Lecture 8 Br Em, CW, EU.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

The British Empire the Commonwealth the European Union Lecture 8

The British Empire A worldwide system of dependencies that over a span of some three centuries was brought under the sovereignty of the crown of GB and the administration of the British government. Colonies, protectorates, dominions, mandates and other territories.

Forms of control Colonies: areas directly ruled by a governor representing the Br Government and Crown. He had wide powers. The most common form of control. Protectorates: local rulers could continue ruling domestically but the foreign and defense aspects were ceded to the Br Government. Dominions: were granted significant freedom to rule themselves. The settler colonies were afforded this freedom. Company Rule: when private British companies tried to set up their own colonies as private commercial concerns.

The British Empire The largest empire in history. For a time was the foremost global power. A product of the European age of discovery. Expanded and contracted wildly over the years.
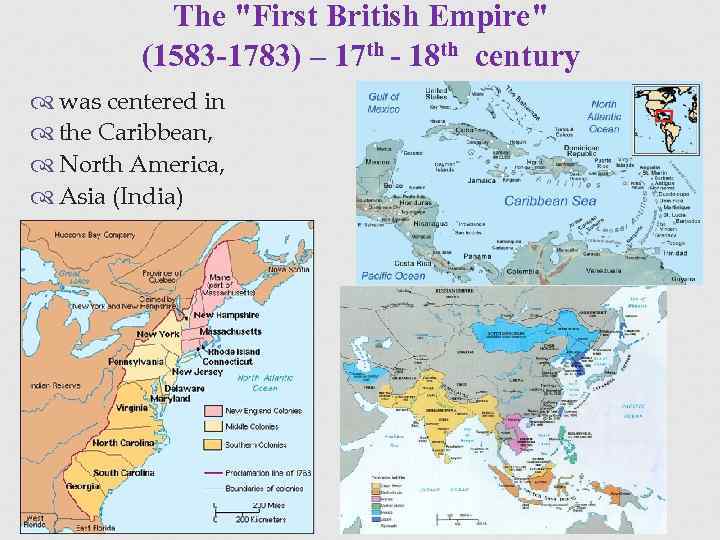
The "First British Empire" (1583 -1783) – 17 th - 18 th century was centered in the Caribbean, North America, Asia (India)

The "First British Empire" (1583 -1783) – 17 th - 18 th century The loss of American colonies in The American War of Independence led to the end of the 1 st British Empire.

The "Second British Empire" (1783 -1931) 1815 the Congress of Vienna: Cape Colony South Africa
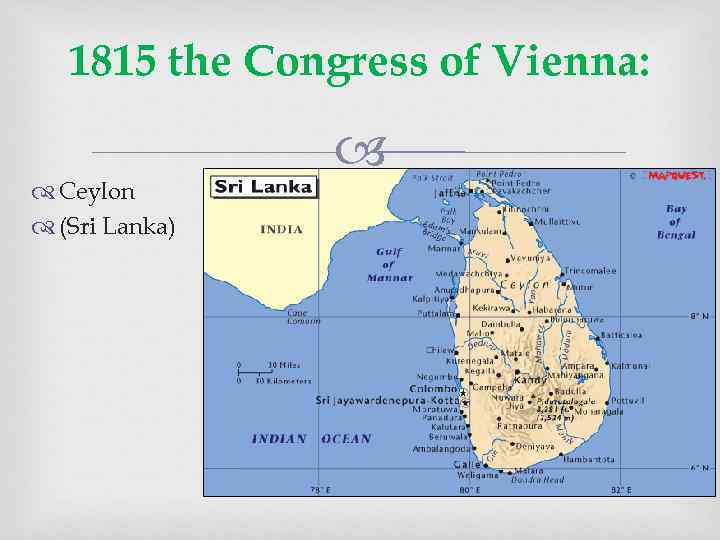
1815 the Congress of Vienna: Ceylon (Sri Lanka)

1815 the Congress of Vienna: Malta

Australia The eastern two thirds of Australia were claimed on behalf of the British Empire in 1770 by Captain James Cook, and was subsequently named New South Wales.
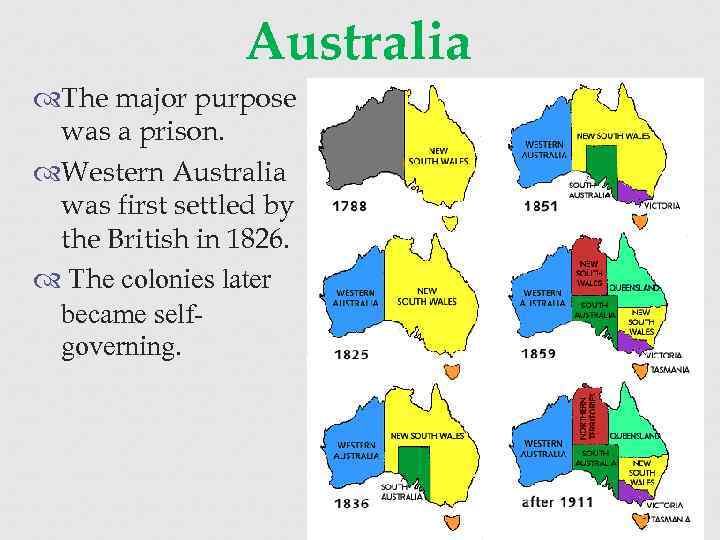
Australia The major purpose was a prison. Western Australia was first settled by the British in 1826. The colonies later became selfgoverning.

China 1840 -60 - Opium Wars Opium , China, since 7 th century, medicinal purpose the practice of mixing it with tobacco for smoking was introduced by Europeans in the 17 th century Br merchants brought opium from India to China, where they sold for a good profit. the number of victims grew

China the Emperor of China demanded that the British stop importing opium The military conflict broke out. The Chinese lost both wars. The victory opened the way for further opium trade, but also Britain got some territory in China including Hong Kong.
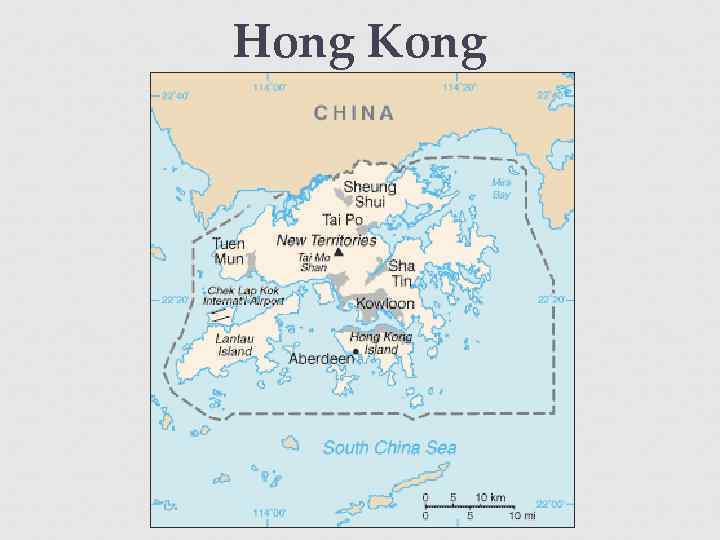
Hong Kong

India Company Rule The British East India Company controlled India (1757 – 1858), until the Indian rebellion of 1857 In 1858, British Crown rule was established in India. It was called the period of the British Raj ("reign" in Hindi). The British Raj lasted since 1858 till until 1947.
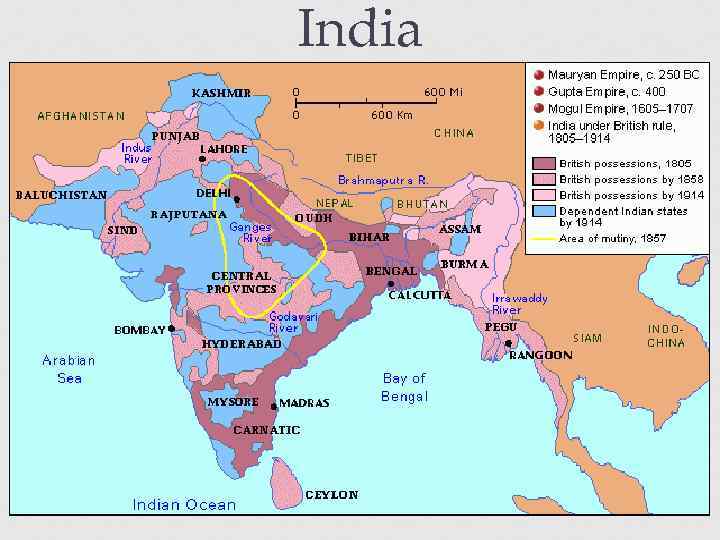
India

The Suez Canal 1875 the Br Government bought from the indebted Egyptian ruler 44% shareholding in the Suez Canal to secure control of this strategic waterway, a channel for shipping between the UK and India.

The Suez Canal
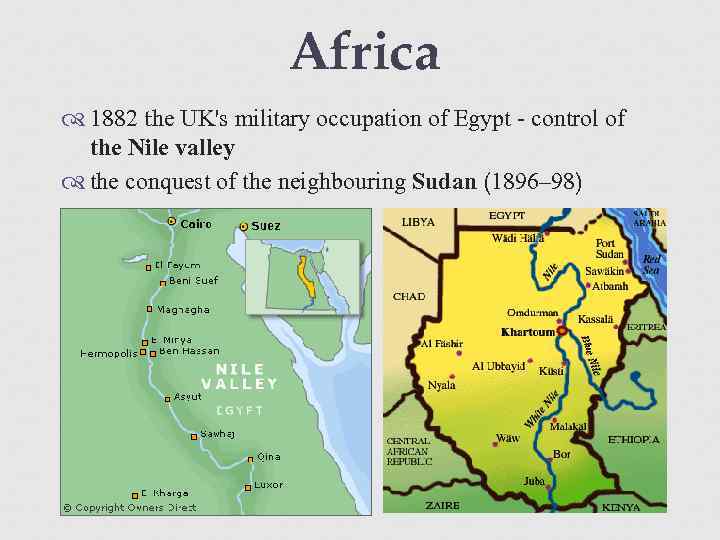
Africa 1882 the UK's military occupation of Egypt - control of the Nile valley the conquest of the neighbouring Sudan (1896– 98)

Africa 1899 – 1902 - the Boer War Gold was discovered in southern Transvaal lured thousands of British miners and prospectors to settle in the area the city of Johannesburg was created almost overnight

Johannesburg

Africa resented the The Afrikaners (Dutch settlers) newcomers The resentment on both sides grew The wars started. The British Empire against the Dutch settlers of two Boer republics - Afrikaners Peace began in 1902. Britain got self-government to the Transvaal and the Orange Free State as its colonies.
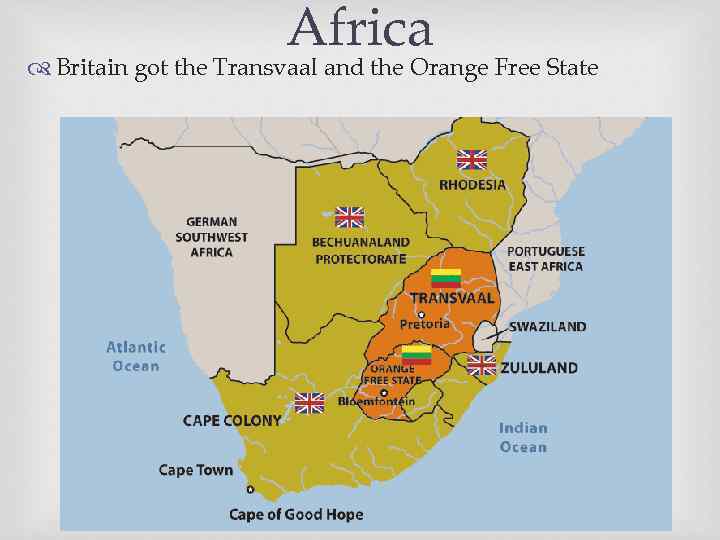
Africa Britain got the Transvaal and the Orange Free State

World War One (1914 – 1918) The Treaty of Versailles in 1919 German and Turkish colonies were passes to Britain Mandate was a legal status transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I. Mandates were administered according to the internationally agreed-upon terms on behalf of the League of Nations.
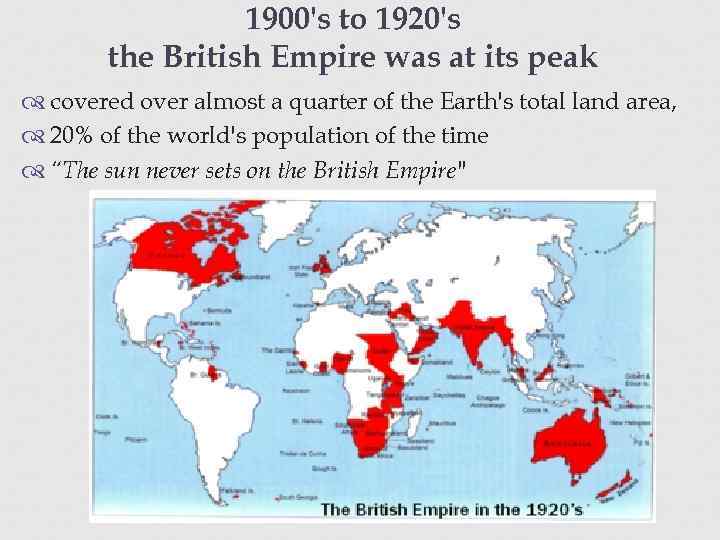
1900's to 1920's the British Empire was at its peak covered over almost a quarter of the Earth's total land area, 20% of the world's population of the time “The sun never sets on the British Empire"

The LN and the UN The League of Nations (abbreviated as LN in English), was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. The United Nations was founded in 1945 after World War II (it replaced the LN), to stop wars between countries, and to provide a platform for dialogue.

The transformation of the British Empire into the Commonwealth After World War I Britain was exhausted, and the empire was overextended. Britain searched for policies that would reduce the cost of the empire and the risk of its falling apart. 1931 – the Statute of Westminster was passed by the Br Parliament

1931 – the Statute of Westminster was the official collapse of the BE each Dominion was henceforth to be equal in status to the UK eliminated all control by the British Parliament over dominion government, free of British legislative interference and autonomous in international relations

The transformation of the British Empire into the Commonwealth By 1931 The UK’s empire had already begun its transformation into the modern Commonwealth with the extension of Dominion status to the already selfgoverning colonies of Canada (1867) Australia (1901) New Zealand (1907) Newfoundland (1907) Union of South Africa (1910)

Decolonization After World War II ended, the British Empire was gradually dismantled to the 14 British overseas territories still held by the United Kingdom. 1941 – the Atlantic Charter - Prime Minister Winston Churchill with US President Roosevelt issued it This document affirmed the basic principles of international justice. It declared the right of self-determination for all countries. Mobilized the empire for the war but hastened its end.

Dismantling of the Empire the Indian Independence Act 1947 1948 Ceylon and Burma In 1948 Palestine African nations in the late 1950 s and early 1960 s Jamaica and Trinidad and Tobago 1962 Throughout this process, British governments did not resist decolonization. Where British prestige was hurt, as in the war with Argentina over the Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas) in 1982, the response was militant. Hong Kong was still under British control after 1950, and it was returned to the People’s Republic of China in 1997

The British Commonwealth 1884 Lord Rosebery described the changing British Empire as a "Commonwealth of Nations”. Conferences of British and colonial prime ministers were held periodically from the first one in 1887, leading to the creation of the Imperial Conferences in 1911. The Commonwealth developed from the Imperial Conferences.

The British Commonwealth At the 1926 Imperial Conference, Britain and its dominions agreed they were "equal in status…united by common allegiance to the Crown, and freely associated as members of the British Commonwealth of Nations". These aspects to the relationship were formalized by the Statute of Westminster in 1931.

Legacy a legal system based upon English law. a military, police and civil service based upon British models. the imperial system of measurement eduational Institutions modelled on Oxford and Cambridge. driving on the left hand side of the road popularity of football, rugby union and/or cricket, as well as related sports.

Legacy sovereignty over fourteen overseas territories, which remain under British rule most former British colonies are members of the Commonwealth of Nations many former British colonies share or shared certain characteristics: the English language a parliamentary system of government modelled on the Westminster system.
Lecture 8 Br Em, CW, EU.ppt