73457dbb613b41b5a0b34e93937627a7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 The 1920’s
The 1920’s
 The Red Scare • 1917 – Russian Revolution = Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin = communism • Att. Gen. A Mitchell Palmer = Palmer Raids – hunt for communists, socialists, and anarchists – Invaded homes/businesses without warrants – Suspects jailed for weeks without hearings – 100’s of foreign-born radicals deported • Sacco & Vanzetti – put to death for murder and robbery – evidence was very weak (but they were Italian immigrants)
The Red Scare • 1917 – Russian Revolution = Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin = communism • Att. Gen. A Mitchell Palmer = Palmer Raids – hunt for communists, socialists, and anarchists – Invaded homes/businesses without warrants – Suspects jailed for weeks without hearings – 100’s of foreign-born radicals deported • Sacco & Vanzetti – put to death for murder and robbery – evidence was very weak (but they were Italian immigrants)


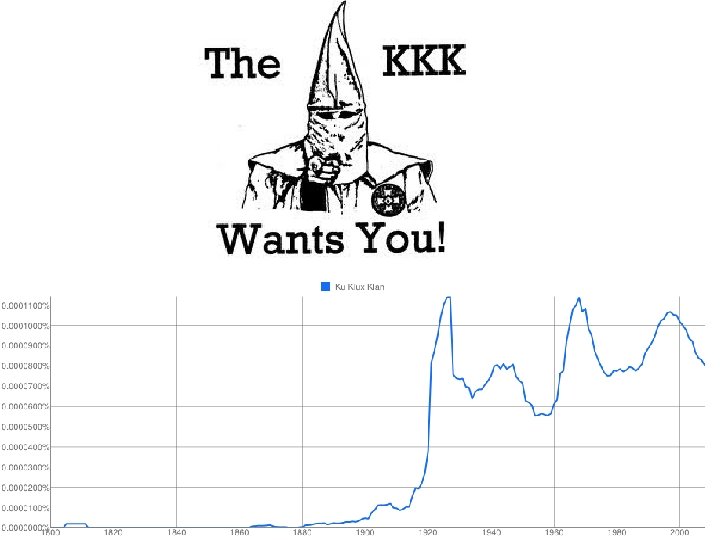
 The Rise of the KKK (again) • 1915 = revived KKK because of the great migration = KKK in the North • 1924 = 4. 5 million members • They oppose – blacks, Catholics, unions, Jews, and foreign-born peoples
The Rise of the KKK (again) • 1915 = revived KKK because of the great migration = KKK in the North • 1924 = 4. 5 million members • They oppose – blacks, Catholics, unions, Jews, and foreign-born peoples

 Labor Unrest • 1919 = 3, 000 strikes by four million workers – Boston Police – new officers hired and given what the strikers wanted – The Steel Mill Strike – 18 workers killed – no change in working conditions until 1923 when muckrakers made the conditions well known – The Coal Miners’ Strike – miners get 27% raise • Unions lose their appeal = membership down – Immigrants – hard to organize (language) – Old farmers are independent – Excluded blacks
Labor Unrest • 1919 = 3, 000 strikes by four million workers – Boston Police – new officers hired and given what the strikers wanted – The Steel Mill Strike – 18 workers killed – no change in working conditions until 1923 when muckrakers made the conditions well known – The Coal Miners’ Strike – miners get 27% raise • Unions lose their appeal = membership down – Immigrants – hard to organize (language) – Old farmers are independent – Excluded blacks
 Warren G. Harding • Return to “Normalcy” = Isolationism, nativism, conservatism = less government activism – Kellogg-Briand Pact – 64 nations = no war – Tariffs up 60% = Allies unable to repay loans – Dawes Plan – Germany given $2. 5 billion loan – they pay England France – they pay us – Immigration limited by quotas (0 Japanese) 1919 = 141, 000 1921 = 805, 000
Warren G. Harding • Return to “Normalcy” = Isolationism, nativism, conservatism = less government activism – Kellogg-Briand Pact – 64 nations = no war – Tariffs up 60% = Allies unable to repay loans – Dawes Plan – Germany given $2. 5 billion loan – they pay England France – they pay us – Immigration limited by quotas (0 Japanese) 1919 = 141, 000 1921 = 805, 000

 Harding Scandals • Ohio Gang = poker buddies = his cabinet – Forbes – Veterans bureau – overcharge by $250 million – Colonel Miller – selling German patents seized during the war – Albert Fall – leasing government owned oil reserves to companies for $325, 000 = Teapot Dome Scandal • Aug. 2, 1923 = Harding dies from heart attack • Calvin Coolidge takes over and wins in 1924
Harding Scandals • Ohio Gang = poker buddies = his cabinet – Forbes – Veterans bureau – overcharge by $250 million – Colonel Miller – selling German patents seized during the war – Albert Fall – leasing government owned oil reserves to companies for $325, 000 = Teapot Dome Scandal • Aug. 2, 1923 = Harding dies from heart attack • Calvin Coolidge takes over and wins in 1924

 Economics • Harding/Coolidge = low taxes and high profits • 1920’s = U. S. 40% of world’s wealth • The Automobile = economic multiplier – Roads, garages, gas stations, repair shops, motels, shopping centers, oil – 80% of cars in U. S. = 1 car for every 5 people – Airplane also becomes means of transportation Electrical Conveniences = easier for housewives = more family leisure time
Economics • Harding/Coolidge = low taxes and high profits • 1920’s = U. S. 40% of world’s wealth • The Automobile = economic multiplier – Roads, garages, gas stations, repair shops, motels, shopping centers, oil – 80% of cars in U. S. = 1 car for every 5 people – Airplane also becomes means of transportation Electrical Conveniences = easier for housewives = more family leisure time

 Superficial Prosperity • Average factory worker producing 50% more • Nat. Income – 1921 = $58 billion 1929 = $83 billion • Businesses expanded – merged – created chain stores • Income gap between workers and management grew = no real middle class • Iron and railroad industries weren’t prosperous • Mining and farming suffering losses • Producers needed people to continue to buy = easy credit and installment plans
Superficial Prosperity • Average factory worker producing 50% more • Nat. Income – 1921 = $58 billion 1929 = $83 billion • Businesses expanded – merged – created chain stores • Income gap between workers and management grew = no real middle class • Iron and railroad industries weren’t prosperous • Mining and farming suffering losses • Producers needed people to continue to buy = easy credit and installment plans
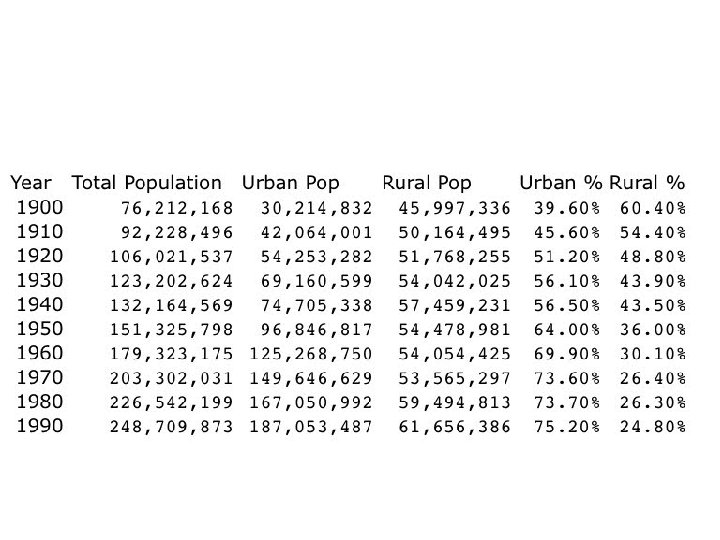
 Changing Demographics • 1920 Census = 51. 4% live in cities (2, 500) • Farm Life – church, neighbors, fairs/church socials • 1922 -1929 – 2 million leave farms • City Life – morals? , neighbors? , social life
Changing Demographics • 1920 Census = 51. 4% live in cities (2, 500) • Farm Life – church, neighbors, fairs/church socials • 1922 -1929 – 2 million leave farms • City Life – morals? , neighbors? , social life
 Prohibition • Jan. 1920 – 18 th Amendment • Government failed to budget enough – 1, 550 poorly paid federal agents (bribes) • Many immigrants – drinking = part of socializing • Speakeasies – hidden saloons and nightclubs • Bootleggers – people who smuggled alcohol (mostly from Canada)
Prohibition • Jan. 1920 – 18 th Amendment • Government failed to budget enough – 1, 550 poorly paid federal agents (bribes) • Many immigrants – drinking = part of socializing • Speakeasies – hidden saloons and nightclubs • Bootleggers – people who smuggled alcohol (mostly from Canada)
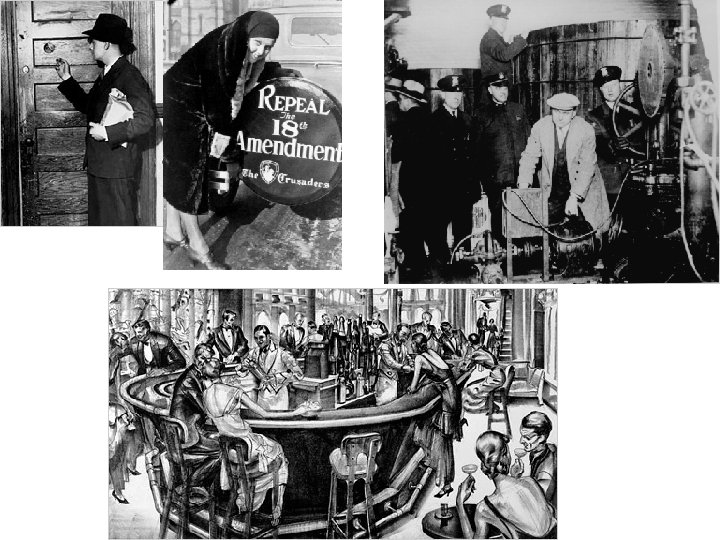



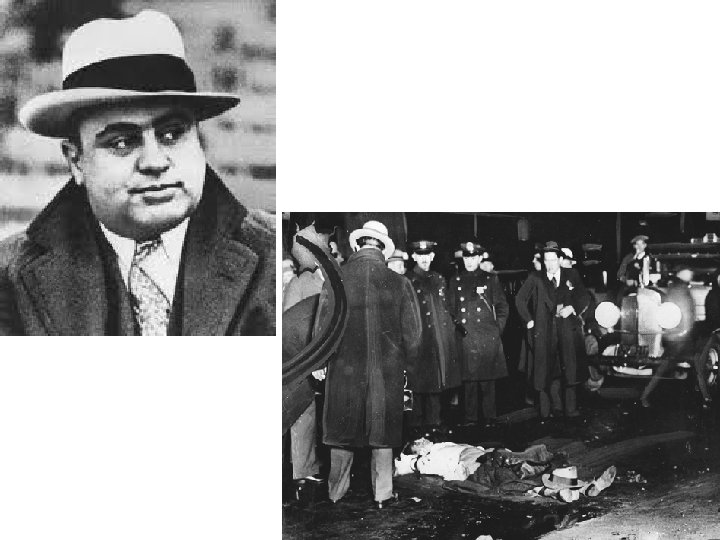
 • Prohibition generated disrespect for the law • Organized Crime – Chicago – Al Capone • By mid 1920’s – 19% favored prohibition • 1933 – repealed by the 21 st Amendment • It did slow drinking down but did not stop it.
• Prohibition generated disrespect for the law • Organized Crime – Chicago – Al Capone • By mid 1920’s – 19% favored prohibition • 1933 – repealed by the 21 st Amendment • It did slow drinking down but did not stop it.

 Science vs. Religion • Fundamentalism – Protestant movement = literal translation of the Bible • Darwin’s Theory of Evolution – not allowed • Scopes Trial – 1925 Tennessee (Bible Belt) – John Scopes taught evolution in science class – Found guilty and fined $100 – Tenn. Supreme Court changed the verdict on a technicality but law remained on the books
Science vs. Religion • Fundamentalism – Protestant movement = literal translation of the Bible • Darwin’s Theory of Evolution – not allowed • Scopes Trial – 1925 Tennessee (Bible Belt) – John Scopes taught evolution in science class – Found guilty and fined $100 – Tenn. Supreme Court changed the verdict on a technicality but law remained on the books

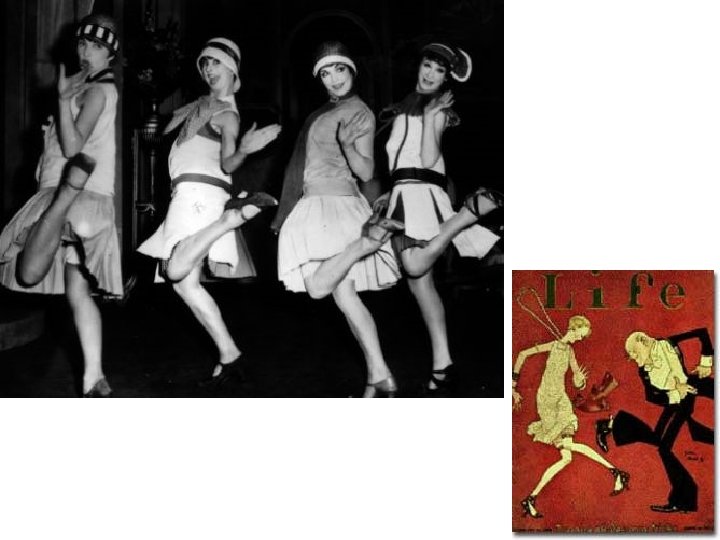
 1920’s Women • Some assert their independence and demanded the same freedoms as men • Flapper – emancipated young women who embraced the new fashions and urban attitudes of the day - Smoking and drinking in public - Short dresses and skirts Double Standard – casual dating acceptable for men only
1920’s Women • Some assert their independence and demanded the same freedoms as men • Flapper – emancipated young women who embraced the new fashions and urban attitudes of the day - Smoking and drinking in public - Short dresses and skirts Double Standard – casual dating acceptable for men only
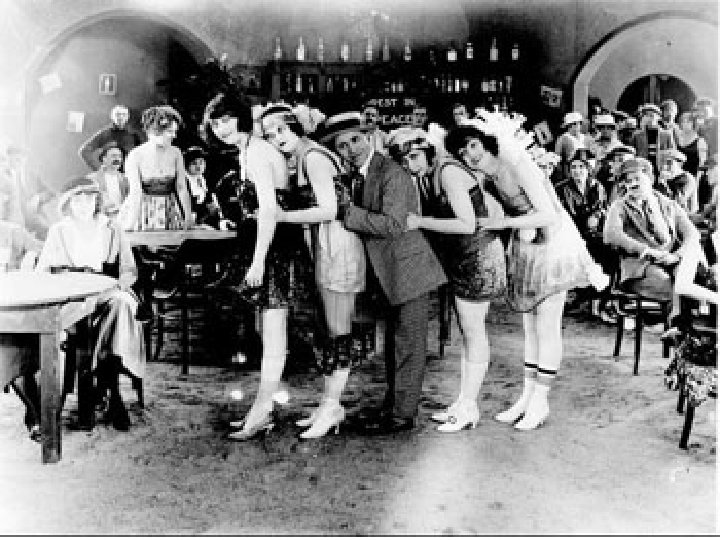


 • Industrial Economy = new opportunities for women • 1920’s = one million women college graduates – two million clerical jobs – 800, 000 clerks in stores – two million on assembly lines • By 1930 – ten million women workers/ 24% of work force • Birthrate dropped rapidly – birth control • A woman working was sometimes seen as a failure by her husband (breadwinner)
• Industrial Economy = new opportunities for women • 1920’s = one million women college graduates – two million clerical jobs – 800, 000 clerks in stores – two million on assembly lines • By 1930 – ten million women workers/ 24% of work force • Birthrate dropped rapidly – birth control • A woman working was sometimes seen as a failure by her husband (breadwinner)
 Education • 1914 = one million H. S. students; 1926 = four million • Increased literacy = newspapers and magazines • Sinclair Lewis – first American to win Nobel Prize in literature • F. Scott Fitzgerald – The Great Gatsby • Ernest Hemingway – A Farewell to Arms (he was wounded in WW I)
Education • 1914 = one million H. S. students; 1926 = four million • Increased literacy = newspapers and magazines • Sinclair Lewis – first American to win Nobel Prize in literature • F. Scott Fitzgerald – The Great Gatsby • Ernest Hemingway – A Farewell to Arms (he was wounded in WW I)

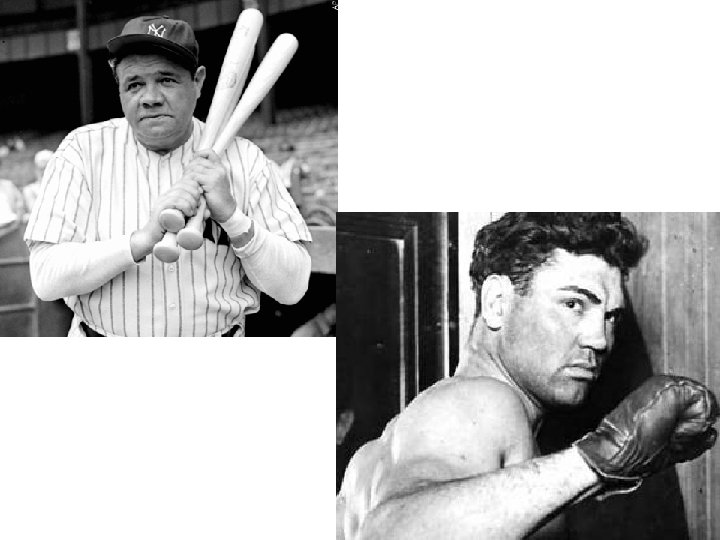
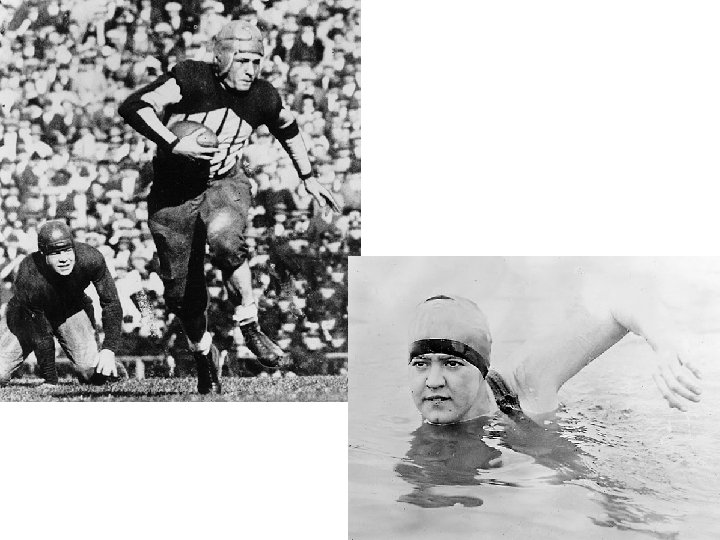
 Sports • Babe Ruth – 60 homeruns for 1927 Yankees • Negro Leagues founded in 1920 • Knute Rockne – N. D. football coach • Red Grange - running back (galloping ghost) • Jack Dempsey – heavyweight champion • Gertrude Ederle – 1 st woman to swim the English Channel
Sports • Babe Ruth – 60 homeruns for 1927 Yankees • Negro Leagues founded in 1920 • Knute Rockne – N. D. football coach • Red Grange - running back (galloping ghost) • Jack Dempsey – heavyweight champion • Gertrude Ederle – 1 st woman to swim the English Channel


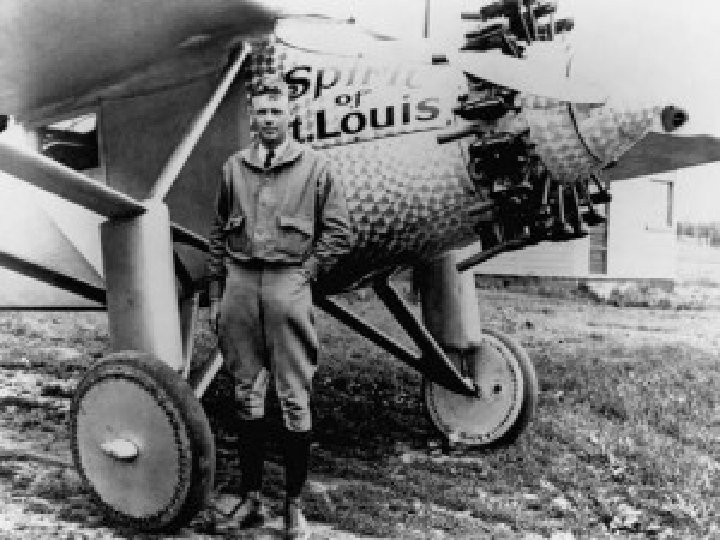
 Charles Lindbergh • May 20 th, 1927 – took off from New York City in the Spirit of St. Louis – 33 hours and 29 minutes later = landed in Paris • Megastar – Hero • Changes the World – isolationism won’t really work anymore
Charles Lindbergh • May 20 th, 1927 – took off from New York City in the Spirit of St. Louis – 33 hours and 29 minutes later = landed in Paris • Megastar – Hero • Changes the World – isolationism won’t really work anymore

 Movies and the Arts • 1925 – 20, 000 movie houses – 4 th largest industry • 1927 – The Jazz Singer -1 st movie with sound • George Gershwin – combined Jazz and traditional music • Georgia O’Keefe – S. W. paintings and flowers • Some writers, upset with U. S. culture, moved to Paris = the lost generation
Movies and the Arts • 1925 – 20, 000 movie houses – 4 th largest industry • 1927 – The Jazz Singer -1 st movie with sound • George Gershwin – combined Jazz and traditional music • Georgia O’Keefe – S. W. paintings and flowers • Some writers, upset with U. S. culture, moved to Paris = the lost generation


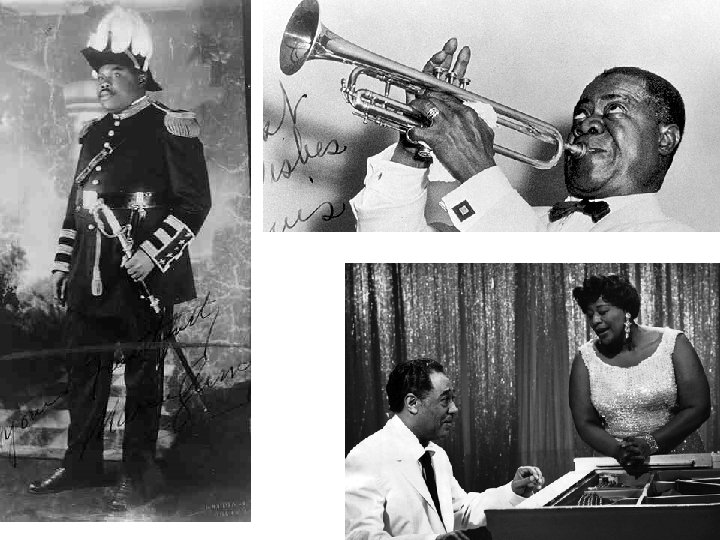
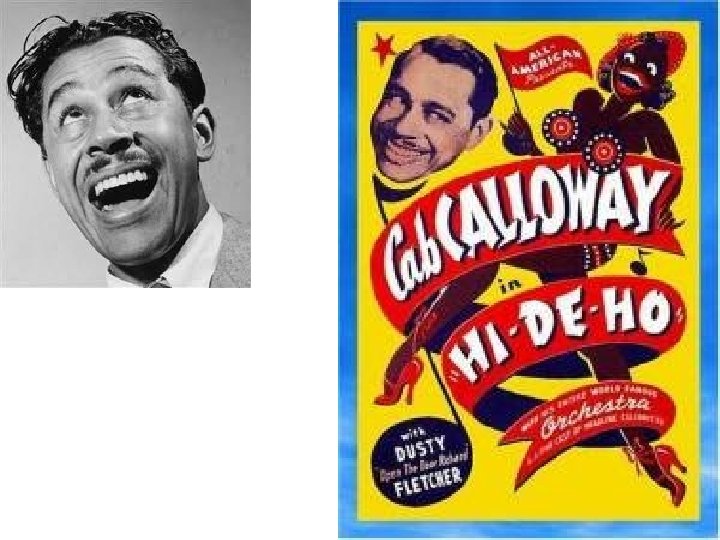
 The Harlem Renaissance • 1920’s = African American attitudes changing = Black is beautiful • By 1929 – 40% lived in cities • Marcus Garvey – blacks should separate from society • The Harlem Renaissance – artistic movement celebrating African-American culture – – – Louis Armstrong – most important Jazz musician “Duke” Ellington – jazz pianist and composer Cab Calloway – popularized “scat” jazz Bessie Smith – Blues singer Josephine Baker – most popular black artist in Europe
The Harlem Renaissance • 1920’s = African American attitudes changing = Black is beautiful • By 1929 – 40% lived in cities • Marcus Garvey – blacks should separate from society • The Harlem Renaissance – artistic movement celebrating African-American culture – – – Louis Armstrong – most important Jazz musician “Duke” Ellington – jazz pianist and composer Cab Calloway – popularized “scat” jazz Bessie Smith – Blues singer Josephine Baker – most popular black artist in Europe






