b7dfb0adef68d7cf537a3d1abd6dc00f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 The Ancient Near East
The Ancient Near East
 The Ancient Near East l Common themes? l Differences?
The Ancient Near East l Common themes? l Differences?
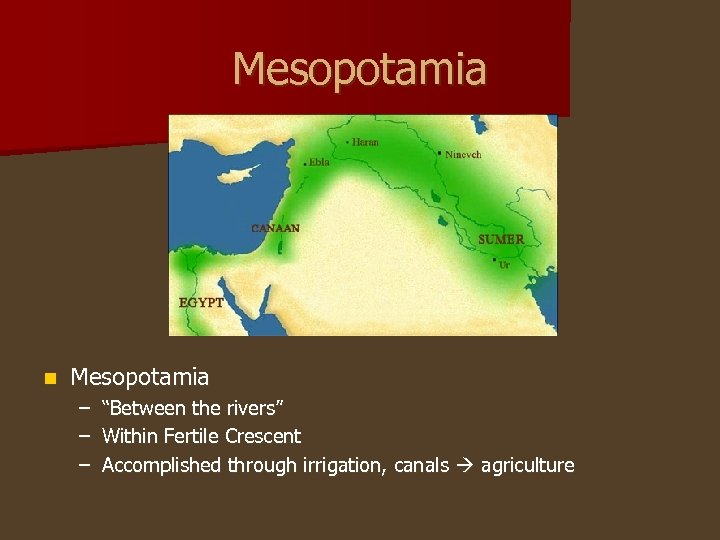 Mesopotamia n Mesopotamia – – – “Between the rivers” Within Fertile Crescent Accomplished through irrigation, canals agriculture
Mesopotamia n Mesopotamia – – – “Between the rivers” Within Fertile Crescent Accomplished through irrigation, canals agriculture
 Mesopotamia n The Sumerians (ca. 3800 -2400 BC) – Settled in Fertile Crescent – Sumer § § § 30 city-states Common culture, trade City-states often at war
Mesopotamia n The Sumerians (ca. 3800 -2400 BC) – Settled in Fertile Crescent – Sumer § § § 30 city-states Common culture, trade City-states often at war
 Mesopotamia n Accomplishments – Inventions: wheel, plow – Agriculture – Writing: CUNEIFORM Tablets with cuneiform
Mesopotamia n Accomplishments – Inventions: wheel, plow – Agriculture – Writing: CUNEIFORM Tablets with cuneiform
 Mesopotamia n Government – MONARCHY, by 2700 BC – Almost always kings – Functions § § King Sargon II (r. 722 -705 BC) Representatives of gods Legislators Justice Patrons
Mesopotamia n Government – MONARCHY, by 2700 BC – Almost always kings – Functions § § King Sargon II (r. 722 -705 BC) Representatives of gods Legislators Justice Patrons
 Mesopotamia n King Hammurabi (r. 1792 -1750 BC) – Ruler of Amorites – Conquered all Mesopotamia – Capital: Babylon – Great legislator
Mesopotamia n King Hammurabi (r. 1792 -1750 BC) – Ruler of Amorites – Conquered all Mesopotamia – Capital: Babylon – Great legislator
 Mesopotamia n The Code of Hammurabi – 282 legal rulings – Violent punishments! – Hammurabi and Shamash depicted – “When the god Marduk commanded me to provide just ways for the people of the land in order to attain appropriate behavior, I established truth and justice as the declaration of the land, I enhanced the well-being of the people. ”
Mesopotamia n The Code of Hammurabi – 282 legal rulings – Violent punishments! – Hammurabi and Shamash depicted – “When the god Marduk commanded me to provide just ways for the people of the land in order to attain appropriate behavior, I established truth and justice as the declaration of the land, I enhanced the well-being of the people. ”
 Mesopotamia n The Code of Hammurabi – “ 196. If a man put out the eye of another man, his eye shall be put out. – 197. If he break the other man’s bone, his bone shall be broken. – 198. If he put out the eye of a freed man, or break the bone of a freed man, he shall pay one gold mina. – 199. If he put out the eye of a man’s slave, or break the bone of a man’s slave, he shall pay one-half of its value. ”
Mesopotamia n The Code of Hammurabi – “ 196. If a man put out the eye of another man, his eye shall be put out. – 197. If he break the other man’s bone, his bone shall be broken. – 198. If he put out the eye of a freed man, or break the bone of a freed man, he shall pay one gold mina. – 199. If he put out the eye of a man’s slave, or break the bone of a man’s slave, he shall pay one-half of its value. ”
 Mesopotamia n Religion – POLYTHEISTIC – The gods § § § ANTHROPOMORPHIC Immortal, powerful Feared – Afterlife Hammurabi and Shamash
Mesopotamia n Religion – POLYTHEISTIC – The gods § § § ANTHROPOMORPHIC Immortal, powerful Feared – Afterlife Hammurabi and Shamash
 Mesopotamia Statuettes of worshipers from the Square Temple at Eshnunna (ca. 2700 BC)
Mesopotamia Statuettes of worshipers from the Square Temple at Eshnunna (ca. 2700 BC)
 Mesopotamia n Ziggurat – – – “Towering” structures Temple on top Nucleus of city
Mesopotamia n Ziggurat – – – “Towering” structures Temple on top Nucleus of city
 Mesopotamia Nanna Ziggurat, Ur (Muqaiyir, Iraq), ca. 2100 – ca. 2050 BC
Mesopotamia Nanna Ziggurat, Ur (Muqaiyir, Iraq), ca. 2100 – ca. 2050 BC
 Mesopotamia n Literature – Epic of Gilgamesh (ca. 2500 BC) § About semi-divine king of Uruk, friend Enkidu § Explores pursuit of immortality – Enuma Elish (ca. 11 th-cent. BC) § Origins Enkidu and Gilgamesh
Mesopotamia n Literature – Epic of Gilgamesh (ca. 2500 BC) § About semi-divine king of Uruk, friend Enkidu § Explores pursuit of immortality – Enuma Elish (ca. 11 th-cent. BC) § Origins Enkidu and Gilgamesh
 Mesopotamia n Questions?
Mesopotamia n Questions?
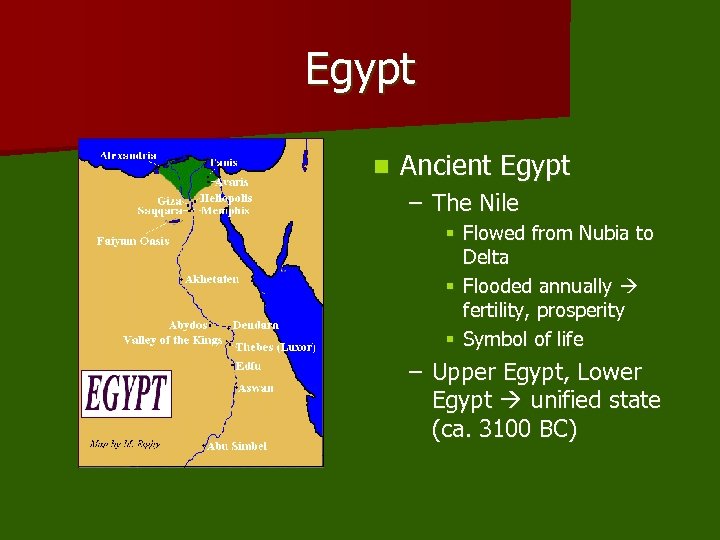 Egypt n Ancient Egypt – The Nile § Flowed from Nubia to Delta § Flooded annually fertility, prosperity § Symbol of life – Upper Egypt, Lower Egypt unified state (ca. 3100 BC)
Egypt n Ancient Egypt – The Nile § Flowed from Nubia to Delta § Flooded annually fertility, prosperity § Symbol of life – Upper Egypt, Lower Egypt unified state (ca. 3100 BC)
 Egypt n The Pharaoh – Egypt’s monarch – Divine offspring of sun god – Ruled through bureaucracy – Worshiped after death Pharaoh Tutankhamun (r. 1333 -1324 BC)
Egypt n The Pharaoh – Egypt’s monarch – Divine offspring of sun god – Ruled through bureaucracy – Worshiped after death Pharaoh Tutankhamun (r. 1333 -1324 BC)
 Egypt n Religion – Very spiritual people – Polytheistic
Egypt n Religion – Very spiritual people – Polytheistic
 Egypt n The Afterlife – Ka lives on after death – Judgment before divine tribunal – Mummification
Egypt n The Afterlife – Ka lives on after death – Judgment before divine tribunal – Mummification
 Egypt Mummies, British Museum, London
Egypt Mummies, British Museum, London
 Egypt
Egypt
 Egypt Mummy with amulets, Vatican Museum
Egypt Mummy with amulets, Vatican Museum
 Egypt
Egypt
 Egypt n Writing – Papyrus – HIEROGLYPHICS
Egypt n Writing – Papyrus – HIEROGLYPHICS
 Egypt The Rosetta Stone at the British Museum
Egypt The Rosetta Stone at the British Museum
 Egypt n The Pyramids – Purpose: pharaohs’ glory, tombs – Great Pyramids, Gizeh (ca. 2500 BC) § Near Cairo § Gold once visible § Aligned with stars? Great Pyramids, Gizeh, Egypt Tombs of Menkaure, Khafre, Khufu (ca. 2500 BC)
Egypt n The Pyramids – Purpose: pharaohs’ glory, tombs – Great Pyramids, Gizeh (ca. 2500 BC) § Near Cairo § Gold once visible § Aligned with stars? Great Pyramids, Gizeh, Egypt Tombs of Menkaure, Khafre, Khufu (ca. 2500 BC)
 Egypt n The Great Sphinx (ca. 2500 BC) – Lion, human head – Guardian
Egypt n The Great Sphinx (ca. 2500 BC) – Lion, human head – Guardian
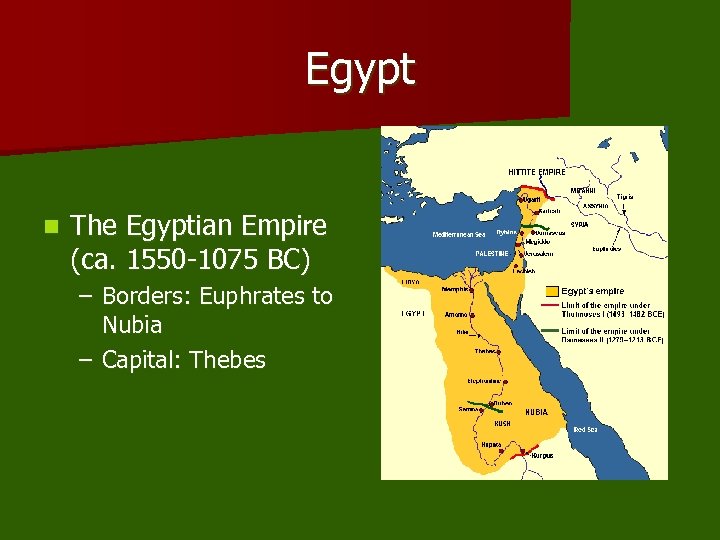 Egypt n The Egyptian Empire (ca. 1550 -1075 BC) – Borders: Euphrates to Nubia – Capital: Thebes
Egypt n The Egyptian Empire (ca. 1550 -1075 BC) – Borders: Euphrates to Nubia – Capital: Thebes
 Egypt n Hatshepsut (r. 1479 -1457 BC) – Widow of Thutmose II, regent to Thutmose III – Declared herself pharaoh! – Peaceful reign – Thutmose sought to destroy memory of her
Egypt n Hatshepsut (r. 1479 -1457 BC) – Widow of Thutmose II, regent to Thutmose III – Declared herself pharaoh! – Peaceful reign – Thutmose sought to destroy memory of her
 Egypt n Decline of Egypt (ca. 1076 BC) – Pharaohs lost power to priests – Empire disintegrated – Prominent international role lost – Suffered invasions, occupations
Egypt n Decline of Egypt (ca. 1076 BC) – Pharaohs lost power to priests – Empire disintegrated – Prominent international role lost – Suffered invasions, occupations
 Egypt n Questions?
Egypt n Questions?
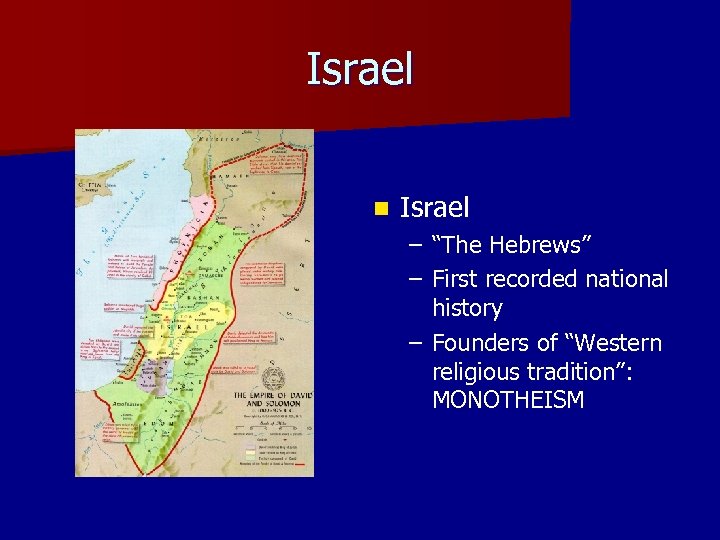 Israel n Israel – “The Hebrews” – First recorded national history – Founders of “Western religious tradition”: MONOTHEISM
Israel n Israel – “The Hebrews” – First recorded national history – Founders of “Western religious tradition”: MONOTHEISM
 Israel n The Patriarchs (ca. 2000 -1500 BC) – – Abraham Isaac Jacob Twelve tribes, *Joseph Abraham and Isaac
Israel n The Patriarchs (ca. 2000 -1500 BC) – – Abraham Isaac Jacob Twelve tribes, *Joseph Abraham and Isaac
 Israel n The Exodus (ca. 1300 BC) – Israelites oppressed in Egypt – Moses led them out – Journey through wilderness “Promised Land” – THE TEN COMMANDMENTS Moses and the Ten Commandments
Israel n The Exodus (ca. 1300 BC) – Israelites oppressed in Egypt – Moses led them out – Journey through wilderness “Promised Land” – THE TEN COMMANDMENTS Moses and the Ten Commandments
 Israel n The Ten Commandments (Exodus 20: 1 -17) – “And God spoke all these words: ‘I am the Lord your God, who brought you out of Egypt, out of the land of slavery. You shall have no other gods before me. You shall not make for yourself an image in the form of anything in heaven above or on the earth beneath or in the waters below. You shall not bow down to them or worship them…You shall not misuse the name of the Lord your God, for the Lord will not hold anyone guiltless who misuses his name. Remember the Sabbath day by keeping it holy. Six days you shall labor and do all your work, but the seventh day is a sabbath to the Lord your God. On it you shall not do any work, neither you, nor your son or daughter, nor your male or female servant, nor your animals, nor any foreigner residing in your towns…’”
Israel n The Ten Commandments (Exodus 20: 1 -17) – “And God spoke all these words: ‘I am the Lord your God, who brought you out of Egypt, out of the land of slavery. You shall have no other gods before me. You shall not make for yourself an image in the form of anything in heaven above or on the earth beneath or in the waters below. You shall not bow down to them or worship them…You shall not misuse the name of the Lord your God, for the Lord will not hold anyone guiltless who misuses his name. Remember the Sabbath day by keeping it holy. Six days you shall labor and do all your work, but the seventh day is a sabbath to the Lord your God. On it you shall not do any work, neither you, nor your son or daughter, nor your male or female servant, nor your animals, nor any foreigner residing in your towns…’”
 Israel n The Ten Commandments (Exodus 20: 1 -17) – “‘Honor your father and your mother, so that you may live long in the land the Lord your God is giving you. You shall not murder. You shall not commit adultery. You shall not steal. You shall not give false testimony against your neighbor. You shall not covet your neighbor’s house. You shall not covet your neighbor’s wife, or his male or female servant, his ox or donkey, or anything that belongs to your neighbor. ’”
Israel n The Ten Commandments (Exodus 20: 1 -17) – “‘Honor your father and your mother, so that you may live long in the land the Lord your God is giving you. You shall not murder. You shall not commit adultery. You shall not steal. You shall not give false testimony against your neighbor. You shall not covet your neighbor’s house. You shall not covet your neighbor’s wife, or his male or female servant, his ox or donkey, or anything that belongs to your neighbor. ’”
 Israel
Israel
 Israel
Israel
 Israel n Religion – Hebrew God: YHWH § Creator, redeemer § No images! – Cult § Male priesthood § Tabernacle, altars § Holy days – Sacred text: TORAH
Israel n Religion – Hebrew God: YHWH § Creator, redeemer § No images! – Cult § Male priesthood § Tabernacle, altars § Holy days – Sacred text: TORAH
 Israel
Israel
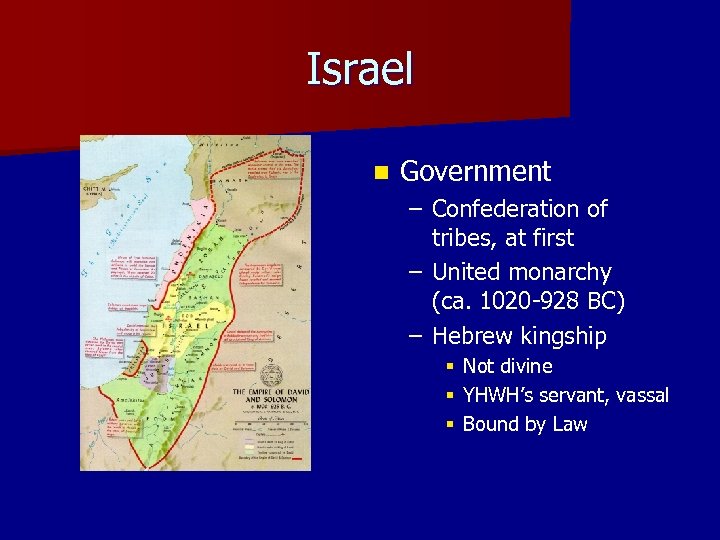 Israel n Government – Confederation of tribes, at first – United monarchy (ca. 1020 -928 BC) – Hebrew kingship § Not divine § YHWH’s servant, vassal § Bound by Law
Israel n Government – Confederation of tribes, at first – United monarchy (ca. 1020 -928 BC) – Hebrew kingship § Not divine § YHWH’s servant, vassal § Bound by Law
 Israel n The United Monarchy – KING DAVID (r. 1004 -965 BC) § Origins: shepherd, mercenary § Expansion, conquest – KING SOLOMON (r. 965 -928 BC) David § Israel at its zenith § Temple
Israel n The United Monarchy – KING DAVID (r. 1004 -965 BC) § Origins: shepherd, mercenary § Expansion, conquest – KING SOLOMON (r. 965 -928 BC) David § Israel at its zenith § Temple
 Israel Tomb of King David, Mt. Zion, Jerusalem
Israel Tomb of King David, Mt. Zion, Jerusalem
 Israel Edward Poynter, The Queen of Sheba before Solomon (1890)
Israel Edward Poynter, The Queen of Sheba before Solomon (1890)
 Israel Solomon’s Temple, Jerusalem
Israel Solomon’s Temple, Jerusalem
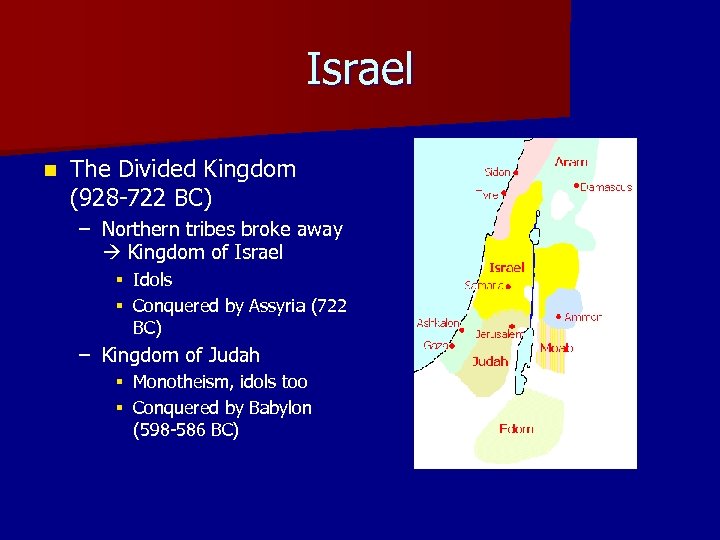 Israel n The Divided Kingdom (928 -722 BC) – Northern tribes broke away Kingdom of Israel § Idols § Conquered by Assyria (722 BC) – Kingdom of Judah § Monotheism, idols too § Conquered by Babylon (598 -586 BC)
Israel n The Divided Kingdom (928 -722 BC) – Northern tribes broke away Kingdom of Israel § Idols § Conquered by Assyria (722 BC) – Kingdom of Judah § Monotheism, idols too § Conquered by Babylon (598 -586 BC)
 Israel n Questions?
Israel n Questions?
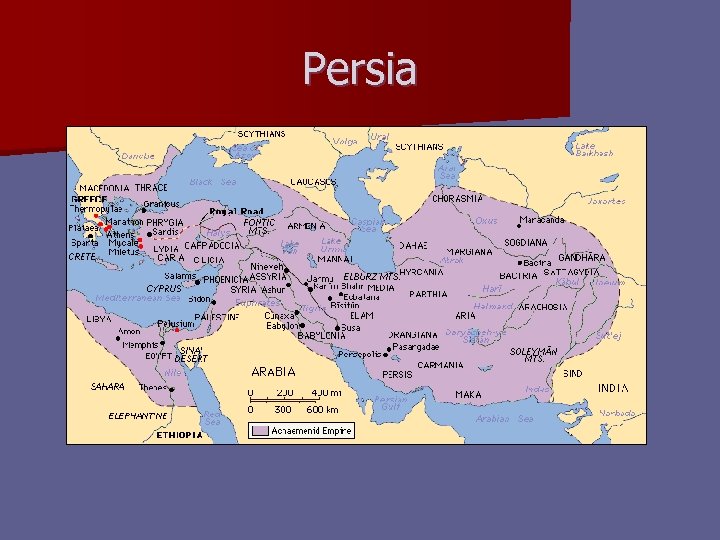
 Persia n The Persian Empire (559 -331 BC) – Iran: home of Medes and Persians – The Empire King Cyrus the Great § Initiated by Cyrus the Great (r. 559 -530 BC) § Conquered Medes, Babylon, beyond § Largest empire yet
Persia n The Persian Empire (559 -331 BC) – Iran: home of Medes and Persians – The Empire King Cyrus the Great § Initiated by Cyrus the Great (r. 559 -530 BC) § Conquered Medes, Babylon, beyond § Largest empire yet
 Persia
Persia
 Persia n The Military – Ruled by warrior aristocracy – 300, 000 soldiers! – Cavalry – First great navy
Persia n The Military – Ruled by warrior aristocracy – 300, 000 soldiers! – Cavalry – First great navy
 Persia n The King – – “King of kings” Had khvarna Brilliant in appearance! Bound by rule of law, nobility King Darius I (r. 521 -486 BC)
Persia n The King – – “King of kings” Had khvarna Brilliant in appearance! Bound by rule of law, nobility King Darius I (r. 521 -486 BC)
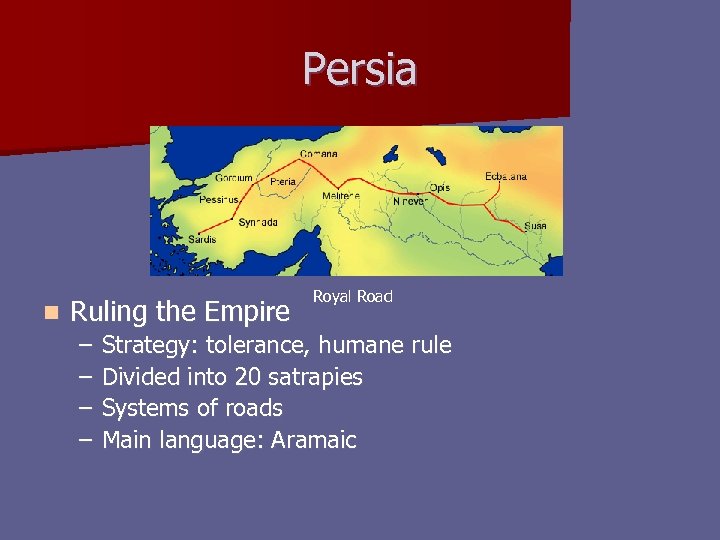 Persia n Ruling the Empire – – Royal Road Strategy: tolerance, humane rule Divided into 20 satrapies Systems of roads Main language: Aramaic
Persia n Ruling the Empire – – Royal Road Strategy: tolerance, humane rule Divided into 20 satrapies Systems of roads Main language: Aramaic
 Persia n Religion – Initially polytheism – Zoroastrianism § Prophet: Zarathustra (ca. 1000 -550 BC) § Ethical, inward-looking § Dualistic: Light vs. Darkness § Magi Open-air fire altar dedicated to Supreme Creator
Persia n Religion – Initially polytheism – Zoroastrianism § Prophet: Zarathustra (ca. 1000 -550 BC) § Ethical, inward-looking § Dualistic: Light vs. Darkness § Magi Open-air fire altar dedicated to Supreme Creator
 Persia n Questions?
Persia n Questions?
 The Ancient Near East l Common themes? l Differences?
The Ancient Near East l Common themes? l Differences?


