f8f211fd67f69160659e1373b3d877aa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

The 1950 s Prosperity in Suburbia

Economic Recovery • World War II ended the Great Depression – The U. S. had been the ‘arsenal of democracy’, providing weapons and supplies to the allies – This brought us great wealth – In the 1950 s and 60 s, the U. S. experienced one of the greatest economic booms in world history • Returning American soldiers, heroes to their countrymen, were rewarded by a grateful nation with the GI Bill – Helped ‘GI’s’ (soldiers) pay for college – helped them buy homes

Suburbia • So many GI’s could now buy homes that there was a housing shortage • Home builders created (often from scratch) huge new neighborhoods near to, but outside of, major cities – Suburbs – Homes built by ‘assembly line’ techniques often rows of identical houses – Levitt and Levittown • Baby Boom
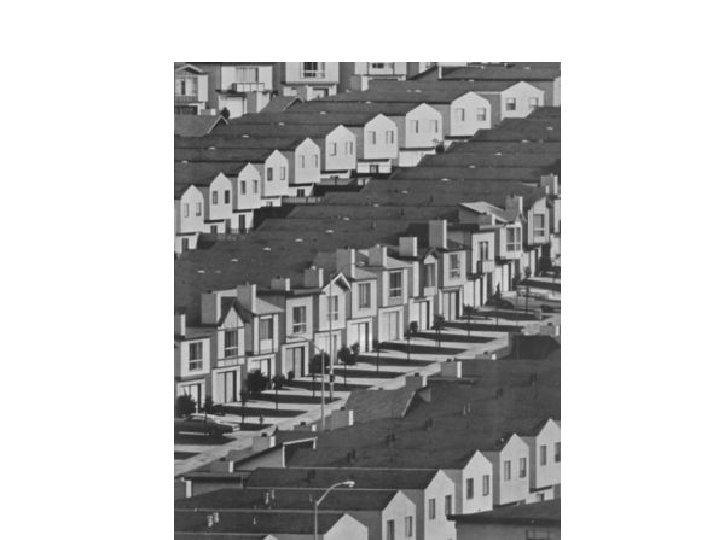




Automobile Culture • Suburbs were largely made possible by the increase in car ownership – Commute to work in the city • Eisenhower, Republican president after Truman, built 41, 000 miles of new highway – The Interstate Highway Act

Golden Age of the ‘Teenager’ • End of Great Depression and WWII + economic boom teens have $ to spend • Car = freedom from your parents – Drive in diners – Drive in movies – Etc.



Better Jobs Available for Americans • Primary producer = you get the raw materials – farmer, miner, fisherman • Blue Collar (secondary producer)= you turn primary product into consumer goods – Factory worker, butcher, etc. • White Collar (tertiary producer) = you manage blue collar workers and/or provide services for customers who are using the consumer goods – More of these jobs available after WWII – Better Pay – Often require a college education. Hey, GI Bill. Nice!
• Primary • Secondary (blue collar) • Tertiary (white collar)

Conformity • To make it in Suburbia and in the White Collar workplace, one must conform (be like everyone else) – Same house, same clothes, same haircut, same race, etc. • To people who had been through the Great Depression and WWII, conforming was a small trade off for prosperity (wealth) • Ozzie and Harriet

Hansen U. S. History Name ________________ Prosperity in the Suburbs (the 1950 s) Economic Recovery • World War II ended the Great Depression – – – • The U. S. had been the ‘_________’, providing weapons and supplies _____________ This brought us ___________ In the 1950 s and 60 s, the U. S. experienced one of the ________________________ Returning American soldiers, heroes to their countrymen, were rewarded by a grateful nation ___________________ – – Helped ‘GI’s’ (_____) pay for ______ helped them buy __________ Suburbia • So many GI’s could now buy homes that there was a ______________________ • Home builders created (often from scratch) huge _________near to, but outside of, _____ – – – • Suburbs Homes built by ‘_________’ techniques often rows of ________________ Levitt and Levittown - _______________________________________ Baby Boom – ________________________ Automobile Culture • Suburbs were largely ___________the increase in car ownership – • _________________, Republican president after Truman, built _________of new highway – The Interstate Highway Act Golden Age of the Teenager • End of Great Depression and WWII + _______ = teens have __________ • Car = ___________________ – Drive in __________ – Etc. Better Jobs Available for Americans • Primary producer = you get the raw materials • _________ (secondary producer)= you turn primary product into consumer goods • ________ (tertiary producer) = you manage blue collar workers and/or provide _______ who are using the consumer goods – – – farmer, miner, fisherman Factory worker, butcher, etc. More of these jobs available ___________________________ Often require a _________. Hey, GI Bill. Nice! Conformity • To make it in Suburbia and in the White Collar workplace, one must conform (_________) – • • Same house, same clothes, same haircut, same race, etc. To people who had been through the Great Depression and WWII, conforming was a _________ for prosperity (______) Ozzie and Harriet

f8f211fd67f69160659e1373b3d877aa.ppt