89897f2f8792f993d5144d83e74a574d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

The British Constitution What is a Constitution?

What is a Constitution? n ‘The system or body of fundamental principles according to which a nation state or body politic is constituted and governed’

A Constitution… n Establishes Rules and Principles that govern an organisation n Can be found in political groups, pressure groups and trade unions n In case of countries it refers to the fundamental political principles, establishing the structure, procedures, powers and duties of a government

What do Constitutions set out? n The division of governmental activities, outlining which structures will perform which tasks n The power relationship between the various institutions, showing how each is dependent upon or independent of the operations of the others n The limitations upon the powers of the rulers and a guarantee of the rights of the people who are being ruled (I. e. A Bill of Rights)

What is the purpose of a Constitution? n n n Provide legitimacy to those in power (even in non-democratic states) Protect freedom – defining limits of power Encourages stability – ensuring everyone knows and understands the rules n n Draws attention to the goals and values that characterize a particular state Create a fresh start – especially after a period of long term upheaval – The US Constitution followed the War for Independence etc

Discussion Points n Why do countries need constitutions? n Have they any value?

Classifications of Constitutions n Written n Unwritten n Codified – A Constitution where all the main provisions are brought together in a single document n Un-codified (such as the UK) – Exist where many of the constitutional rules are written down but have not been gathered together
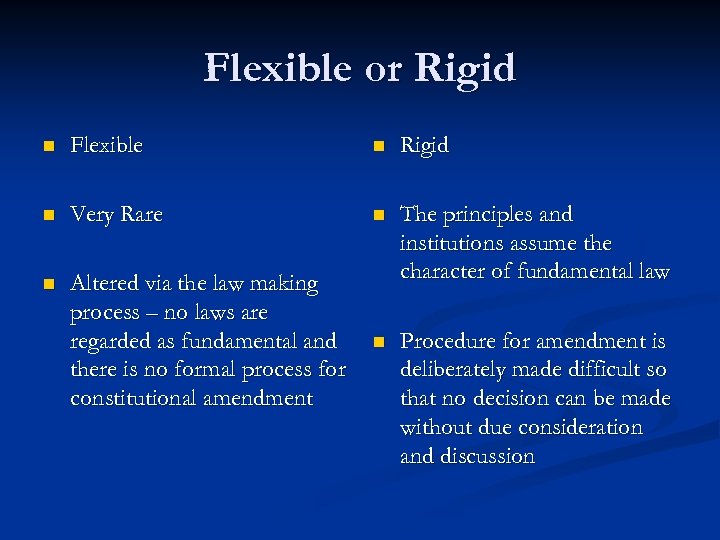
Flexible or Rigid n Flexible n Rigid n Very Rare n n Altered via the law making process – no laws are regarded as fundamental and there is no formal process for constitutional amendment The principles and institutions assume the character of fundamental law n Procedure for amendment is deliberately made difficult so that no decision can be made without due consideration and discussion

Unitary and Federal Constitutionals n Unitary n Federal n Found in France, Israel, Ireland… where small enough to work and without significant ethnic, linguistic and religious differences n A division of rule between Federal (central) and various regional units (America / States – Germany / Landers) n In federal countries - powers and functions clearly written down and clearly defined in a written constitution n Power is concentrated in the hands of the central government

Other Characteristics n Monarchical or Republic n Presidential or Parliamentary n Separation of Powers or Fusion of Powers n n n Executive – Branch of government responsible for directing the nations affairs (UK Govt) Legislature – Branch of government responsible for discussing and passing laws, a watchdog over the govt (Parliament) Separation of Powers – Doctrine that political power should be divided between the executive, legislature and the judiciary
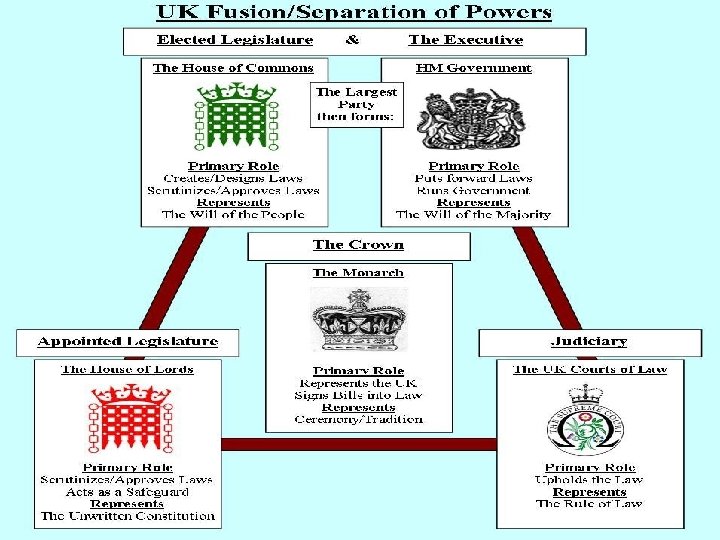
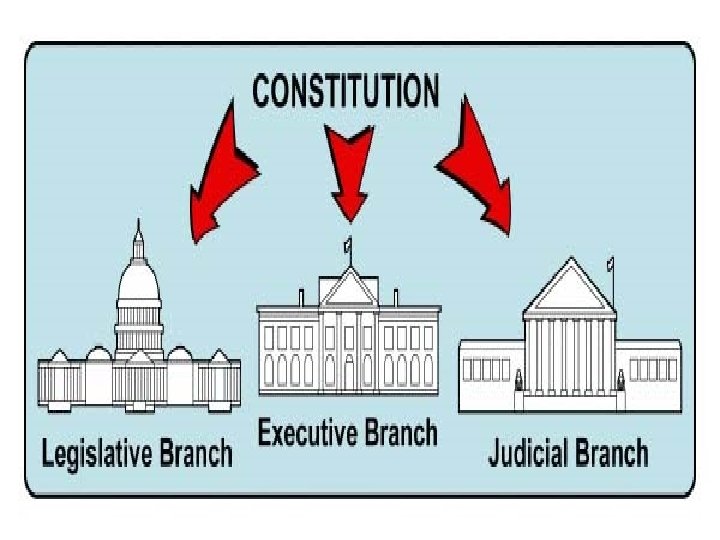
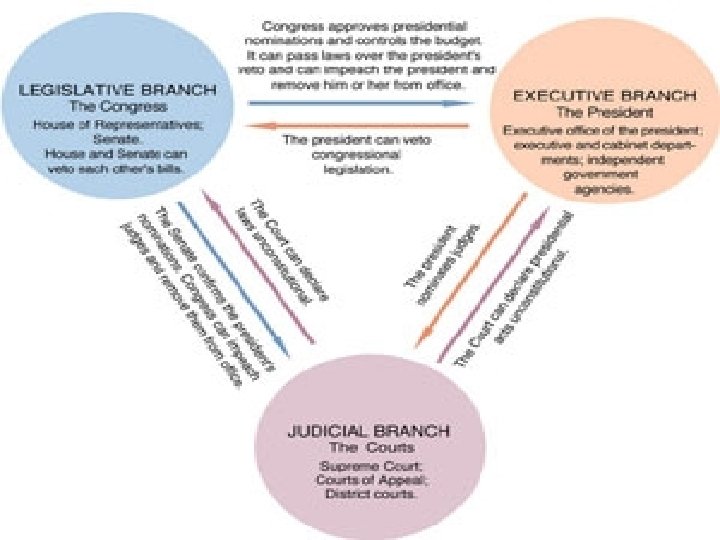

Activity n In pairs, you have been tasked by the UN to rewrite a constitution for a country that has just emerged from a long term Civil War where many people have been killed and millions more displaced from their homes n What basic things would you look to include?
89897f2f8792f993d5144d83e74a574d.ppt