d9f66c13e16c475f6850800b976cfb72.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 The application of new technology for payments Moderator: • Gilbert Lichter, EBA CLEARING Speakers: • Luc Belpaire, Sun. Gard • Etienne Castiaux, Clear 2 Pay • Maurice Cleaves, Deutsche Bank • Gene Neyer, Fundtech • Renzo Vanetti, SIA-SSB
The application of new technology for payments Moderator: • Gilbert Lichter, EBA CLEARING Speakers: • Luc Belpaire, Sun. Gard • Etienne Castiaux, Clear 2 Pay • Maurice Cleaves, Deutsche Bank • Gene Neyer, Fundtech • Renzo Vanetti, SIA-SSB
 The application of new technology for payments Renzo Vanetti – CEO SIA SSB
The application of new technology for payments Renzo Vanetti – CEO SIA SSB
 Banks’ challenges: Market approach Time to think how to strategically innovate payment systems 1. 2. 3. 3. 4. 5. Technology Innovations must first service Clients’ requirements. SEPA forcing Banks to face the reality: payments are becoming more high profile, visible and strategic Consumers, Merchants, SMBs and Corporates are dissatisfied with Banks’ services and do not understand the value of SEPA Demand is changing, quickly supported by the new technologies (i. e. Web 2. 0, BPM, . . ) Banks must be prepared for “unexpected” business models Payment systems innovation is global, business case are local European market under influence from global payment system innovations Non-banking payment providers preparing to enjoy the SEPA
Banks’ challenges: Market approach Time to think how to strategically innovate payment systems 1. 2. 3. 3. 4. 5. Technology Innovations must first service Clients’ requirements. SEPA forcing Banks to face the reality: payments are becoming more high profile, visible and strategic Consumers, Merchants, SMBs and Corporates are dissatisfied with Banks’ services and do not understand the value of SEPA Demand is changing, quickly supported by the new technologies (i. e. Web 2. 0, BPM, . . ) Banks must be prepared for “unexpected” business models Payment systems innovation is global, business case are local European market under influence from global payment system innovations Non-banking payment providers preparing to enjoy the SEPA
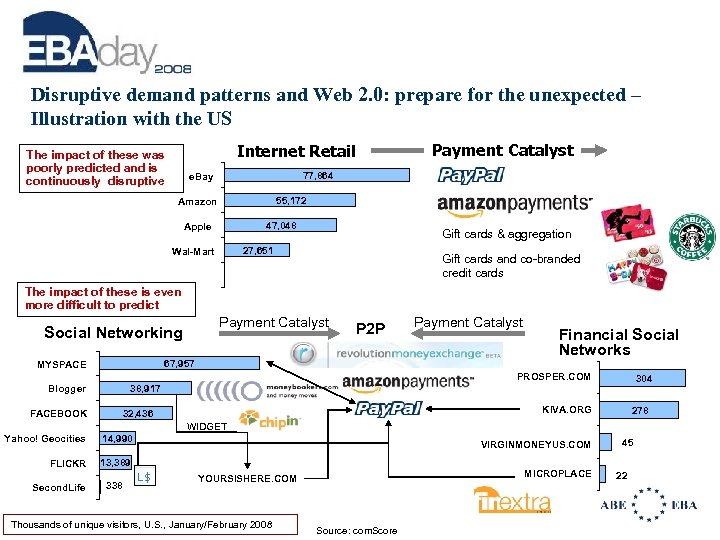 Disruptive demand patterns and Web 2. 0: prepare for the unexpected – Illustration with the US Internet Retail The impact of these was poorly predicted and is continuously disruptive Payment Catalyst 77, 864 e. Bay 55, 172 Amazon 47, 048 Apple Gift cards & aggregation 27, 651 Wal-Mart Gift cards and co-branded credit cards The impact of these is even more difficult to predict Payment Catalyst Social Networking P 2 P 67, 957 MYSPACE Payment Catalyst Financial Social Networks PROSPER. COM FACEBOOK 304 38, 917 Blogger KIVA. ORG 32, 436 278 WIDGET Yahoo! Geocities 14, 990 FLICKR 13, 389 Second. Life 338 VIRGINMONEYUS. COM MICROPLACE YOURSISHERE. COM Thousands of unique visitors, U. S. , January/February 2008 Source: com. Score 45 22
Disruptive demand patterns and Web 2. 0: prepare for the unexpected – Illustration with the US Internet Retail The impact of these was poorly predicted and is continuously disruptive Payment Catalyst 77, 864 e. Bay 55, 172 Amazon 47, 048 Apple Gift cards & aggregation 27, 651 Wal-Mart Gift cards and co-branded credit cards The impact of these is even more difficult to predict Payment Catalyst Social Networking P 2 P 67, 957 MYSPACE Payment Catalyst Financial Social Networks PROSPER. COM FACEBOOK 304 38, 917 Blogger KIVA. ORG 32, 436 278 WIDGET Yahoo! Geocities 14, 990 FLICKR 13, 389 Second. Life 338 VIRGINMONEYUS. COM MICROPLACE YOURSISHERE. COM Thousands of unique visitors, U. S. , January/February 2008 Source: com. Score 45 22
 Banks’ challenges: Technological Time to think how to strategically innovate payment approach systems 4. An integrated view of payment systems’ innovations From Visible to Invisible innovations: innovation in each payment system can not happen in isolation of the whole payment value chain 5. From Transaction value to Information value Banks must develop new competitive services (i. e. PIVAS), based on contextual and aggregate information, as key differentiator 6. Payment Service Hub (PSH) as the main payment ‘invisible’ innovation for Banks The payment architectural space must evolve to support more complex payment flows and combination of payments instruments and networks PSH is a middle-aware financial IT orchestrator Banks must move gradually towards it
Banks’ challenges: Technological Time to think how to strategically innovate payment approach systems 4. An integrated view of payment systems’ innovations From Visible to Invisible innovations: innovation in each payment system can not happen in isolation of the whole payment value chain 5. From Transaction value to Information value Banks must develop new competitive services (i. e. PIVAS), based on contextual and aggregate information, as key differentiator 6. Payment Service Hub (PSH) as the main payment ‘invisible’ innovation for Banks The payment architectural space must evolve to support more complex payment flows and combination of payments instruments and networks PSH is a middle-aware financial IT orchestrator Banks must move gradually towards it
 Strategic approach 1. Create a strategic payment governing body 2. Partnership 3. Outsourcing
Strategic approach 1. Create a strategic payment governing body 2. Partnership 3. Outsourcing
 The application of new technology for payments Etienne Castiaux Chief Technical Officer, Clear 2 Pay
The application of new technology for payments Etienne Castiaux Chief Technical Officer, Clear 2 Pay
 SOA payments architecture is being rolled out on a wide scale • • “SOA is a mindset more than a technology, and SOA concepts will outlast technology fads” Big vendors are backing SOA because large banks demand it, e. g. SAP and Microsoft Join Global Banks in a New Association to Help Banks Establish a Service-Oriented Architecture. Bank customers are asking more and more services and banks view an enterprise payment programme as a way to deliver increased service at a cheaper TCO. Vast majority of Tier-1 banks are busy rolling out enterprise payment programs based on SOA. Several standards are there: – Formats: ISO 20022, SWIFT range, … – Transformation and orchestration: XML, BPEL – Middleware: JEE, … Banks want to avoid being locked into proprietary technology. Mature SOA technology – Gluing granular components, written in J 2 EE and exposed with WSDL interfaces and EJB bindings – Standard J 2 EE security – Optional usage of BPEL to orchestrate (e. g. IBM BPEL in facts generates J 2 EE apps using JMS and EJBs) – Large processing sites live on SOA/J 2 EE (NYSE, . . . )
SOA payments architecture is being rolled out on a wide scale • • “SOA is a mindset more than a technology, and SOA concepts will outlast technology fads” Big vendors are backing SOA because large banks demand it, e. g. SAP and Microsoft Join Global Banks in a New Association to Help Banks Establish a Service-Oriented Architecture. Bank customers are asking more and more services and banks view an enterprise payment programme as a way to deliver increased service at a cheaper TCO. Vast majority of Tier-1 banks are busy rolling out enterprise payment programs based on SOA. Several standards are there: – Formats: ISO 20022, SWIFT range, … – Transformation and orchestration: XML, BPEL – Middleware: JEE, … Banks want to avoid being locked into proprietary technology. Mature SOA technology – Gluing granular components, written in J 2 EE and exposed with WSDL interfaces and EJB bindings – Standard J 2 EE security – Optional usage of BPEL to orchestrate (e. g. IBM BPEL in facts generates J 2 EE apps using JMS and EJBs) – Large processing sites live on SOA/J 2 EE (NYSE, . . . )
 Benefits of SOA for SEPA • SDD and SCT are a greenfield opportunity to roll out a 1 st phase of a new enterprise payment programme replacement. They should not be addressed in isolation. • Bring your TCO down. • Build on standards: platforms, formats, … • Avoid creating another silo when rolling out SDD and SCT. • Our customers are building SDD and SCT on an SOA enterprise payment programme and view it as a way to actively win new customers and markets.
Benefits of SOA for SEPA • SDD and SCT are a greenfield opportunity to roll out a 1 st phase of a new enterprise payment programme replacement. They should not be addressed in isolation. • Bring your TCO down. • Build on standards: platforms, formats, … • Avoid creating another silo when rolling out SDD and SCT. • Our customers are building SDD and SCT on an SOA enterprise payment programme and view it as a way to actively win new customers and markets.
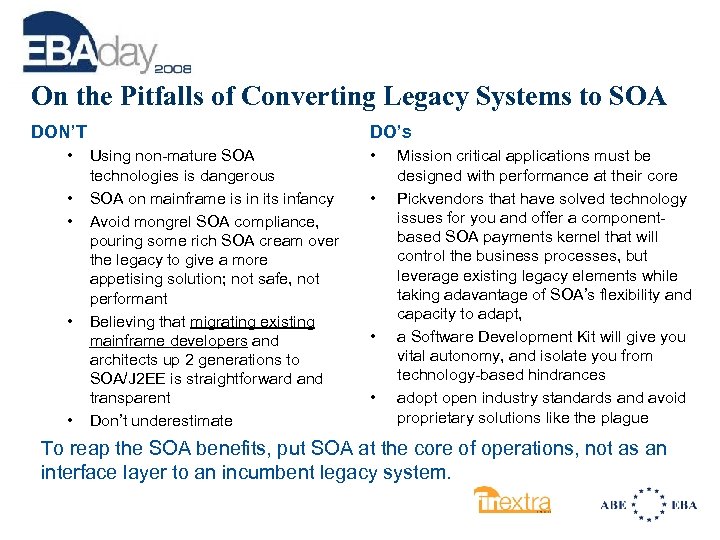 On the Pitfalls of Converting Legacy Systems to SOA DON’T • • • DO’s Using non-mature SOA technologies is dangerous SOA on mainframe is in its infancy Avoid mongrel SOA compliance, pouring some rich SOA cream over the legacy to give a more appetising solution; not safe, not performant Believing that migrating existing mainframe developers and architects up 2 generations to SOA/J 2 EE is straightforward and transparent Don’t underestimate • • Mission critical applications must be designed with performance at their core Pickvendors that have solved technology issues for you and offer a componentbased SOA payments kernel that will control the business processes, but leverage existing legacy elements while taking adavantage of SOA’s flexibility and capacity to adapt, a Software Development Kit will give you vital autonomy, and isolate you from technology-based hindrances adopt open industry standards and avoid proprietary solutions like the plague To reap the SOA benefits, put SOA at the core of operations, not as an interface layer to an incumbent legacy system.
On the Pitfalls of Converting Legacy Systems to SOA DON’T • • • DO’s Using non-mature SOA technologies is dangerous SOA on mainframe is in its infancy Avoid mongrel SOA compliance, pouring some rich SOA cream over the legacy to give a more appetising solution; not safe, not performant Believing that migrating existing mainframe developers and architects up 2 generations to SOA/J 2 EE is straightforward and transparent Don’t underestimate • • Mission critical applications must be designed with performance at their core Pickvendors that have solved technology issues for you and offer a componentbased SOA payments kernel that will control the business processes, but leverage existing legacy elements while taking adavantage of SOA’s flexibility and capacity to adapt, a Software Development Kit will give you vital autonomy, and isolate you from technology-based hindrances adopt open industry standards and avoid proprietary solutions like the plague To reap the SOA benefits, put SOA at the core of operations, not as an interface layer to an incumbent legacy system.
 SEPA and new payments technology – are we ready? Gene Neyer, SVP, Product Management, Fundtech
SEPA and new payments technology – are we ready? Gene Neyer, SVP, Product Management, Fundtech
 SEPA focus has been on new clearing compliance • SEPA compliance does not require investments into new technology or changes to the core operating models • Complexity/Uncertainty blocked innovation/strategic investments blocked – Banks focused on internal tactical improvements. Many have: • Overspent on Credit Transfers implementations with limited strategic value • Feel the burden of having to support existing national ACH infrastructures during the ever extending transition period – Corporate acceptance and uptake have been “measured” • These pushed advanced corporate access and improved customer service to the back-burner in bank’s strategic programmes 82% banks surveyed plan to maintain the same staffing levels
SEPA focus has been on new clearing compliance • SEPA compliance does not require investments into new technology or changes to the core operating models • Complexity/Uncertainty blocked innovation/strategic investments blocked – Banks focused on internal tactical improvements. Many have: • Overspent on Credit Transfers implementations with limited strategic value • Feel the burden of having to support existing national ACH infrastructures during the ever extending transition period – Corporate acceptance and uptake have been “measured” • These pushed advanced corporate access and improved customer service to the back-burner in bank’s strategic programmes 82% banks surveyed plan to maintain the same staffing levels
 Yet, many banks wish to leverage new technology • Accidental vs. Planned architecture – the power of the platform – Tactical investments layered into a strategic programme – The promise of SOA • Efficiency/Agility/Re-Usability • Utility followed by new products: – More efficient corporate access – New delivery channels – mobile, smart cards, electronic wallets • The concerns are: – Risk with new technology/Time to market/Resource contention/ Revenue loss 57% banks surveyed felt that it will take at least 5 years (or never) to recover revenues lost to SEPA Back Office Consolidation
Yet, many banks wish to leverage new technology • Accidental vs. Planned architecture – the power of the platform – Tactical investments layered into a strategic programme – The promise of SOA • Efficiency/Agility/Re-Usability • Utility followed by new products: – More efficient corporate access – New delivery channels – mobile, smart cards, electronic wallets • The concerns are: – Risk with new technology/Time to market/Resource contention/ Revenue loss 57% banks surveyed felt that it will take at least 5 years (or never) to recover revenues lost to SEPA Back Office Consolidation
 How, when and where • Architect Rules Driven organisation – Infrastructure based on SOA, Integration Patterns, and ISO standards • Progress SEPA from “necessary evil” to the foundation of the rejuvenated customer service strategy – SEPA does not provide any implicit or explicit customer service guidelines – a differentiation opportunity • Gradually mesh and evolve legacy and SOA offerings – focus on technology to ease customer access, integration and the enabling of new channels
How, when and where • Architect Rules Driven organisation – Infrastructure based on SOA, Integration Patterns, and ISO standards • Progress SEPA from “necessary evil” to the foundation of the rejuvenated customer service strategy – SEPA does not provide any implicit or explicit customer service guidelines – a differentiation opportunity • Gradually mesh and evolve legacy and SOA offerings – focus on technology to ease customer access, integration and the enabling of new channels
 The Application of new technology for Payments Luc Belpaire Product Director Payments, Sun. Gard
The Application of new technology for Payments Luc Belpaire Product Director Payments, Sun. Gard
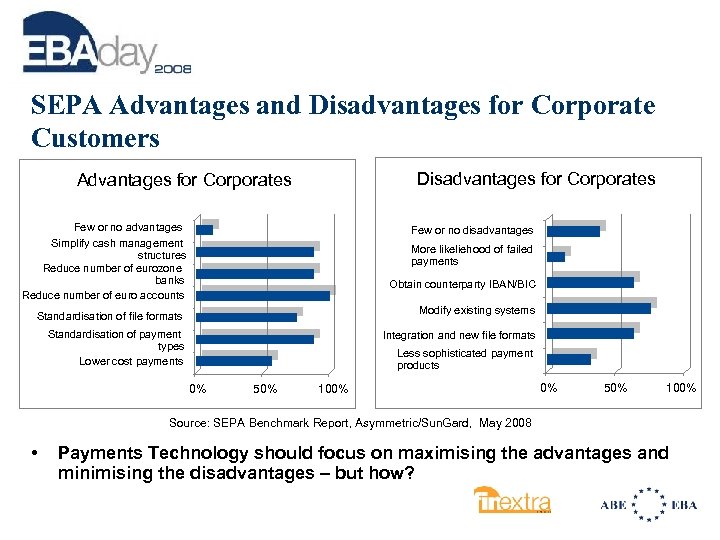 SEPA Advantages and Disadvantages for Corporate Customers Disadvantages for Corporates Advantages for Corporates Few or no advantages Simplify cash management structures Reduce number of eurozone banks Reduce number of euro accounts Few or no disadvantages More likeliehood of failed payments Obtain counterparty IBAN/BIC Modify existing systems Standardisation of file formats Standardisation of payment types Lower cost payments Integration and new file formats Less sophisticated payment products 0% 50% 100% Source: SEPA Benchmark Report, Asymmetric/Sun. Gard, May 2008 • Payments Technology should focus on maximising the advantages and minimising the disadvantages – but how?
SEPA Advantages and Disadvantages for Corporate Customers Disadvantages for Corporates Advantages for Corporates Few or no advantages Simplify cash management structures Reduce number of eurozone banks Reduce number of euro accounts Few or no disadvantages More likeliehood of failed payments Obtain counterparty IBAN/BIC Modify existing systems Standardisation of file formats Standardisation of payment types Lower cost payments Integration and new file formats Less sophisticated payment products 0% 50% 100% Source: SEPA Benchmark Report, Asymmetric/Sun. Gard, May 2008 • Payments Technology should focus on maximising the advantages and minimising the disadvantages – but how?
 How can Corporates use Payments Technology to maximise the SEPA benefits? • • • Corporates can centralise the payments and cash reporting in a payment factory – Shield the business applications (Treasury Systems, ERP, Payroll, AP, AR, . . . ) from the complexity of SEPA – Build the required changes once instead of in every system – Don’t forget payments outside SEPA, the architecture needs to support multiple formats as well as local instruments Corporates can standardise all layers using the available technology – Bank Connectivity – Business Process & Workflow • Approvals and Signatures • Bank Reporting – Bank Account Management Corporates can extract business intelligence using the central platform – Management Dashboards – Operational Dashboards
How can Corporates use Payments Technology to maximise the SEPA benefits? • • • Corporates can centralise the payments and cash reporting in a payment factory – Shield the business applications (Treasury Systems, ERP, Payroll, AP, AR, . . . ) from the complexity of SEPA – Build the required changes once instead of in every system – Don’t forget payments outside SEPA, the architecture needs to support multiple formats as well as local instruments Corporates can standardise all layers using the available technology – Bank Connectivity – Business Process & Workflow • Approvals and Signatures • Bank Reporting – Bank Account Management Corporates can extract business intelligence using the central platform – Management Dashboards – Operational Dashboards
 Conclusion • Build a business case around business benefits – Use SEPA as a catalyst / facilitator for cash management centralisation • Simplification and improvement versus pre-SEPA situation – Other elements can add to the business case • Improve working capital management • Enforce security and best practice processes • Reduce costs – Facilitate growth • Technology is available today – – Payment Factory Software Standardised Corporate-Bank channel Business Intelligence Tools Service Oriented Architectures facilitating integration
Conclusion • Build a business case around business benefits – Use SEPA as a catalyst / facilitator for cash management centralisation • Simplification and improvement versus pre-SEPA situation – Other elements can add to the business case • Improve working capital management • Enforce security and best practice processes • Reduce costs – Facilitate growth • Technology is available today – – Payment Factory Software Standardised Corporate-Bank channel Business Intelligence Tools Service Oriented Architectures facilitating integration
 The Application of New Technology for Payments Maurice Cleaves, Deutsche Bank
The Application of New Technology for Payments Maurice Cleaves, Deutsche Bank
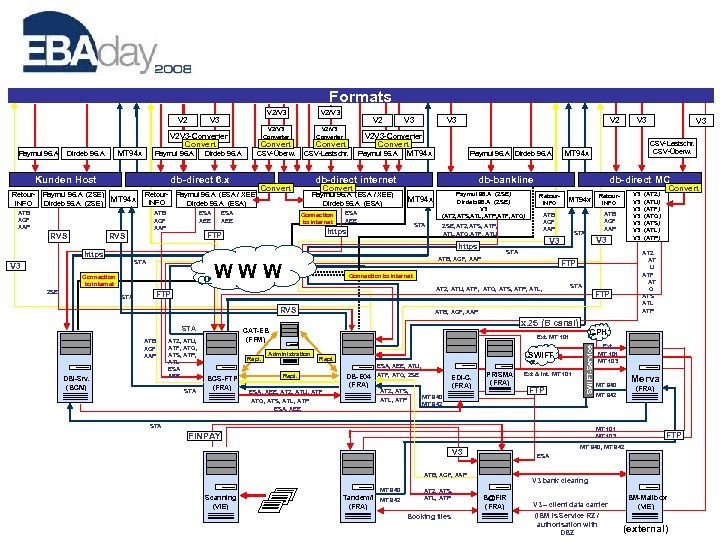 Formats V 2/V 3 Converter V 3 V 2 V 3 -Converter Convert MT 94 x Dirdeb 96. A Paymul 96. A Kunden Host Retour. INFO ATB XCF XAP ESA XEE CSV-Lastschr. V 3 V 2 V 3 -Converter Convert Paymul 96. A MT 94 x Paymul 96. A Dirdeb 96. A db-direct internet Convert ESA XEE V 2 Convert Paymul 96. A (ESA / XEE) Dirdeb 96. A (ESA) Connection to Internet MT 94 x ESA XEE Paymul 96. A (ZSE) Dirdeb 96. A (ZSE) V 3 (ATZ, ATS, ATL, ATP, ATF, ATQ) STA https ZSE, ATZ, ATS, ATP, ATL, ATQ, ATF, ATU https STA V 3 STA RVS ATB XCF XAP DBI-Srv. (BCN) Retour. INFO MT 94 x ATB XCF XAP ATZ, ATU, ATF, ATQ, ATS, ATP, ATL ESA XEE STA FTP ATB, XCF, XAP x. 25 (B canal) CPH Ext. MT 101 Administration SWIFT Repl. ESA, XEE, ATZ, ATU, ATF ATQ, ATS, ATL, ATP ESA, XEE DB-E 04 ATF, ATQ, ZSE (FRA) ATZ, ATS, ATL, ATP EDI-C. (FRA) PRISMA (FRA) MT 940 MT 942 Ext & Int. MT 101 FTP STA Merva MT 940 (FRA) MT 942 ESA ATB, XCF, XAP Tandem/i MT 942 (FRA) ATZ, ATS, ATL, ATP Booking files FTP MT 940, MT 942 V 3 Scanning (VIE) Ext. MT 101 MT 103 FINPAY MT 940 Convert (ATZ) (ATU) (ATF) (ATQ) (ATS) (ATL) (ATP) ATZ AT U ATF AT Q ATS ATL ATP FTP ESA, XEE, ATU, BCS-FTP (FRA) V 3 STA CAT-EB (FFM) Repl. V 3 V 3 Retour. INFO ATB XCF XAP STA V 3 ATZ, ATU, ATF, ATQ, ATS, ATP, ATL, STA CSV-Lastschr. CSV-Überw. Connection to Internet FTP V 3 db-direct MC ATB, XCF, XAP WWW Connection to Internet V 3 MT 94 x db-bankline Convert FTP RVS ZSE CSV-Überw. Paymul 96. A (ESA / XEE) Dirdeb 96. A (ESA) ATB XCF XAP V 2/V 3 Converter Convert db-direct 6. x Paymul 96. A (ZSE) MT 94 x Dirdeb 96. A (ZSE) RVS Dirdeb 96. A V 2/V 3 SWIFT-Service V 2/V 3 bank clearing B@FIR (FRA) V 3 – client data carrier (IBM is Service RZ / authorisation with DBZ IBM-Mailbox (VIE) (external)
Formats V 2/V 3 Converter V 3 V 2 V 3 -Converter Convert MT 94 x Dirdeb 96. A Paymul 96. A Kunden Host Retour. INFO ATB XCF XAP ESA XEE CSV-Lastschr. V 3 V 2 V 3 -Converter Convert Paymul 96. A MT 94 x Paymul 96. A Dirdeb 96. A db-direct internet Convert ESA XEE V 2 Convert Paymul 96. A (ESA / XEE) Dirdeb 96. A (ESA) Connection to Internet MT 94 x ESA XEE Paymul 96. A (ZSE) Dirdeb 96. A (ZSE) V 3 (ATZ, ATS, ATL, ATP, ATF, ATQ) STA https ZSE, ATZ, ATS, ATP, ATL, ATQ, ATF, ATU https STA V 3 STA RVS ATB XCF XAP DBI-Srv. (BCN) Retour. INFO MT 94 x ATB XCF XAP ATZ, ATU, ATF, ATQ, ATS, ATP, ATL ESA XEE STA FTP ATB, XCF, XAP x. 25 (B canal) CPH Ext. MT 101 Administration SWIFT Repl. ESA, XEE, ATZ, ATU, ATF ATQ, ATS, ATL, ATP ESA, XEE DB-E 04 ATF, ATQ, ZSE (FRA) ATZ, ATS, ATL, ATP EDI-C. (FRA) PRISMA (FRA) MT 940 MT 942 Ext & Int. MT 101 FTP STA Merva MT 940 (FRA) MT 942 ESA ATB, XCF, XAP Tandem/i MT 942 (FRA) ATZ, ATS, ATL, ATP Booking files FTP MT 940, MT 942 V 3 Scanning (VIE) Ext. MT 101 MT 103 FINPAY MT 940 Convert (ATZ) (ATU) (ATF) (ATQ) (ATS) (ATL) (ATP) ATZ AT U ATF AT Q ATS ATL ATP FTP ESA, XEE, ATU, BCS-FTP (FRA) V 3 STA CAT-EB (FFM) Repl. V 3 V 3 Retour. INFO ATB XCF XAP STA V 3 ATZ, ATU, ATF, ATQ, ATS, ATP, ATL, STA CSV-Lastschr. CSV-Überw. Connection to Internet FTP V 3 db-direct MC ATB, XCF, XAP WWW Connection to Internet V 3 MT 94 x db-bankline Convert FTP RVS ZSE CSV-Überw. Paymul 96. A (ESA / XEE) Dirdeb 96. A (ESA) ATB XCF XAP V 2/V 3 Converter Convert db-direct 6. x Paymul 96. A (ZSE) MT 94 x Dirdeb 96. A (ZSE) RVS Dirdeb 96. A V 2/V 3 SWIFT-Service V 2/V 3 bank clearing B@FIR (FRA) V 3 – client data carrier (IBM is Service RZ / authorisation with DBZ IBM-Mailbox (VIE) (external)
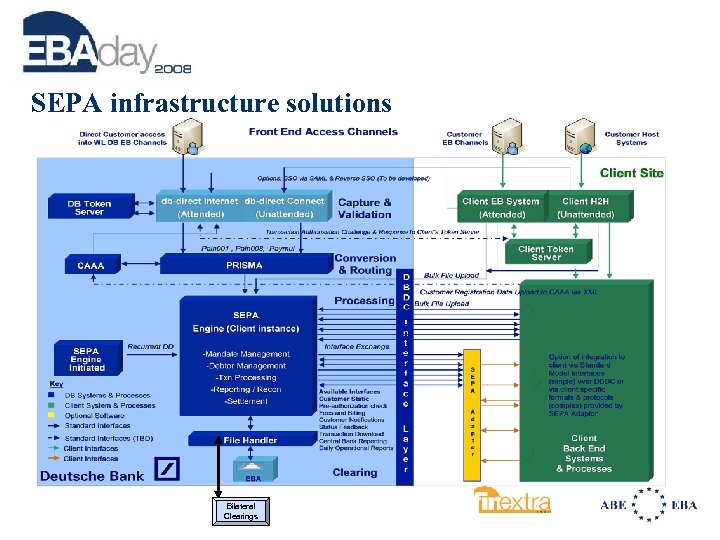 SEPA infrastructure solutions Bilateral Clearings
SEPA infrastructure solutions Bilateral Clearings
 Keys to survival in the Cash Management Business Revenue Enhancement Managing Cost and Compliance Customer Retention Product Innovation
Keys to survival in the Cash Management Business Revenue Enhancement Managing Cost and Compliance Customer Retention Product Innovation
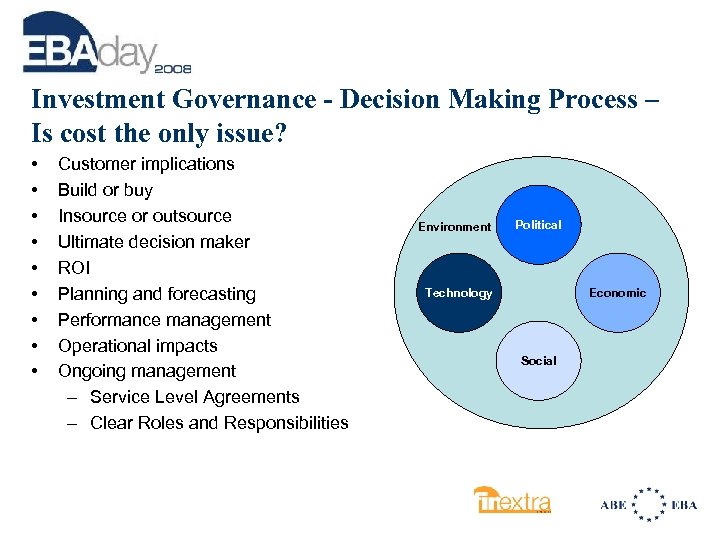 Investment Governance - Decision Making Process – Is cost the only issue? • • • Customer implications Build or buy Insource or outsource Ultimate decision maker ROI Planning and forecasting Performance management Operational impacts Ongoing management – Service Level Agreements – Clear Roles and Responsibilities Environment Political Technology Economic Social
Investment Governance - Decision Making Process – Is cost the only issue? • • • Customer implications Build or buy Insource or outsource Ultimate decision maker ROI Planning and forecasting Performance management Operational impacts Ongoing management – Service Level Agreements – Clear Roles and Responsibilities Environment Political Technology Economic Social


