44764210e246a6d4b78016319d840a0f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

The ABC’s of DI

THIS PRESENTATION • Provides Accurate and Authoritative Information • Content Accuracy is not Guaranteed • Does not Render Legal, Accounting, Tax or other Professional Services If legal advice or other expert assistance is required, the services of a competent professional should be sought.

Why Disability Income Protection? • • Your Clients Need the Protection Effect on the Family Effect on the Client Effect on Society • According To The U. S. Housing Authority • Mortgage Foreclosures - 48% Due To Disabilities • Potential Effect On Small Business And Employment
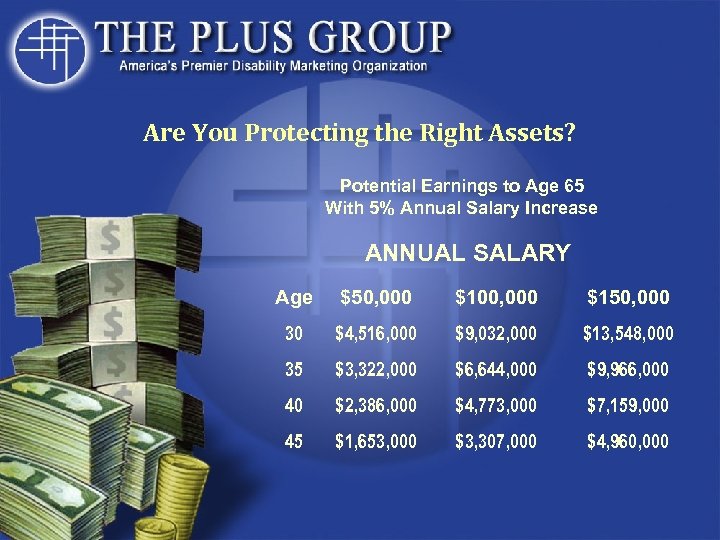
Are You Protecting the Right Assets? Potential Earnings to Age 65 With 5% Annual Salary Increase ANNUAL SALARY Age $50, 000 $100, 000 $150, 000 30 $4, 516, 000 $9, 032, 000 $13, 548, 000 35 $3, 322, 000 $6, 644, 000 $9, 966, 000 40 $2, 386, 000 $4, 773, 000 $7, 159, 000 45 $1, 653, 000 $3, 307, 000 $4, 960, 000
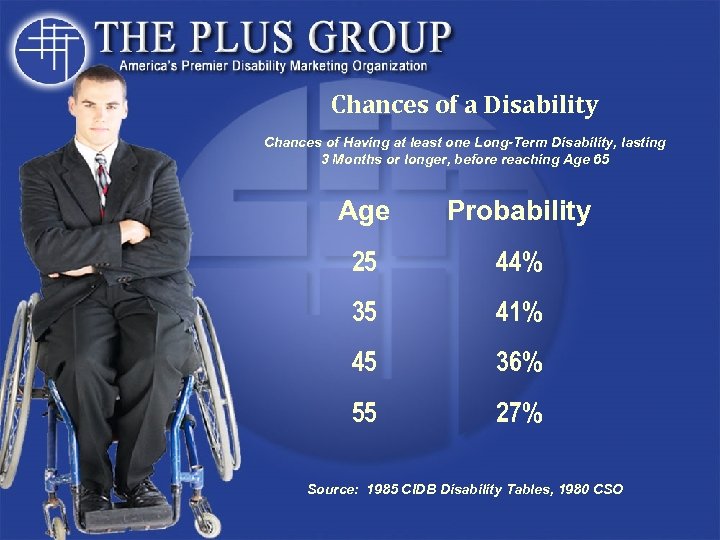
Chances of a Disability Chances of Having at least one Long-Term Disability, lasting 3 Months or longer, before reaching Age 65 Age Probability 25 44% 35 41% 45 36% 55 27% Source: 1985 CIDB Disability Tables, 1980 CSO
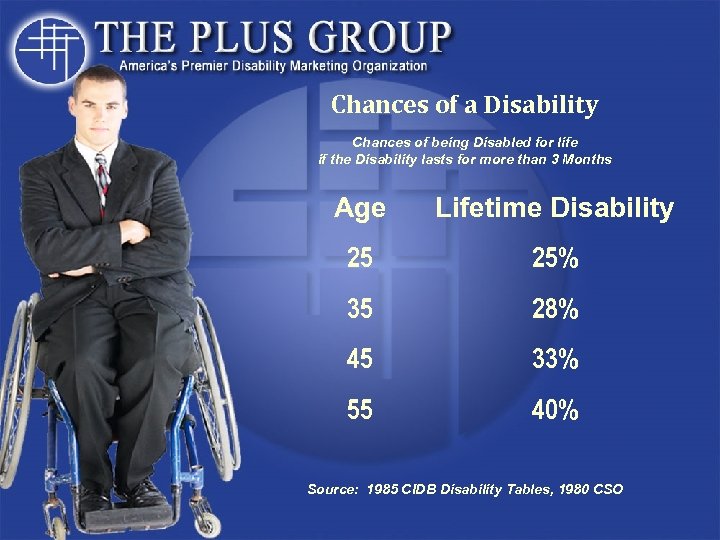
Chances of a Disability Chances of being Disabled for life if the Disability lasts for more than 3 Months Age Lifetime Disability 25 25% 35 28% 45 33% 55 40% Source: 1985 CIDB Disability Tables, 1980 CSO

Types of Disability Income Insurance • Noncancelable • Guaranteed Renewable • Noncancelable and Guaranteed Renewable • Conditionally Renewable

Understanding the Basics • Benefit Period • How Long Benefits Will Be Paid • Elimination Period • How Long the Insured Waits • Benefit Amount • The Monthly Benefit Payable Under a Total Disability • Occupation Class • Risk Class Affecting Benefits & Premium

COMMON DEFINITIONS OF TOTAL DISABILITY The Cornerstone of the DI Policy • Pure or True Own Occupation • Cannot perform the Substantial & Material duties of Occupation • 2 years, 5 years to age 65/67 • Your Occupation • Cannot perform the Substantial & Material duties of Occupation; and • Not Working in Another Occupation

Any Reasonable OR Gainful Occupation • 24 or 36 Month Own Occupation Period • Insured is Reasonably Fitted • Education • Training • Experience • Income Qualifier • 50%-60% of Pre-disability Earnings

COMMON DEFINITION OF RESIDUAL DISABILITY • Loss of Income • Loss of Time or Duties • % Income Lost=% Income Paid • Partial Disability • 50% Benefit • 6 or 12 Months

PREDISABILITY EARNINGS • Gross Income Less Expenses • Cash or Accrual Basis • Calculated As Average • 12 Months • Last 24 Months • Highest 2 of Previous 5 Years • Simple or Compounded Basis

INDEXING EXAMPLE Assuming 50% Loss of Income and $5, 000/Month Benefit • $100, 000 Indexed over 10 Years • • 5% Compounded = $162, 889 $50, 000 Income = $81, 444 = 50% $2, 500 Monthly Benefit • $100, 000 Indexed over 10 Years • • 5% Simple = $150, 000 $50, 000 Income = $81, 444 = 54% $2, 300 Monthly Benefit

COMMON DEFINITION OF ACCIDENT OR ILLNESS • Accident • Directly & Independently of All Other Causes • Accidental Event • Bodily Injury • Illness • Commences after Effective Date • Manifests itself after Effective Date

GROUP LONG TERM DISABILITY • Myth: It’s Cheaper Because it’s Group • More Conservative Benefits • Pre-Existing Condition Limitations • Shorter Duration • Less Adverse Selection • Premiums/Benefits can be Modified • Plans can be Cancelled

WHY SUPPLEMENTAL GROUP LTD WITH INDIVIDUAL POLICIES • • • Benefits too Low May Discriminate Rates Not Guaranteed Not Portable Conservative Definitions Bonus/Pension not Covered • Group Plans are offsetting Individual Policies • Your Client Needs It • You are in Business for Yourself

PAYROLL DEDUCTION • The Employees Need It • Benefits of Group LTD • Guaranteed Issue • Minimum Participation • Inexpensive • Higher Participation • Benefits to Individual • Supplements the LTD • Portable with Discounts • Direct Billed

COMMON OPTIONAL RIDERS • • • Cost of Living Benefits Future Insurability Benefits Automatic Increases Premium Refund Catastrophic Benefits Long Term Care Conversion • Variation and State Availability

COST OF LIVING BENEFITS • Benefit Increases on Anniversary Date • Compounded or Simple • Minimum Benefit of 3%-4% • Overall Cap of 2 X Monthly Benefit
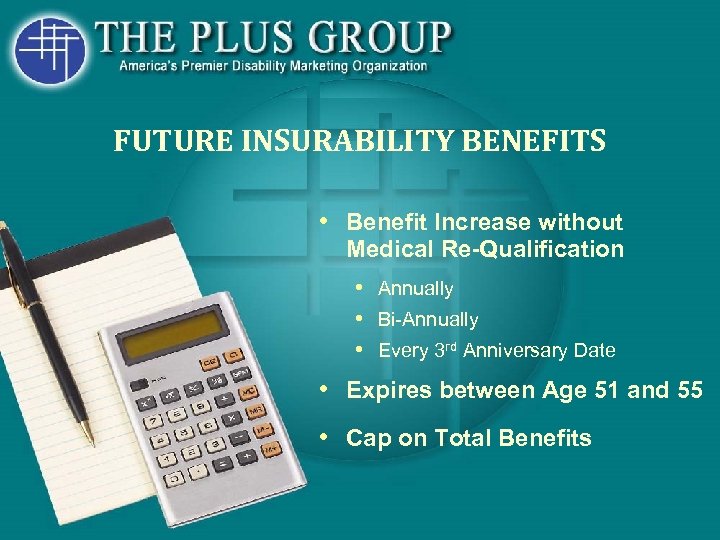
FUTURE INSURABILITY BENEFITS • Benefit Increase without Medical Re-Qualification • Annually • Bi-Annually • Every 3 rd Anniversary Date • Expires between Age 51 and 55 • Cap on Total Benefits

CATASTROPHIC BENEFITS • Qualifying Definitions • 2 of 5 Activities of Daily Living • Presumptive Disability • Loss of • • Speech Hearing Sight Use of any Two Limbs • Increase Monthly Benefit or Extend Benefit Period

RETURN OF PREMIUM • Client Pays an Extra Premium • Receives % of Premium • After X Years • Claim Benefits Paid First • Come out of Return of Premium Benefit
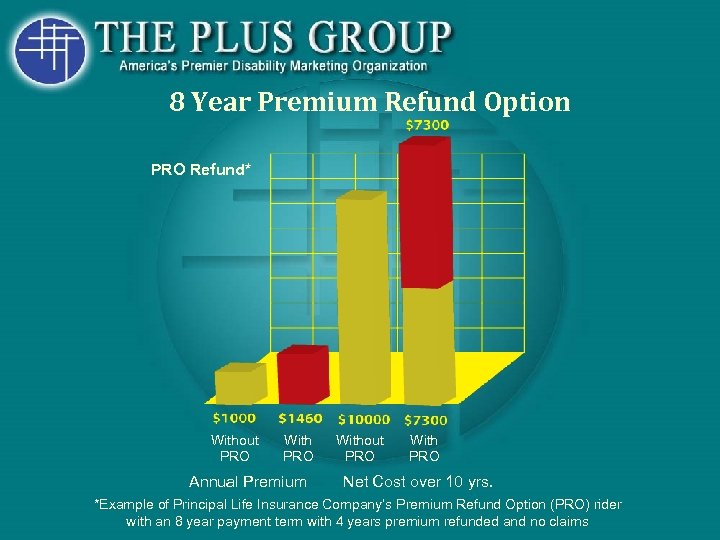
8 Year Premium Refund Option PRO Refund* Without PRO With PRO Annual Premium Without PRO With PRO Net Cost over 10 yrs. *Example of Principal Life Insurance Company’s Premium Refund Option (PRO) rider with an 8 year payment term with 4 years premium refunded and no claims

OCCUPATION CLASSES • Insuring Duties, Not Job Titles • What is the Client’s Day Like? • Manual Duties? • What Are They? • Represent What % of Time? • Ownership? • Employees? • Affects Costs and Benefit

TAX CONSEQUENCES • Premiums Paid with Pre-Tax Dollars • Taxable • Premiums Paid with After-Tax Dollars • Tax Free • More than 2% Ownership cannot deduct Premiums • Partnerships • S-Corps • LLC’s • Which is Better? • Depends on Marginal Tax Rate

TAX CONSEQUENCES EXAMPLE • $100, 000 Income • $4, 800 Tax Free or • $5, 950 Taxable • 28% Marginal Tax Bracket • $4, 800 Income Tax= • $6, 666 Gross Monthly Income • No FICA paid after 6 Months

MEDICAL UNDERWRITING • Common Concerns • • • Musculoskeletal Mental/Nervous/Drug/Alchohol Stress/Anxiety Counseling Diabetes Blood Pressure Cholesterol • Attending Physician Statements • Blood • Urinalysis

FINANCIAL UNDERWRITING • Client’s Net Income • After Business Expenses • Income History • Bonuses • Pension Contributions • Tax Returns • All Schedules for Business Owners • Unearned Income

DISABILITY OVERHEAD EXPENSE

HOW DOES IT WORK? • This is a Reimbursement Policy • Client Purchases a “Pot of Money” • Carry Forward Provision • Possible Limitations • Total Number of Months Benefits will be Paid

WHAT IS COVERED? • Normally Deductible Business Expenses • • • Utilities Rent Insurance Taxes Office Expenses • Employee Salaries • Not in the Same Occupation as Owner • In the Same Occupation by Rider

TAXATION • Premiums are Tax Deductible • Received Benefits are Taxable • Write Off for Incurred Expenses • Taxation a Wash

DISABILITY BUY-OUT INSURANCE

HOW DOES IT WORK? • Reimburses the Non-Disabled Stockholder or Entity to Buy Out the Disabled Stockholder • Premiums are not tax Deductible • Benefits Received Tax Free • May be a Taxable Event • When Buy-Out Executed by Entity

ADVANTAGES FOR THE DISABLED OWNER • Assures a Definite Price and Buyer • Mutual Terms • Firm can Meet the Buyout Commitment • Family Members can Care for the Disabled • Business is Protected • Provides Cash for Disabled Care

ADVANTAGES FOR THE ACTIVE BUSINESS OWNERS • Assures: • A Predetermined Price • A Predetermined Time Frame • Business Continuity • Owners Retain Control • Competitors Unable to buy any interest in the Firm

HOW DOES THE POLICY PAY? • Definition of Disability • Own Occ As Long as not Working in the Company • Total Disability Only • 12/18/24 Month Waiting Period • Payments • Lump Sum • Monthly Funding • Combination

WHO ARE THE LIKELY PROSPECTS? • Client Understands the Need • Ability to Earn an Income • Age 30 -45 • Premium at 2% or Less of Gross Income • Healthy

SELLING THE PLAN • Discuss Life while Disabled • Sell the Benefits • Sell the Price • Be Creative

Thank You
44764210e246a6d4b78016319d840a0f.ppt