 The actuality of the course work: Nowadays English is an international language. For this reason, students need to develop Vocabulary to learn English language.
The actuality of the course work: Nowadays English is an international language. For this reason, students need to develop Vocabulary to learn English language.
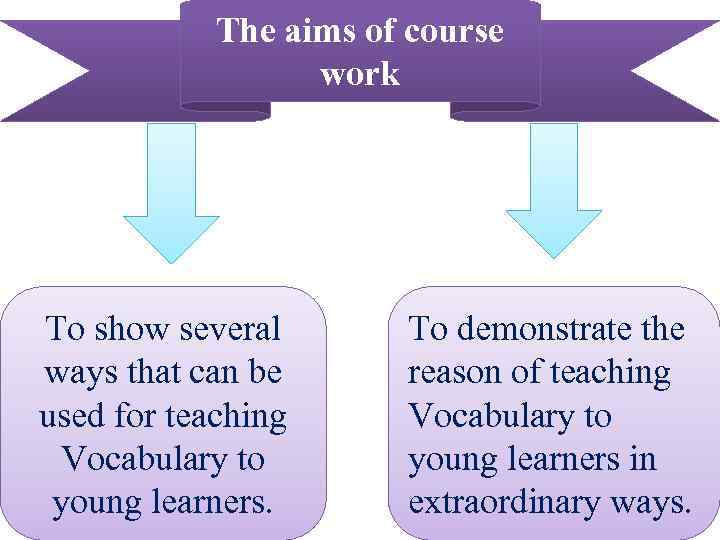 The aims of course work To show several To demonstrate the ways that can be reason of teaching used for teaching Vocabulary to young learners in young learners. extraordinary ways.
The aims of course work To show several To demonstrate the ways that can be reason of teaching used for teaching Vocabulary to young learners in young learners. extraordinary ways.
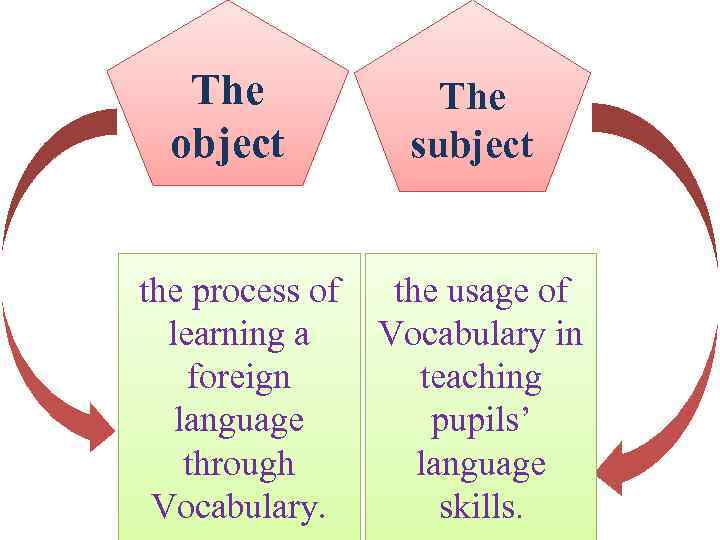 The object subject the process of the usage of learning a Vocabulary in foreign teaching language pupils’ through language Vocabulary. skills.
The object subject the process of the usage of learning a Vocabulary in foreign teaching language pupils’ through language Vocabulary. skills.
 Teaching vocabulary What is vocabulary? Ø Vocabulary can be defined as the words we teach in the foreign language. Ø Vocabulary is the glue that holds stories, ideas and content together making comprehension accessible. What needs to be taught? Ø Meaning. Form: pronunciation and spelling. Ø Grammar Ø Collocation
Teaching vocabulary What is vocabulary? Ø Vocabulary can be defined as the words we teach in the foreign language. Ø Vocabulary is the glue that holds stories, ideas and content together making comprehension accessible. What needs to be taught? Ø Meaning. Form: pronunciation and spelling. Ø Grammar Ø Collocation
 How to teach vocabulary Step 1: Provide a description, explanation or example of the new term. Step 2: Ask students the description, explanation or example in their own words. Step 3: Ask students to construct a picture, symbol, or graphic representing the term or phrase. Step 4: Engage students periodically in activities that help them add to their knowledge of the terms in their notebooks. Step 5: Periodically ask student to discuss the term with a partner Step 6: Involve students periodically in games that allow them to play with terms.
How to teach vocabulary Step 1: Provide a description, explanation or example of the new term. Step 2: Ask students the description, explanation or example in their own words. Step 3: Ask students to construct a picture, symbol, or graphic representing the term or phrase. Step 4: Engage students periodically in activities that help them add to their knowledge of the terms in their notebooks. Step 5: Periodically ask student to discuss the term with a partner Step 6: Involve students periodically in games that allow them to play with terms.
 Steps in teaching a new word • Pronounce the word 2 or 3 times while the pupils listen. • Show the meaning of a word by using suitable technique. • Have the pupils repeat the word after the teacher (in chorus , groups and individually) • Write the word on the board and pupils read and copy it. • Ask questions for comprehension. • Encourage pupils to use the word themselves.
Steps in teaching a new word • Pronounce the word 2 or 3 times while the pupils listen. • Show the meaning of a word by using suitable technique. • Have the pupils repeat the word after the teacher (in chorus , groups and individually) • Write the word on the board and pupils read and copy it. • Ask questions for comprehension. • Encourage pupils to use the word themselves.
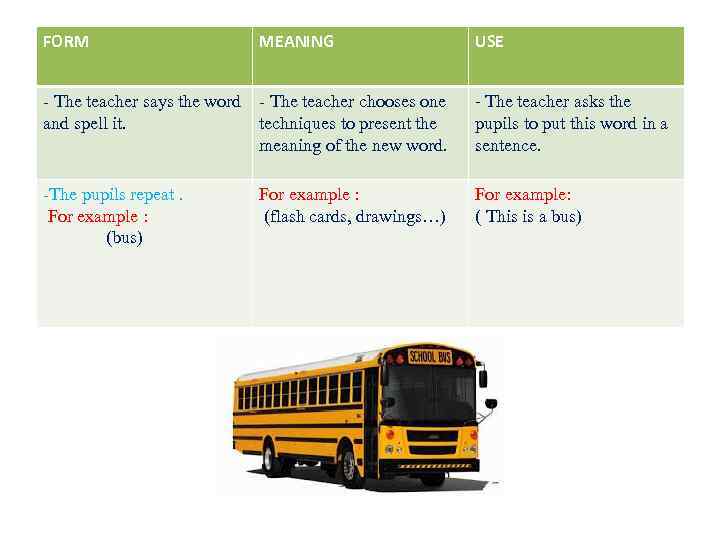 FORM MEANING USE - The teacher says the word - The teacher chooses one - The teacher asks the and spell it. techniques to present the pupils to put this word in a meaning of the new word. sentence. -The pupils repeat. For example : For example: For example : (flash cards, drawings…) ( This is a bus) (bus)
FORM MEANING USE - The teacher says the word - The teacher chooses one - The teacher asks the and spell it. techniques to present the pupils to put this word in a meaning of the new word. sentence. -The pupils repeat. For example : For example: For example : (flash cards, drawings…) ( This is a bus) (bus)
 Сonclusion Practical part was realized as an experiment in the classroom. I presented the same target language for two groups of students, using different approach for each. Phenomena proved during the practical part could be summed up in short: - grammar-translation students tend to use rather narrow range of language with problems to integrate it within context - conscious learning of rules does not lead to language acquisition - communicative approach prepares students for real communication, students are not anxious about experiments with language and they are able to respond the context well.
Сonclusion Practical part was realized as an experiment in the classroom. I presented the same target language for two groups of students, using different approach for each. Phenomena proved during the practical part could be summed up in short: - grammar-translation students tend to use rather narrow range of language with problems to integrate it within context - conscious learning of rules does not lead to language acquisition - communicative approach prepares students for real communication, students are not anxious about experiments with language and they are able to respond the context well.
