8efd89f67403be3013a231dbc393bc79.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 The 40 Me. V proton / deuteron linac at SARAF August 27 th, 2008 Jacob Rodnizki on behalf of SARAF team J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008
The 40 Me. V proton / deuteron linac at SARAF August 27 th, 2008 Jacob Rodnizki on behalf of SARAF team J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008
 Content of the talk 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction SARAF accelerator - technologies and commissioning process Beam dynamics simulation and lost estimation Derivation of a safety criterion Diagnostics box along the linac J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 2
Content of the talk 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction SARAF accelerator - technologies and commissioning process Beam dynamics simulation and lost estimation Derivation of a safety criterion Diagnostics box along the linac J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 2
 SARAF – Soreq Applied Research Accelerator Facility To modernize the source of neutrons at Soreq and extend neutron based research and applications. To develop and produce radioisotopes primarily for bio-medical applications. To enlarge the experimental nuclear science infrastructure and promote the research in Israel. J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 3
SARAF – Soreq Applied Research Accelerator Facility To modernize the source of neutrons at Soreq and extend neutron based research and applications. To develop and produce radioisotopes primarily for bio-medical applications. To enlarge the experimental nuclear science infrastructure and promote the research in Israel. J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 3
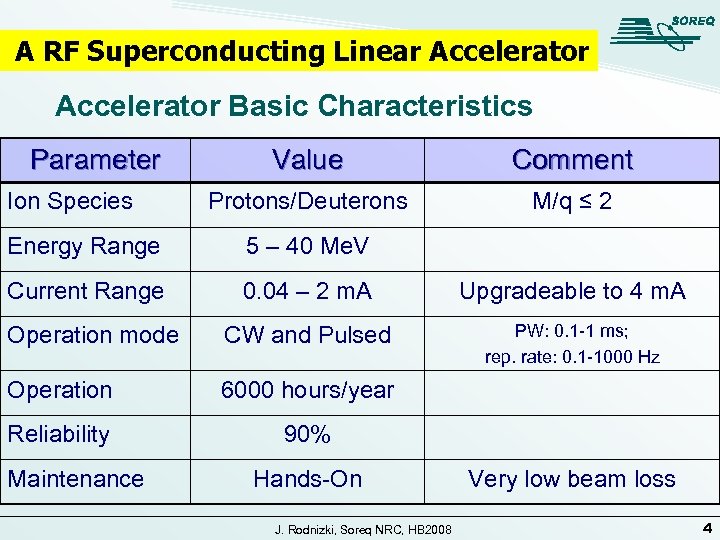 A RF Superconducting Linear Accelerator Basic Characteristics Parameter Ion Species Value Comment Protons/Deuterons M/q ≤ 2 Energy Range 5 – 40 Me. V Current Range 0. 04 – 2 m. A Upgradeable to 4 m. A Operation mode CW and Pulsed PW: 0. 1 -1 ms; rep. rate: 0. 1 -1000 Hz Operation 6000 hours/year Reliability 90% Maintenance Hands-On J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 Very low beam loss 4
A RF Superconducting Linear Accelerator Basic Characteristics Parameter Ion Species Value Comment Protons/Deuterons M/q ≤ 2 Energy Range 5 – 40 Me. V Current Range 0. 04 – 2 m. A Upgradeable to 4 m. A Operation mode CW and Pulsed PW: 0. 1 -1 ms; rep. rate: 0. 1 -1000 Hz Operation 6000 hours/year Reliability 90% Maintenance Hands-On J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 Very low beam loss 4
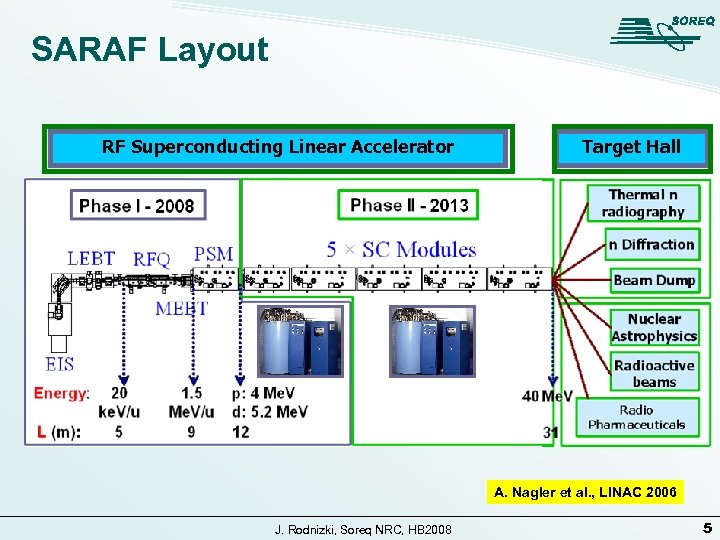 SARAF Layout RF Superconducting Linear Accelerator Target Hall A. Nagler et al. , LINAC 2006 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 5
SARAF Layout RF Superconducting Linear Accelerator Target Hall A. Nagler et al. , LINAC 2006 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 5
 2005 Beam and Service Corridors J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 6
2005 Beam and Service Corridors J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 6
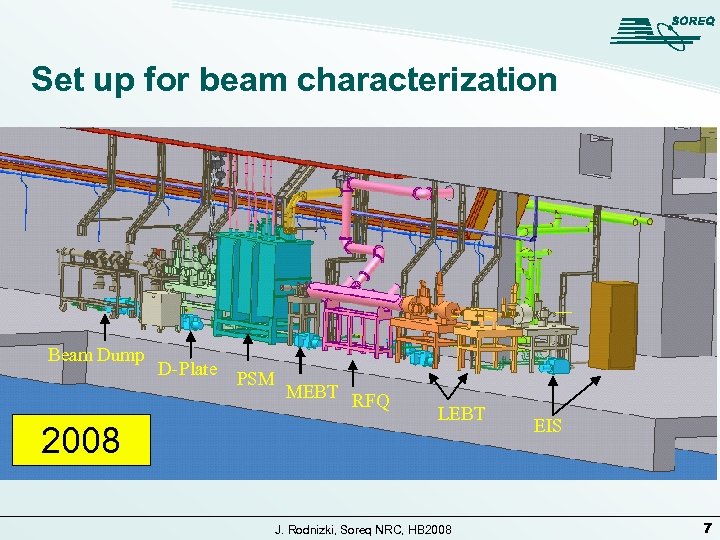 Set up for beam characterization Beam Dump 2008 D-Plate PSM MEBT RFQ LEBT J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 EIS 7
Set up for beam characterization Beam Dump 2008 D-Plate PSM MEBT RFQ LEBT J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 EIS 7
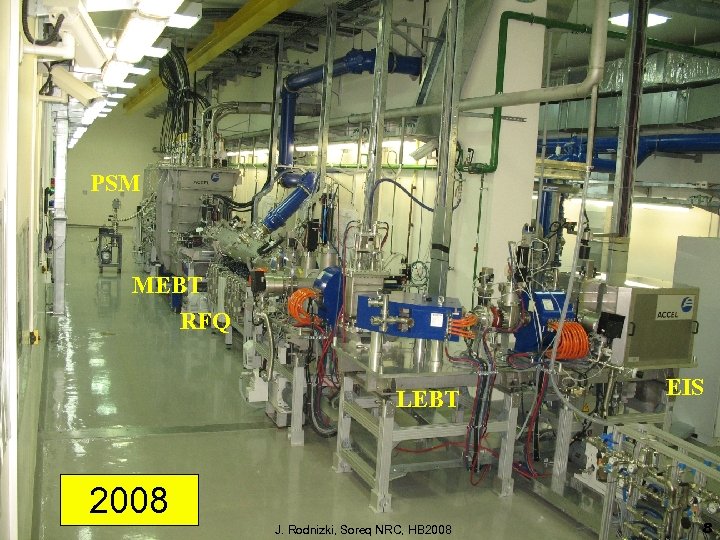 PSM MEBT RFQ LEBT 2008 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 EIS 8
PSM MEBT RFQ LEBT 2008 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 EIS 8
 Phase-I technologies and commissioning J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 9
Phase-I technologies and commissioning J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 9
 LEBT J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 10
LEBT J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 10
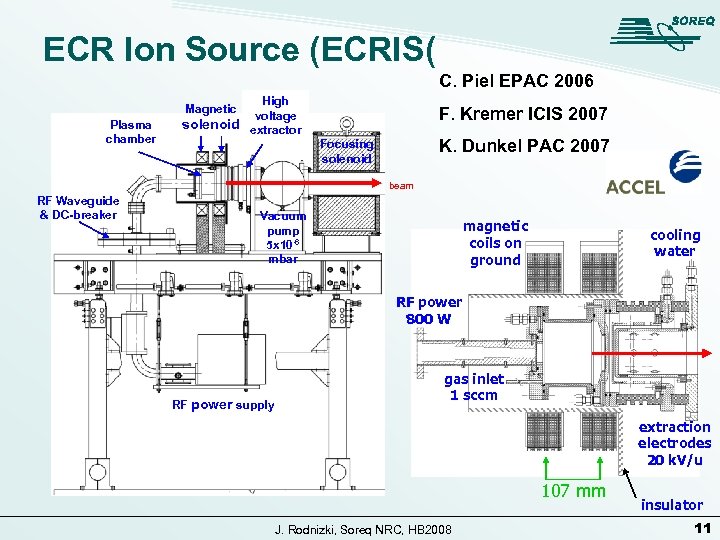 ECR Ion Source (ECRIS( C. Piel EPAC 2006 High voltage solenoid extractor Magnetic Plasma chamber F. Kremer ICIS 2007 K. Dunkel PAC 2007 Focusing solenoid beam RF Waveguide & DC-breaker Vacuum pump 5 x 10 -6 mbar magnetic coils on ground cooling water RF power 800 W RF power supply gas inlet 1 sccm extraction electrodes 20 k. V/u 107 mm J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 insulator 11
ECR Ion Source (ECRIS( C. Piel EPAC 2006 High voltage solenoid extractor Magnetic Plasma chamber F. Kremer ICIS 2007 K. Dunkel PAC 2007 Focusing solenoid beam RF Waveguide & DC-breaker Vacuum pump 5 x 10 -6 mbar magnetic coils on ground cooling water RF power 800 W RF power supply gas inlet 1 sccm extraction electrodes 20 k. V/u 107 mm J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 insulator 11
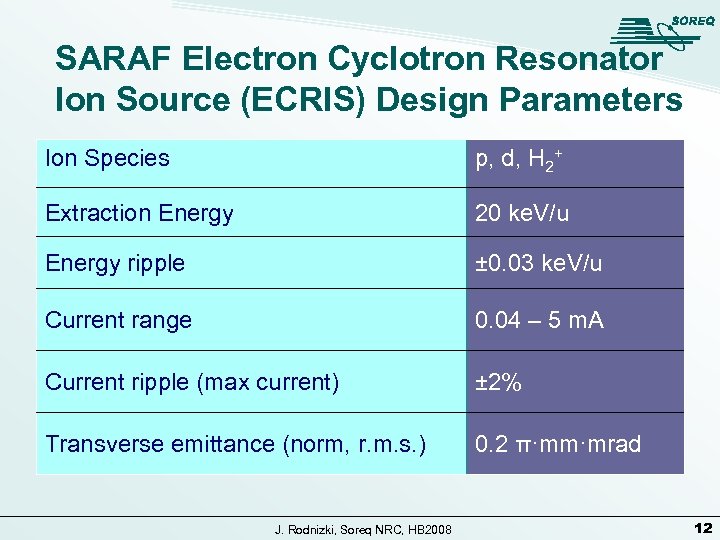 SARAF Electron Cyclotron Resonator Ion Source (ECRIS) Design Parameters Ion Species p, d, H 2+ Extraction Energy 20 ke. V/u Energy ripple ± 0. 03 ke. V/u Current range 0. 04 – 5 m. A Current ripple (max current) ± 2% Transverse emittance (norm, r. m. s. ) 0. 2 π·mm·mrad J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 12
SARAF Electron Cyclotron Resonator Ion Source (ECRIS) Design Parameters Ion Species p, d, H 2+ Extraction Energy 20 ke. V/u Energy ripple ± 0. 03 ke. V/u Current range 0. 04 – 5 m. A Current ripple (max current) ± 2% Transverse emittance (norm, r. m. s. ) 0. 2 π·mm·mrad J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 12
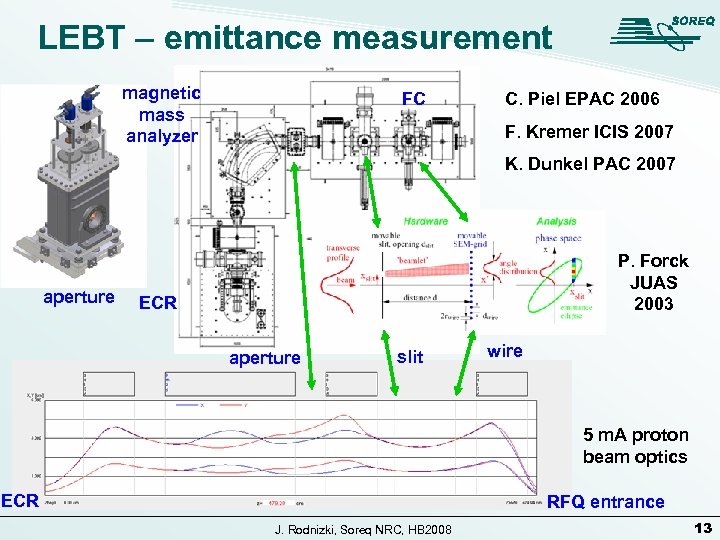 LEBT – emittance measurement magnetic mass analyzer FC C. Piel EPAC 2006 F. Kremer ICIS 2007 K. Dunkel PAC 2007 aperture P. Forck JUAS 2003 ECR aperture slit wire 5 m. A proton beam optics ECR RFQ entrance J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 13
LEBT – emittance measurement magnetic mass analyzer FC C. Piel EPAC 2006 F. Kremer ICIS 2007 K. Dunkel PAC 2007 aperture P. Forck JUAS 2003 ECR aperture slit wire 5 m. A proton beam optics ECR RFQ entrance J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 13
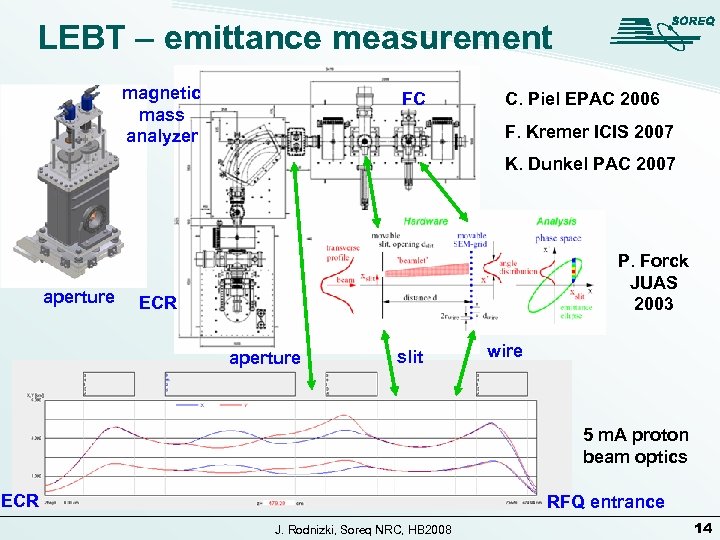 LEBT – emittance measurement magnetic mass analyzer FC C. Piel EPAC 2006 F. Kremer ICIS 2007 K. Dunkel PAC 2007 aperture P. Forck JUAS 2003 ECR aperture slit wire 5 m. A proton beam optics ECR RFQ entrance J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 14
LEBT – emittance measurement magnetic mass analyzer FC C. Piel EPAC 2006 F. Kremer ICIS 2007 K. Dunkel PAC 2007 aperture P. Forck JUAS 2003 ECR aperture slit wire 5 m. A proton beam optics ECR RFQ entrance J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 14
![EIS: emittance values during FAT erms_norm. _100% [p mm mrad] Particles Beam current Protons EIS: emittance values during FAT erms_norm. _100% [p mm mrad] Particles Beam current Protons](https://present5.com/presentation/8efd89f67403be3013a231dbc393bc79/image-15.jpg) EIS: emittance values during FAT erms_norm. _100% [p mm mrad] Particles Beam current Protons X/Y H 2+ X/Y Deuterons X/Y 5. 0 m. A 0. 2 / 0. 17 0. 34 / 0. 36 0. 13 / 0. 12 2. 0 m. A 0. 13 / 0. 13 0. 30 / 0. 34 0. 14 / 0. 13 0. 04 m. A 0. 18 / 0. 19 0. 05 / 0. 05 Specified value = 0. 2 / 0. 2 [p mm mrad] J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 15
EIS: emittance values during FAT erms_norm. _100% [p mm mrad] Particles Beam current Protons X/Y H 2+ X/Y Deuterons X/Y 5. 0 m. A 0. 2 / 0. 17 0. 34 / 0. 36 0. 13 / 0. 12 2. 0 m. A 0. 13 / 0. 13 0. 30 / 0. 34 0. 14 / 0. 13 0. 04 m. A 0. 18 / 0. 19 0. 05 / 0. 05 Specified value = 0. 2 / 0. 2 [p mm mrad] J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 15
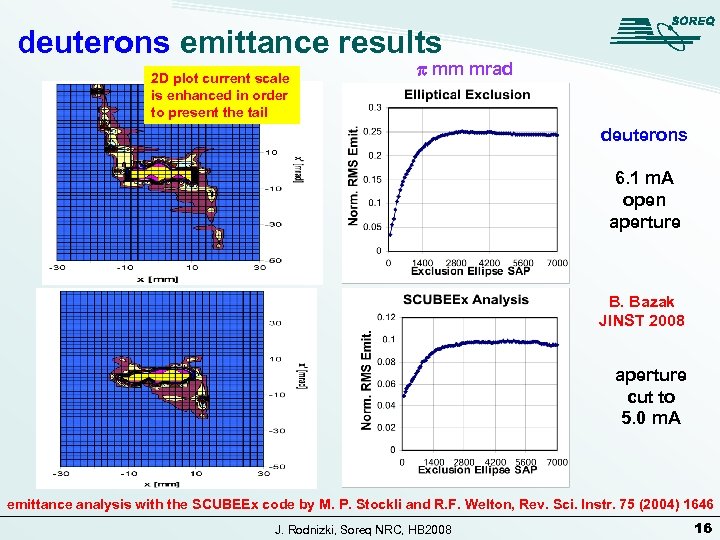 deuterons emittance results 2 D plot current scale is enhanced in order to present the tail p mm mrad deuterons 6. 1 m. A open aperture B. Bazak JINST 2008 aperture cut to 5. 0 m. A emittance analysis with the SCUBEEx code by M. P. Stockli and R. F. Welton, Rev. Sci. Instr. 75 (2004) 1646 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 16
deuterons emittance results 2 D plot current scale is enhanced in order to present the tail p mm mrad deuterons 6. 1 m. A open aperture B. Bazak JINST 2008 aperture cut to 5. 0 m. A emittance analysis with the SCUBEEx code by M. P. Stockli and R. F. Welton, Rev. Sci. Instr. 75 (2004) 1646 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 16
 RFQ J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 17
RFQ J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 17
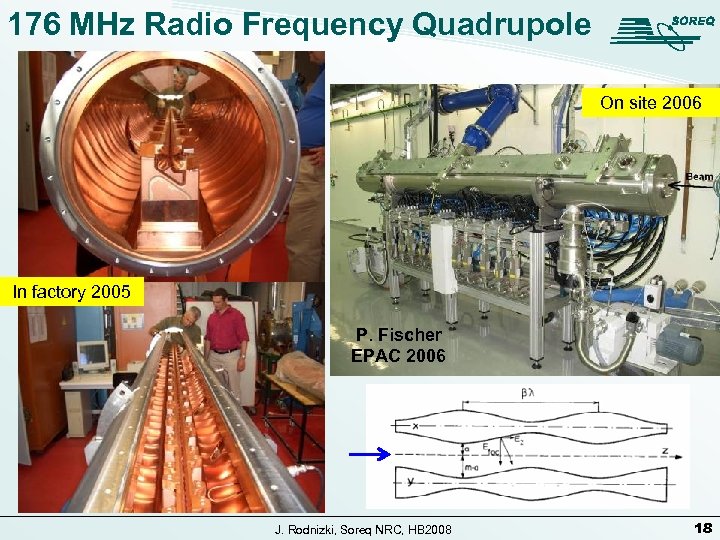 176 MHz Radio Frequency Quadrupole On site 2006 In factory 2005 P. Fischer EPAC 2006 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 18
176 MHz Radio Frequency Quadrupole On site 2006 In factory 2005 P. Fischer EPAC 2006 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 18
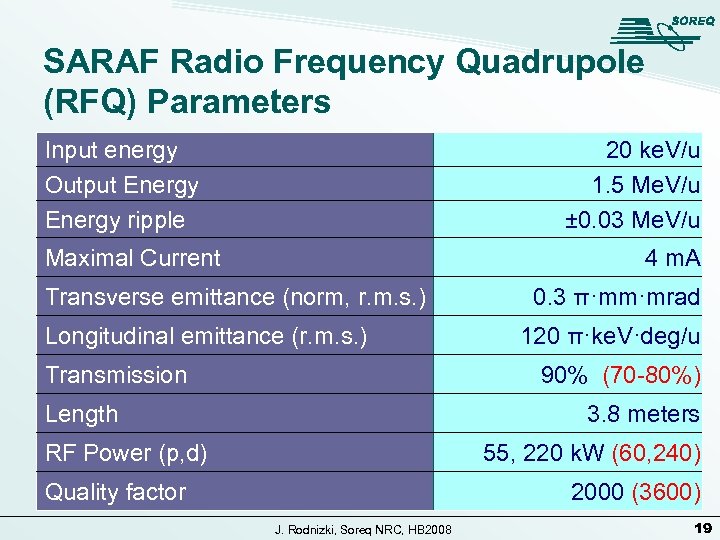 SARAF Radio Frequency Quadrupole (RFQ) Parameters Input energy Output Energy ripple 20 ke. V/u 1. 5 Me. V/u ± 0. 03 Me. V/u Maximal Current 4 m. A Transverse emittance (norm, r. m. s. ) Longitudinal emittance (r. m. s. ) Transmission 0. 3 π·mm·mrad 120 π·ke. V·deg/u 90% (70 -80%) Length 3. 8 meters RF Power (p, d) 55, 220 k. W (60, 240) Quality factor 2000 (3600) J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 19
SARAF Radio Frequency Quadrupole (RFQ) Parameters Input energy Output Energy ripple 20 ke. V/u 1. 5 Me. V/u ± 0. 03 Me. V/u Maximal Current 4 m. A Transverse emittance (norm, r. m. s. ) Longitudinal emittance (r. m. s. ) Transmission 0. 3 π·mm·mrad 120 π·ke. V·deg/u 90% (70 -80%) Length 3. 8 meters RF Power (p, d) 55, 220 k. W (60, 240) Quality factor 2000 (3600) J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 19
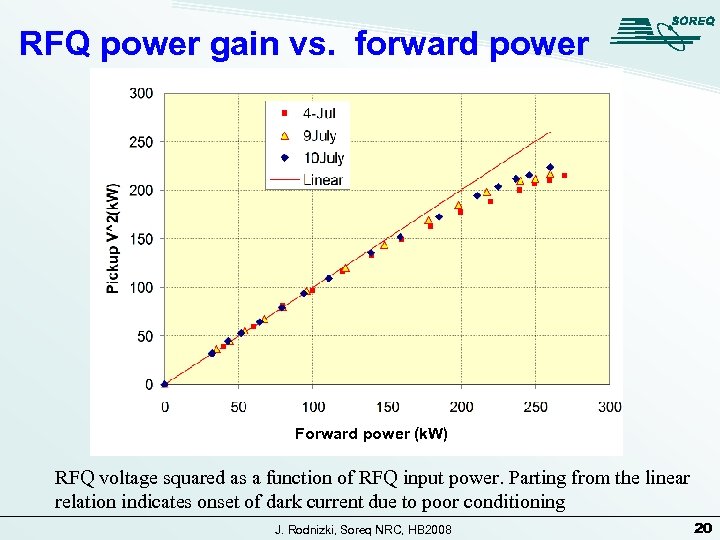 RFQ power gain vs. forward power Forward power (k. W) RFQ voltage squared as a function of RFQ input power. Parting from the linear relation indicates onset of dark current due to poor conditioning J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 20
RFQ power gain vs. forward power Forward power (k. W) RFQ voltage squared as a function of RFQ input power. Parting from the linear relation indicates onset of dark current due to poor conditioning J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 20
 RFQ Conditioning – current status Expected conditioning rate improvement: Rounding off sharp edges of rods bottom part Cleaning of rods Installation of circuit for fast recovery after sparks But the Reached power: 195 k. W CW 280 k. W with duty cycle of 15% J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 21
RFQ Conditioning – current status Expected conditioning rate improvement: Rounding off sharp edges of rods bottom part Cleaning of rods Installation of circuit for fast recovery after sparks But the Reached power: 195 k. W CW 280 k. W with duty cycle of 15% J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 21
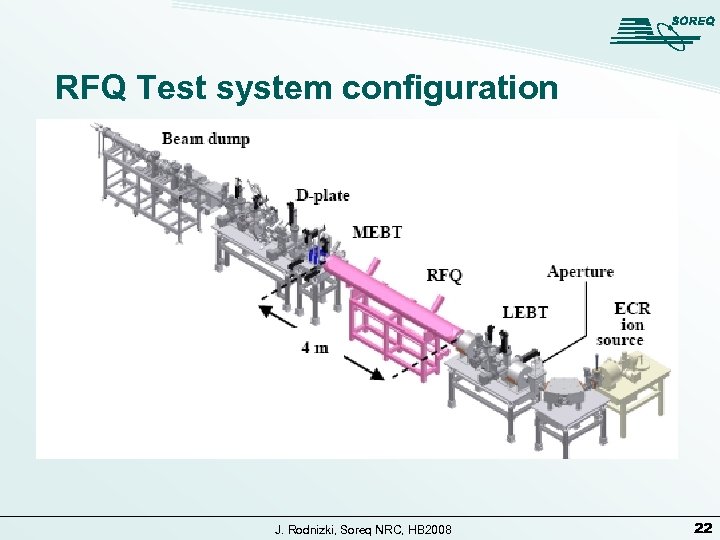 RFQ Test system configuration J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 22
RFQ Test system configuration J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 22
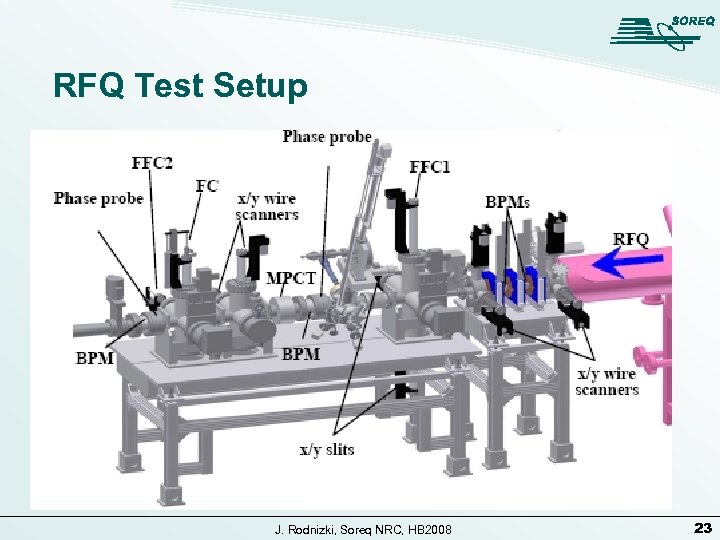 RFQ Test Setup J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 23
RFQ Test Setup J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 23
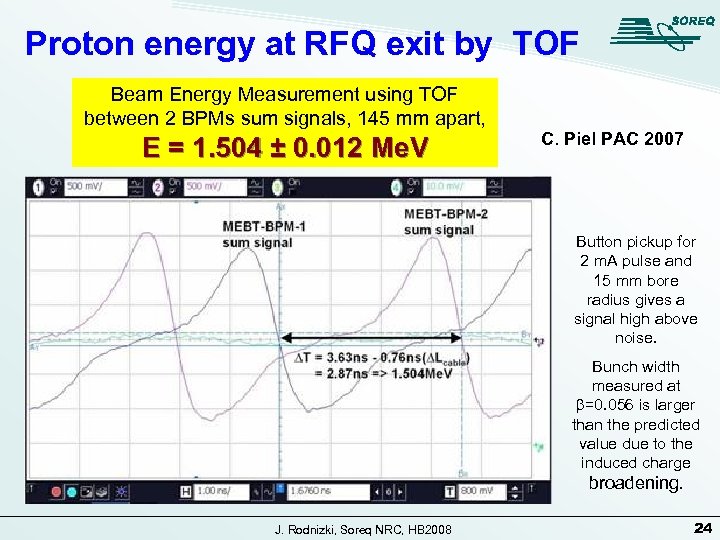 Proton energy at RFQ exit by TOF Beam Energy Measurement using TOF between 2 BPMs sum signals, 145 mm apart, E = 1. 504 ± 0. 012 Me. V C. Piel PAC 2007 Button pickup for 2 m. A pulse and 15 mm bore radius gives a signal high above noise. Bunch width measured at b=0. 056 is larger than the predicted value due to the induced charge broadening. J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 24
Proton energy at RFQ exit by TOF Beam Energy Measurement using TOF between 2 BPMs sum signals, 145 mm apart, E = 1. 504 ± 0. 012 Me. V C. Piel PAC 2007 Button pickup for 2 m. A pulse and 15 mm bore radius gives a signal high above noise. Bunch width measured at b=0. 056 is larger than the predicted value due to the induced charge broadening. J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 24
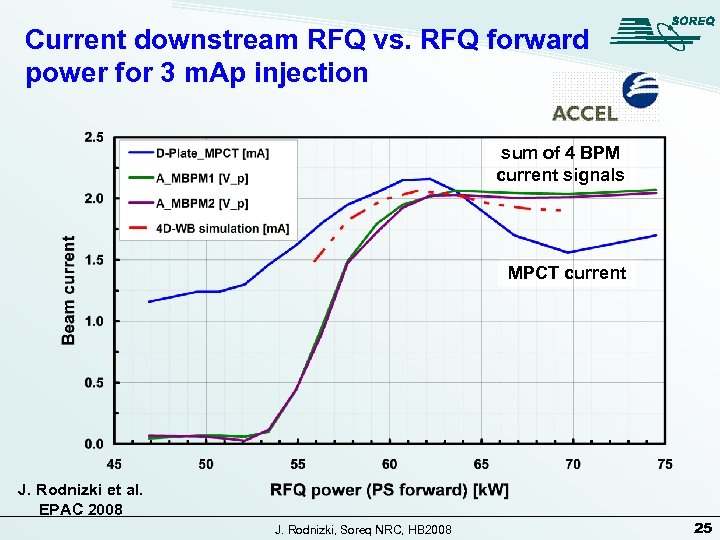 Current downstream RFQ vs. RFQ forward power for 3 m. Ap injection sum of 4 BPM current signals MPCT current J. Rodnizki et al. EPAC 2008 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 25
Current downstream RFQ vs. RFQ forward power for 3 m. Ap injection sum of 4 BPM current signals MPCT current J. Rodnizki et al. EPAC 2008 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 25
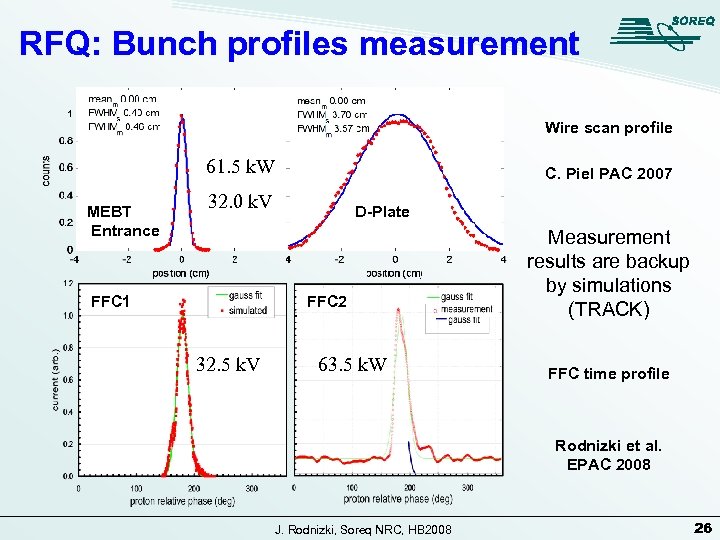 RFQ: Bunch profiles measurement Wire scan profile 61. 5 k. W MEBT Entrance C. Piel PAC 2007 32. 0 k. V FFC 1 D-Plate FFC 2 32. 5 k. V 63. 5 k. W Measurement results are backup by simulations (TRACK) FFC time profile Rodnizki et al. EPAC 2008 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 26
RFQ: Bunch profiles measurement Wire scan profile 61. 5 k. W MEBT Entrance C. Piel PAC 2007 32. 0 k. V FFC 1 D-Plate FFC 2 32. 5 k. V 63. 5 k. W Measurement results are backup by simulations (TRACK) FFC time profile Rodnizki et al. EPAC 2008 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 26
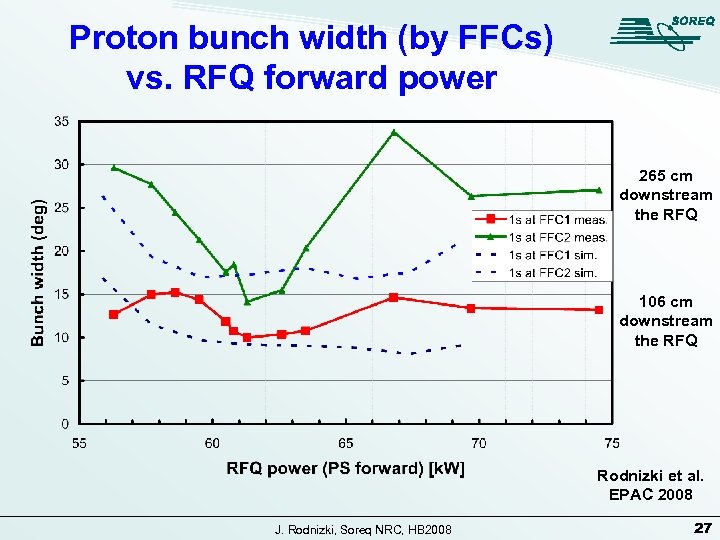 Proton bunch width (by FFCs) vs. RFQ forward power 265 cm downstream the RFQ 106 cm downstream the RFQ Rodnizki et al. EPAC 2008 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 27
Proton bunch width (by FFCs) vs. RFQ forward power 265 cm downstream the RFQ 106 cm downstream the RFQ Rodnizki et al. EPAC 2008 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 27
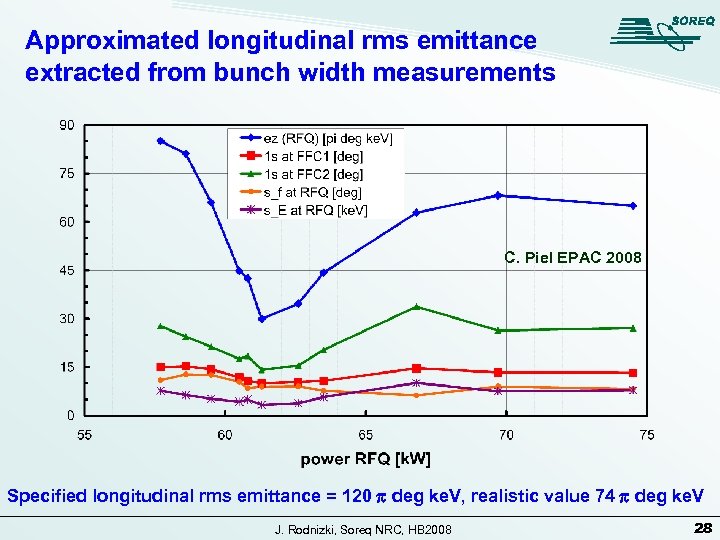 Approximated longitudinal rms emittance extracted from bunch width measurements C. Piel EPAC 2008 Specified longitudinal rms emittance = 120 p deg ke. V, realistic value 74 p deg ke. V J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 28
Approximated longitudinal rms emittance extracted from bunch width measurements C. Piel EPAC 2008 Specified longitudinal rms emittance = 120 p deg ke. V, realistic value 74 p deg ke. V J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 28
 PSM J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 29
PSM J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 29
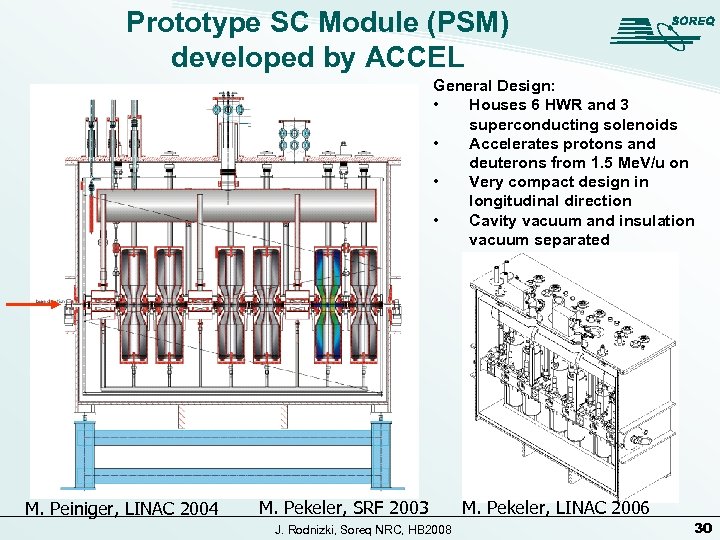 Prototype SC Module (PSM) developed by ACCEL General Design: • Houses 6 HWR and 3 superconducting solenoids • Accelerates protons and deuterons from 1. 5 Me. V/u on • Very compact design in longitudinal direction • Cavity vacuum and insulation vacuum separated M. Peiniger, LINAC 2004 M. Pekeler, SRF 2003 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 M. Pekeler, LINAC 2006 30
Prototype SC Module (PSM) developed by ACCEL General Design: • Houses 6 HWR and 3 superconducting solenoids • Accelerates protons and deuterons from 1. 5 Me. V/u on • Very compact design in longitudinal direction • Cavity vacuum and insulation vacuum separated M. Peiniger, LINAC 2004 M. Pekeler, SRF 2003 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 M. Pekeler, LINAC 2006 30
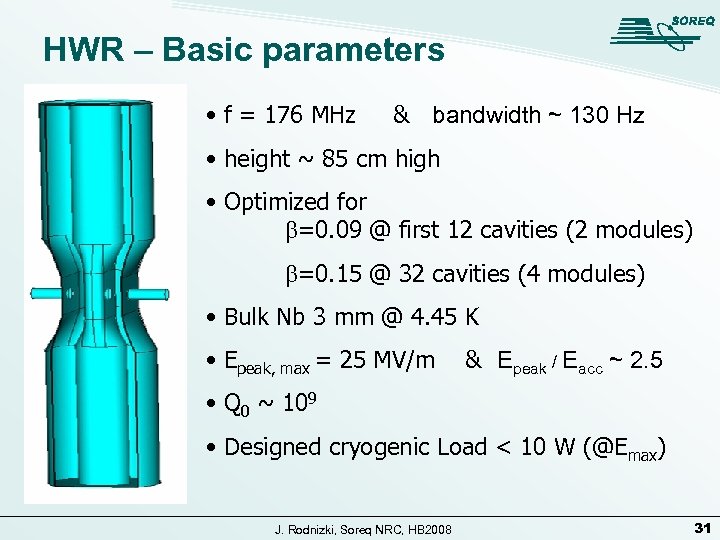 HWR – Basic parameters • f = 176 MHz & bandwidth ~ 130 Hz • height ~ 85 cm high • Optimized for b=0. 09 @ first 12 cavities (2 modules) b=0. 15 @ 32 cavities (4 modules) • Bulk Nb 3 mm @ 4. 45 K • Epeak, max = 25 MV/m & Epeak / Eacc ~ 2. 5 • Q 0 ~ 109 • Designed cryogenic Load < 10 W (@Emax) J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 31
HWR – Basic parameters • f = 176 MHz & bandwidth ~ 130 Hz • height ~ 85 cm high • Optimized for b=0. 09 @ first 12 cavities (2 modules) b=0. 15 @ 32 cavities (4 modules) • Bulk Nb 3 mm @ 4. 45 K • Epeak, max = 25 MV/m & Epeak / Eacc ~ 2. 5 • Q 0 ~ 109 • Designed cryogenic Load < 10 W (@Emax) J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 31
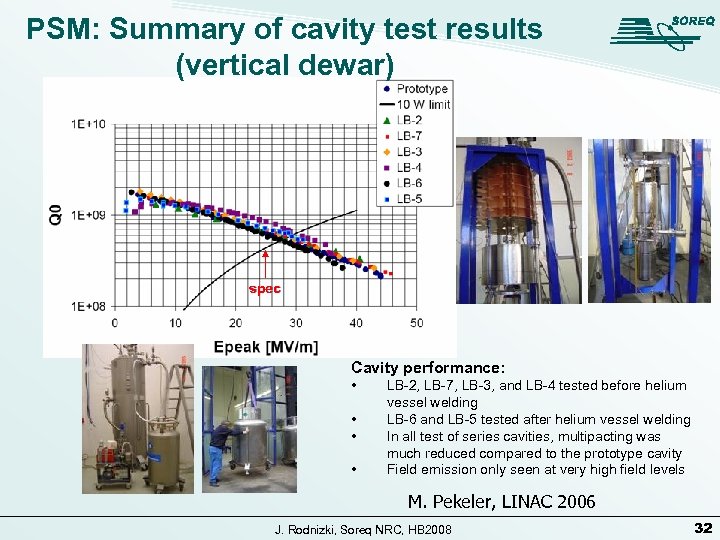 PSM: Summary of cavity test results (vertical dewar) spec Cavity performance: • • LB-2, LB-7, LB-3, and LB-4 tested before helium vessel welding LB-6 and LB-5 tested after helium vessel welding In all test of series cavities, multipacting was much reduced compared to the prototype cavity Field emission only seen at very high field levels M. Pekeler, LINAC 2006 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 32
PSM: Summary of cavity test results (vertical dewar) spec Cavity performance: • • LB-2, LB-7, LB-3, and LB-4 tested before helium vessel welding LB-6 and LB-5 tested after helium vessel welding In all test of series cavities, multipacting was much reduced compared to the prototype cavity Field emission only seen at very high field levels M. Pekeler, LINAC 2006 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 32
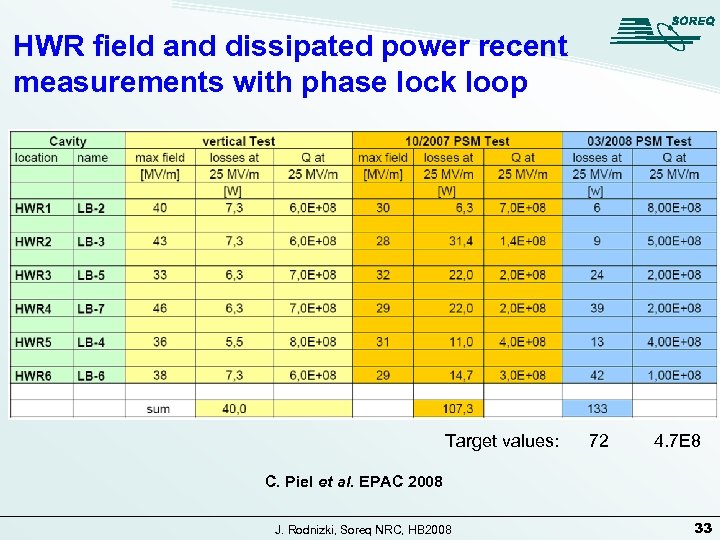 HWR field and dissipated power recent measurements with phase lock loop Target values: 72 4. 7 E 8 C. Piel et al. EPAC 2008 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 33
HWR field and dissipated power recent measurements with phase lock loop Target values: 72 4. 7 E 8 C. Piel et al. EPAC 2008 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 33
 Beam dynamics error simulations for phase-II J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 34
Beam dynamics error simulations for phase-II J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 34
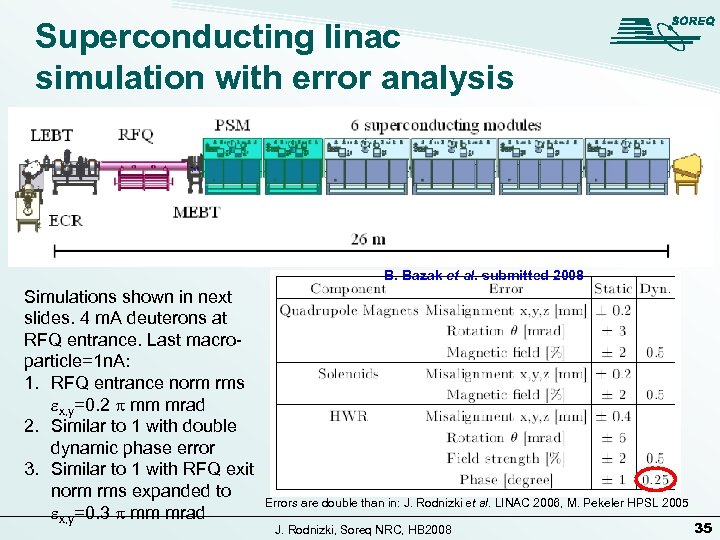 Superconducting linac simulation with error analysis B. Bazak et al. submitted 2008 Simulations shown in next slides. 4 m. A deuterons at RFQ entrance. Last macroparticle=1 n. A: 1. RFQ entrance norm rms ex, y=0. 2 p mm mrad 2. Similar to 1 with double dynamic phase error 3. Similar to 1 with RFQ exit norm rms expanded to ex, y=0. 3 p mm mrad Errors are double than in: J. Rodnizki et al. LINAC 2006, M. Pekeler HPSL 2005 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 35
Superconducting linac simulation with error analysis B. Bazak et al. submitted 2008 Simulations shown in next slides. 4 m. A deuterons at RFQ entrance. Last macroparticle=1 n. A: 1. RFQ entrance norm rms ex, y=0. 2 p mm mrad 2. Similar to 1 with double dynamic phase error 3. Similar to 1 with RFQ exit norm rms expanded to ex, y=0. 3 p mm mrad Errors are double than in: J. Rodnizki et al. LINAC 2006, M. Pekeler HPSL 2005 J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 35
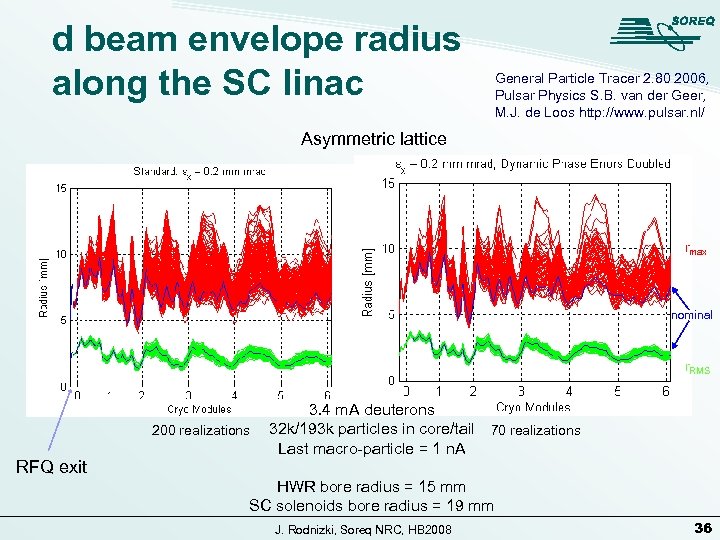 d beam envelope radius along the SC linac General Particle Tracer 2. 80 2006, Pulsar Physics S. B. van der Geer, M. J. de Loos http: //www. pulsar. nl/ Asymmetric lattice rmax nominal r. RMS 200 realizations RFQ exit 3. 4 m. A deuterons 32 k/193 k particles in core/tail 70 realizations Last macro-particle = 1 n. A HWR bore radius = 15 mm SC solenoids bore radius = 19 mm J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 36
d beam envelope radius along the SC linac General Particle Tracer 2. 80 2006, Pulsar Physics S. B. van der Geer, M. J. de Loos http: //www. pulsar. nl/ Asymmetric lattice rmax nominal r. RMS 200 realizations RFQ exit 3. 4 m. A deuterons 32 k/193 k particles in core/tail 70 realizations Last macro-particle = 1 n. A HWR bore radius = 15 mm SC solenoids bore radius = 19 mm J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 36
 Loss limit J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 37
Loss limit J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 37
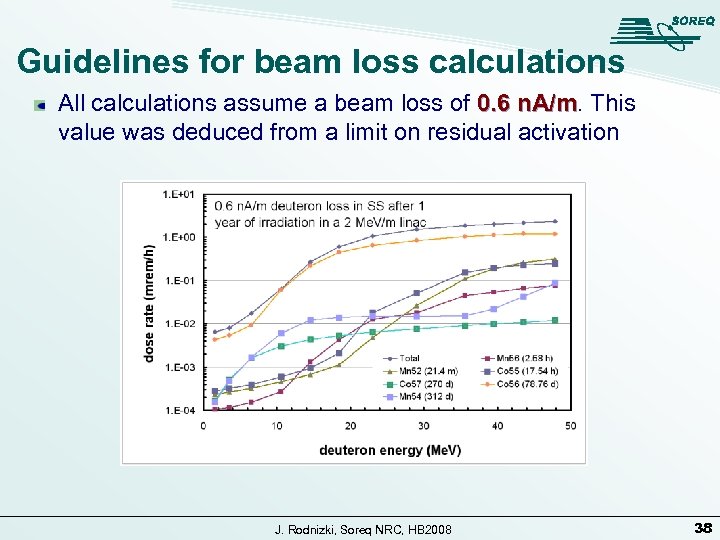 Guidelines for beam loss calculations All calculations assume a beam loss of 0. 6 n. A/m. This n. A/m value was deduced from a limit on residual activation J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 38
Guidelines for beam loss calculations All calculations assume a beam loss of 0. 6 n. A/m. This n. A/m value was deduced from a limit on residual activation J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 38
 Determination of 0. 6 n. A/m limit (1( This limit was determined in order to limit the dose to 2 mrem/h (100 h of hands-on maintenance per technician per year gives 10% of the annual dose limit) at: 30 cm away from beam line 4 hours after accelerator shutdown After the accelerator has been operating for a year Conservative assumptions leading to this limit: Effects of 40 Me. V applied for entire linac Accelerator is operating 365 days per year (~65%) Run deuterons at 40 Me. V all the time (25 -50%) Accelerator made entirely of stainless steel (~50% Nb) J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 39
Determination of 0. 6 n. A/m limit (1( This limit was determined in order to limit the dose to 2 mrem/h (100 h of hands-on maintenance per technician per year gives 10% of the annual dose limit) at: 30 cm away from beam line 4 hours after accelerator shutdown After the accelerator has been operating for a year Conservative assumptions leading to this limit: Effects of 40 Me. V applied for entire linac Accelerator is operating 365 days per year (~65%) Run deuterons at 40 Me. V all the time (25 -50%) Accelerator made entirely of stainless steel (~50% Nb) J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 39
 Diagnostics between cryostats J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 41
Diagnostics between cryostats J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 41
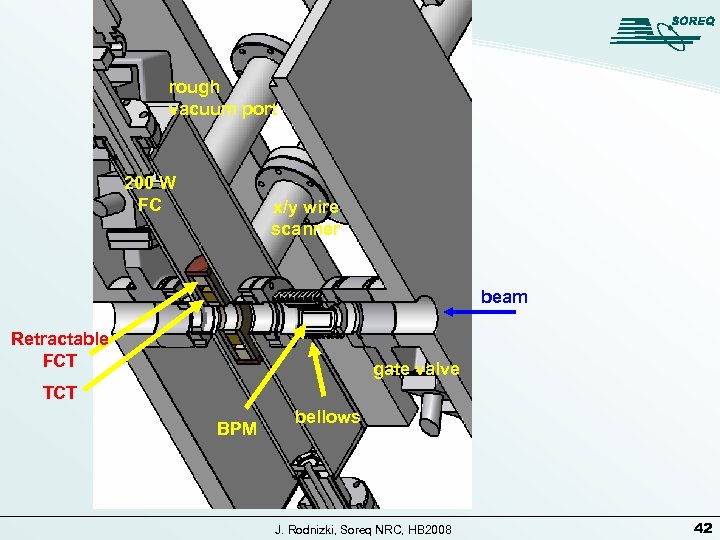 rough vacuum port 200 W FC x/y wire scanner beam Retractable FCT gate valve TCT BPM bellows J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 42
rough vacuum port 200 W FC x/y wire scanner beam Retractable FCT gate valve TCT BPM bellows J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 42
 END J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 43
END J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 43
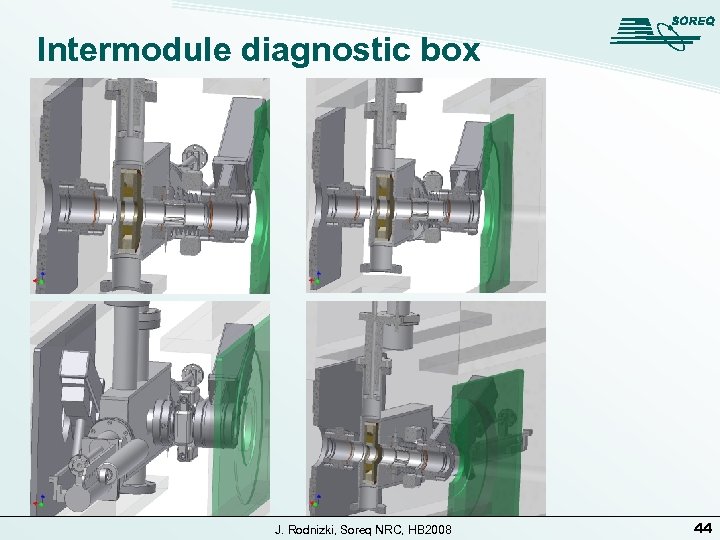 Intermodule diagnostic box J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 44
Intermodule diagnostic box J. Rodnizki, Soreq NRC, HB 2008 44


