f0355b27fd0172cee25087bb58605aed.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 The Atlantic Slave Trade Telling more than just the American version. By: Brian Innes
The Atlantic Slave Trade Telling more than just the American version. By: Brian Innes
 Sugar is King! o o The expansion of the Atlantic Slave Trade was driven by the profitability of sugar. The Canary Islands off the West Coast of Africa provided the starting point for the expansion of slavery to the Atlantic World. Next came ventures to Madeira, Cape Verdes and Sao Tome. Eventually, Europeans had the ability to move west across the Atlantic.
Sugar is King! o o The expansion of the Atlantic Slave Trade was driven by the profitability of sugar. The Canary Islands off the West Coast of Africa provided the starting point for the expansion of slavery to the Atlantic World. Next came ventures to Madeira, Cape Verdes and Sao Tome. Eventually, Europeans had the ability to move west across the Atlantic.
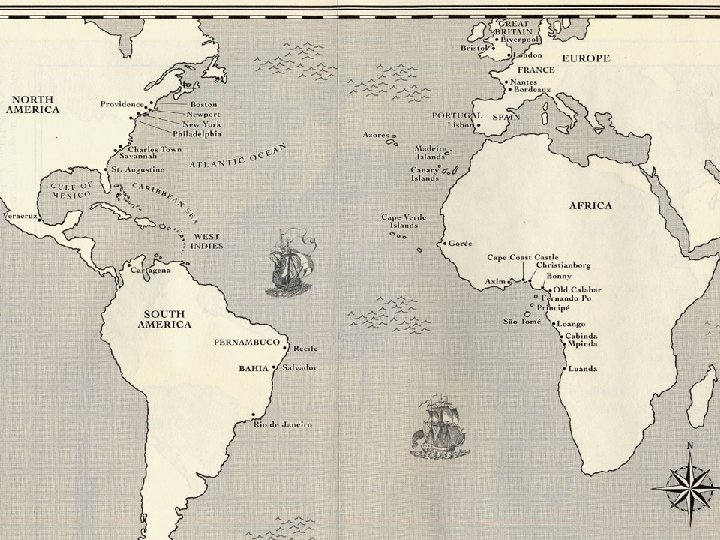
 On their own terms o o o While early Europeans believed that they would be able to raid African coasts, they were largely unable to do so. African maritime technology forced Europeans to trade with Africans for slaves Europeans were advised to conduct trade properly, waiting until African officials made contact and grant permission for trade. John Thornton, Africa and Africans in the Making of the Atlantic World, 1400 -1800 p. 39.
On their own terms o o o While early Europeans believed that they would be able to raid African coasts, they were largely unable to do so. African maritime technology forced Europeans to trade with Africans for slaves Europeans were advised to conduct trade properly, waiting until African officials made contact and grant permission for trade. John Thornton, Africa and Africans in the Making of the Atlantic World, 1400 -1800 p. 39.
 Slaves, not Captives o o The vast majority of slaves taken from Africa were already slaves when the Europeans arrived The west coast of Africa was dominated by hundreds of nations, constantly warring for territory and power Their goal in warfare was to take prisoners not to kill more than their enemy Land does not define wealth, people do Philip Curtin, The Rise and Fall of the Plantation Complex.
Slaves, not Captives o o The vast majority of slaves taken from Africa were already slaves when the Europeans arrived The west coast of Africa was dominated by hundreds of nations, constantly warring for territory and power Their goal in warfare was to take prisoners not to kill more than their enemy Land does not define wealth, people do Philip Curtin, The Rise and Fall of the Plantation Complex.
 J. W. Buel, Heroes of the Dark Continent (New York, 1890), p. 66; also, Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division, LC-USZ 62 -32008.
J. W. Buel, Heroes of the Dark Continent (New York, 1890), p. 66; also, Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division, LC-USZ 62 -32008.
 Slaves not Captives, cont’d o o o This situation created a large number of slaves for the warring nations Africans viewed those outside of their nation as not being of the same kin and therefore subject to being enslaved The rulers or kings of these nations would trade these slaves for desired luxury items from the Europeans Claude Meillassoux The Anthropology of Slavery
Slaves not Captives, cont’d o o o This situation created a large number of slaves for the warring nations Africans viewed those outside of their nation as not being of the same kin and therefore subject to being enslaved The rulers or kings of these nations would trade these slaves for desired luxury items from the Europeans Claude Meillassoux The Anthropology of Slavery
 Luxury not Necessity o o o Africans traded with Europeans for luxury goods because it was the kings who were in charge of the trading Africans produced plenty of textiles, they saw the possession of European textiles as a matter of prestige Early on they rarely traded for weapons, their warfare was different than that of Europeans
Luxury not Necessity o o o Africans traded with Europeans for luxury goods because it was the kings who were in charge of the trading Africans produced plenty of textiles, they saw the possession of European textiles as a matter of prestige Early on they rarely traded for weapons, their warfare was different than that of Europeans
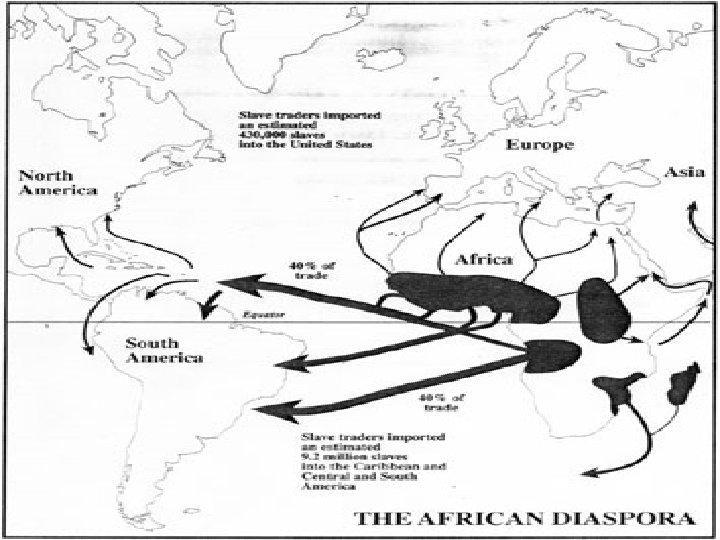
 Why Africans? o o The Africans that Europeans traded for to develop the New World were already enslaved Indigenous populations were killed off by European diseases Indigenous populations knew the territory Africans from different nations were unable to communicate in the early stages
Why Africans? o o The Africans that Europeans traded for to develop the New World were already enslaved Indigenous populations were killed off by European diseases Indigenous populations knew the territory Africans from different nations were unable to communicate in the early stages
 Resources o o o Curtin, Philip D. The Rise and Fall of the Plantation Complex. Cambridge University Press, 1990. Klein, Herbert S. The Atlantic Slave Trade. Cambridge University Press, 1999. Manning, Patrick. Slavery and African Life. Cambridge University Press, 1990. Northrup, David. The Atlantic Slave Trade. Boston College, 2002. Thornton, John. African and Africans in the Making f the Atlantic World, 1400 -1800. Cambridge University Press, 1998. o o o Websites: http: //hitchcock. itc. virginia. edu/Slav ery/ http: //africanhistory. about. com/librar y/weekly/aa 080601 a. htm http: //encarta. msn. com/encyclopedia _761595721/Atlantic_Slave_Trade. h tml http: //www. bbc. co. uk/worldservice/ africa/features/storyofafrica/9 chapter 4. shtml Email: bdi 0547@uncw. edu
Resources o o o Curtin, Philip D. The Rise and Fall of the Plantation Complex. Cambridge University Press, 1990. Klein, Herbert S. The Atlantic Slave Trade. Cambridge University Press, 1999. Manning, Patrick. Slavery and African Life. Cambridge University Press, 1990. Northrup, David. The Atlantic Slave Trade. Boston College, 2002. Thornton, John. African and Africans in the Making f the Atlantic World, 1400 -1800. Cambridge University Press, 1998. o o o Websites: http: //hitchcock. itc. virginia. edu/Slav ery/ http: //africanhistory. about. com/librar y/weekly/aa 080601 a. htm http: //encarta. msn. com/encyclopedia _761595721/Atlantic_Slave_Trade. h tml http: //www. bbc. co. uk/worldservice/ africa/features/storyofafrica/9 chapter 4. shtml Email: bdi 0547@uncw. edu
 The Roles of Adolescence in the Lives of Civil Rights Activists Kerry Schwallenburg
The Roles of Adolescence in the Lives of Civil Rights Activists Kerry Schwallenburg
 Ida B. Wells-Barnett o o Greatest anti-lynching activist Writer for the Free Speech Filed lawsuit in 1884 against the Chesapeake, Ohio, & Southwestern Railroad Founding member of the NAACP www. pbs. org/. . . / peopleevents/p_wells. html
Ida B. Wells-Barnett o o Greatest anti-lynching activist Writer for the Free Speech Filed lawsuit in 1884 against the Chesapeake, Ohio, & Southwestern Railroad Founding member of the NAACP www. pbs. org/. . . / peopleevents/p_wells. html
 Childhood and Adolescence o o www. africawithin. com/ bios/ida_wells. htm Father, Jim Wells, influenced her passion for justice & equality He was a member of the board of trustees at Shaw University At 16, her parents died of yellow fever She became the guardian of her 6 siblings and worked as a teacher
Childhood and Adolescence o o www. africawithin. com/ bios/ida_wells. htm Father, Jim Wells, influenced her passion for justice & equality He was a member of the board of trustees at Shaw University At 16, her parents died of yellow fever She became the guardian of her 6 siblings and worked as a teacher
 Childhood & Adolescence o o Born into slavery in 1856 Was a house boy for a wealthy white family Worked in mines during the day & attended night school Worked his way through the Hampton Institute as a janitor http: //docsouth. unc. edu/washstory/washin. html
Childhood & Adolescence o o Born into slavery in 1856 Was a house boy for a wealthy white family Worked in mines during the day & attended night school Worked his way through the Hampton Institute as a janitor http: //docsouth. unc. edu/washstory/washin. html
 The Aftermath of Childhood o o Her father’s love of education gave her the will to gain a formal education His determination was apparent in the lawsuit she filed in 1884. Began a lifelong crusade against lynching in 1892 after 3 of her friends were murdered Her father’s fearlessness was once again apparent in her writings www. loc. gov/exhibits/ odyssey/educate/barnett. html
The Aftermath of Childhood o o Her father’s love of education gave her the will to gain a formal education His determination was apparent in the lawsuit she filed in 1884. Began a lifelong crusade against lynching in 1892 after 3 of her friends were murdered Her father’s fearlessness was once again apparent in her writings www. loc. gov/exhibits/ odyssey/educate/barnett. html
 Booker T. Washington o o o www. historycooperative. org/ btw/info. html Accomodationist Ran the “Tuskegee Machine” Considered an axis between the races
Booker T. Washington o o o www. historycooperative. org/ btw/info. html Accomodationist Ran the “Tuskegee Machine” Considered an axis between the races
 Hard Work Pays Off o o o http: //www. tuskegee. edu 1881 established the Tuskegee Institute, perhaps motivated by his mentor at Hampton, General Chapman Armstrong 1 st college to open with an all black faculty Behind the scenes he exploited white philanthropists by funding several newspapers and court cases
Hard Work Pays Off o o o http: //www. tuskegee. edu 1881 established the Tuskegee Institute, perhaps motivated by his mentor at Hampton, General Chapman Armstrong 1 st college to open with an all black faculty Behind the scenes he exploited white philanthropists by funding several newspapers and court cases
 Malcolm X o o “A man who stands for nothing will fall for anything. ” “Education is our passport to the future, for tomorrow belongs to the people who prepare for it today. ” “I want Dr. King to know that I didn’t come to Selma to make his job difficult. I really did come thinking I could make it easier. If the white people realize what the alternative is, perhaps they will be more willing to hear Dr. King. ” o
Malcolm X o o “A man who stands for nothing will fall for anything. ” “Education is our passport to the future, for tomorrow belongs to the people who prepare for it today. ” “I want Dr. King to know that I didn’t come to Selma to make his job difficult. I really did come thinking I could make it easier. If the white people realize what the alternative is, perhaps they will be more willing to hear Dr. King. ” o
 Childhood & Adolescence o o As a child, teachers told him he could not become a lawyer Grew up in Michigan, where his father was murdered As a teenager he moved to Boston and later to Harlem, where he saw the separation within his own race “I think that an objective reader may see how in the society to which I was exposed as a young black youth here in America, for me to wind up in prison was really just about inevitable. ”
Childhood & Adolescence o o As a child, teachers told him he could not become a lawyer Grew up in Michigan, where his father was murdered As a teenager he moved to Boston and later to Harlem, where he saw the separation within his own race “I think that an objective reader may see how in the society to which I was exposed as a young black youth here in America, for me to wind up in prison was really just about inevitable. ”
 The Struggle o o o Introduced to the Nation of Islam by his brother while in prison In 1963, he was one of the most desired speakers in the U. S. Just prior to his assassination Malcolm X made a trip to Mecca where he adopted orthodox Islam and changed his militant views
The Struggle o o o Introduced to the Nation of Islam by his brother while in prison In 1963, he was one of the most desired speakers in the U. S. Just prior to his assassination Malcolm X made a trip to Mecca where he adopted orthodox Islam and changed his militant views
 Resources o General n “African American Odyssey” Library of Congress http: //rs 6. loc. gov/ammem/aaohtml/exhibit/aointro. html n The History of Jim Crow http: //www. jimcrowhistory. org/home. htm n The Rise and Fall of Jim Crow http: //www. pbs. org/wnet/jimcrow o Ida B. Wells-Barnett n Ida B. Wells-Barnett: Crusader of Freedom http: //www. learntoquestion. com/seevak/groups/2002/sites/wells/NEW n “Ida B. Wells” Just the Arti-FACTS http: //www. chicagohs. org/aotm/Mar 98/mar 98 fact 2. html o Booker T. Washington n “The Booker T. Washington Papers. ” The History Cooperative http: //www. historycooperative. org/btw/index. html n “Booker T. & W. E. B. : The Debate between W. E. B. Du. Bois and Booker T. Washington. ” Frontline: The Two Nations of Black America http: //www. pbs. org/wgbh/pages/frontline/shows/race/etc/road. html
Resources o General n “African American Odyssey” Library of Congress http: //rs 6. loc. gov/ammem/aaohtml/exhibit/aointro. html n The History of Jim Crow http: //www. jimcrowhistory. org/home. htm n The Rise and Fall of Jim Crow http: //www. pbs. org/wnet/jimcrow o Ida B. Wells-Barnett n Ida B. Wells-Barnett: Crusader of Freedom http: //www. learntoquestion. com/seevak/groups/2002/sites/wells/NEW n “Ida B. Wells” Just the Arti-FACTS http: //www. chicagohs. org/aotm/Mar 98/mar 98 fact 2. html o Booker T. Washington n “The Booker T. Washington Papers. ” The History Cooperative http: //www. historycooperative. org/btw/index. html n “Booker T. & W. E. B. : The Debate between W. E. B. Du. Bois and Booker T. Washington. ” Frontline: The Two Nations of Black America http: //www. pbs. org/wgbh/pages/frontline/shows/race/etc/road. html
 More Resources o Malcolm X n n n Malcom-X. org http: //www. malcolm-x. org/index. html The Official Website of Malcolm X http: //www. cmgww. com/historic/malcolm/home. php “What he said Archive” Malcolm X: A Research Site http: //www. brothermalcolm. net/mxwords/whathesaidarch ive. html
More Resources o Malcolm X n n n Malcom-X. org http: //www. malcolm-x. org/index. html The Official Website of Malcolm X http: //www. cmgww. com/historic/malcolm/home. php “What he said Archive” Malcolm X: A Research Site http: //www. brothermalcolm. net/mxwords/whathesaidarch ive. html
 Gender Relations in Early America: Myths about the Native American and English Woman
Gender Relations in Early America: Myths about the Native American and English Woman
 o The Authentic History Center: Primary Sources from American Popular Culture http: //www. authentichistory. com/diversity/native/images/diversity_native_images 04. html
o The Authentic History Center: Primary Sources from American Popular Culture http: //www. authentichistory. com/diversity/native/images/diversity_native_images 04. html
 The Myths and Stereotypes o Indian Women Had No Status n o Example: Pocahontas portrayal by Disney English women were highly revered n More status than Native American Women
The Myths and Stereotypes o Indian Women Had No Status n o Example: Pocahontas portrayal by Disney English women were highly revered n More status than Native American Women
 Mary Jemison o o Child of two Irish immigrants She was captured by six Indians and four Frenchmen Adopted by Seneca Tribe Mary described her new life as better than the life of most English, white women.
Mary Jemison o o Child of two Irish immigrants She was captured by six Indians and four Frenchmen Adopted by Seneca Tribe Mary described her new life as better than the life of most English, white women.
 European Ideals vs. Native American Ideals o Native American societies were based upon ideals that promoted equality n o Many tribes were matrilineal and matrilocal European n Patriarchy o Male head of household and Woman were submissive followers
European Ideals vs. Native American Ideals o Native American societies were based upon ideals that promoted equality n o Many tribes were matrilineal and matrilocal European n Patriarchy o Male head of household and Woman were submissive followers
 The English Woman o Cotton Mather n o “produce the fear of, a cautious diligence never to displease him. ” Ideal English women of late 17 th century n n n Pious Virtuous Domestic SUBMISSIVE Thrifty Hardworking
The English Woman o Cotton Mather n o “produce the fear of, a cautious diligence never to displease him. ” Ideal English women of late 17 th century n n n Pious Virtuous Domestic SUBMISSIVE Thrifty Hardworking
 The Iroquois Woman o Sir William Johnson on Native American Women’s Power n n n o Very strong Hard to undermine Women were present at council meetings and conferences of each tribe in the Five Nation Iroquois Ideal Iroquois Woman: n n n Political Active Economic provider of stable food source—Corn Head of household based on matrilocal traditions
The Iroquois Woman o Sir William Johnson on Native American Women’s Power n n n o Very strong Hard to undermine Women were present at council meetings and conferences of each tribe in the Five Nation Iroquois Ideal Iroquois Woman: n n n Political Active Economic provider of stable food source—Corn Head of household based on matrilocal traditions
 Contact, Conflict and the Causes of the Gender Shift o o Diseases Trade: Increasing Dependency of Iroquois on European goods n o ‘Consumer Revolution” Warfare (damaged crops)
Contact, Conflict and the Causes of the Gender Shift o o Diseases Trade: Increasing Dependency of Iroquois on European goods n o ‘Consumer Revolution” Warfare (damaged crops)
 The English Woman’s Increasing Status o Religious Realm n n o Leaders of church Moral leaders in Community Domestic Realm n Deputy husbands during times of war and also during other times of the husband’s absence
The English Woman’s Increasing Status o Religious Realm n n o Leaders of church Moral leaders in Community Domestic Realm n Deputy husbands during times of war and also during other times of the husband’s absence
 The Iroquois Woman’s Declining Status o No longer able to provide stable food source n n o Authority transfers to Native American men n o Loss economic power Loss of political status Biggest industry—trading. Sir William Johnson and the Effects of Englishmen
The Iroquois Woman’s Declining Status o No longer able to provide stable food source n n o Authority transfers to Native American men n o Loss economic power Loss of political status Biggest industry—trading. Sir William Johnson and the Effects of Englishmen
 Towards Today’s Gender Conventions o Gradual beginning of a women’s movement that is still ongoing in today’s society. o Iroquois women assimilate into English patriarchal view o English women gain status o Step outside of the domestic sphere
Towards Today’s Gender Conventions o Gradual beginning of a women’s movement that is still ongoing in today’s society. o Iroquois women assimilate into English patriarchal view o English women gain status o Step outside of the domestic sphere
 For Further Information o o o Link to paper and Powerpoint Presentation: : Email address: cne 6687@uncw. edu Helpful Links: n Information on Iroquois o o o n n n o “The Longest Living Democracy on Earth”: http: //www. ratical. org/many_worlds/6 Nations/#CREDITS http: //www. iroquois. net/ http: //www. iroquoismuseum. org/ Halder, Bornali. “Native American Women, ” n. d. ,
For Further Information o o o Link to paper and Powerpoint Presentation: : Email address: cne 6687@uncw. edu Helpful Links: n Information on Iroquois o o o n n n o “The Longest Living Democracy on Earth”: http: //www. ratical. org/many_worlds/6 Nations/#CREDITS http: //www. iroquois. net/ http: //www. iroquoismuseum. org/ Halder, Bornali. “Native American Women, ” n. d. ,


