190254052766ec431b5f637b52bbec16.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 The 1980 s Chapter 25
The 1980 s Chapter 25
 Ronald Reagan: The Great Communicator H Former Actor. H Charming and cheerful. H Superb analyst of the public mood.
Ronald Reagan: The Great Communicator H Former Actor. H Charming and cheerful. H Superb analyst of the public mood.
 Reagan and the Economy H Economy changes role of government i“Government is the problem” i. Market should control economy, not the government (deregulation of business) H Supply-side economics i. Tax cuts will actually raise government revenues that would help reduce the budget deficit because wealth will be increased. i. The wealthy would engage in productive investment. “trickle down”
Reagan and the Economy H Economy changes role of government i“Government is the problem” i. Market should control economy, not the government (deregulation of business) H Supply-side economics i. Tax cuts will actually raise government revenues that would help reduce the budget deficit because wealth will be increased. i. The wealthy would engage in productive investment. “trickle down”
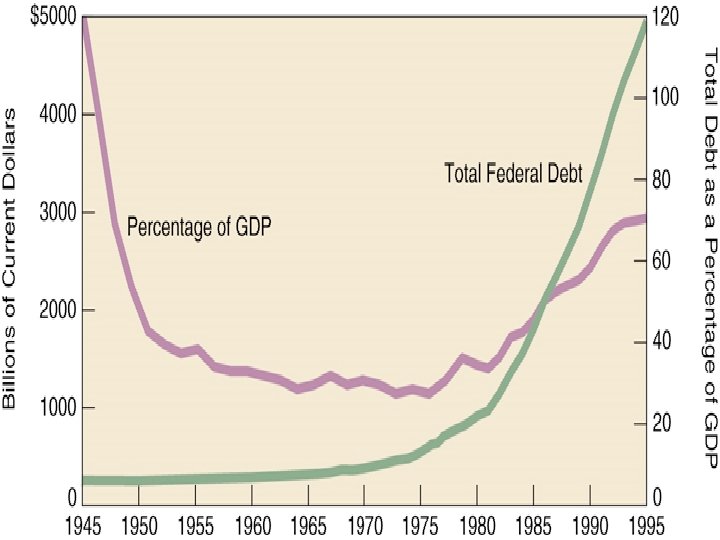
 Reagan and the Economy H Economic Recovery Act (1981) i. Cut personal income taxes by 25% i. Lowed max from 70% to 50% H Reagan tax cuts, however, were accompanied by massive increases in defense spending. H The combination of massive defense spending and substantial tax cuts left the federal government with massive deficits. i. The United States, a creditor nation since WWI, had by 1986 become the world’s largest debtor.
Reagan and the Economy H Economic Recovery Act (1981) i. Cut personal income taxes by 25% i. Lowed max from 70% to 50% H Reagan tax cuts, however, were accompanied by massive increases in defense spending. H The combination of massive defense spending and substantial tax cuts left the federal government with massive deficits. i. The United States, a creditor nation since WWI, had by 1986 become the world’s largest debtor.
 The End of the Cold War H détente – (an easing of tensions) in an effort to end the rivalry between the Soviets and the Americans. i. Ever since the Cuban missile crisis in 1962, the Soviets had steadily expanded their nuclear arsenal. H Reagan i. Peace through Strength i. The heart of the Reagan revolution was a sharp rise in military spending. Defense spending jumped about 50%.
The End of the Cold War H détente – (an easing of tensions) in an effort to end the rivalry between the Soviets and the Americans. i. Ever since the Cuban missile crisis in 1962, the Soviets had steadily expanded their nuclear arsenal. H Reagan i. Peace through Strength i. The heart of the Reagan revolution was a sharp rise in military spending. Defense spending jumped about 50%.
 The Defense Buildup H He also pushed the strategic defense initiative (SDI) i. A space based anti-missile defense shield. i“Star Wars” i. Forced the Soviets to launch an expensive research and development program of their own to keep pace.
The Defense Buildup H He also pushed the strategic defense initiative (SDI) i. A space based anti-missile defense shield. i“Star Wars” i. Forced the Soviets to launch an expensive research and development program of their own to keep pace.
 Cold War Rhetoric H He combined the increases in spending with strong rhetoric such as calling the Soviet Union an “evil empire” and demanding that the Berlin Wall come down.
Cold War Rhetoric H He combined the increases in spending with strong rhetoric such as calling the Soviet Union an “evil empire” and demanding that the Berlin Wall come down.
 Reagan and Gorbachev H Geneva Summit (1985) i. Reagan and Gorbachev met and signed several cultural and scientific agreements and promised arms limitation talks. H INF Treaty (1987) i. A treaty to eliminate intermediate-range nuclear forces. i. First step toward the eventual end of the arms race.
Reagan and Gorbachev H Geneva Summit (1985) i. Reagan and Gorbachev met and signed several cultural and scientific agreements and promised arms limitation talks. H INF Treaty (1987) i. A treaty to eliminate intermediate-range nuclear forces. i. First step toward the eventual end of the arms race.
 U. S. in the 1980 s H Sandra Day O’Connor - first woman justice of the Supreme Court. (1981) H AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) i. Gay men and intravenous drug users were especially at risk. i. No prospect of cure. H “Yuppies” (Young, upwardly mobile professionals) caught up in the race for materialism. H “Black Monday” (October 1987) i. Stock market plummeted 22. 6 percent i 1929 – 12. 8 percent
U. S. in the 1980 s H Sandra Day O’Connor - first woman justice of the Supreme Court. (1981) H AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) i. Gay men and intravenous drug users were especially at risk. i. No prospect of cure. H “Yuppies” (Young, upwardly mobile professionals) caught up in the race for materialism. H “Black Monday” (October 1987) i. Stock market plummeted 22. 6 percent i 1929 – 12. 8 percent
 The Iran-Contra Affair H Scandal surfaced in his second administration (1986) H The Reagan administration had secretly and against the expressed orders of Congress sold weapons to Iran in an attempt to free U. S. hostages held in Lebanon by terrorists. H They then used money from the sale of these weapons to buy weapons for the Contra rebels in Nicaragua who were freedom fighters fighting against communism. i. Marine Lieutenant-Colonel Oliver North had been running secret operations from the basement of the
The Iran-Contra Affair H Scandal surfaced in his second administration (1986) H The Reagan administration had secretly and against the expressed orders of Congress sold weapons to Iran in an attempt to free U. S. hostages held in Lebanon by terrorists. H They then used money from the sale of these weapons to buy weapons for the Contra rebels in Nicaragua who were freedom fighters fighting against communism. i. Marine Lieutenant-Colonel Oliver North had been running secret operations from the basement of the
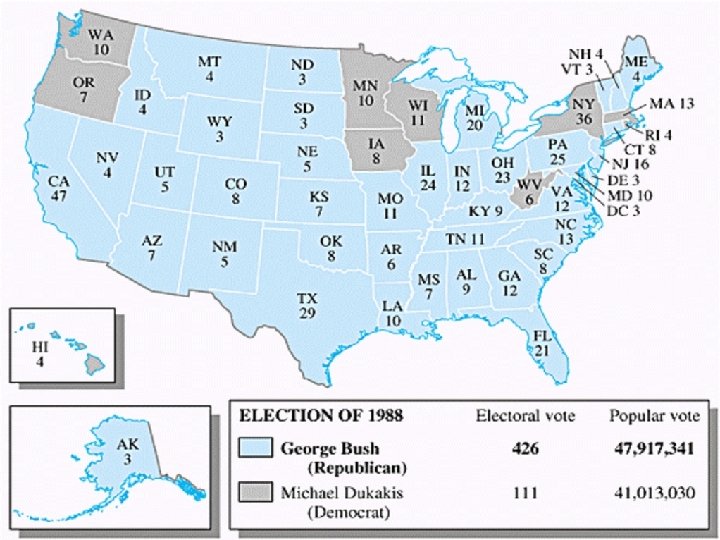
 George H. W. Bush H Despite the scandal, Reagan’s popularity remained high because of the improvement in Soviet-American relations and his V. P. George Bush won the 1988 election largely because of his connection to Reagan.
George H. W. Bush H Despite the scandal, Reagan’s popularity remained high because of the improvement in Soviet-American relations and his V. P. George Bush won the 1988 election largely because of his connection to Reagan.
 Reagan Baggage H Savings and Loan Scandals i. Had been set up by Reagan to help people buy homes. i. By 1989 hundreds of S&L’s had failed. i. Bush tried to close or sell ailing S&L’s and bail out the depositors. H National Debt i$2. 6 trillion by 1988. i“a horrendous fiscal mess” i 1990 - Bush approves a combination of tax hikes and spending cuts to reduce deficit despite “Read my lips, no new taxes” campaign pledge
Reagan Baggage H Savings and Loan Scandals i. Had been set up by Reagan to help people buy homes. i. By 1989 hundreds of S&L’s had failed. i. Bush tried to close or sell ailing S&L’s and bail out the depositors. H National Debt i$2. 6 trillion by 1988. i“a horrendous fiscal mess” i 1990 - Bush approves a combination of tax hikes and spending cuts to reduce deficit despite “Read my lips, no new taxes” campaign pledge
 Bush’s Domestic Agenda H Bush had difficulty defining and asserting his own political identity on domestic issues. H Americans with Disabilities Act (1990)
Bush’s Domestic Agenda H Bush had difficulty defining and asserting his own political identity on domestic issues. H Americans with Disabilities Act (1990)
 Bush and Gorbachev H Bush was in many ways the perfect foreign policy president. i. He sought to move “Beyond the Cold War. ” i. Bush was pragmatic and was an expert at personal diplomacy. i. Bush would guide the end of the Cold War so that it ended peacefully. H Gorbachev’s foreign policy sought rapprochement and trade with the West, to relieve the Soviet economy of burdensome military costs.
Bush and Gorbachev H Bush was in many ways the perfect foreign policy president. i. He sought to move “Beyond the Cold War. ” i. Bush was pragmatic and was an expert at personal diplomacy. i. Bush would guide the end of the Cold War so that it ended peacefully. H Gorbachev’s foreign policy sought rapprochement and trade with the West, to relieve the Soviet economy of burdensome military costs.
 Revolutions of 1989 H Soviet troops left Afghanistan in 1989. H Fall of the Berlin Wall (November 9, 1989) H Reunification of Germany (October 3, 1990)
Revolutions of 1989 H Soviet troops left Afghanistan in 1989. H Fall of the Berlin Wall (November 9, 1989) H Reunification of Germany (October 3, 1990)


