0b39e7228834a346b5a36b8016d7f932.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 The Archway. . . to Telemedicine 1
The Archway. . . to Telemedicine 1
 What is Telemedicine? . . . the use of electronic information and communications technologies to provide and support health care when distance separates the participants. Institute of Medicine, 1996 2
What is Telemedicine? . . . the use of electronic information and communications technologies to provide and support health care when distance separates the participants. Institute of Medicine, 1996 2
 Telemedicine • • • Background Applications Benefits and Challenges Research Conclusions Recommendations 3
Telemedicine • • • Background Applications Benefits and Challenges Research Conclusions Recommendations 3
 Background The evidence suggest that the concept dates to 1924. 4
Background The evidence suggest that the concept dates to 1924. 4
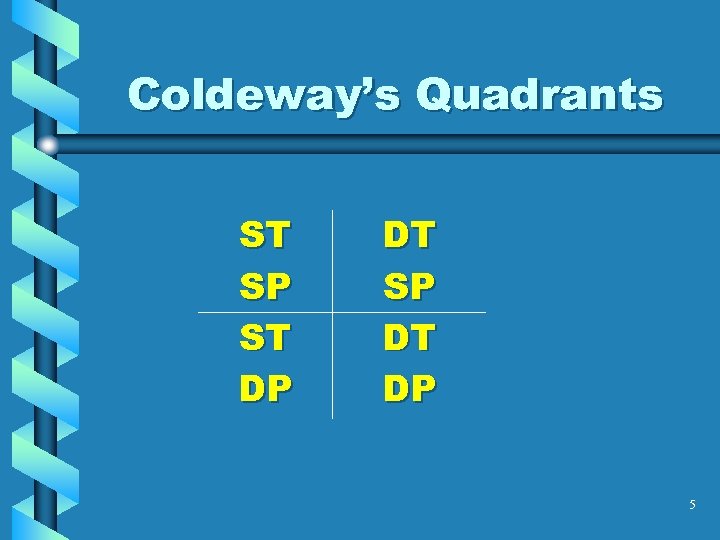 Coldeway’s Quadrants ST SP ST DP DT SP DT DP 5
Coldeway’s Quadrants ST SP ST DP DT SP DT DP 5
 Quadrants Defined • ST/SP – Same Time/Same Place • DT/SP – Different Time/Same Place • ST/DP – Same Time/Different Place • DT/DP – Different Time/Different Place 6
Quadrants Defined • ST/SP – Same Time/Same Place • DT/SP – Different Time/Same Place • ST/DP – Same Time/Different Place • DT/DP – Different Time/Different Place 6
 Who… … is involved with telemedicine? 7
Who… … is involved with telemedicine? 7
 Telemedicine Networks 8
Telemedicine Networks 8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 Telemedicine Applications 1. Remote Consultation 2. Remote Monitoring 3. Remote Education 4. Telementoring 14
Telemedicine Applications 1. Remote Consultation 2. Remote Monitoring 3. Remote Education 4. Telementoring 14
 1. Remote Consultation 15
1. Remote Consultation 15
 Video Clip #1 16
Video Clip #1 16
 1. a Telepsychiatry 17
1. a Telepsychiatry 17
 1. b. Telemedicine for Children with Disabilities 18
1. b. Telemedicine for Children with Disabilities 18
 2. Remote Monitoring 19
2. Remote Monitoring 19
 Video Clip #2 20
Video Clip #2 20
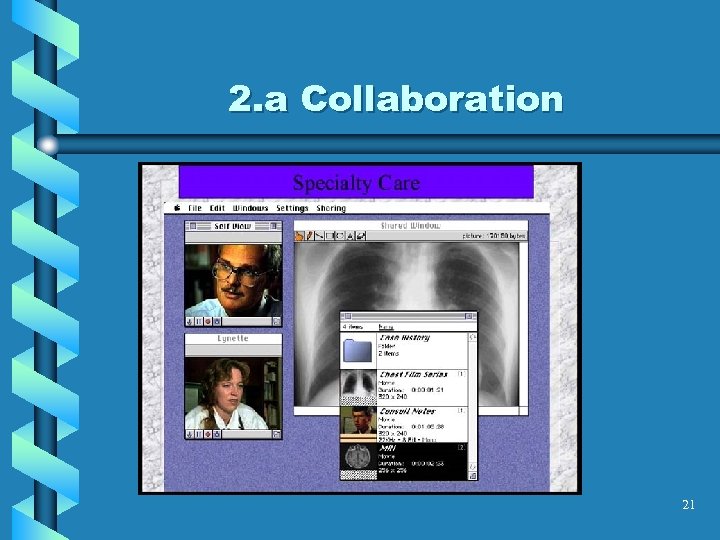 2. a Collaboration 21
2. a Collaboration 21
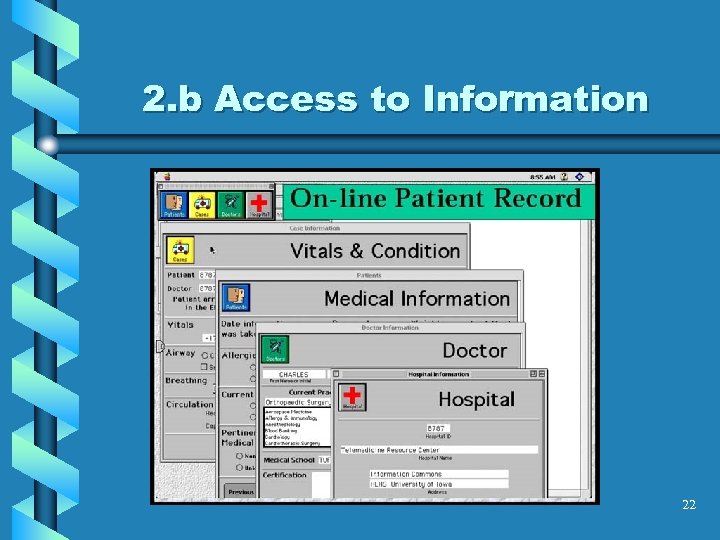 2. b Access to Information 22
2. b Access to Information 22
 3. Remote Education 23
3. Remote Education 23
 24
24
 Video Clip #3 25
Video Clip #3 25
 4. Telementoring 26
4. Telementoring 26
 Video Clip #4 27
Video Clip #4 27
 When… …do we use telemedicine? 28
When… …do we use telemedicine? 28
 When do we use telemedicine? • Maldistribution of health resources urban and/or rural • Capitated populations • Access • Distance/Time/Travel • Patients and Families • Outreach Physician • Isolation of Provider • National/International 29
When do we use telemedicine? • Maldistribution of health resources urban and/or rural • Capitated populations • Access • Distance/Time/Travel • Patients and Families • Outreach Physician • Isolation of Provider • National/International 29
 When do we ‘NOT’ use telemedicine? 30
When do we ‘NOT’ use telemedicine? 30
 Telemedicine Benefits and Challenges “It is an amazing invention, but who would ever want to use one” Rutherford Hayes, 1882 on the using telephone for the first time 31
Telemedicine Benefits and Challenges “It is an amazing invention, but who would ever want to use one” Rutherford Hayes, 1882 on the using telephone for the first time 31
 Trends • Market place reform/managed care • Shifting site of care Hospital>Clinic>Home • Case Management/Team Care • Improved communications between provider and patient • Health care practices and affiliations • Digital convergence 32
Trends • Market place reform/managed care • Shifting site of care Hospital>Clinic>Home • Case Management/Team Care • Improved communications between provider and patient • Health care practices and affiliations • Digital convergence 32
 Benefits Patient Perspective • Access: Time, Travel, Expense • Health Provider Collaboration • Enhanced Communications • TV & Computer Applications common and nonthreatening • Added attention may enhance confidence that all that can be done is being done 33
Benefits Patient Perspective • Access: Time, Travel, Expense • Health Provider Collaboration • Enhanced Communications • TV & Computer Applications common and nonthreatening • Added attention may enhance confidence that all that can be done is being done 33
 Benefits Provider Perspective • Communication/Collaboration with specialists • ER ‘front-line’ support • CME/Life Long Learning • Saves time, travel to outreach clinics 34
Benefits Provider Perspective • Communication/Collaboration with specialists • ER ‘front-line’ support • CME/Life Long Learning • Saves time, travel to outreach clinics 34
 Challenges • Lack of reimbursement • Licensing and Credentialing issues • Liability • Privacy • Infrastructure • End-user Issues 35
Challenges • Lack of reimbursement • Licensing and Credentialing issues • Liability • Privacy • Infrastructure • End-user Issues 35
 Recommendations • Conduct a comprehensive telemedicine audit/assessment • Explore Financial Issues • Develop a short, mid and long range telemedicine plan • Build training initiatives • Systematic implementation of plan 36
Recommendations • Conduct a comprehensive telemedicine audit/assessment • Explore Financial Issues • Develop a short, mid and long range telemedicine plan • Build training initiatives • Systematic implementation of plan 36
 Audit and Assessment • Medical Services Data – Descriptive elements – Current Services – Current technologies • Service Opportunities/Needs • Miscellaneous Observations/Comments 37
Audit and Assessment • Medical Services Data – Descriptive elements – Current Services – Current technologies • Service Opportunities/Needs • Miscellaneous Observations/Comments 37
 Financial Issues • Program Budgets • Finding Funds • Maximizing Investments • Measuring Intangibles 38
Financial Issues • Program Budgets • Finding Funds • Maximizing Investments • Measuring Intangibles 38
 The Plan • Clarifying Goals • Prioritizing Objectives • Policies and Procedures • Operational Issues • Personnel 39
The Plan • Clarifying Goals • Prioritizing Objectives • Policies and Procedures • Operational Issues • Personnel 39
 Training is essential! 40
Training is essential! 40
 Video Clip #5 : A Typical Telemedicine System 41
Video Clip #5 : A Typical Telemedicine System 41
 Mere Vehicles Telemedicine and information technologies are mere vehicles that permit the delivery of health care services but which have no greater impact on health care than the truck that delivers our groceries has on our nutrition. It is the content of the vehicle that permits effective health care, not the vehicle. 42
Mere Vehicles Telemedicine and information technologies are mere vehicles that permit the delivery of health care services but which have no greater impact on health care than the truck that delivers our groceries has on our nutrition. It is the content of the vehicle that permits effective health care, not the vehicle. 42


