4a1055335e50acf4b4710340540d579b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

The Arab-Israeli Conflict The heart of this conflict is a dispute over land/changing borders and religion.
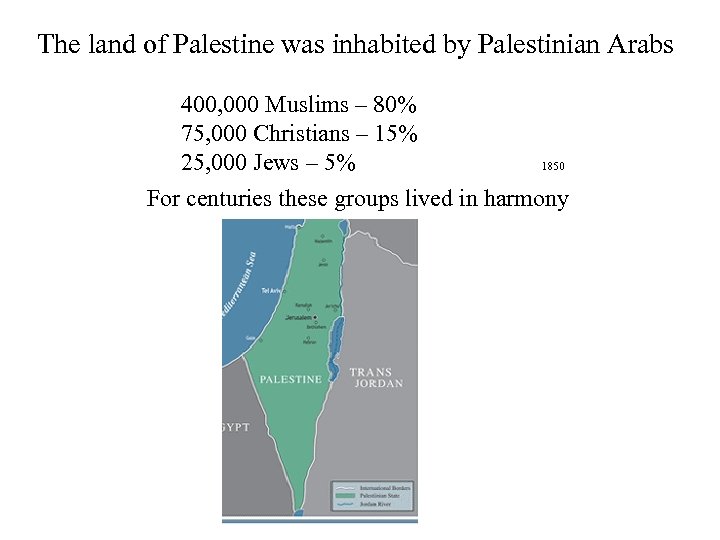
The land of Palestine was inhabited by Palestinian Arabs 400, 000 Muslims – 80% 75, 000 Christians – 15% 25, 000 Jews – 5% 1850 For centuries these groups lived in harmony

Zionism • In the late 1800 s; Extremist European Jews decided to colonize Palestinian land • Goal - Create a Jewish homeland • As more Zionists immigrated the Palestinians became increasingly alarmed fighting

The Balfour Declaration, 1917

British Mandate for Palestine • The League of Nations formalized British rule over Palestine in 1922

1947 – The UN gets involved • In the aftermath of WWII and the Holocaust the UN gave 55% of Palestine to a newly created Jewish State – Israel – Zionist Jews were 30% of the population and owned only 7% of the land • The partition plan looked like this………
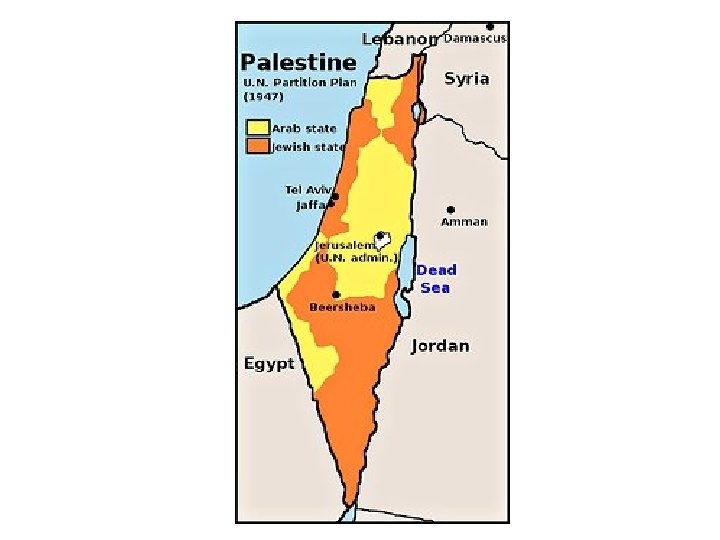

1948: Arab Israeli War • The day after Israel declared itself a nation and the partition plan was made official. The armies of Egypt, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Iraq invaded the territory partitioned for the Arab state, thus starting the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. • 90, 000 European-trained Zionist soldiers possessing modern weaponry • 30, 000 ill-equipped, poorly trained Arab soldiers
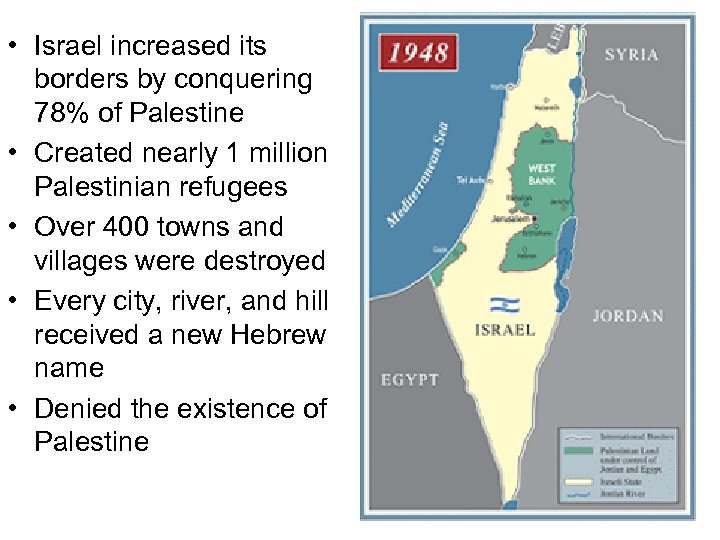
• Israel increased its borders by conquering 78% of Palestine • Created nearly 1 million Palestinian refugees • Over 400 towns and villages were destroyed • Every city, river, and hill received a new Hebrew name • Denied the existence of Palestine
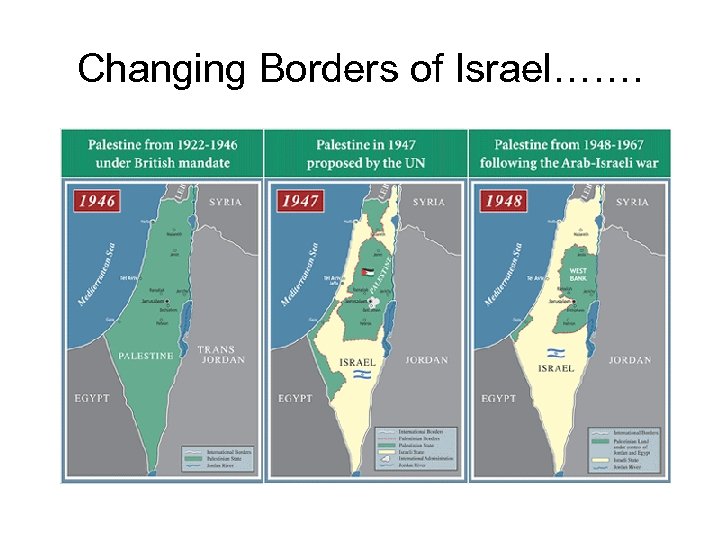
Changing Borders of Israel…….

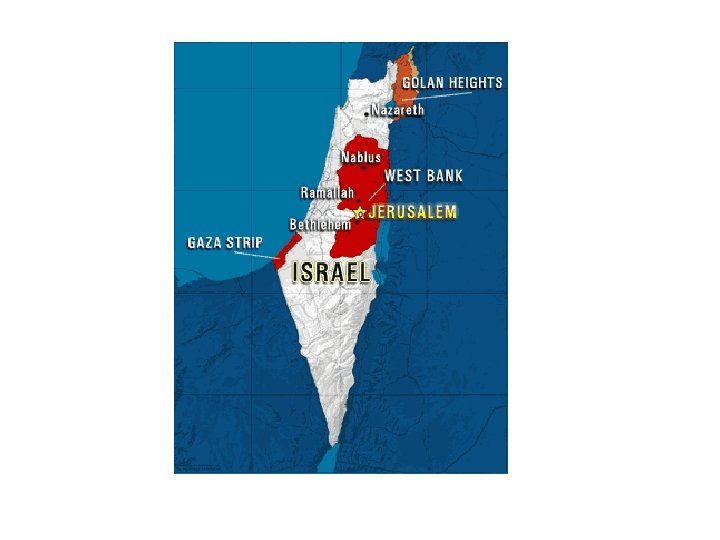
Six Day War of 1967 (AKA: 1967 Arab-Israeli War, the Third Arab-Israeli War, Six Days' War, an‑Naksah (The Setback), or the June War. ) The Egyptian President expelled UN troops from the Egypt / Israel border and a battle ensues. • Israel again increased their land to include Sinai Peninsula, the Gaza Strip, the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights
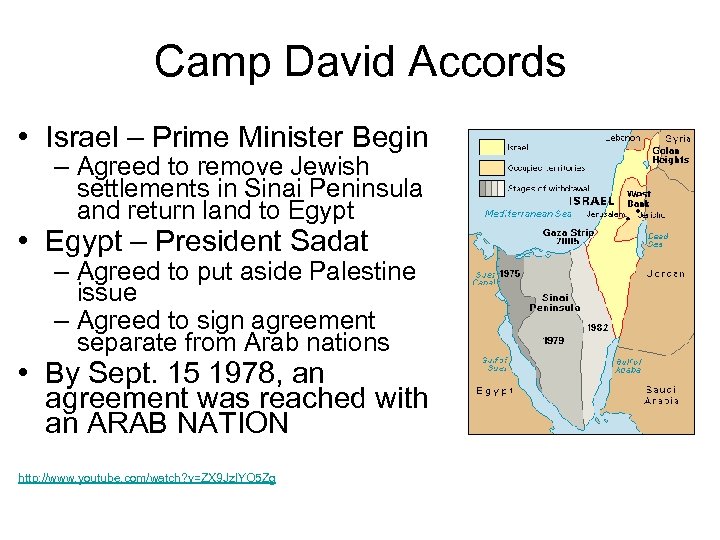
Camp David Accords • Israel – Prime Minister Begin – Agreed to remove Jewish settlements in Sinai Peninsula and return land to Egypt • Egypt – President Sadat – Agreed to put aside Palestine issue – Agreed to sign agreement separate from Arab nations • By Sept. 15 1978, an agreement was reached with an ARAB NATION http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=ZX 9 Jz. IYO 5 Zg

US Agreement and Involvement • Carter travels to Middle East to finalize deal • U. S. agrees to organize international peacekeeping force to occupy Sinai after Israeli withdrawal • U. S. promised $2 billion to Israel to pay for relocation of airfield from Sinai to Israel • U. S. guarantees economic assistance to Egypt in exchange for Sadat’s signing of the Peace treaty

Consequences of the Signing • Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO)denounces Camp David Accords and Sadat • Egypt expelled from Arab League • Palestine Issue unresolved • Temporary peace is achieved between Egypt and Israel • Carter is praised for his foreign policy success • U. S. establishes new alliances in Middle East but loses some old • Anwar Sadat loses his life 1981 https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=rhu-Yg. Cy. Pz 4

The First Intifada 1987 -1993 • (In English “shaking off”) was an uprising that began in the Jabalia refugee camp and quickly spread throughout Palestinian territories. http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=EYsd_2 pr 7 tk

How does this intifada lead to a new peace plan?

1973 Yom Kippur War • (AKA: the 1973 Arab-Israeli War and the Fourth Arab. Israeli War) • Egypt and Syria attack Israel on the ‘Day of Atonement’, the most important Jewish religious festival, celebrated by a 25 hour fasting and praying period.

1974 PLO legitimised • By 1974 the United Nations, largely as a result of the Oslo Accords, had recognised the PLO as the official voice and representative of the Palestinian people.

1993 Oslo Accords • Palestinian Liberation Organization chairman Yassar Arafat (Palestine/ PLO), Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin (Israel) and then U. S. President Bill Clinton meet to work out a plan for future relationships between Israel and the Palestinians. • The Plan - Allow the Palestinians to govern and retain their territories on the West Bank and the Gaza Strip.

2000 Second Intifada Starts when the leader of Israel’s opposition (Ariel Sharon) visited the temple mount which houses both the Al-Aqsa Mosque (the third most important holy site in Islam) and is also the holiest site in the Jewish faith. Israeli reserve soldiers, lynched Palestinian father and son

2002 Wall begins to be constructed • In June of 2002 Israel begins construction of a barrier separating Israel from the West Bank.
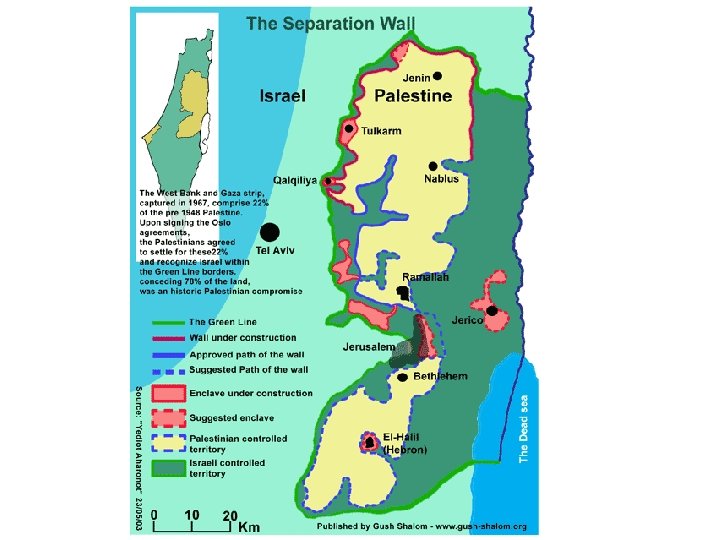

2005 Gaza withdrawal • Israel begins a unilateral withdrawal of nine thousand Jews from settlements in Gaza in August. • Some settlers accept government compensation and leave voluntarily, while others are forcibly removed by the Israel Defense Forces

2006 Hamas Victory In 2006 the terrorist group Hamas gains victory in the January elections, as they are believed to be less corrupt than their opponents.
4a1055335e50acf4b4710340540d579b.ppt