ea0e8231c3d16034bad5b07da951cbfa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

The Bicameral Legislature & Congressional Leadership

#1 Love-Hate Relationship Fact 1 • Since 1974, Congress has never had an approval rating higher than 56% (Gallup Polls). Fact 2 • Since 1948, incumbents in the House have a 90% chance of winning their reelection. Write a persuasive paragraph which explains the two facts.

#2 Protect this House!! • Describe the significance of the Reapportionment Act of 1929 and the role it has played in gerrymandering.

#3 Smaller, Smarter, Senators! • “It is indispensable that besides the House of Representatives which runs on all fours with popular sentiment, we should have a body like the Senate which may refuse to run with it at all when it seems to be wrong- a body which has time and security enough to keep its head, if only now and then and but for a little while, till other people have had time to think. ” –Woodrow Wilson -What is Woodrow Wilson saying about members in the House? -Why does the Senate have time and security, but not the House?

Congress The National Legislature • Bicameral Congress – two-houses • House of Representatives – Lower House • Senate – Upper House • Historical – Framers were familiar with the British bicameral • • system Practical – It is a reflection of federalism. Theoretical – One house of Congress would be able to check the other.

Terms and Sessions of Congress • A term of Congress extends over two years – each term is • consecutively numbered – two regular sessions each term–one per year. Each term of Congress consists of two sessions. • 20 th Amendment – Start of the new two year term begins at noon on January 3 rd of every odd numbered year.

• Special Session – Only a President can call congress into special session – A meeting to deal with an emergency situation – Only 26 Special Sessions have ever been called

The House of Representatives • the larger of the two chambers • 435 seats (voting members) – – • based on population Each State is entitled to at least one seat – Reapportionment • 1929 term of two years

The House of Representatives • Congressional Elections – elections are held on the Tuesday following the first Monday in November of each even numbered year • Off year elections – elections occurring in non-presidential years • Districts – chosen by the voters in geographical districts • Gerrymandering

The House of Representatives • Qualifications – must be at least 25 years of age – a citizen for at least seven years – an inhabitant of the state

Senate • Consists of 100 members – two from each state • Since 1914 – regular November elections • Senators serve six-year terms – Elections every two years – 1/3 up for reelection – “Continuous Body” • 17 th Amendment – Direct election of Senators

Senate • Qualifications – must be at least 30 years of age – a citizen for at least nine years – an inhabitant of the state • Constitution – each State is to have two senators – sets higher qualifications for senators than it does for representatives • Example – Age and Citizenship

Congressional Leadership Structure Senate House of Representatives President of Senate Speaker of the House President pro tempore Majority Floor Leader Minority Floor Leader Majority Whip Minority Whip
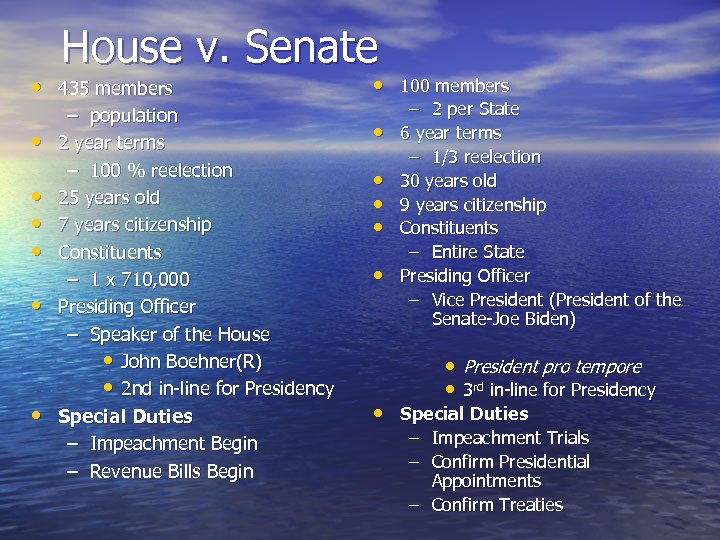
House v. Senate • 435 members • • • – population 2 year terms – 100 % reelection 25 years old 7 years citizenship Constituents – 1 x 710, 000 Presiding Officer – Speaker of the House • John Boehner(R) • 2 nd in-line for Presidency Special Duties – Impeachment Begin – Revenue Bills Begin • 100 members • • • – 2 per State 6 year terms – 1/3 reelection 30 years old 9 years citizenship Constituents – Entire State Presiding Officer – Vice President (President of the Senate-Joe Biden) • President pro tempore • 3 rd in-line for Presidency • Special Duties – – Impeachment Trials Confirm Presidential Appointments – Confirm Treaties

The Members of Congress • Members of Congress are not a representative cross • • section of the American people. Members of Congress are legislators and also serve as representatives and servants of their constituents, committee members, and politicians. Most members usually adopt one of four behavioral styles: – 1. trustees whose decisions are based solely on their best judgments – 2. delegates who follow the wishes of their constituents – 3. partisans who feel duty-bound to support their parties’ position • politicos who try to balance these roles as situations demand

How to Represent the People? Discuss with a partner if you should make decisions for the people based on their (constituents) views or make your own decisions • Trustees • • o Many members see themselves as holders of the public trust who must decide issues based on merit alone v And not based on the opinions of constituents or any other groups Delegates o Many members see themselves as agents of those who elected them v And believe they should suppress their own views in favor of those of the electorate Partisans o Many members see themselves as bound to vote on issues according to the party platform and the wishes of party leaders Politicos o Many members attempt to balance the roles of trustee, delegate, and partisan Other Roles o All members of Congress also must act as servants of their constituents v Providing the people back home with a wide range of services v From making appointments to military academies to helping companies in their districts obtain governmental contracts

Personal and Political Backgrounds • Congress is not a representative cross section of the American people • The average member of Congress is a white male in his mid-50 s • Most members are – o Married, have children, are members of a Christian church • Most members are lawyers – o Though many have backgrounds in business • Education, agriculture, journalism, or professional politics

Compensation • Senators and Representatives o Receive salaries of $174, 000 per year • Non salary Compensation o Members of Congress receive a wide range of fringe benefits v From low-cost medical care v Free printing and distribution of speeches v Newsletters v And other materials • The Politics of Pay o Congress sets its own pay and benefits (27 th amendment) but it wont be implemented until after an election (time for voters to vote them out) • The President’s Veto and Voter backlash act to limit salaries

Membership Privileges • Members may not be arrested for misdemeanors while Congress is in session • Members are immune from court action because of any speech they make in Congress
ea0e8231c3d16034bad5b07da951cbfa.ppt