a5c55a3b0c8c4c570b45292981812a9a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 -Thailand International Health Policy Program Lesson Learnt from the Estimate of Maternal Death in Thailand Kanjana Tisayaticom Sudarat Tantivivat Phusit Prakongsai International Health Policy Program (IHPP), Thailand The 3 rd Global Forum on Gender Statistics 11 -13 October 2010 Manila, Philippines ESA/STAT/AC. 219/36
-Thailand International Health Policy Program Lesson Learnt from the Estimate of Maternal Death in Thailand Kanjana Tisayaticom Sudarat Tantivivat Phusit Prakongsai International Health Policy Program (IHPP), Thailand The 3 rd Global Forum on Gender Statistics 11 -13 October 2010 Manila, Philippines ESA/STAT/AC. 219/36
 International Health Policy Program -Thailand Outline • Introduction – MDG achievements and maternal death in Thailand • Different approaches and statistics of maternal death – Vital statistics - Bureau of Policy and Strategy, MOPH – Multiple sources of data - Thailand Development Research Institute (TDRI) – Reproductive age mortality surveys (RAMOS) and verbal autopsy (VA) • Conclusions and policy recommendations
International Health Policy Program -Thailand Outline • Introduction – MDG achievements and maternal death in Thailand • Different approaches and statistics of maternal death – Vital statistics - Bureau of Policy and Strategy, MOPH – Multiple sources of data - Thailand Development Research Institute (TDRI) – Reproductive age mortality surveys (RAMOS) and verbal autopsy (VA) • Conclusions and policy recommendations
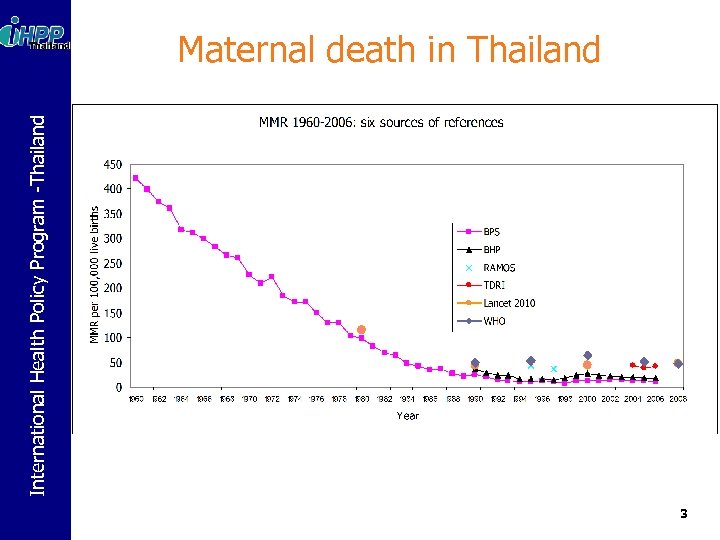 International Health Policy Program -Thailand Maternal death in Thailand 3
International Health Policy Program -Thailand Maternal death in Thailand 3
 International Health Policy Program -Thailand Objectives of the study • To describe differences in maternal death in Thailand using different types of data sources and data collection approaches, • To explore strengths and weaknesses of three different approaches in estimation of maternal deaths in Thailand – Using vital registration by BPS, MOPH – Using multiple data by TDRI, – RAMOS technique and verbal autopsy (VA).
International Health Policy Program -Thailand Objectives of the study • To describe differences in maternal death in Thailand using different types of data sources and data collection approaches, • To explore strengths and weaknesses of three different approaches in estimation of maternal deaths in Thailand – Using vital registration by BPS, MOPH – Using multiple data by TDRI, – RAMOS technique and verbal autopsy (VA).
 Bureau of Policy and Strategy (BPS), MOPH International Health Policy Program -Thailand • Vital registration – Death registration (coverage 95. 2% in 2006: SPC 2005 -2006) – Birth registration (coverage 96. 7% in 2006: SPC 2005 -2006) • Coding cause of death using ICD 10 by BPS staff • Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium O 00 -O 99 • O 00 -O 08 Pregnancy with abortive outcome • O 10 -O 16 Oedema, proteinuria and hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium • O 20 -O 29 Other maternal disorders predominantly related to pregnancy • O 30 -O 48 Maternal care related to the fetus and amniotic cavity and possible delivery problems • O 60 -O 75 Complications of labour and delivery • O 80 -O 84 Delivery • O 85 -O 92 Complications predominantly related to the puerperium • O 94 -O 99 Other obstetric conditions, not elsewhere classified 5
Bureau of Policy and Strategy (BPS), MOPH International Health Policy Program -Thailand • Vital registration – Death registration (coverage 95. 2% in 2006: SPC 2005 -2006) – Birth registration (coverage 96. 7% in 2006: SPC 2005 -2006) • Coding cause of death using ICD 10 by BPS staff • Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium O 00 -O 99 • O 00 -O 08 Pregnancy with abortive outcome • O 10 -O 16 Oedema, proteinuria and hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium • O 20 -O 29 Other maternal disorders predominantly related to pregnancy • O 30 -O 48 Maternal care related to the fetus and amniotic cavity and possible delivery problems • O 60 -O 75 Complications of labour and delivery • O 80 -O 84 Delivery • O 85 -O 92 Complications predominantly related to the puerperium • O 94 -O 99 Other obstetric conditions, not elsewhere classified 5
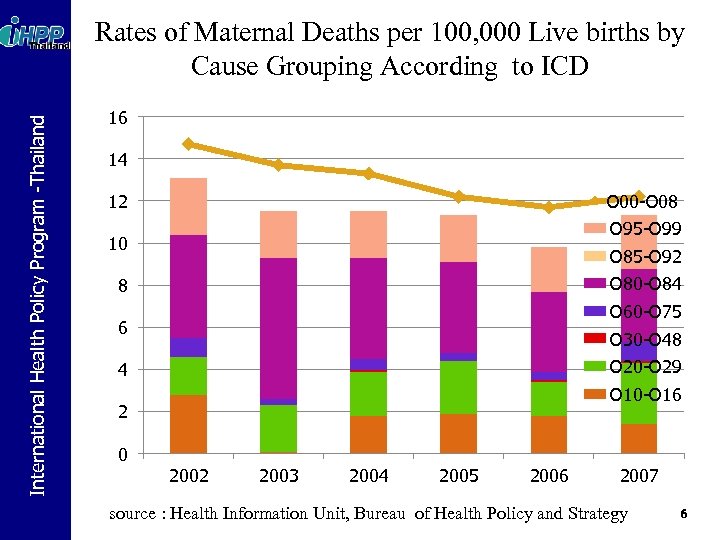 International Health Policy Program -Thailand Rates of Maternal Deaths per 100, 000 Live births by Cause Grouping According to ICD 16 14 O 00 -O 08 12 O 95 -O 99 10 O 85 -O 92 O 80 -O 84 8 O 60 -O 75 6 O 30 -O 48 O 20 -O 29 4 O 10 -O 16 2 0 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 source : Health Information Unit, Bureau of Health Policy and Strategy 6
International Health Policy Program -Thailand Rates of Maternal Deaths per 100, 000 Live births by Cause Grouping According to ICD 16 14 O 00 -O 08 12 O 95 -O 99 10 O 85 -O 92 O 80 -O 84 8 O 60 -O 75 6 O 30 -O 48 O 20 -O 29 4 O 10 -O 16 2 0 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 source : Health Information Unit, Bureau of Health Policy and Strategy 6
 International Health Policy Program -Thailand Using Multiple Data for Calculating the Maternal Mortality Ratio in Thailand by TDRI • Data sources – Vital registration • Birth registration • Death registration – Inpatient data set • Civil Servant beneficiaries scheme • Universal coverage scheme • Methods – Method 1: Mothers Who Died after Giving a Live Birth – Method 2: Women Ending Pregnancy with Stillbirth or Neonatal Death 7
International Health Policy Program -Thailand Using Multiple Data for Calculating the Maternal Mortality Ratio in Thailand by TDRI • Data sources – Vital registration • Birth registration • Death registration – Inpatient data set • Civil Servant beneficiaries scheme • Universal coverage scheme • Methods – Method 1: Mothers Who Died after Giving a Live Birth – Method 2: Women Ending Pregnancy with Stillbirth or Neonatal Death 7
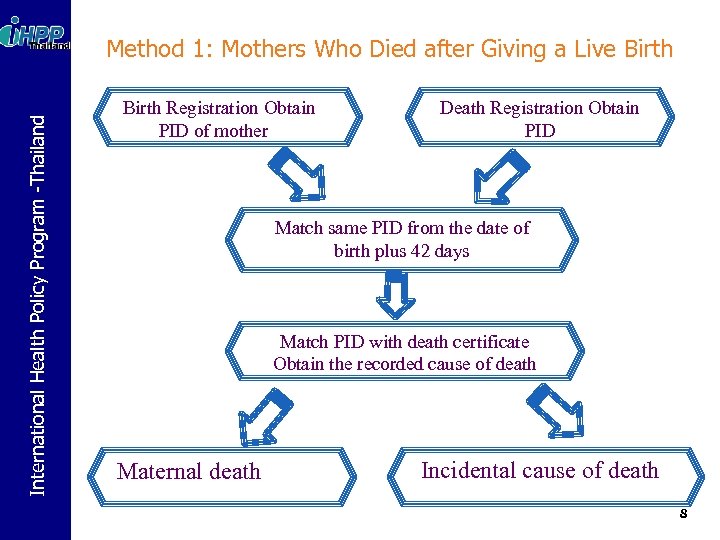 International Health Policy Program -Thailand Method 1: Mothers Who Died after Giving a Live Birth Registration Obtain PID of mother Death Registration Obtain PID Match same PID from the date of birth plus 42 days Match PID with death certificate Obtain the recorded cause of death Maternal death Incidental cause of death 8
International Health Policy Program -Thailand Method 1: Mothers Who Died after Giving a Live Birth Registration Obtain PID of mother Death Registration Obtain PID Match same PID from the date of birth plus 42 days Match PID with death certificate Obtain the recorded cause of death Maternal death Incidental cause of death 8
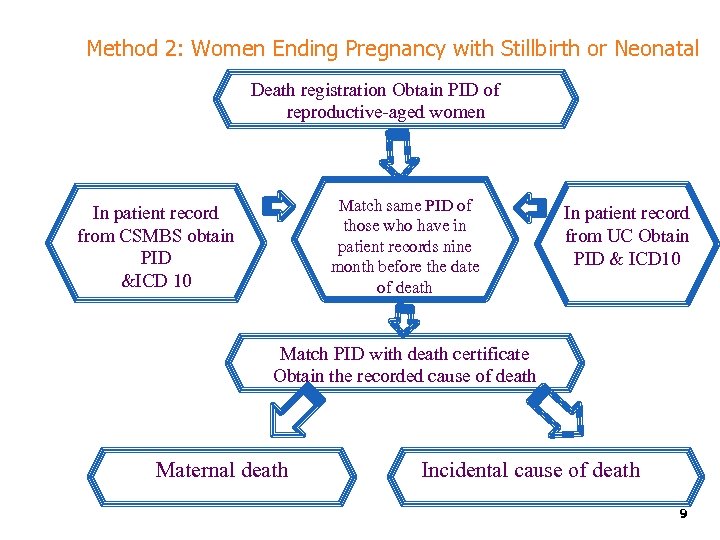 Method 2: Women Ending Pregnancy with Stillbirth or Neonatal Death registration Obtain PID of reproductive-aged women Match same PID of those who have in patient records nine month before the date of death In patient record from CSMBS obtain PID &ICD 10 In patient record from UC Obtain PID & ICD 10 Match PID with death certificate Obtain the recorded cause of death Maternal death Incidental cause of death 9
Method 2: Women Ending Pregnancy with Stillbirth or Neonatal Death registration Obtain PID of reproductive-aged women Match same PID of those who have in patient records nine month before the date of death In patient record from CSMBS obtain PID &ICD 10 In patient record from UC Obtain PID & ICD 10 Match PID with death certificate Obtain the recorded cause of death Maternal death Incidental cause of death 9
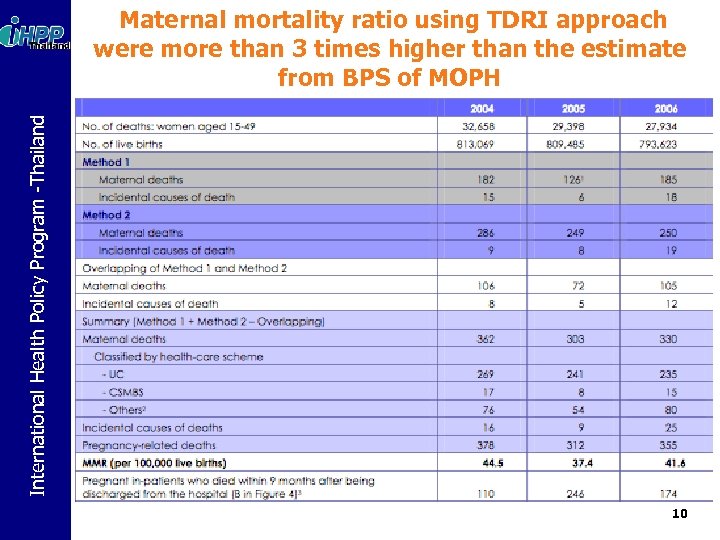 International Health Policy Program -Thailand Maternal mortality ratio using TDRI approach were more than 3 times higher than the estimate from BPS of MOPH 10
International Health Policy Program -Thailand Maternal mortality ratio using TDRI approach were more than 3 times higher than the estimate from BPS of MOPH 10
 International Health Policy Program -Thailand The Reproductive Age Mortality Survey (RAMOS) Method • Primarily quantitative • Qualitative for verbal autopsies Approach Identifies and investigates all deaths of women of reproductive age (15 -49 years) using multiple data sources. Phase 1: Death Identification Phase 2: Death Review
International Health Policy Program -Thailand The Reproductive Age Mortality Survey (RAMOS) Method • Primarily quantitative • Qualitative for verbal autopsies Approach Identifies and investigates all deaths of women of reproductive age (15 -49 years) using multiple data sources. Phase 1: Death Identification Phase 2: Death Review
 International Health Policy Program -Thailand The 1 st Phase: Death Identification Identify all deaths in the community through one or more sources as listed below: • • • Routine death registrations Medical records in health facilities Interviews with health care providers Census Multiples sources of information
International Health Policy Program -Thailand The 1 st Phase: Death Identification Identify all deaths in the community through one or more sources as listed below: • • • Routine death registrations Medical records in health facilities Interviews with health care providers Census Multiples sources of information
 International Health Policy Program -Thailand The 2 nd Phase: Death Review Investigate deaths of women reproductive age to determine the cause of death and relatedness to pregnancy through various sources as list below: • Medical records and coroners’ reports • Interview of health care providers • Interview of family members (Verbal Autopsy) 13
International Health Policy Program -Thailand The 2 nd Phase: Death Review Investigate deaths of women reproductive age to determine the cause of death and relatedness to pregnancy through various sources as list below: • Medical records and coroners’ reports • Interview of health care providers • Interview of family members (Verbal Autopsy) 13
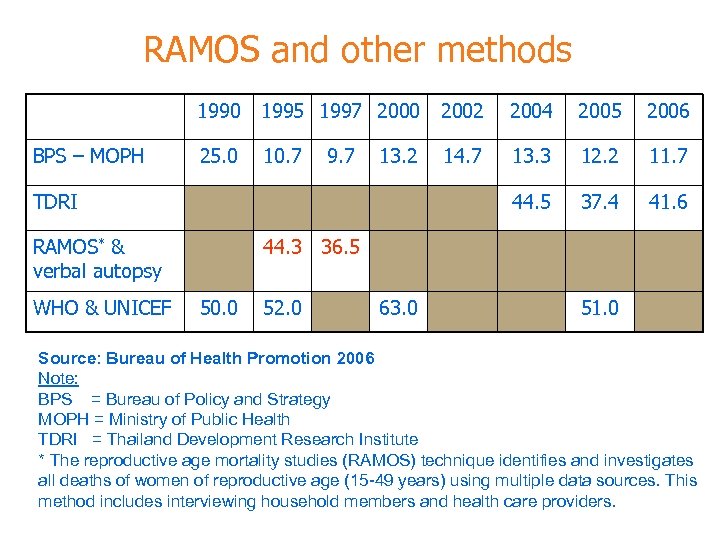 RAMOS and other methods 1990 BPS – MOPH 1995 1997 2000 2002 2004 2005 2006 25. 0 10. 7 14. 7 13. 3 12. 2 11. 7 44. 5 37. 4 41. 6 9. 7 13. 2 TDRI RAMOS* & verbal autopsy WHO & UNICEF 44. 3 36. 5 50. 0 52. 0 63. 0 51. 0 Source: Bureau of Health Promotion 2006 Note: BPS = Bureau of Policy and Strategy MOPH = Ministry of Public Health TDRI = Thailand Development Research Institute * The reproductive age mortality studies (RAMOS) technique identifies and investigates all deaths of women of reproductive age (15 -49 years) using multiple data sources. This method includes interviewing household members and health care providers.
RAMOS and other methods 1990 BPS – MOPH 1995 1997 2000 2002 2004 2005 2006 25. 0 10. 7 14. 7 13. 3 12. 2 11. 7 44. 5 37. 4 41. 6 9. 7 13. 2 TDRI RAMOS* & verbal autopsy WHO & UNICEF 44. 3 36. 5 50. 0 52. 0 63. 0 51. 0 Source: Bureau of Health Promotion 2006 Note: BPS = Bureau of Policy and Strategy MOPH = Ministry of Public Health TDRI = Thailand Development Research Institute * The reproductive age mortality studies (RAMOS) technique identifies and investigates all deaths of women of reproductive age (15 -49 years) using multiple data sources. This method includes interviewing household members and health care providers.
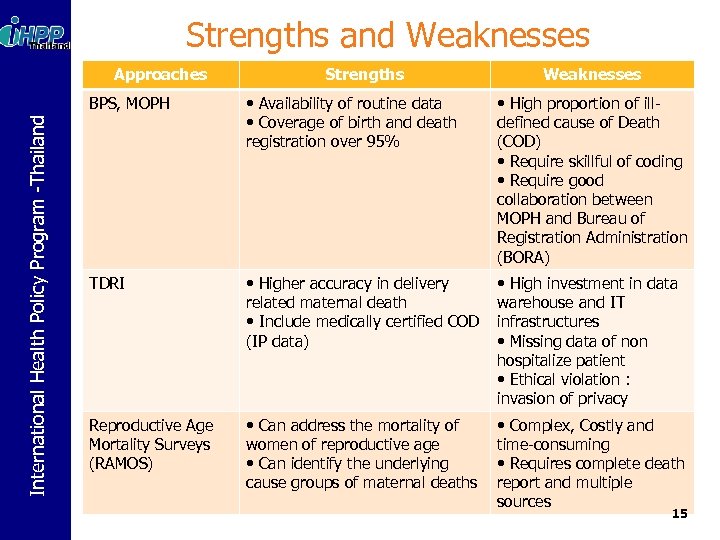 Strengths and Weaknesses Approaches Strengths Weaknesses • Availability of routine data • Coverage of birth and death registration over 95% • High proportion of illdefined cause of Death (COD) • Require skillful of coding • Require good collaboration between MOPH and Bureau of Registration Administration (BORA) TDRI • Higher accuracy in delivery related maternal death • Include medically certified COD (IP data) • High investment in data warehouse and IT infrastructures • Missing data of non hospitalize patient • Ethical violation : invasion of privacy Reproductive Age Mortality Surveys (RAMOS) • Can address the mortality of women of reproductive age • Can identify the underlying cause groups of maternal deaths • Complex, Costly and time-consuming • Requires complete death report and multiple sources International Health Policy Program -Thailand BPS, MOPH 15
Strengths and Weaknesses Approaches Strengths Weaknesses • Availability of routine data • Coverage of birth and death registration over 95% • High proportion of illdefined cause of Death (COD) • Require skillful of coding • Require good collaboration between MOPH and Bureau of Registration Administration (BORA) TDRI • Higher accuracy in delivery related maternal death • Include medically certified COD (IP data) • High investment in data warehouse and IT infrastructures • Missing data of non hospitalize patient • Ethical violation : invasion of privacy Reproductive Age Mortality Surveys (RAMOS) • Can address the mortality of women of reproductive age • Can identify the underlying cause groups of maternal deaths • Complex, Costly and time-consuming • Requires complete death report and multiple sources International Health Policy Program -Thailand BPS, MOPH 15
 International Health Policy Program -Thailand Conclusions and policy recommendation • High gaps between the estimate of MMR from vital registration and other approaches, • Improve accuracy of estimate MMR in any approaches inevitably need completeness and accuracy of vital registration, • In developing countries, it is unlikely to conduct RAMOS either annually or biennially due to limited resources and time consuming, • Though Thailand has achieved high coverage of birth and death registration, high proportion of ill-defined cause of death (COD) is the major challenge. 16
International Health Policy Program -Thailand Conclusions and policy recommendation • High gaps between the estimate of MMR from vital registration and other approaches, • Improve accuracy of estimate MMR in any approaches inevitably need completeness and accuracy of vital registration, • In developing countries, it is unlikely to conduct RAMOS either annually or biennially due to limited resources and time consuming, • Though Thailand has achieved high coverage of birth and death registration, high proportion of ill-defined cause of death (COD) is the major challenge. 16
 Thank you for your attention
Thank you for your attention


