aa8f6bad9f3163f25b22c11dc5e948e4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 The Anticoagulation Clinic of the Future Edith Nutescu, Pharm. D Clinical Assistant Professor Director Antithrombosis Service The University of Illinois at Chicago College of Pharmacy & Medical Center
The Anticoagulation Clinic of the Future Edith Nutescu, Pharm. D Clinical Assistant Professor Director Antithrombosis Service The University of Illinois at Chicago College of Pharmacy & Medical Center
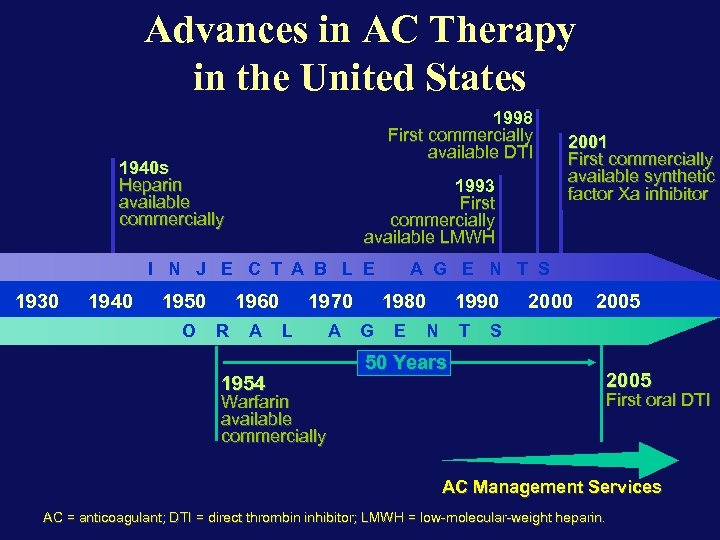 Advances in AC Therapy in the United States 1998 First commercially available DTI 1940 s Heparin available commercially 1993 First commercially available LMWH I N J E C T A B L E 1930 1940 1950 O 1960 R A 1954 1970 L Warfarin available commercially A A G E N T S 1980 G 2001 First commercially available synthetic factor Xa inhibitor E 1990 N T 50 Years 2000 2005 S 2005 First oral DTI AC Management Services AC = anticoagulant; DTI = direct thrombin inhibitor; LMWH = low-molecular-weight heparin.
Advances in AC Therapy in the United States 1998 First commercially available DTI 1940 s Heparin available commercially 1993 First commercially available LMWH I N J E C T A B L E 1930 1940 1950 O 1960 R A 1954 1970 L Warfarin available commercially A A G E N T S 1980 G 2001 First commercially available synthetic factor Xa inhibitor E 1990 N T 50 Years 2000 2005 S 2005 First oral DTI AC Management Services AC = anticoagulant; DTI = direct thrombin inhibitor; LMWH = low-molecular-weight heparin.
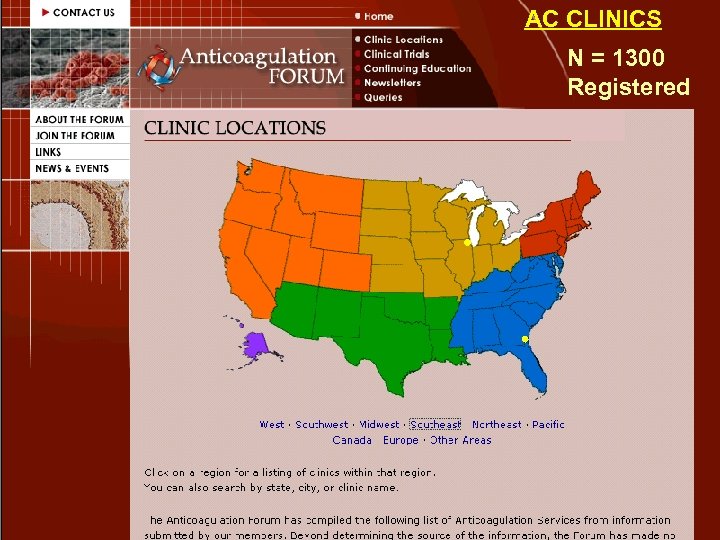 AC CLINICS N = 1300 Registered
AC CLINICS N = 1300 Registered
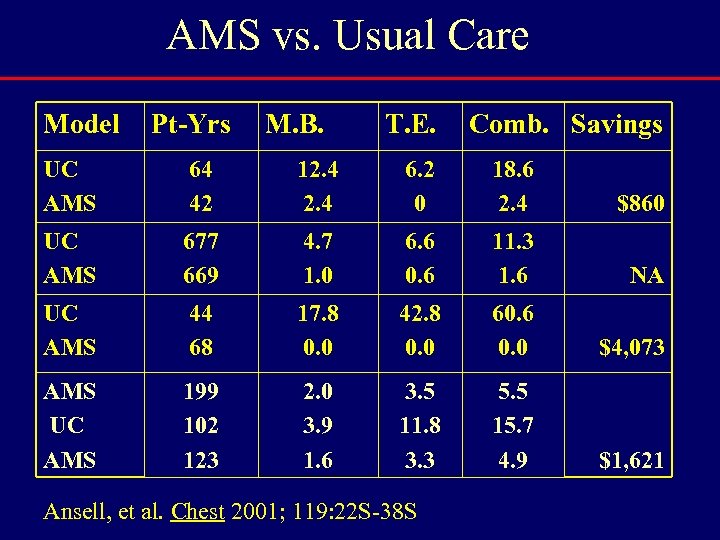 AMS vs. Usual Care Model Pt-Yrs M. B. T. E. Comb. Savings UC AMS 64 42 12. 4 6. 2 0 18. 6 2. 4 $860 UC AMS 677 669 4. 7 1. 0 6. 6 0. 6 11. 3 1. 6 NA UC AMS 44 68 17. 8 0. 0 42. 8 0. 0 60. 6 0. 0 $4, 073 AMS UC AMS 199 102 123 2. 0 3. 9 1. 6 3. 5 11. 8 3. 3 5. 5 15. 7 4. 9 $1, 621 Ansell, et al. Chest 2001; 119: 22 S-38 S
AMS vs. Usual Care Model Pt-Yrs M. B. T. E. Comb. Savings UC AMS 64 42 12. 4 6. 2 0 18. 6 2. 4 $860 UC AMS 677 669 4. 7 1. 0 6. 6 0. 6 11. 3 1. 6 NA UC AMS 44 68 17. 8 0. 0 42. 8 0. 0 60. 6 0. 0 $4, 073 AMS UC AMS 199 102 123 2. 0 3. 9 1. 6 3. 5 11. 8 3. 3 5. 5 15. 7 4. 9 $1, 621 Ansell, et al. Chest 2001; 119: 22 S-38 S
 ACCP 2001: Chapter on AMS • Reviews Models Of Care…Recommends Anticoagulation Clinics Over Usual Medical Care, Grade 1 C Ansell, et al. Managing Oral Anticoagulant Therapy. Chest 2001; 119: 22 S-38 S
ACCP 2001: Chapter on AMS • Reviews Models Of Care…Recommends Anticoagulation Clinics Over Usual Medical Care, Grade 1 C Ansell, et al. Managing Oral Anticoagulant Therapy. Chest 2001; 119: 22 S-38 S
 Medicolegal Considerations : AMS “…there is little doubt that practitioners who use the “less effective” system are at higher risk of legal liability…and may be seen by a jury as not having exercised a level of diligence demanded by the risk …to the patient…it will be very difficult to mount a defense sufficient to overcome this charge. ” Mc. Intyre K. Chest 2001; 119: 342 S (also 1998 Chest suppl)
Medicolegal Considerations : AMS “…there is little doubt that practitioners who use the “less effective” system are at higher risk of legal liability…and may be seen by a jury as not having exercised a level of diligence demanded by the risk …to the patient…it will be very difficult to mount a defense sufficient to overcome this charge. ” Mc. Intyre K. Chest 2001; 119: 342 S (also 1998 Chest suppl)
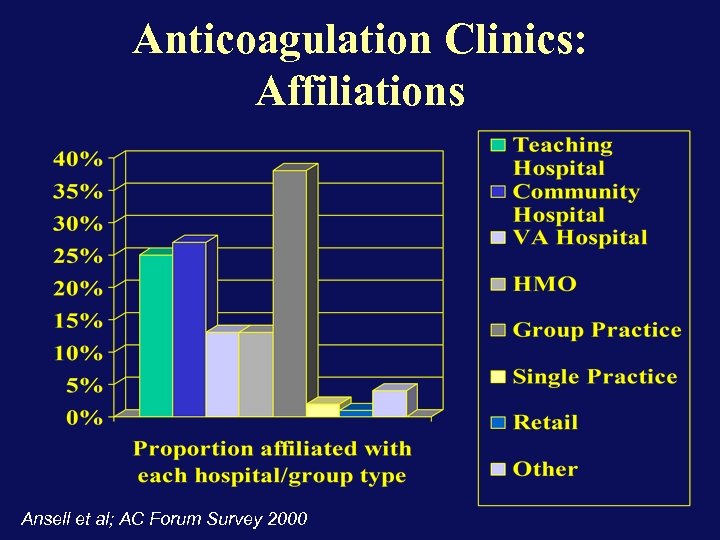 Anticoagulation Clinics: Affiliations Ansell et al; AC Forum Survey 2000
Anticoagulation Clinics: Affiliations Ansell et al; AC Forum Survey 2000
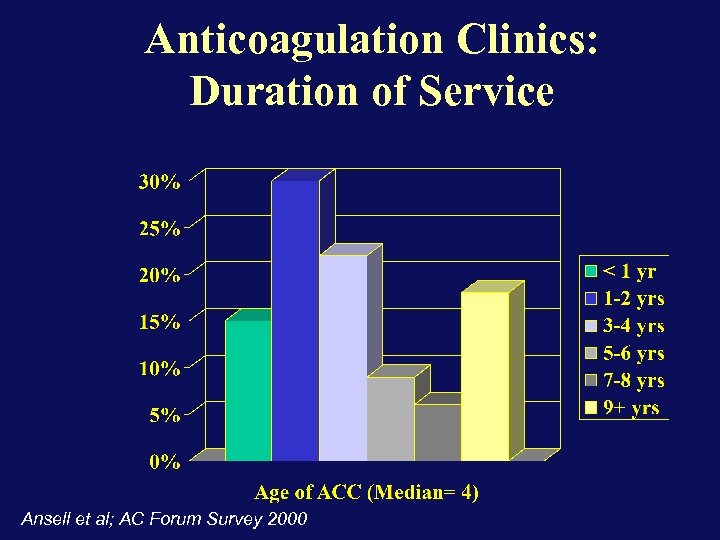 Anticoagulation Clinics: Duration of Service Ansell et al; AC Forum Survey 2000
Anticoagulation Clinics: Duration of Service Ansell et al; AC Forum Survey 2000
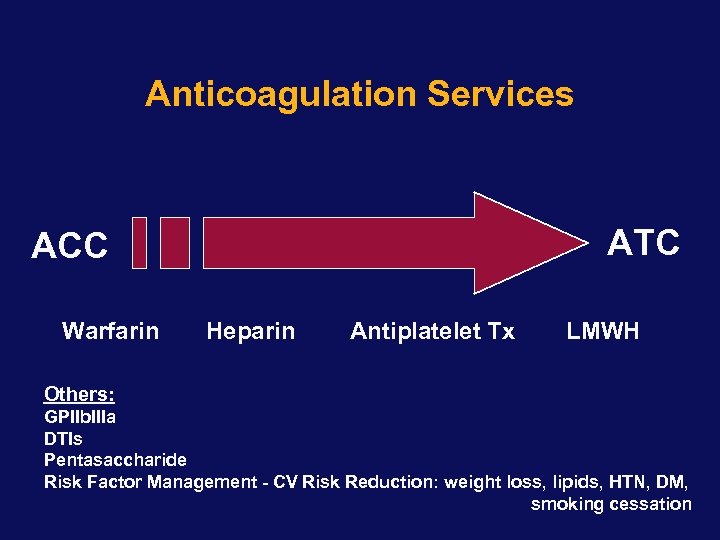 Anticoagulation Services ATC ACC Warfarin Heparin Antiplatelet Tx LMWH Others: GPIIb. IIIa DTIs Pentasaccharide Risk Factor Management - CV Risk Reduction: weight loss, lipids, HTN, DM, smoking cessation
Anticoagulation Services ATC ACC Warfarin Heparin Antiplatelet Tx LMWH Others: GPIIb. IIIa DTIs Pentasaccharide Risk Factor Management - CV Risk Reduction: weight loss, lipids, HTN, DM, smoking cessation
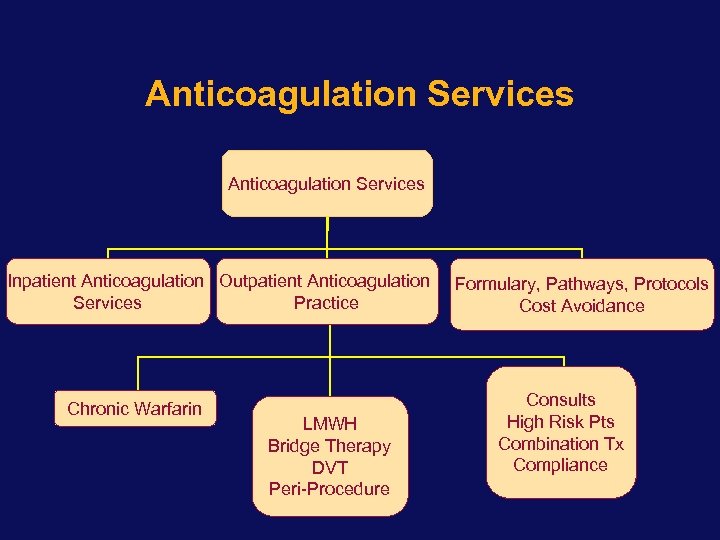 Anticoagulation Services Inpatient Anticoagulation Outpatient Anticoagulation Services Practice Chronic Warfarin LMWH Bridge Therapy DVT Peri-Procedure Formulary, Pathways, Protocols Cost Avoidance Consults High Risk Pts Combination Tx Compliance
Anticoagulation Services Inpatient Anticoagulation Outpatient Anticoagulation Services Practice Chronic Warfarin LMWH Bridge Therapy DVT Peri-Procedure Formulary, Pathways, Protocols Cost Avoidance Consults High Risk Pts Combination Tx Compliance
 Anticoagulation Management Services • Systematic, organized management of anticoagulation • Improved dose regulation • Continuous patient education • Early identification of potential risk factors for thrombotic or hemorrhagic complications • Timely, appropriate intervention to avoid or minimize complications
Anticoagulation Management Services • Systematic, organized management of anticoagulation • Improved dose regulation • Continuous patient education • Early identification of potential risk factors for thrombotic or hemorrhagic complications • Timely, appropriate intervention to avoid or minimize complications
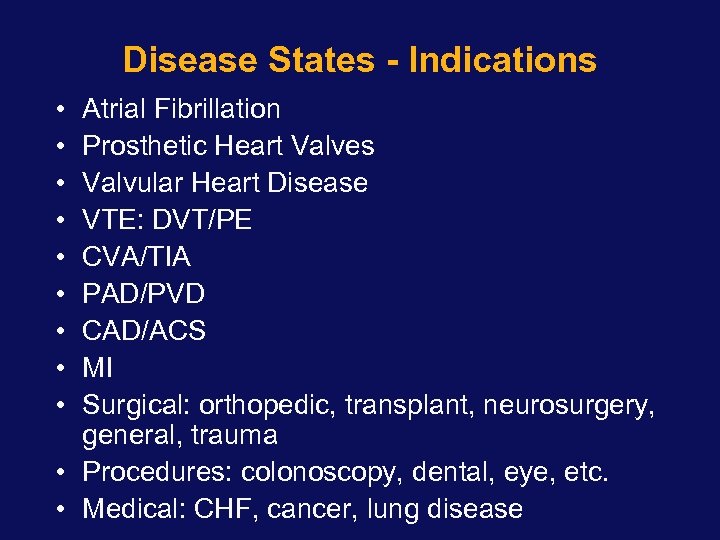 Disease States - Indications • • • Atrial Fibrillation Prosthetic Heart Valves Valvular Heart Disease VTE: DVT/PE CVA/TIA PAD/PVD CAD/ACS MI Surgical: orthopedic, transplant, neurosurgery, general, trauma • Procedures: colonoscopy, dental, eye, etc. • Medical: CHF, cancer, lung disease
Disease States - Indications • • • Atrial Fibrillation Prosthetic Heart Valves Valvular Heart Disease VTE: DVT/PE CVA/TIA PAD/PVD CAD/ACS MI Surgical: orthopedic, transplant, neurosurgery, general, trauma • Procedures: colonoscopy, dental, eye, etc. • Medical: CHF, cancer, lung disease
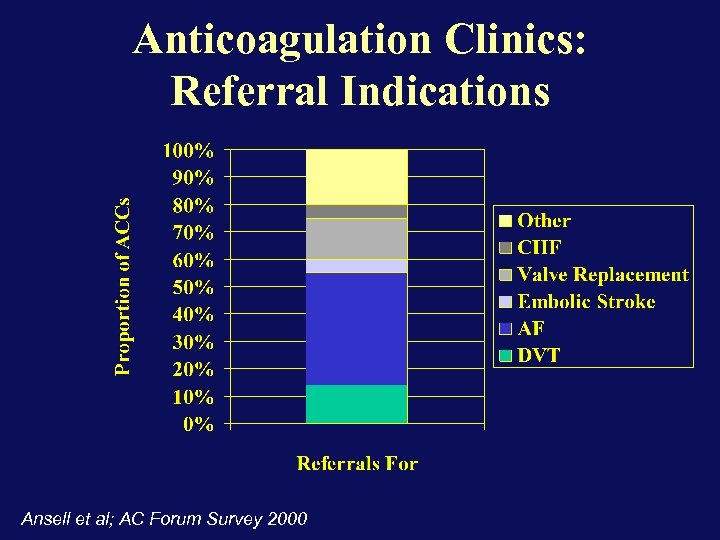 Anticoagulation Clinics: Referral Indications Ansell et al; AC Forum Survey 2000
Anticoagulation Clinics: Referral Indications Ansell et al; AC Forum Survey 2000
 Patient Volume • Small Volume Clinic – 150 -200 active patients – 300 visits/month • Mid Volume Clinic – 400 -500 active patients – 750 visits/month • High Volume Clinic – 500 -1000 active patients – 1500 visits/month • Staffing: – 1 FTE/200 -300 patients
Patient Volume • Small Volume Clinic – 150 -200 active patients – 300 visits/month • Mid Volume Clinic – 400 -500 active patients – 750 visits/month • High Volume Clinic – 500 -1000 active patients – 1500 visits/month • Staffing: – 1 FTE/200 -300 patients
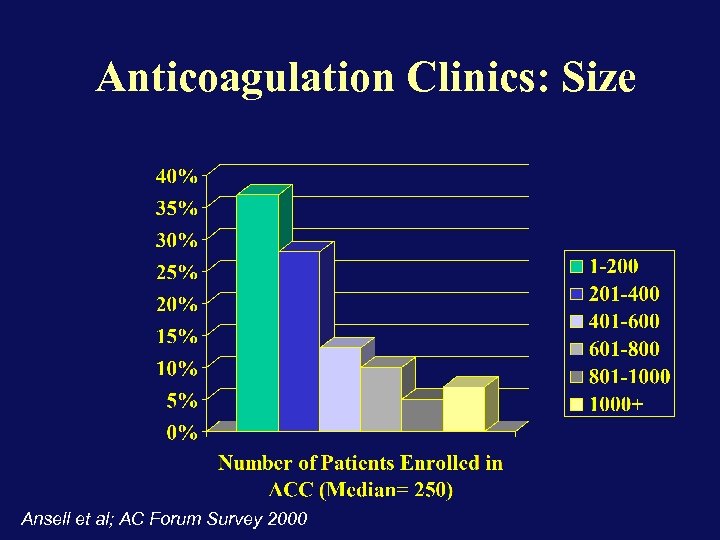 Anticoagulation Clinics: Size Ansell et al; AC Forum Survey 2000
Anticoagulation Clinics: Size Ansell et al; AC Forum Survey 2000
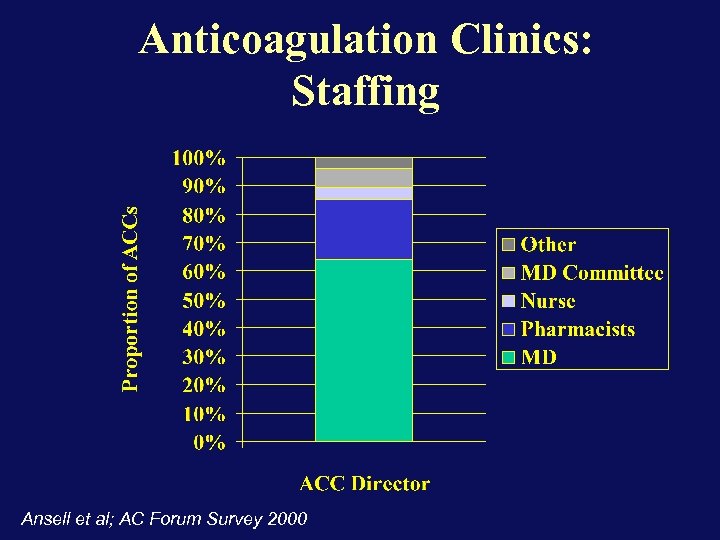 Anticoagulation Clinics: Staffing Ansell et al; AC Forum Survey 2000
Anticoagulation Clinics: Staffing Ansell et al; AC Forum Survey 2000
 Anticoagulation Services: Functions-Roles • • • • Patient education Treatment initiation/change LOT, Intensity AC selection Dose adjustment Monitoring; order labs Refills Physical assessment Minimum complications/maximum efficacy: QA Health care provider education Research Formulary, protocols, pathways Reversal of over-anticoagulation Peri-procedure management Patient triage: first line access to healthcare Administrative
Anticoagulation Services: Functions-Roles • • • • Patient education Treatment initiation/change LOT, Intensity AC selection Dose adjustment Monitoring; order labs Refills Physical assessment Minimum complications/maximum efficacy: QA Health care provider education Research Formulary, protocols, pathways Reversal of over-anticoagulation Peri-procedure management Patient triage: first line access to healthcare Administrative
 Ximelagatran: Potential Initial Indications • Orthopedic Surgery (THR/TKR) – METHRO – PLATINUM – EXPRESS • DVT/PE Treatment – THRIVE • Atrial Fibrillation – SPORTIF
Ximelagatran: Potential Initial Indications • Orthopedic Surgery (THR/TKR) – METHRO – PLATINUM – EXPRESS • DVT/PE Treatment – THRIVE • Atrial Fibrillation – SPORTIF
 ACCP Recommended DVT Prophylaxis Geerts et al, Chest 2001.
ACCP Recommended DVT Prophylaxis Geerts et al, Chest 2001.
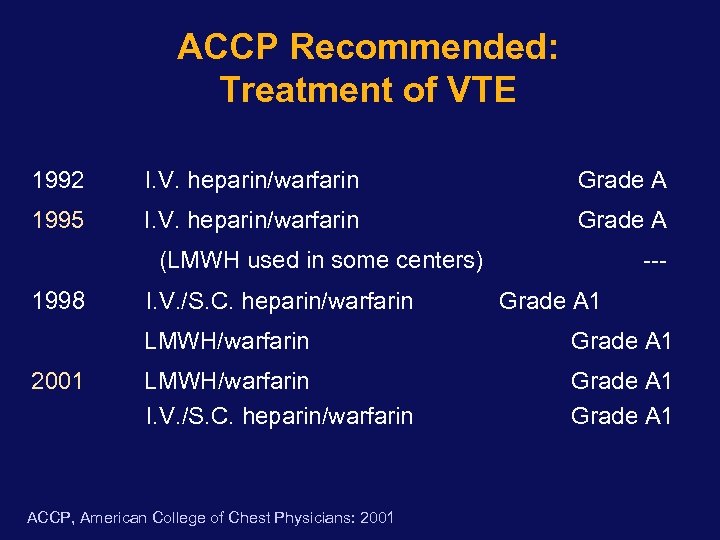 ACCP Recommended: Treatment of VTE 1992 I. V. heparin/warfarin Grade A 1995 I. V. heparin/warfarin Grade A (LMWH used in some centers) 1998 I. V. /S. C. heparin/warfarin --Grade A 1 LMWH/warfarin 2001 Grade A 1 LMWH/warfarin I. V. /S. C. heparin/warfarin Grade A 1 ACCP, American College of Chest Physicians: 2001
ACCP Recommended: Treatment of VTE 1992 I. V. heparin/warfarin Grade A 1995 I. V. heparin/warfarin Grade A (LMWH used in some centers) 1998 I. V. /S. C. heparin/warfarin --Grade A 1 LMWH/warfarin 2001 Grade A 1 LMWH/warfarin I. V. /S. C. heparin/warfarin Grade A 1 ACCP, American College of Chest Physicians: 2001
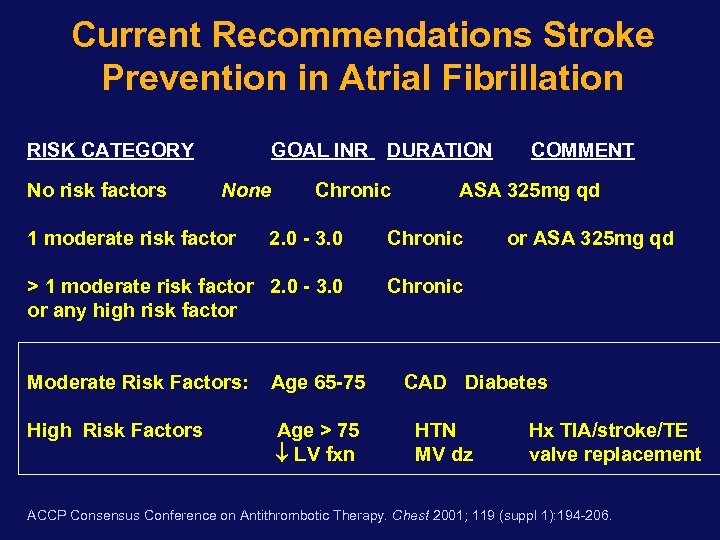 Current Recommendations Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation RISK CATEGORY No risk factors GOAL INR DURATION None 1 moderate risk factor Chronic COMMENT ASA 325 mg qd 2. 0 - 3. 0 Chronic > 1 moderate risk factor 2. 0 - 3. 0 or any high risk factor Chronic Moderate Risk Factors: High Risk Factors Age 65 -75 Age > 75 LV fxn or ASA 325 mg qd CAD Diabetes HTN MV dz Hx TIA/stroke/TE valve replacement ACCP Consensus Conference on Antithrombotic Therapy. Chest 2001; 119 (suppl 1): 194 -206.
Current Recommendations Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation RISK CATEGORY No risk factors GOAL INR DURATION None 1 moderate risk factor Chronic COMMENT ASA 325 mg qd 2. 0 - 3. 0 Chronic > 1 moderate risk factor 2. 0 - 3. 0 or any high risk factor Chronic Moderate Risk Factors: High Risk Factors Age 65 -75 Age > 75 LV fxn or ASA 325 mg qd CAD Diabetes HTN MV dz Hx TIA/stroke/TE valve replacement ACCP Consensus Conference on Antithrombotic Therapy. Chest 2001; 119 (suppl 1): 194 -206.
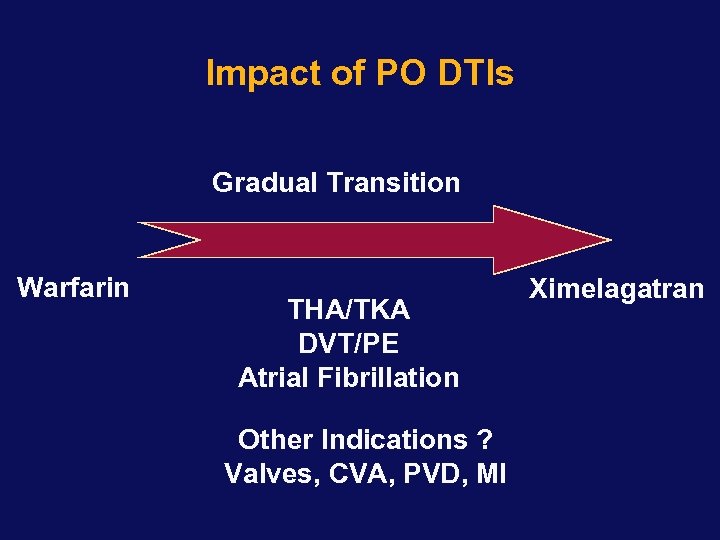 Impact of PO DTIs Gradual Transition Warfarin THA/TKA DVT/PE Atrial Fibrillation Other Indications ? Valves, CVA, PVD, MI Ximelagatran
Impact of PO DTIs Gradual Transition Warfarin THA/TKA DVT/PE Atrial Fibrillation Other Indications ? Valves, CVA, PVD, MI Ximelagatran
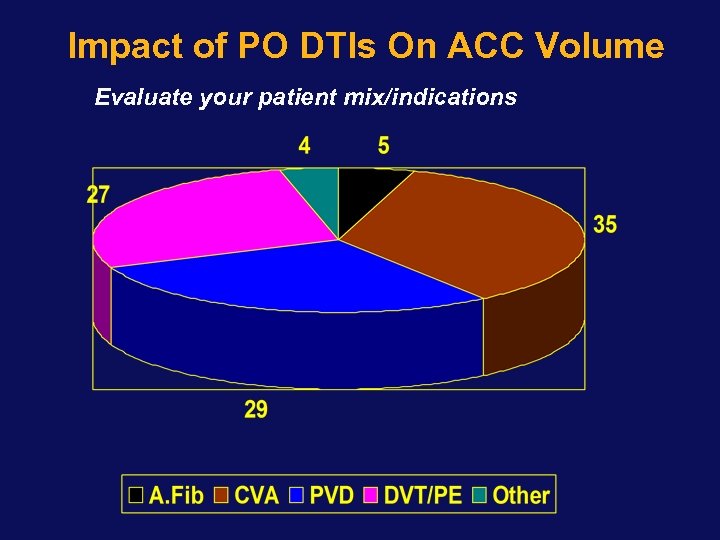 Impact of PO DTIs On ACC Volume Evaluate your patient mix/indications
Impact of PO DTIs On ACC Volume Evaluate your patient mix/indications
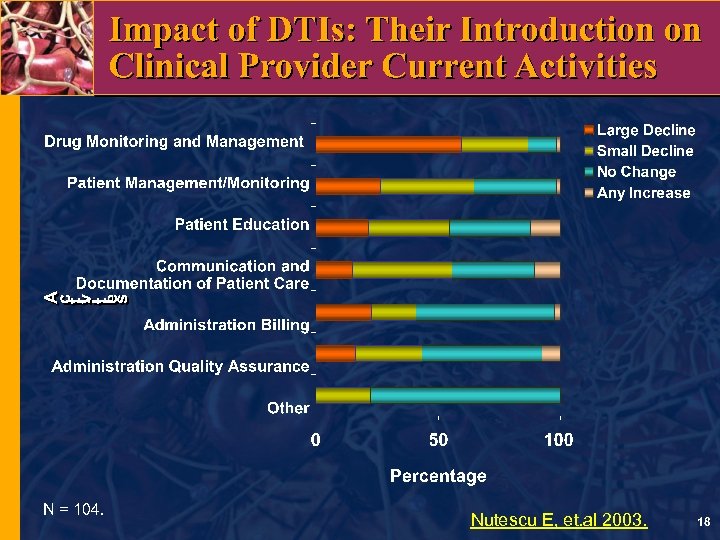 Nutescu E, et. al 2003.
Nutescu E, et. al 2003.
 Antithrombosis Services Risk Reduction Clinics ACC Warfarin ATC Antithrombotic Therapy UFH LMWH Anti-Xa Antiplatelet Agents PO DTIs Others
Antithrombosis Services Risk Reduction Clinics ACC Warfarin ATC Antithrombotic Therapy UFH LMWH Anti-Xa Antiplatelet Agents PO DTIs Others
 Will Ximelagatran Eliminate ALL Follow-Up ? • Baseline Education Crucial – Disease state – Importance of compliance • Routine Follow-Up ? – Initially q few weeks (esp DVT/PE) – Long-term: Q 3 -6 months – Treatment failures ? – Bleeding complications ? – Special patient circumstances
Will Ximelagatran Eliminate ALL Follow-Up ? • Baseline Education Crucial – Disease state – Importance of compliance • Routine Follow-Up ? – Initially q few weeks (esp DVT/PE) – Long-term: Q 3 -6 months – Treatment failures ? – Bleeding complications ? – Special patient circumstances
 UIC
UIC
 Antithrombosis Services • • • Expertise in “all” antithrombotic agents Risk stratification Patient education Compliance management Special patient populations (high risk patients) – Monitoring • Disease management – Overall risk reduction (CV, stroke, etc. ) • Guidelines, Pathways, Protocols
Antithrombosis Services • • • Expertise in “all” antithrombotic agents Risk stratification Patient education Compliance management Special patient populations (high risk patients) – Monitoring • Disease management – Overall risk reduction (CV, stroke, etc. ) • Guidelines, Pathways, Protocols
 Will Anticoagulation Clinics Survive ? YES!!! Antithrombosis Risk Reduction Services Warfarin/Coumadin Clinics
Will Anticoagulation Clinics Survive ? YES!!! Antithrombosis Risk Reduction Services Warfarin/Coumadin Clinics
 AC Management: The Road Ahead Disease Management Thromboembolic Highway Warfarin Management
AC Management: The Road Ahead Disease Management Thromboembolic Highway Warfarin Management


