate their academic studies during their stay in Catalonia. In particular, these language courses aim to help students and their university teachers communicate more satisfactorily. Exchange students also have the opportunity to learn Catalan by using the self-access centres. As we shall see, however, language learning can also be conducted before the beginning of the academic year or even before the student has arrived in Catalonia. By clicking on the logotype of each university, information can be obtained about the various language courses on offer. 8
PRESENTACIÓ Courses taught at the universities of Catalonia INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN All Catalan universities offer visiting students either free or subsidised Catalan language instruction to facilitate their academic studies during their stay in Catalonia. In particular, these language courses aim to help students and their university teachers communicate more satisfactorily. Exchange students also have the opportunity to learn Catalan by using the self-access centres. As we shall see, however, language learning can also be conducted before the beginning of the academic year or even before the student has arrived in Catalonia. By clicking on the logotype of each university, information can be obtained about the various language courses on offer. 8
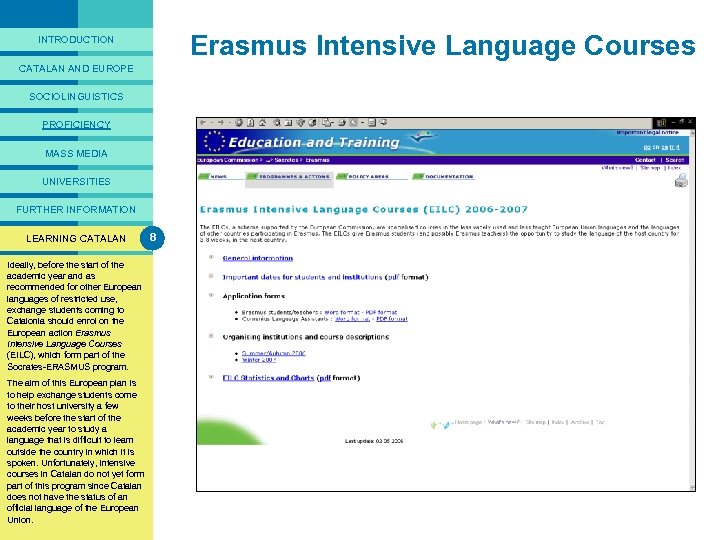 PRESENTACIÓ Erasmus Intensive Language Courses INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Ideally, before the start of the academic year and as recommended for other European languages of restricted use, exchange students coming to Catalonia should enrol on the European action Erasmus Intensive Language Courses (EILC), which form part of the Socrates-ERASMUS program. The aim of this European plan is to help exchange students come to their host university a few weeks before the start of the academic year to study a language that is difficult to learn outside the country in which it is spoken. Unfortunately, intensive courses in Catalan do not yet form part of this program since Catalan does not have the status of an official language of the European Union. 8
PRESENTACIÓ Erasmus Intensive Language Courses INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Ideally, before the start of the academic year and as recommended for other European languages of restricted use, exchange students coming to Catalonia should enrol on the European action Erasmus Intensive Language Courses (EILC), which form part of the Socrates-ERASMUS program. The aim of this European plan is to help exchange students come to their host university a few weeks before the start of the academic year to study a language that is difficult to learn outside the country in which it is spoken. Unfortunately, intensive courses in Catalan do not yet form part of this program since Catalan does not have the status of an official language of the European Union. 8
 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION Programs for language exchange CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN To complete a student’s language training, a further facility provided by virtually all the universities is the conversation exchange program. These programs aim to give exchange students the opportunity to practise the language they are studying. The success of these programs depends on the participation of local students and the various language volunteers. In addition to the language exchange programs, some universities also organise a range of social activities, from weekly meetings, parties and guided visits to places of interest to weekend outings, cinema clubs or theatre and cinema trips. 8
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION Programs for language exchange CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN To complete a student’s language training, a further facility provided by virtually all the universities is the conversation exchange program. These programs aim to give exchange students the opportunity to practise the language they are studying. The success of these programs depends on the participation of local students and the various language volunteers. In addition to the language exchange programs, some universities also organise a range of social activities, from weekly meetings, parties and guided visits to places of interest to weekend outings, cinema clubs or theatre and cinema trips. 8
 PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION Programs for language exchange Index CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA Mentor. Association des États Généraux des Étudiants de l’Europe Conversation exchange web. UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN You can use this selection of links as a list of programs for language exchange or shortlist of useful information about conversation exchange programmes. It is well worth taking advantage of the language resource programs offered at universities. First, learning Catalan will help you to keep better track of what our towns and cities can offer in terms of cultural and social events; second, you’ll find that you feel more at home in the local community and can become more involved in community initiatives. Once you’ve learned a little of the language, there will be many opportunities to practise it both inside and outside the University; and finally, the Catalan language learning activities are also a good way to meet other students! 8 University of Barcelona Ajuda’m (Help in English). Language and cultural reception programme for mobility students at UAB. Autonomous University of Barcelona Ajuda’m (Help in English) is a cultural umbrella program aimed at students from outside Catalonia who come to study at UPC. Technical Universitat of Catalonia Linguistic exchange. University of Girona Conversation exchange. Pompeu Fabra University Gràcies, beginner’s Catalan. Rovira i Virgili University Linguistic exchange. University of Lleida
PRESENTACIÓ INTRODUCTION Programs for language exchange Index CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA Mentor. Association des États Généraux des Étudiants de l’Europe Conversation exchange web. UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN You can use this selection of links as a list of programs for language exchange or shortlist of useful information about conversation exchange programmes. It is well worth taking advantage of the language resource programs offered at universities. First, learning Catalan will help you to keep better track of what our towns and cities can offer in terms of cultural and social events; second, you’ll find that you feel more at home in the local community and can become more involved in community initiatives. Once you’ve learned a little of the language, there will be many opportunities to practise it both inside and outside the University; and finally, the Catalan language learning activities are also a good way to meet other students! 8 University of Barcelona Ajuda’m (Help in English). Language and cultural reception programme for mobility students at UAB. Autonomous University of Barcelona Ajuda’m (Help in English) is a cultural umbrella program aimed at students from outside Catalonia who come to study at UPC. Technical Universitat of Catalonia Linguistic exchange. University of Girona Conversation exchange. Pompeu Fabra University Gràcies, beginner’s Catalan. Rovira i Virgili University Linguistic exchange. University of Lleida
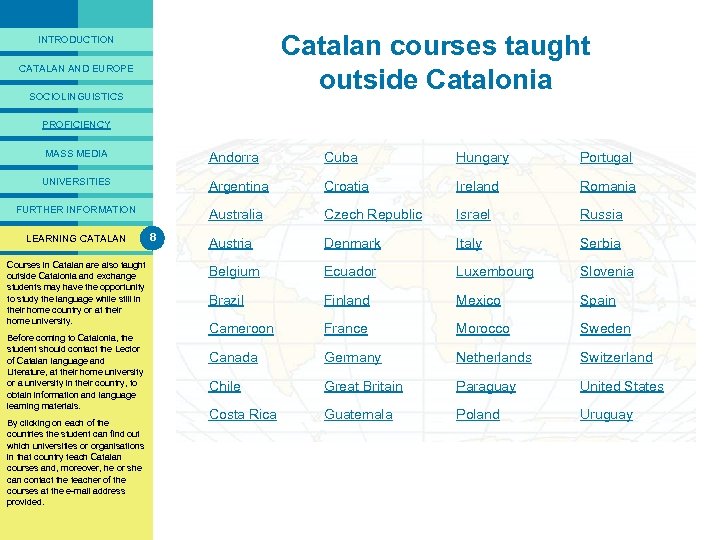 PRESENTACIÓ Catalan courses taught outside Catalonia INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA Andorra Cuba Hungary Portugal UNIVERSITIES Argentina Croatia Ireland Romania FURTHER INFORMATION Australia Czech Republic Israel Russia Austria Denmark Italy Serbia Belgium Ecuador Luxembourg Slovenia Brazil Finland Mexico Spain Cameroon France Morocco Sweden Canada Germany Netherlands Switzerland Chile Great Britain Paraguay United States Costa Rica Guatemala Poland Uruguay LEARNING CATALAN Courses in Catalan are also taught outside Catalonia and exchange students may have the opportunity to study the language while still in their home country or at their home university. Before coming to Catalonia, the student should contact the Lector of Catalan language and Literature, at their home university or a university in their country, to obtain information and language learning materials. By clicking on each of the countries the student can find out which universities or organisations in that country teach Catalan courses and, moreover, he or she can contact the teacher of the courses at the e-mail address provided. 8
PRESENTACIÓ Catalan courses taught outside Catalonia INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA Andorra Cuba Hungary Portugal UNIVERSITIES Argentina Croatia Ireland Romania FURTHER INFORMATION Australia Czech Republic Israel Russia Austria Denmark Italy Serbia Belgium Ecuador Luxembourg Slovenia Brazil Finland Mexico Spain Cameroon France Morocco Sweden Canada Germany Netherlands Switzerland Chile Great Britain Paraguay United States Costa Rica Guatemala Poland Uruguay LEARNING CATALAN Courses in Catalan are also taught outside Catalonia and exchange students may have the opportunity to study the language while still in their home country or at their home university. Before coming to Catalonia, the student should contact the Lector of Catalan language and Literature, at their home university or a university in their country, to obtain information and language learning materials. By clicking on each of the countries the student can find out which universities or organisations in that country teach Catalan courses and, moreover, he or she can contact the teacher of the courses at the e-mail address provided. 8
 Internet resources for learning Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN 8 Among the resources for learning Because Catalan is a minority Catalan, there is the on-line language, it is not widely taught course the Catalan-speaking the outside Parla. cat, promoted byarea. Language Policy Secretariat of the That is why the Internet is Institut Catalan Government, the a very good tool forand the Consortium Ramon Llull learning Catalan, particularly because many for Language Normalisation. exchange students do not have the opportunity to go to class in their home country. By clicking on the image, a range of possibilities available for learning Catalan on the Internet are shown. In addition to materials organised by level of difficulty, you can also find the web site addresses of the various sectors of the media in Catalan. http: //www. parla. cat PRESENTACIÓ
Internet resources for learning Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN 8 Among the resources for learning Because Catalan is a minority Catalan, there is the on-line language, it is not widely taught course the Catalan-speaking the outside Parla. cat, promoted byarea. Language Policy Secretariat of the That is why the Internet is Institut Catalan Government, the a very good tool forand the Consortium Ramon Llull learning Catalan, particularly because many for Language Normalisation. exchange students do not have the opportunity to go to class in their home country. By clicking on the image, a range of possibilities available for learning Catalan on the Internet are shown. In addition to materials organised by level of difficulty, you can also find the web site addresses of the various sectors of the media in Catalan. http: //www. parla. cat PRESENTACIÓ
 PRESENTACIÓ Speakc@t Survival Catalan course INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS (for exchange students) PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Among the resources available to exchange students for studying Catalan before coming to Catalonia, there are the language training materials provided by Intercat. All the resources of this multimedia system have been designed in particular anticipation of the language needs of the exchange students, and the typical situations in which they might find themselves. Furthermore, they use the latest technology, exploiting the teaching possibilities that they provide to the full. Intercat also provides access to the Catalan survival course Speakc@t. 8
PRESENTACIÓ Speakc@t Survival Catalan course INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS (for exchange students) PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Among the resources available to exchange students for studying Catalan before coming to Catalonia, there are the language training materials provided by Intercat. All the resources of this multimedia system have been designed in particular anticipation of the language needs of the exchange students, and the typical situations in which they might find themselves. Furthermore, they use the latest technology, exploiting the teaching possibilities that they provide to the full. Intercat also provides access to the Catalan survival course Speakc@t. 8
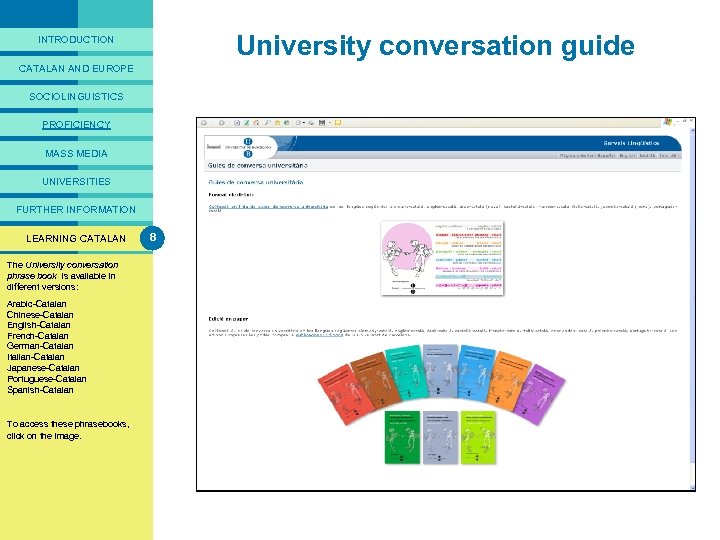 PRESENTACIÓ University conversation guide INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The University of this phrase book web page conversation phrasebook canavailableaccessed phrase book is also be in contains voice files so that the through can listen to how the different versions: student Intercat. words and phrases in each This phrasebook contains basic Arabic-Catalan chapter should be pronounced. Chinese-Catalan vocabulary and phrases for those English-Catalan situations that exchange students French-Catalan themselves in are sure to find German-Catalan when studying abroad. Italian-Catalan Japanese-Catalan Portuguese-Catalan Spanish-Catalan To access these phrasebooks, click on the image. 8
PRESENTACIÓ University conversation guide INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN The University of this phrase book web page conversation phrasebook canavailableaccessed phrase book is also be in contains voice files so that the through can listen to how the different versions: student Intercat. words and phrases in each This phrasebook contains basic Arabic-Catalan chapter should be pronounced. Chinese-Catalan vocabulary and phrases for those English-Catalan situations that exchange students French-Catalan themselves in are sure to find German-Catalan when studying abroad. Italian-Catalan Japanese-Catalan Portuguese-Catalan Spanish-Catalan To access these phrasebooks, click on the image. 8
 PRESENTACIÓ Exercises for practising oral Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Sisplau (Please) is a collection of exercises for those just beginning to study Catalan. The activities in this learning pack are designed as extra material to be used with other communicative language learning methods and reflect more closely the language needs of students at university. 8
PRESENTACIÓ Exercises for practising oral Catalan INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Sisplau (Please) is a collection of exercises for those just beginning to study Catalan. The activities in this learning pack are designed as extra material to be used with other communicative language learning methods and reflect more closely the language needs of students at university. 8
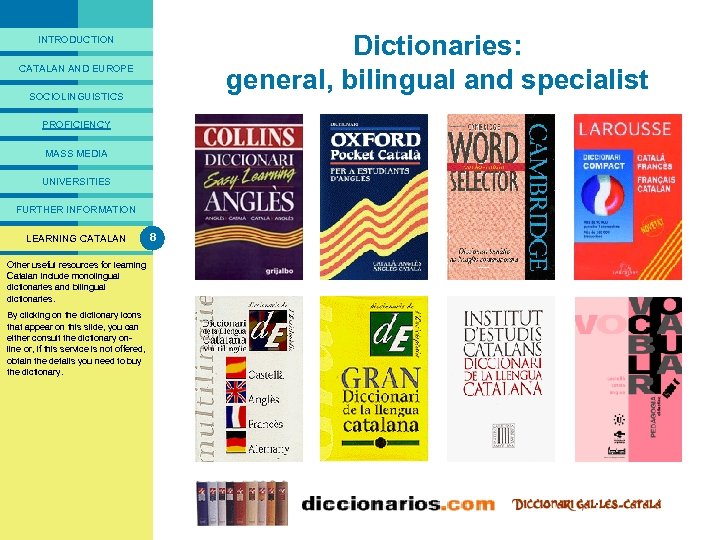 PRESENTACIÓ Dictionaries: general, bilingual and specialist INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Other useful resources for learning Catalan include monolingual dictionaries and bilingual dictionaries. By clicking on the dictionary icons that appear on this slide, you can either consult the dictionary online or, if this service is not offered, obtain the details you need to buy the dictionary. 8
PRESENTACIÓ Dictionaries: general, bilingual and specialist INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Other useful resources for learning Catalan include monolingual dictionaries and bilingual dictionaries. By clicking on the dictionary icons that appear on this slide, you can either consult the dictionary online or, if this service is not offered, obtain the details you need to buy the dictionary. 8
 PRESENTACIÓ On-line translation and language advice INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Another highly useful tool are online translators, most of which translate from Castilian into Catalan. Some of those shown on this slide also translate from other languages, such as English and Portuguese. Catalan spelling, grammar and style correctors can all be found on the market today. 8
PRESENTACIÓ On-line translation and language advice INTRODUCTION CATALAN AND EUROPE SOCIOLINGUISTICS PROFICIENCY MASS MEDIA UNIVERSITIES FURTHER INFORMATION LEARNING CATALAN Another highly useful tool are online translators, most of which translate from Castilian into Catalan. Some of those shown on this slide also translate from other languages, such as English and Portuguese. Catalan spelling, grammar and style correctors can all be found on the market today. 8
 BIBLIOGRAPHY “Acollida lingüística”. At: Argumenta. Vols millorar les competències lingüístiques i comunicatives en l’àmbit acadèmic i professional? Serveis lingüístics de les universitats catalanes, 2006.
BIBLIOGRAPHY “Acollida lingüística”. At: Argumenta. Vols millorar les competències lingüístiques i comunicatives en l’àmbit acadèmic i professional? Serveis lingüístics de les universitats catalanes, 2006.
![BIBLIOGRAPHY Europa y las lenguas. [on line]. [Brussels]: Comisión Europea. [Visited: 26. 07]. <http: BIBLIOGRAPHY Europa y las lenguas. [on line]. [Brussels]: Comisión Europea. [Visited: 26. 07]. <http:](https://present5.com/presentation/4de85ba1fa39b8a8fd10e2614ea2bf87/image-76.jpg) BIBLIOGRAPHY Europa y las lenguas. [on line]. [Brussels]: Comisión Europea. [Visited: 26. 07].
BIBLIOGRAPHY Europa y las lenguas. [on line]. [Brussels]: Comisión Europea. [Visited: 26. 07].
![BIBLIOGRAPHY Lingua+ [cd-rom]. [Barcelona]: Eusko Jaurlaritza, Hizkuntza Politikarako Sailordetza; Nafarroako Gobernua, Hizkuntza Politikarako Zuzendaritza BIBLIOGRAPHY Lingua+ [cd-rom]. [Barcelona]: Eusko Jaurlaritza, Hizkuntza Politikarako Sailordetza; Nafarroako Gobernua, Hizkuntza Politikarako Zuzendaritza](https://present5.com/presentation/4de85ba1fa39b8a8fd10e2614ea2bf87/image-77.jpg) BIBLIOGRAPHY Lingua+ [cd-rom]. [Barcelona]: Eusko Jaurlaritza, Hizkuntza Politikarako Sailordetza; Nafarroako Gobernua, Hizkuntza Politikarako Zuzendaritza Nagusia; Xunta de Galicia, Dirección Xeral de Política Lingüística; Generalitat de Catalunya, Direcció General de Política Lingüística; University of Wales Bangor; Office Régional du Bilinguisme-Alsace, [1999]. Lingu@net. Europa. [on line]. Lingua-Socrates Programme. European Commission. [Visited: 26. 07].
BIBLIOGRAPHY Lingua+ [cd-rom]. [Barcelona]: Eusko Jaurlaritza, Hizkuntza Politikarako Sailordetza; Nafarroako Gobernua, Hizkuntza Politikarako Zuzendaritza Nagusia; Xunta de Galicia, Dirección Xeral de Política Lingüística; Generalitat de Catalunya, Direcció General de Política Lingüística; University of Wales Bangor; Office Régional du Bilinguisme-Alsace, [1999]. Lingu@net. Europa. [on line]. Lingua-Socrates Programme. European Commission. [Visited: 26. 07].
![ILLUSTRATIONS A close look at Catalonia [cd-rom]. Barcelona: Generalitat de Catalunya, [1995]. Barcelona University ILLUSTRATIONS A close look at Catalonia [cd-rom]. Barcelona: Generalitat de Catalunya, [1995]. Barcelona University](https://present5.com/presentation/4de85ba1fa39b8a8fd10e2614ea2bf87/image-78.jpg) ILLUSTRATIONS A close look at Catalonia [cd-rom]. Barcelona: Generalitat de Catalunya, [1995]. Barcelona University Center. Barcelona: Barcelona Centre Universitari; Generalitat de Catalunya; Ajuntament de Barcelona; Universitats catalanes, 2000. Comediants [on line]. [Barcelona]: Comediants, [Visited: 24. 03. 04].
ILLUSTRATIONS A close look at Catalonia [cd-rom]. Barcelona: Generalitat de Catalunya, [1995]. Barcelona University Center. Barcelona: Barcelona Centre Universitari; Generalitat de Catalunya; Ajuntament de Barcelona; Universitats catalanes, 2000. Comediants [on line]. [Barcelona]: Comediants, [Visited: 24. 03. 04].
![ILLUSTRATIONS Europa Audiovisual Library [on line]. [Brussels]: European Union, [Visited: 26. 07]. <http: //ec. ILLUSTRATIONS Europa Audiovisual Library [on line]. [Brussels]: European Union, [Visited: 26. 07]. <http: //ec.](https://present5.com/presentation/4de85ba1fa39b8a8fd10e2614ea2bf87/image-79.jpg) ILLUSTRATIONS Europa Audiovisual Library [on line]. [Brussels]: European Union, [Visited: 26. 07].
ILLUSTRATIONS Europa Audiovisual Library [on line]. [Brussels]: European Union, [Visited: 26. 07].
 ILLUSTRATIONS PUIGJANER, J. M. Conocer Catalunya. Barcelona: Generalitat de Catalunya, Departament de la Presidència, 1991. PUIGJANER, Josep-Maria. Perfil de Catalunya. Barcelona: Generalitat de Catalunya, Departament de la Presidència, 1997. RITUERTO, Ricardo M. De. “El español, contra las cuerdas en la UE”. A: El País, 27 de febrero de 2005.
ILLUSTRATIONS PUIGJANER, J. M. Conocer Catalunya. Barcelona: Generalitat de Catalunya, Departament de la Presidència, 1991. PUIGJANER, Josep-Maria. Perfil de Catalunya. Barcelona: Generalitat de Catalunya, Departament de la Presidència, 1997. RITUERTO, Ricardo M. De. “El español, contra las cuerdas en la UE”. A: El País, 27 de febrero de 2005.
 http: //www. intercat. gencat. es/lingcat@ub. edu
http: //www. intercat. gencat. es/lingcat@ub. edu


