e24760fe4f2701b21f6db42e1d012949.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

The Boltzmann factor
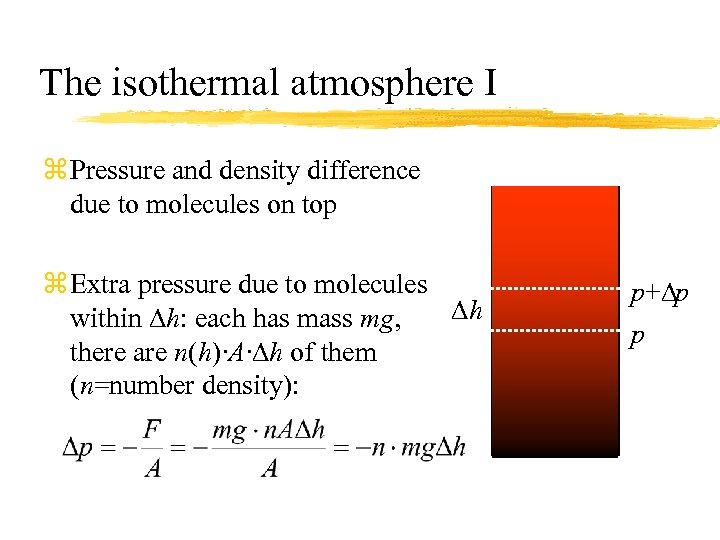
The isothermal atmosphere I z Pressure and density difference due to molecules on top z Extra pressure due to molecules Dh within Dh: each has mass mg, there are n(h)·A·Dh of them (n=number density): p+Dp p
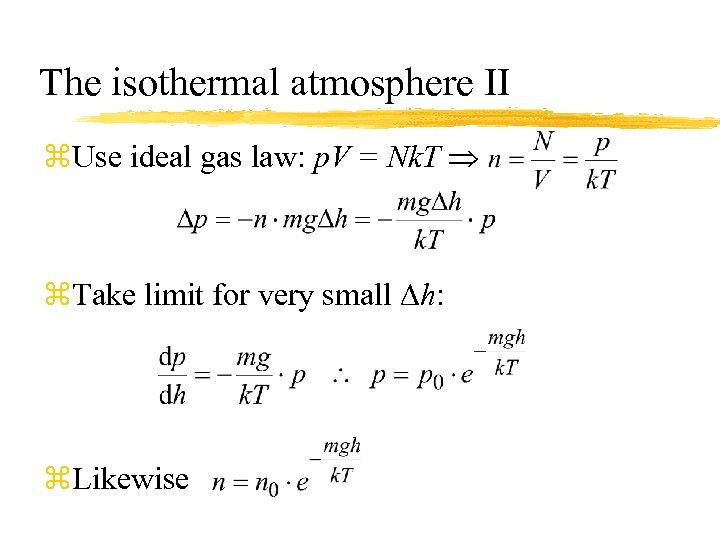
The isothermal atmosphere II z. Use ideal gas law: p. V = Nk. T z. Take limit for very small Dh: z. Likewise

Generalisation z. Note that mgh is P. E. of particle in gravitational field z. This is generally true: z is called the Boltzmann factor

Kinetic energy z. Likewise, it can be shown that the probability of finding a molecule with kinetic energy Ek is z. For the distribution of velocities we find (normalising to a total probability of 1)
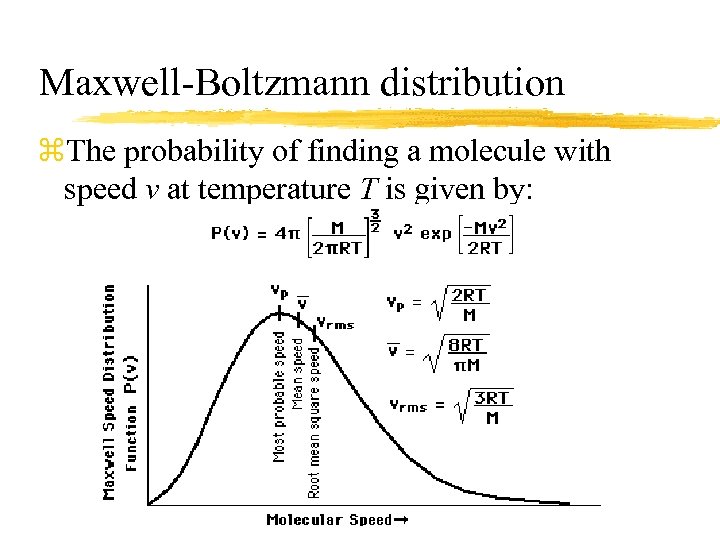
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution z. The probability of finding a molecule with speed v at temperature T is given by:

Diffusion and mobility
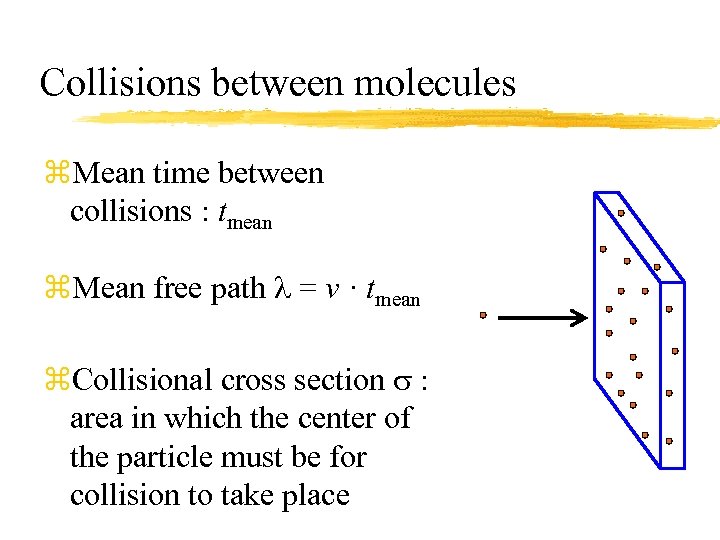
Collisions between molecules z. Mean time between collisions : tmean z. Mean free path = v · tmean z. Collisional cross section s : area in which the center of the particle must be for collision to take place
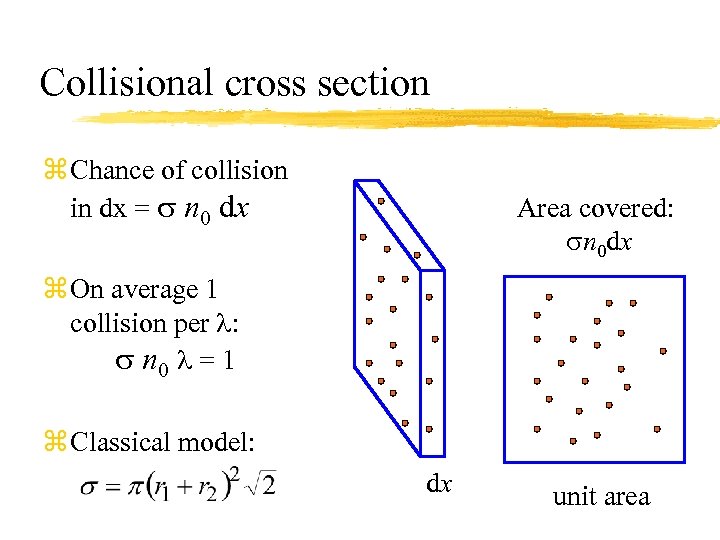
Collisional cross section z Chance of collision in dx = s n 0 dx Area covered: sn 0 dx z On average 1 collision per : s n 0 = 1 z Classical model: dx unit area

Drift speed z. Say that on some molecules we exert a force F z. They collide but make net progress in the direction of F z. Speed picked up since last collision is on average:
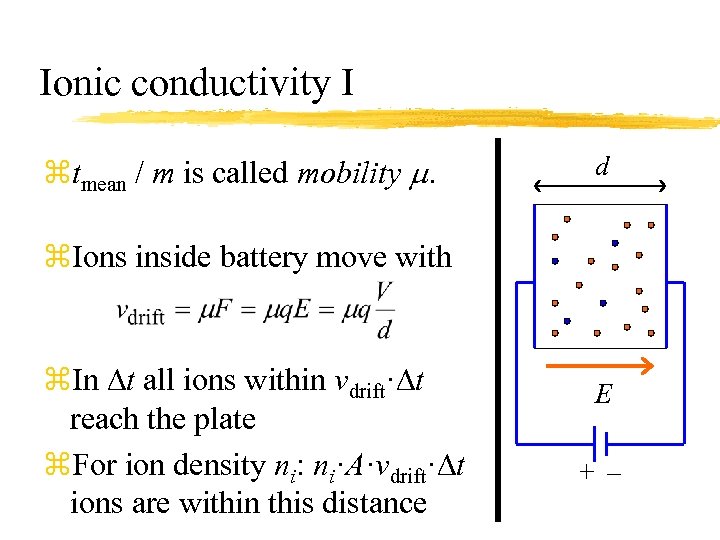
Ionic conductivity I ztmean / m is called mobility m. d z. Ions inside battery move with z. In Dt all ions within vdrift·Dt reach the plate z. For ion density ni: ni·A·vdrift·Dt ions are within this distance E +–
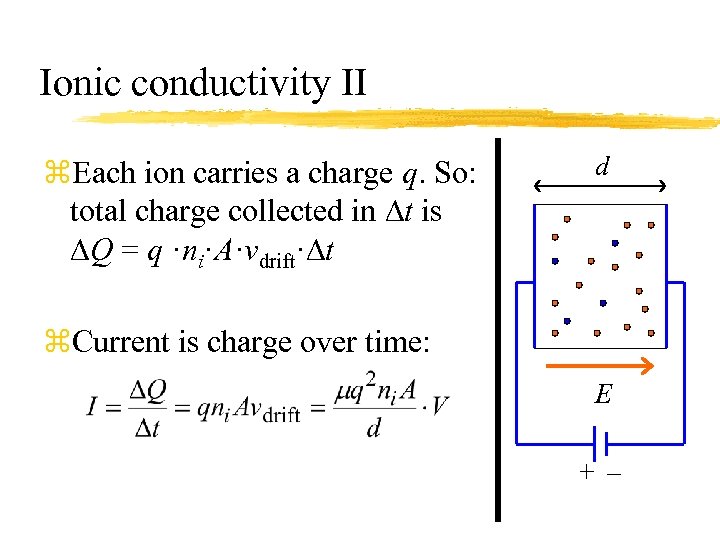
Ionic conductivity II z. Each ion carries a charge q. So: total charge collected in Dt is DQ = q ·ni·A·vdrift·Dt d z. Current is charge over time: E +–
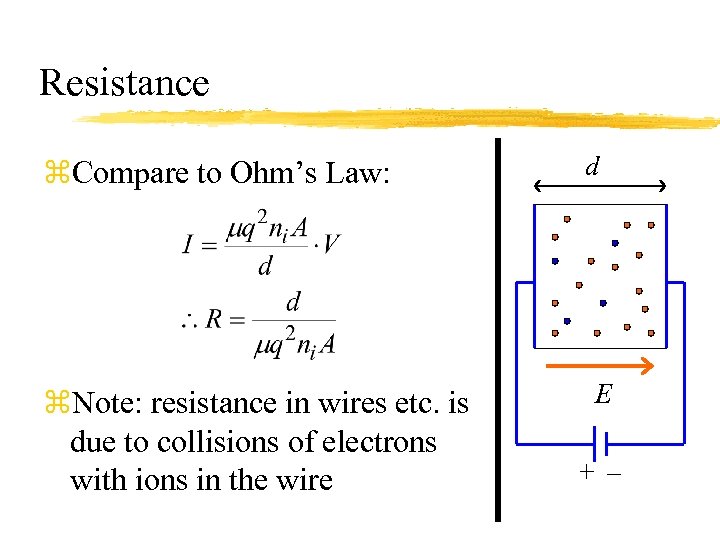
Resistance z. Compare to Ohm’s Law: z. Note: resistance in wires etc. is due to collisions of electrons with ions in the wire d E +–

Diffusion z. Due to random motion molecules spread throughout gas even without additional forces; e. g. smell of cooking spreads through house. z. Net flow depends on difference in density throughout the room: z. D is called diffusion coefficient

Diffusion and drift z. Diffusion coefficient depends on the speed v and the mean free path : z. Recall = v·tmean and tmean = m ·m: z. Use

PS 225 – Thermal Physics topics z. The atomic hypothesis z. Heat and heat transfer z. Kinetic theory z. The Boltzmann factor z. The First Law of Thermodynamics z. Specific Heat z. Entropy z. Heat engines z. Phase transitions
e24760fe4f2701b21f6db42e1d012949.ppt