American Education System.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

+ The American Education System 21 December 2011 Danielle Montagne: English Language Fellow

+ Objective: During today’s lecture, we will discuss: n The American Public School System (K-12) n [A Brief] History of Education in America n The goals/learning objectives of Public Schools in America n Traditional Structure/Variations in Public School Structures n American Public Elementary, Middle and High School n Teacher/Student Case Studies n Alternative Education Options (K-12) n Contemporary Social Issues in k-12 Education n Follow up Discussion Questions & Student Questions

+ Warm Up Questions… The American Public School System n What do you know about the American Education system? n Are there any stereotypes about American education or American students that you know of? n How/where have you learned information about the American School system? n How do you think American school system differs from the Belorussian School system? n How do you think the American School system is similar to the Belorussia School system?

+ The American Public School System (K-12) History of the American Public School System n The first American schools in the thirteen original colonies opened in the 17 th century. n Established for wealthy families who could afford to send their children to school. n One room school houses would often serve primary, middle and high school age students. n For most families, literacy and mathematics education was done in the homes—often by mothers –during America’s early history. n Education for women, African Americans and non-English speaking immigrants was limited or outlawed until the 20 th century.

+ History of the American Public School System n After the American Revolution, an emphasis was put on education: n Especially true in the northern states, which rapidly established public schools. n By the year 1870, all states had free public elementary schools. n Private academies flourished in the towns across the country, but rural areas (where most people lived) had few schools before the 1880 s. n By 1900, the US population had one of the highest literacy in the world. n Education seen as necessary for developing intelligent American citizens capable in participating in all social and political realms of life.

+ Early American Schools…

+ Modern goals of the American Public School System n Education is often seen as a means to deliver equality to all American citizens. n K-12 Education is compulsory for all American children. n Education is mainly provided by the public sector and funded by the federal, state and local governments. n School curricula, funding, teaching, employment, and other policies are set through locally elected school boards who have control over a specified school district. n The modern goals of the American education system is to develop: n A well-rounded individual prepared with n critical thinking skills n problem solving skills n creativity when approaching real life situations.

+ Traditional Structure of the American School System (K-12) n The American School system traditionally consists of: n Pre-school (age 3 -5) –not compulsory n Primary School/Elementary School n Kindergarten (age 5 -6) n Grades 1 -6 (ages 6 -12) n Middle School Grades 7 -8 (ages 12 -14) High School n Grades 9 -12 (ages 14 -18) n n
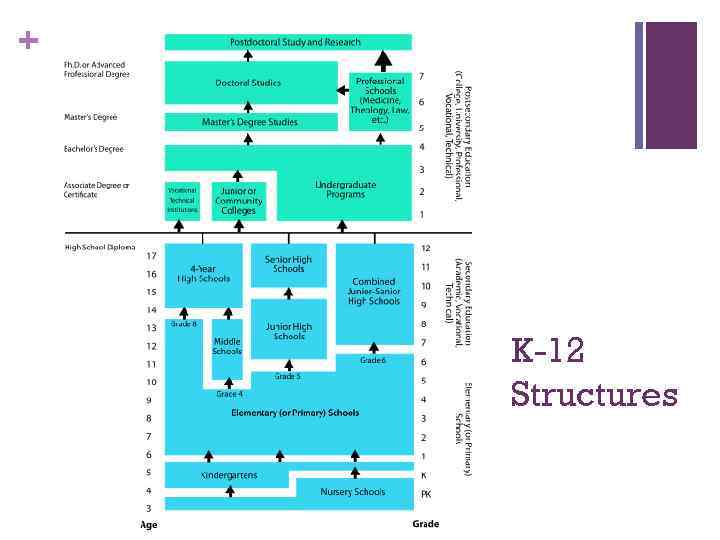
+ K-12 Structures

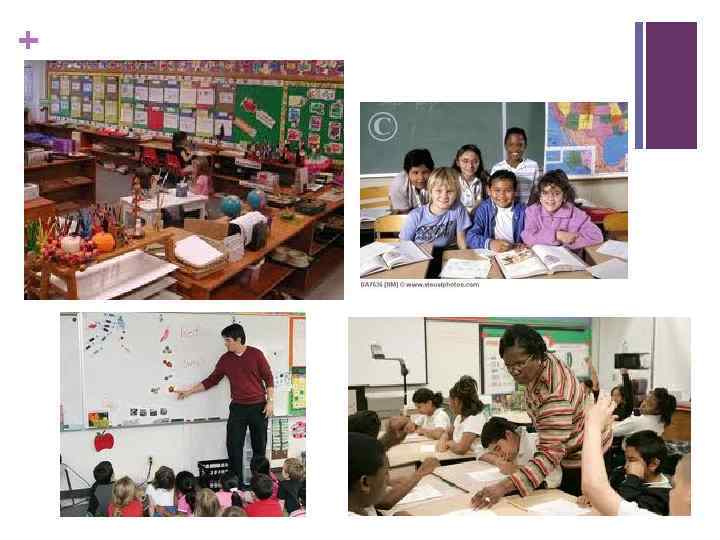
+American Primary/Elementary Schools n Public Elementary School teachers instruct between 20 -30 students of diverse learning needs. n A typical classroom will include children with a range of learning needs or abilities, from those identified as having special needs (special education) to students non-native English speakers (ESL students). n Each local school district gives each teacher a book to give to the students for each subject, and brief overviews of what the teacher are expected to teach. n Learning standards are identified for all areas of a curriculum by individual States, including those for mathematics, social studies, science, physical development, the fine arts, and reading. n Elementary School teachers are trained with emphases on human cognitive and psychological development and the principles of curriculum development and instruction. n Teachers typically earn either a Bachelors or Masters Degree in Early Childhood and Elementary Education. n Certification standards for teachers are determined by individual states.

+ Images of an American Elementary School…

+

+ Case Study: Typical Day of American Primary School Teacher n A typical teacher works 8 hours, 5 days a week, at the same school. [September-June] n Federal Holidays and Summer Vacations off from work. n Primary school teachers traditionally teach the same group of students (20 -30 students) for the full day. n Courses include: Reading, Writing, Mathematics, Science, Social Studies. n Teachers often have one (40 -45 minute) break or “preparation period” during the day. n Students receive classes from a different teacher—Music, Art, Gym (sports), Drama, Chorus, etc. n Teachers must have one lunch break (40 -45 minute) during the day. n Many teachers stay after school to participate in extracurricular activities for students or provide additional teaching time.

+Case Study: Typical Day of American Primary School Student n School begins in early September through the end of June. n Most students arrive to school by a big yellow school bus. n Students generally attend all classes in the same classroom with the same group of [diverse] students. n Students are taught strategies of working independently, in groups and in partners during the school day. n Students usually have “recess” during the school day and often spend time on a playground with their friends. n Being sent to the “principals office” is seen as a major punishment. n Elementary school students are sent home with 30 minutes to 1 ½ hours of homework each night (depending on grade level). n Extracurricular activities are popular for older elementary school students.

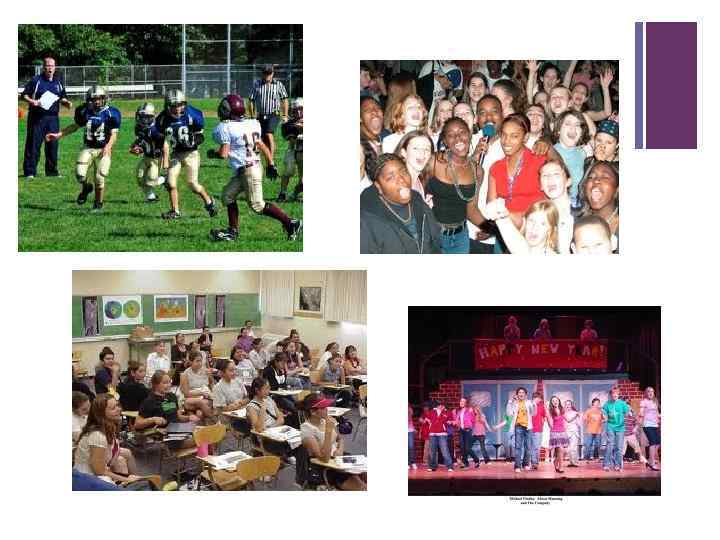
+ American Secondary Schools: Middle School n Middle School include the grade levels intermediate between elementary school and senior high school. n "Middle school" usually includes seventh and eighth grades n n "Junior high" typically includes seventh through ninth grade. At this time, students are given more independence: n Having different teachers for each subjects. n n n Taking on more independent homework assignments and projects. Moving to different classrooms for different subjects being allowed to choose some of their class subjects (electives).

+ Images of an American Middle School…

+

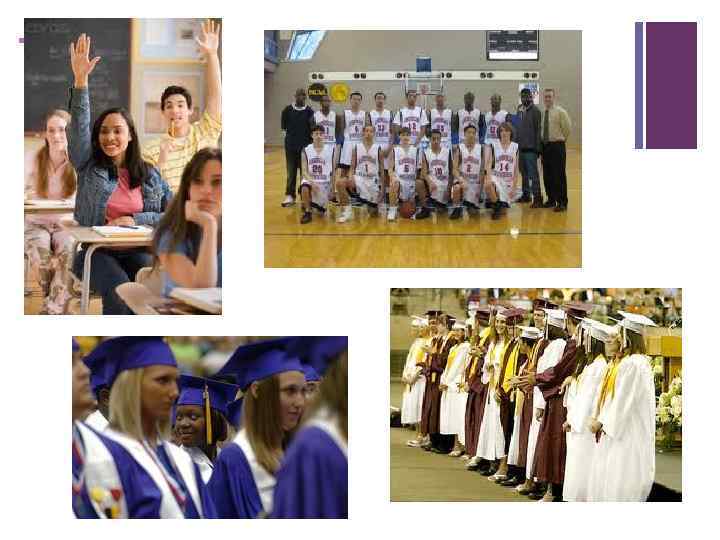
+ American Secondary Schools: Senior High School n Senior High School is a school attended after middle school/ junior high school. n The term “High school” is often used instead of senior high school n High school usually runs either from 9 th through 12 th grade. n The students in these grades are commonly referred to as: n freshmen (grade 9) n n sophomores (grade 10) juniors (grade 11) seniors (grade 12). students take a broad variety of classes without special emphasis in any particular subject

+ Images of an American High School

+

+ High School Curriculum n Students take a broad variety of classes without special emphasis in any particular subject. n Curricula vary widely in quality and rigidity n Some states consider 65 (on a 100 -point scale) a passing grade, while others consider it to be as low as 60 or as high as 75. n Mandatory subjects are required in nearly all U. S. high schools: n n n Science (3 years of biology, chemistry and physics) Mathematics (4 years of algebra, geometry, pre-calculus, statistics, and calculus) English (4 years of literature, humanities, composition, etc. ) Social sciences (3 years world and U. S. history, gov. /economics) Physical education (4 years) Many states require a "health" course (anatomy, first aid, sexuality, birth control)

+ Students Choice: Elective Classes n Computers: n Word processing, programming, graphic design… n Career and Technical Training: n Business Marketing, health occupations, technology education, publishing, journalism, public speaking, creative writing, poetry… n Performing Arts/Visual Arts: n Choir, band, orchestra, drama, art, ceramics, photography, dance… n Foreign Languages: n Spanish/French most common… n Advanced Placement Courses (AP): College Credit Courses n Sciences, History, Economics, Art, Etc…

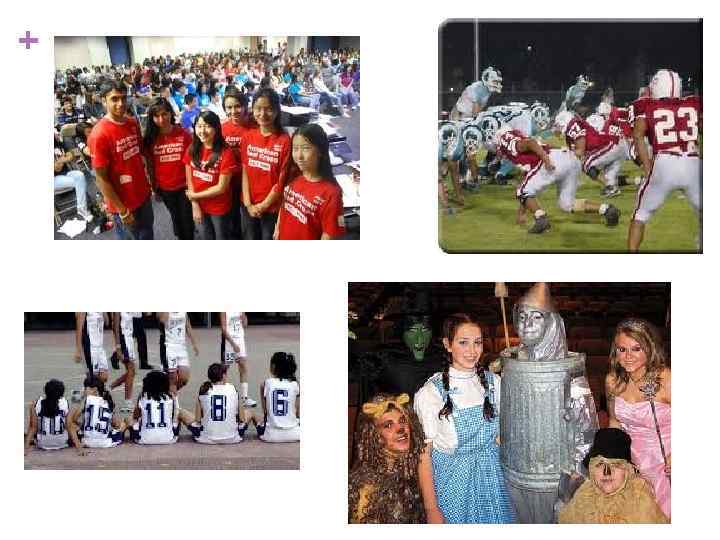
+ Extracurricular Activities in American Schools n A major characteristic of American schools is the high priority given to sports, clubs and activities by the community, the parents, the schools and the students themselves. n Extracurricular activities are educational activities not falling within the scope of the regular curriculum but under the supervision of the school. n These activities can extend to large amounts of time outside the normal school day and include: n Sports Programs—Football, Basketball, Soccer, Swimming, Wrestling, Cheerleading, Rowing, Dance, etc. n Performing Arts—orchestra bands, jazz bands, marching bands, choirs, school plays/drama clubs/musicals n Debate teams, Student Government, Public Awareness Organizations, Various Clubs (Poetry Club, Photography Club, etc. )

+
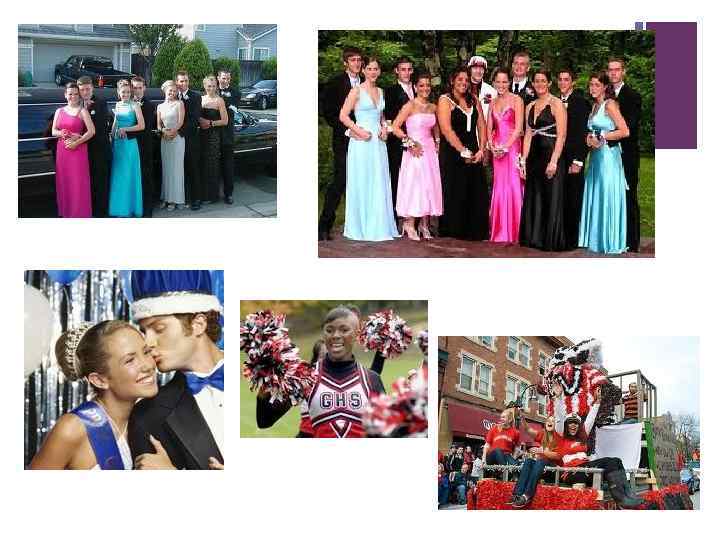
+ Social Life and School Related Activities n A major characteristic of American schools is the rich social events that are planned and organized by the high schools. n Formal Dances n Yearly Semiformal Dances n Junior Prom n Senior Prom/Senior Ball n Homecoming Day and Parade n Organized Parade n Homecoming King and Queen elected by students n Celebration at the school n Sports Activities and related social events n Football games n Bonfires and Rallys n Graduation Celebrations

+
+ Study: Typical Day of American High School Case Teacher n A typical teacher works 8 hours, 5 days a week, at the same school. [September-June] n Federal Holidays and Summer Vacations off from work. n High school teachers teach the same subject to: n 6 groups of students (45 -50 minute classes) each day OR n 3 groups of students (90 minutes) every other day n Teaching specialty depends on teaching degree n Teachers often have one “preparation period” (45 minutes) during the day. n Teachers must have one lunch break (40 -45 minute) during the day. n Many teachers stay after school to participate in extracurricular activities for students or provide additional teaching time.

Case Study: Typical Day of American High School + Student n School begins in early September through the end of June n Some student arrive to school by school bus; many others drive. n Students attend 4 -8 classes each school day. n Students must remain at school for the entire day—leaving for lunch is not allowed. n Students are taught strategies of working independently, in groups and in partners during the school day. n Students usually have “study hall” during the school day and to prepare for classes, study for exams or meet with teachers. n High school students are sent home with 2 to 3 hours of homework each night (depending on grade/skill level). n Many students stay after school to participate in sports, clubs and other extracurricular activities.

+ Alternative forms of Education n Home schooling n In 2007, approximately 1. 5 million children were home ] schooled: 2. 9% of all children. n Often associated with religious groups. n Private Schools/Private Academies n Funded solely by student tuition. n Offer more specialized courses. n Parochial School n n n Run by church organizations. Funded by student tuition and petitioner contributions. Charter School n Funded by both private funds and public funds. n Stricter control over enrollment—controversial.

+ Modern Social Issues in American Educational issues in the United States center on curriculum, funding, and control. n Funding n U. S. is tied for first place with Switzerland for annual spending per student: two countries spending more than $11, 000 USD n U. S. public schools lag behind the schools of other developed countries in the areas of reading, math, and science. n No Child Left Behind Act– George W. Bush : Gives government the right to withhold funding if it believes a school, district, or even a state is improving standardized test scores. n Tracking n Dividing students into learning groups based on classifications of “above average”, “average” or “below average” n Separating ESL students and Special Education students from mainstream classrooms.

+ n Modern Social Issues in American Education English in the Classroom n Questions on how to best accommodate for non-English speaking students and parent interest in foreign language instruction. n ESL programs vs. Bilingual programs n Dual Language Programs n Nationwide Education Content and Education Quality n Different content, grade systems and quality across the nation n Textbook Review and Adoption n Evolution in Kansas n Violence and Drug Use n Preventing violence and drug abuse in schools n Education regarding violence, sex and drug abuse
+ n Questions or Comments? Please ask me any questions about today’s lecture topic, my personal background or any other question you might have. Contact Information n Danielle Marie Montagne n n Email: d. m. montagne@gmail. com Please feel free to contact me anytime with any questions, assistance or guidance you need in any class.
American Education System.ppt