b7c6bf63195fadc70301ab1eed6078d5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 th IAEA – 4 MEETING ON HUMAN RESOURCES OF RB 4 -7 Dec. 12 -VIENNA Galal El. Din ORABI NUCLEAR AND RADIOLOGICAL REGULATORY AUTHORITY (NRRA) EGYPT
th IAEA – 4 MEETING ON HUMAN RESOURCES OF RB 4 -7 Dec. 12 -VIENNA Galal El. Din ORABI NUCLEAR AND RADIOLOGICAL REGULATORY AUTHORITY (NRRA) EGYPT
 Prof. Dr. Galal EL-Din Ibrahim Orabi • 2003 -present: Head of the Regulatory Inspection and Enforcement Unit • 1997 to 2003 : Head of Dept. of Material and Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety at the NCNSRC / EAEA • March 2012 -present : Member of NRRA manager board • National Counterpart of Many IAEA-TCPs • Worked at CEA (Saclay) , EDF (Paris) , ISPRA (Italy) • Ph. D from France , Materials Degradation Mechanisms
Prof. Dr. Galal EL-Din Ibrahim Orabi • 2003 -present: Head of the Regulatory Inspection and Enforcement Unit • 1997 to 2003 : Head of Dept. of Material and Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety at the NCNSRC / EAEA • March 2012 -present : Member of NRRA manager board • National Counterpart of Many IAEA-TCPs • Worked at CEA (Saclay) , EDF (Paris) , ISPRA (Italy) • Ph. D from France , Materials Degradation Mechanisms
 Contents Ø Ø Ø Ø Brief on the Nuclear Organizations in Egypt Nuclear and Radiation Installations in Egypt History of Nuclear Legislation in Egypt New NRRA and LAW 7/ 010 Structure and Organization of NRRA Human Resources Needed for NRRA Training and Qualification Plan
Contents Ø Ø Ø Ø Brief on the Nuclear Organizations in Egypt Nuclear and Radiation Installations in Egypt History of Nuclear Legislation in Egypt New NRRA and LAW 7/ 010 Structure and Organization of NRRA Human Resources Needed for NRRA Training and Qualification Plan
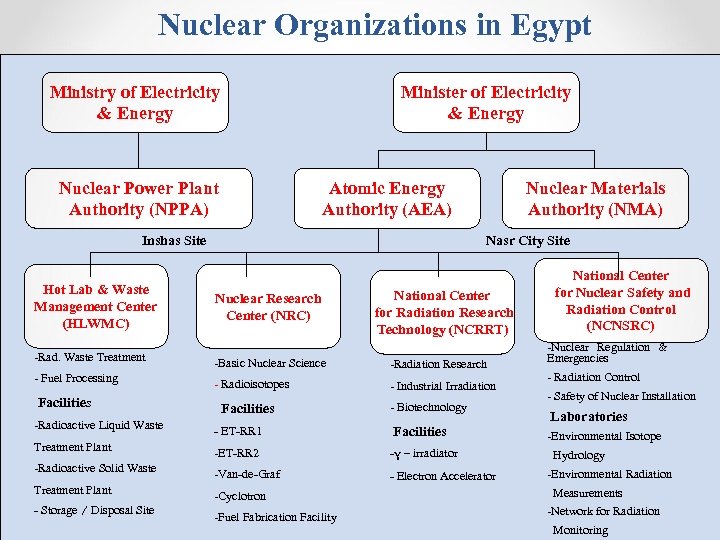 Nuclear Organizations in Egypt Ministry of Electricity & Energy Minister of Electricity & Energy Nuclear Power Plant Authority (NPPA) Atomic Energy Authority (AEA) Inshas Site Hot Lab & Waste Management Center (HLWMC) Nuclear Materials Authority (NMA) Nasr City Site Nuclear Research Center (NRC) National Center for Radiation Research Technology (NCRRT) -Rad. Waste Treatment -Basic Nuclear Science -Radiation Research - Fuel Processing - Radioisotopes - Industrial Irradiation Facilities -Radioactive Liquid Waste Facilities - Biotechnology - ET-RR 1 Facilities Treatment Plant -ET-RR 2 -γ – irradiator -Radioactive Solid Waste -Van-de-Graf - Electron Accelerator Treatment Plant -Cyclotron - Storage / Disposal Site -Fuel Fabrication Facility National Center for Nuclear Safety and Radiation Control (NCNSRC) -Nuclear Regulation & Emergencies - Radiation Control - Safety of Nuclear Installation Laboratories -Environmental Isotope Hydrology -Environmental Radiation Measurements -Network for Radiation Monitoring
Nuclear Organizations in Egypt Ministry of Electricity & Energy Minister of Electricity & Energy Nuclear Power Plant Authority (NPPA) Atomic Energy Authority (AEA) Inshas Site Hot Lab & Waste Management Center (HLWMC) Nuclear Materials Authority (NMA) Nasr City Site Nuclear Research Center (NRC) National Center for Radiation Research Technology (NCRRT) -Rad. Waste Treatment -Basic Nuclear Science -Radiation Research - Fuel Processing - Radioisotopes - Industrial Irradiation Facilities -Radioactive Liquid Waste Facilities - Biotechnology - ET-RR 1 Facilities Treatment Plant -ET-RR 2 -γ – irradiator -Radioactive Solid Waste -Van-de-Graf - Electron Accelerator Treatment Plant -Cyclotron - Storage / Disposal Site -Fuel Fabrication Facility National Center for Nuclear Safety and Radiation Control (NCNSRC) -Nuclear Regulation & Emergencies - Radiation Control - Safety of Nuclear Installation Laboratories -Environmental Isotope Hydrology -Environmental Radiation Measurements -Network for Radiation Monitoring
 Regulating Nuclear installations and activities in Egypt Ø Planned Nuclear Power Plants Ø All the fuel cycle installations Ø Research centers (reactors, laboratories) Ø Medical and industrial installations using radioactive sources Ø Handling of radioactive materials and radiation sources
Regulating Nuclear installations and activities in Egypt Ø Planned Nuclear Power Plants Ø All the fuel cycle installations Ø Research centers (reactors, laboratories) Ø Medical and industrial installations using radioactive sources Ø Handling of radioactive materials and radiation sources
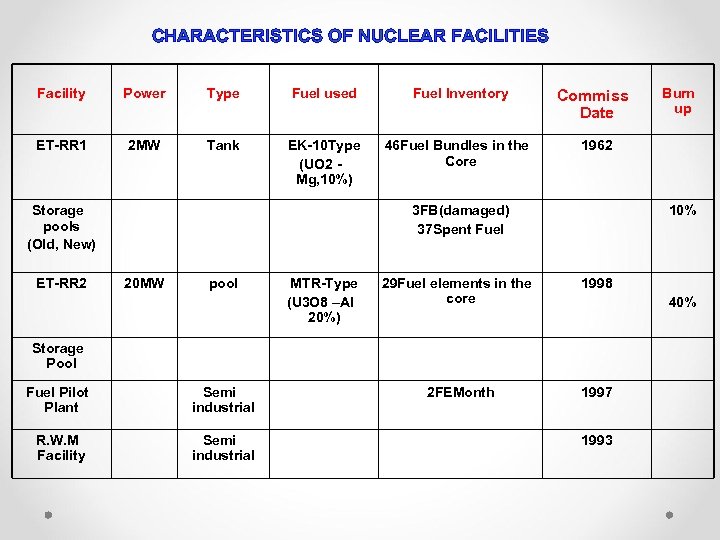 CHARACTERISTICS OF NUCLEAR FACILITIES Facility Power Type Fuel used Fuel Inventory ET-RR 1 2 MW Tank EK-10 Type (UO 2 Mg, 10%) 46 Fuel Bundles in the Core Storage pools (Old, New) ET-RR 2 Commiss Date 1962 3 FB(damaged) 37 Spent Fuel 20 MW pool MTR-Type (U 3 O 8 –Al 20%) 10% 29 Fuel elements in the core 1998 2 FEMonth 1997 40% Storage Pool Fuel Pilot Plant Semi industrial R. W. M Facility Semi industrial Burn up 1993
CHARACTERISTICS OF NUCLEAR FACILITIES Facility Power Type Fuel used Fuel Inventory ET-RR 1 2 MW Tank EK-10 Type (UO 2 Mg, 10%) 46 Fuel Bundles in the Core Storage pools (Old, New) ET-RR 2 Commiss Date 1962 3 FB(damaged) 37 Spent Fuel 20 MW pool MTR-Type (U 3 O 8 –Al 20%) 10% 29 Fuel elements in the core 1998 2 FEMonth 1997 40% Storage Pool Fuel Pilot Plant Semi industrial R. W. M Facility Semi industrial Burn up 1993
 Radiation Installations In Egypt Ø Two Gamma Irradiation units (one under construction ) Ø Radioisotope Production Facility Ø Low and Medium Radioactive waste Treatment Unit Ø Gamma Radiotherapy Unit Ø 6000 Open and Sealed sources
Radiation Installations In Egypt Ø Two Gamma Irradiation units (one under construction ) Ø Radioisotope Production Facility Ø Low and Medium Radioactive waste Treatment Unit Ø Gamma Radiotherapy Unit Ø 6000 Open and Sealed sources
 History of Nuclear Legislation in Egypt 1957, the Egyptian Atomic Energy Commission (EAEC) was established ( Atomic Energy Act and its enforcement, decree No 288 1960 – 1962, the Ionizing Radiation (IR) law no 59 1962 - 1989, Several Egyptian Decrees and Ordinances for IR sources, Safeguards Agreement, Industrial Radiography 1983 – 1986 , Rules concerning Regulations used for design, construction and operation of NPPs 1994 Environmental Law no 4 2005 , EAEA - Radiation Protection Regulations 2006 - 2007 , Nuclear Material Ordinance (2006)14 2010, Nuclear Law 7/ 010 is issued in Mars 2010 for regulating all Nuclear and Radiation Activities and Facilities in Egypt. Its Executive Regulation is Prepared and issued in Oct. 011 and NRRA is functioned in March 2012.
History of Nuclear Legislation in Egypt 1957, the Egyptian Atomic Energy Commission (EAEC) was established ( Atomic Energy Act and its enforcement, decree No 288 1960 – 1962, the Ionizing Radiation (IR) law no 59 1962 - 1989, Several Egyptian Decrees and Ordinances for IR sources, Safeguards Agreement, Industrial Radiography 1983 – 1986 , Rules concerning Regulations used for design, construction and operation of NPPs 1994 Environmental Law no 4 2005 , EAEA - Radiation Protection Regulations 2006 - 2007 , Nuclear Material Ordinance (2006)14 2010, Nuclear Law 7/ 010 is issued in Mars 2010 for regulating all Nuclear and Radiation Activities and Facilities in Egypt. Its Executive Regulation is Prepared and issued in Oct. 011 and NRRA is functioned in March 2012.
 The National Regulatory Authority in EGYPT ENRRA is presently the national regulatory authority for the regulation, licensing, inspection and safeguards of all nuclear and radioactive materials and nuclear facilities in Egypt.
The National Regulatory Authority in EGYPT ENRRA is presently the national regulatory authority for the regulation, licensing, inspection and safeguards of all nuclear and radioactive materials and nuclear facilities in Egypt.
 NRRA: A long road towards independence 1983: A commission in charge of the regulation of the nuclear installation safety was established within the AEA which belongs to minister for electricity. 1991: Scope extended to radioactive materials. 2001: Scope extended to radiation protection and safety in mining. 2010: The law of mars 2010 makes NRRA an independent administrative authority supervising all nuclear and radiation activities in Egypt.
NRRA: A long road towards independence 1983: A commission in charge of the regulation of the nuclear installation safety was established within the AEA which belongs to minister for electricity. 1991: Scope extended to radioactive materials. 2001: Scope extended to radiation protection and safety in mining. 2010: The law of mars 2010 makes NRRA an independent administrative authority supervising all nuclear and radiation activities in Egypt.
 The Structure of New ENRRA consists of : Ø Safety of Nuclear Installations Sector Ø Safety of Radiological Installations Sector Ø Safeguard and Security Section Ø Institute of Nuclear Safety
The Structure of New ENRRA consists of : Ø Safety of Nuclear Installations Sector Ø Safety of Radiological Installations Sector Ø Safeguard and Security Section Ø Institute of Nuclear Safety
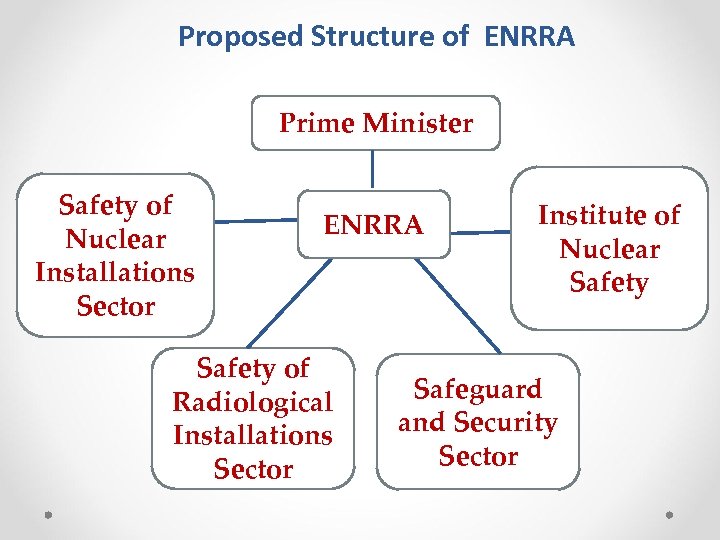 Proposed Structure of ENRRA Prime Minister Safety of Nuclear Installations Sector ENRRA Safety of Radiological Installations Sector Institute of Nuclear Safety Safeguard and Security Sector
Proposed Structure of ENRRA Prime Minister Safety of Nuclear Installations Sector ENRRA Safety of Radiological Installations Sector Institute of Nuclear Safety Safeguard and Security Sector
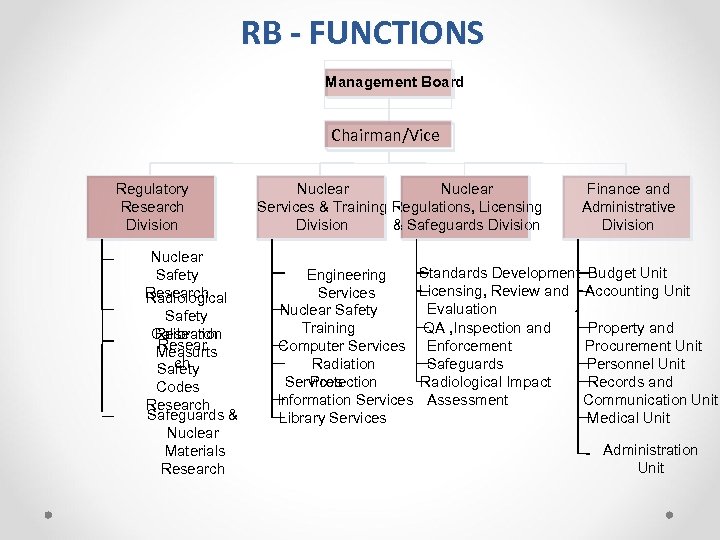 RB - FUNCTIONS Management Board Chairman/Vice Regulatory Research Division Nuclear Safety Research Radiological Safety Calibration Research Resear Measurts ch Safety Codes Research Safeguards & Nuclear Materials Research Nuclear Services & Training Regulations, Licensing Division & Safeguards Division Engineering Services Nuclear Safety Training Computer Services Radiation Protection Services Information Services Library Services Finance and Administrative Division Standards Development Budget Unit Licensing, Review and Accounting Unit Evaluation QA , Inspection and Property and Enforcement Procurement Unit Safeguards Personnel Unit Radiological Impact Records and Assessment Communication Unit Medical Unit Administration Unit
RB - FUNCTIONS Management Board Chairman/Vice Regulatory Research Division Nuclear Safety Research Radiological Safety Calibration Research Resear Measurts ch Safety Codes Research Safeguards & Nuclear Materials Research Nuclear Services & Training Regulations, Licensing Division & Safeguards Division Engineering Services Nuclear Safety Training Computer Services Radiation Protection Services Information Services Library Services Finance and Administrative Division Standards Development Budget Unit Licensing, Review and Accounting Unit Evaluation QA , Inspection and Property and Enforcement Procurement Unit Safeguards Personnel Unit Radiological Impact Records and Assessment Communication Unit Medical Unit Administration Unit
 NRRA ORGANIZATION • Based on the nuclear law 7/010, NRRA is managed by a Board of 11 members nominated by the president ( 4 members appointed full-time , 7 on Call ) • Nominated For 4 -years term. NRRA Chairman: Prof. M. Aziz Vice Chairman : Prof. S. Mongy Members: 1 -Prof. G. Orabi 2 -Prof. A. Elmsairy. . 9 - Representative of ministry of foreign affairs
NRRA ORGANIZATION • Based on the nuclear law 7/010, NRRA is managed by a Board of 11 members nominated by the president ( 4 members appointed full-time , 7 on Call ) • Nominated For 4 -years term. NRRA Chairman: Prof. M. Aziz Vice Chairman : Prof. S. Mongy Members: 1 -Prof. G. Orabi 2 -Prof. A. Elmsairy. . 9 - Representative of ministry of foreign affairs
 Nuclear and Radiation Law 7/010 New Nuclear Law 7/ 010 is issued in Mars 2010 for regulating all Nuclear and Radiation Activities and Facilities in Egypt by an independent organization belongs directly to the prime minister. Its Executive Regulation is issued in Oct. 2011. This organization is named the ENRRA. To accomplish its task , the NRRA shall establish regulations and conduct licensing process and inspection.
Nuclear and Radiation Law 7/010 New Nuclear Law 7/ 010 is issued in Mars 2010 for regulating all Nuclear and Radiation Activities and Facilities in Egypt by an independent organization belongs directly to the prime minister. Its Executive Regulation is issued in Oct. 2011. This organization is named the ENRRA. To accomplish its task , the NRRA shall establish regulations and conduct licensing process and inspection.
 Nuclear and Radiation Law 7/010 Ø 108 Articles on 7 Chapters + 7 Articles on Preface (55 PA 4) Ø Ch. 2 : NRRA (13) - Ch. 3: Licensees (37) - Ch. 4: Nuclear and Radiation Emergencies(7) Ch. 5 : Safeguard and Security(8) - Ch. 6: Civil Responsibility (18) - Ch. 7: Penelities (14) Ø The Nuclear and Radiation Law reflects the Egyptian obligations against International Treaties, Conventions and Agreements that brought into force.
Nuclear and Radiation Law 7/010 Ø 108 Articles on 7 Chapters + 7 Articles on Preface (55 PA 4) Ø Ch. 2 : NRRA (13) - Ch. 3: Licensees (37) - Ch. 4: Nuclear and Radiation Emergencies(7) Ch. 5 : Safeguard and Security(8) - Ch. 6: Civil Responsibility (18) - Ch. 7: Penelities (14) Ø The Nuclear and Radiation Law reflects the Egyptian obligations against International Treaties, Conventions and Agreements that brought into force.
 The law 7/010 : (Cont`d) Main Characteristics of ENRRA Ø Independently administrative authority. Ø It belongs directly to prime minister Ø Has powers and necessary resources to fulfill its obligations. Ø Reports directly to the prime minister
The law 7/010 : (Cont`d) Main Characteristics of ENRRA Ø Independently administrative authority. Ø It belongs directly to prime minister Ø Has powers and necessary resources to fulfill its obligations. Ø Reports directly to the prime minister
 ARTICLES From LAW 7/010(Cont`d) The NRRA must have adequate financial and other resources to meet its current requirement for staff, staff training, buildings, facilities, equipment, use of consultants, etc. to discharge its responsibilities and maintain its independence.
ARTICLES From LAW 7/010(Cont`d) The NRRA must have adequate financial and other resources to meet its current requirement for staff, staff training, buildings, facilities, equipment, use of consultants, etc. to discharge its responsibilities and maintain its independence.
 ARTICLES From Law 7/010 (Cont`d) ØNRRA should maintain a close liaison with all national organizations such as Environmental Ministry, …. ØNRRA should take the necessary measures to have competent persons in radiation and nuclear safety, safeguard, and security (Regional and Interregional Courses.
ARTICLES From Law 7/010 (Cont`d) ØNRRA should maintain a close liaison with all national organizations such as Environmental Ministry, …. ØNRRA should take the necessary measures to have competent persons in radiation and nuclear safety, safeguard, and security (Regional and Interregional Courses.
 Cooperation between NRRA at International Level (Actual Status) 1. Bilateral cooperation: ~ 3 countries (Korea - KINS, France-IRSN, Argentine-RB) 2. Multilateral organizations: IAEA, EU
Cooperation between NRRA at International Level (Actual Status) 1. Bilateral cooperation: ~ 3 countries (Korea - KINS, France-IRSN, Argentine-RB) 2. Multilateral organizations: IAEA, EU
 REGULATORY INSPECTION IN THE LAW 7/010 (Cont`d) Ø Nuclear Energy Law 7/2010 (art. 53) states that inspection to the nuclear installations and installations that use ionizing radiation shall be performed by the NRRA in order to ensure that the licensing requirements and nuclear safety regulations are complied with. Ø Further directives on the Regulatory Inspection program, procedure, conduct of inspection will be prepared Ø Inspection may be conducted periodically or accidentally, with or without prior notification.
REGULATORY INSPECTION IN THE LAW 7/010 (Cont`d) Ø Nuclear Energy Law 7/2010 (art. 53) states that inspection to the nuclear installations and installations that use ionizing radiation shall be performed by the NRRA in order to ensure that the licensing requirements and nuclear safety regulations are complied with. Ø Further directives on the Regulatory Inspection program, procedure, conduct of inspection will be prepared Ø Inspection may be conducted periodically or accidentally, with or without prior notification.
 LAW 7/010 : RIGHTS OF INSPECTORS (Cont`d) VISITS TO THE FACILITY/ DESIGNER during all stages of the authorization process for: Øcomplementary information Øcheck of the claims made in the documentation Øimprovement in practical understanding of Safety Issues Øestablishment of links with operator’s specialists Øcheck of the QA system of the operator, manufacturers, suppliers
LAW 7/010 : RIGHTS OF INSPECTORS (Cont`d) VISITS TO THE FACILITY/ DESIGNER during all stages of the authorization process for: Øcomplementary information Øcheck of the claims made in the documentation Øimprovement in practical understanding of Safety Issues Øestablishment of links with operator’s specialists Øcheck of the QA system of the operator, manufacturers, suppliers
 Manpower Needed For NRRA The NRRA should : Ø Have full time staff for performing assessments or evaluating the adequacy of the assessments performed for the NRRA by consultants. This manpower requirement and technical competence applies also to regulatory inspections Ø Have staff composed largely of individuals possessing broad technical expertise for engineering judgment and nuclear health and safety skills, who are capable of assessing on an overall basis the safety of a nuclear power plant.
Manpower Needed For NRRA The NRRA should : Ø Have full time staff for performing assessments or evaluating the adequacy of the assessments performed for the NRRA by consultants. This manpower requirement and technical competence applies also to regulatory inspections Ø Have staff composed largely of individuals possessing broad technical expertise for engineering judgment and nuclear health and safety skills, who are capable of assessing on an overall basis the safety of a nuclear power plant.
 FUNCTIONS OF RB (cont`d) 1 - Major functions Ø Authorization Ø Review and assessment Ø Inspection and enforcement Ø Development of regulations and guides 2 - Supplementary functions Ø Coordinating and monitoring Research and Development Ø Emergency preparedness Ø International Co-operation
FUNCTIONS OF RB (cont`d) 1 - Major functions Ø Authorization Ø Review and assessment Ø Inspection and enforcement Ø Development of regulations and guides 2 - Supplementary functions Ø Coordinating and monitoring Research and Development Ø Emergency preparedness Ø International Co-operation
 NRRA Figures CURRENT STRENGTH = 200 PROFESSIONALS. · PROFFESSIONALS : Scientists, Engineers, Health / Medical Physicists , Lawers · Administration and Financial Personnel (300 P) · Supporting Staff (University, Industry, ……. . )
NRRA Figures CURRENT STRENGTH = 200 PROFESSIONALS. · PROFFESSIONALS : Scientists, Engineers, Health / Medical Physicists , Lawers · Administration and Financial Personnel (300 P) · Supporting Staff (University, Industry, ……. . )
 Technical Support For NRRA Technical or other experts professional for advice or services: Ø Ø Ø Advisory bodies Technical support organizations (TSO) Consultants Other regulatory bodies National and international agencies
Technical Support For NRRA Technical or other experts professional for advice or services: Ø Ø Ø Advisory bodies Technical support organizations (TSO) Consultants Other regulatory bodies National and international agencies
 QUALIFICATION PROCESS OF NRRA STAFF • Step 1: Determine the Regulatory Function of Each Unit and the Required Competencies • Step 2: Determine Tasks Corresponding to the Regulatory Functions • Step 3: Determine the competencies and knowledge, skills and attitudes (KSAs) Levels Needed to Perform the Regulatory Functions • Step 4: Conduct the Self-assessment of the Existing Competencies
QUALIFICATION PROCESS OF NRRA STAFF • Step 1: Determine the Regulatory Function of Each Unit and the Required Competencies • Step 2: Determine Tasks Corresponding to the Regulatory Functions • Step 3: Determine the competencies and knowledge, skills and attitudes (KSAs) Levels Needed to Perform the Regulatory Functions • Step 4: Conduct the Self-assessment of the Existing Competencies
 Human Resources Plan In NRRA A human resources plan is developed to: 1. Define number of staff needed and essential knowledge, skills, abilities 2. Address recruitment and rotation, how to obtain staff with the appropriate competence and skills, and strategy to compensate for the loss of qualified staff 3. Address current staffing levels, distribution, composition and lay out the plan for aligning resources to meet the organizational needs
Human Resources Plan In NRRA A human resources plan is developed to: 1. Define number of staff needed and essential knowledge, skills, abilities 2. Address recruitment and rotation, how to obtain staff with the appropriate competence and skills, and strategy to compensate for the loss of qualified staff 3. Address current staffing levels, distribution, composition and lay out the plan for aligning resources to meet the organizational needs
 Organizational Evolution in NRRA Ø Cultural Shift (e. g. from research to regulatory oversight) Ø Changes of activities from basic research to safety and regulatory research Ø Management of organizational change process should be used to make adjustments
Organizational Evolution in NRRA Ø Cultural Shift (e. g. from research to regulatory oversight) Ø Changes of activities from basic research to safety and regulatory research Ø Management of organizational change process should be used to make adjustments
 Competencies Criteria Ø Academic qualifications Ø Work experience Ø Skills (technical, administrative, management, etc. ) Ø Related work experience in facilities and activities including the regulation of non-nuclear hazardous facilities Ø Knowledge of the regulated facilities and activities
Competencies Criteria Ø Academic qualifications Ø Work experience Ø Skills (technical, administrative, management, etc. ) Ø Related work experience in facilities and activities including the regulation of non-nuclear hazardous facilities Ø Knowledge of the regulated facilities and activities
 Training of NRRA staff • • • A training program is established on the basis of IAEA / Four COMPETENCIES QUARDANTS Q 1: Legal Basis and Regulatory Process Q 2: Technical Disciplines Q 3: Regulatory Practice Q 4. Personal and Interpersonal Effectiveness
Training of NRRA staff • • • A training program is established on the basis of IAEA / Four COMPETENCIES QUARDANTS Q 1: Legal Basis and Regulatory Process Q 2: Technical Disciplines Q 3: Regulatory Practice Q 4. Personal and Interpersonal Effectiveness
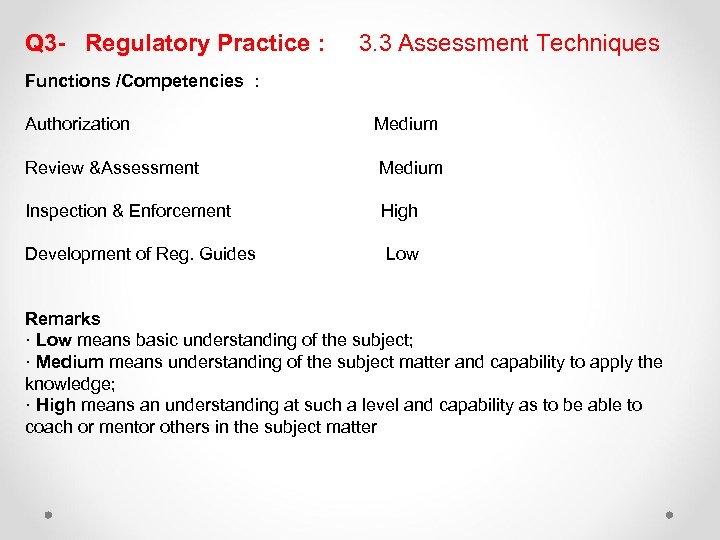 Q 3 - Regulatory Practice : 3. 3 Assessment Techniques Functions /Competencies : Authorization Medium Review &Assessment Medium Inspection & Enforcement High Development of Reg. Guides Low Remarks · Low means basic understanding of the subject; · Medium means understanding of the subject matter and capability to apply the knowledge; · High means an understanding at such a level and capability as to be able to coach or mentor others in the subject matter
Q 3 - Regulatory Practice : 3. 3 Assessment Techniques Functions /Competencies : Authorization Medium Review &Assessment Medium Inspection & Enforcement High Development of Reg. Guides Low Remarks · Low means basic understanding of the subject; · Medium means understanding of the subject matter and capability to apply the knowledge; · High means an understanding at such a level and capability as to be able to coach or mentor others in the subject matter
 Planned Training Program of NRRA staff Ø Self Studies Ø National Training Courses (domestic and international experts) Ø Training Abroad through : • Co-operation with International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) via TC projects, and fellowships • Cooperation with other organizations such as EU & KINS
Planned Training Program of NRRA staff Ø Self Studies Ø National Training Courses (domestic and international experts) Ø Training Abroad through : • Co-operation with International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) via TC projects, and fellowships • Cooperation with other organizations such as EU & KINS
 No of regulatory staff needed for licensing of NPP According to the IAEA recommendations : 1. Siting: (7 -10 P) Geology, Seismology – Hydrology Civil Engineering – Meteorology, Soil Mechanics , Quality Assurance. 2. Mechanical: Equipment & Components and System Structural Mechanics, Fracture Mechanics, Metallurgy, Corrosion Chemistry, NDT , Quality Assurance: (6 -8 p) 3. Piping System: Stress Analysis, Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer , Quality Assurance: (2 -3 p) 4. Electronic: Instrumentation & Control and Computer programs, System Analysis, Control Theory, Quality Assurance: (1 -2 p) 5. Reactor Core: (1 -3 p) Reactor Physics, Criticality Analysis, Shielding, Fuel Performance, Quality Assurance
No of regulatory staff needed for licensing of NPP According to the IAEA recommendations : 1. Siting: (7 -10 P) Geology, Seismology – Hydrology Civil Engineering – Meteorology, Soil Mechanics , Quality Assurance. 2. Mechanical: Equipment & Components and System Structural Mechanics, Fracture Mechanics, Metallurgy, Corrosion Chemistry, NDT , Quality Assurance: (6 -8 p) 3. Piping System: Stress Analysis, Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer , Quality Assurance: (2 -3 p) 4. Electronic: Instrumentation & Control and Computer programs, System Analysis, Control Theory, Quality Assurance: (1 -2 p) 5. Reactor Core: (1 -3 p) Reactor Physics, Criticality Analysis, Shielding, Fuel Performance, Quality Assurance
 No of regulatory staff needed for licensing of NPP ( cont. d) 6. Radiological Control (2 -3 p) Radiation Protection, Radiation Safety, Radiological Consequences, Dosimeter, Environmental Protection, Waste Management, Quality Assurance 7. Electrical Systems (1 -2 p) Electric Power Supply, Network Equipment, Quality Assurance 8. Nuclear Safety (1 -2 p) Safety Analysis, Probabilistic Safety Assessment, Reliability, System Integration. 9. Reactor Operation Safety (1 -2 p) Reactor Operation, Human Factors, Fire Protection, Plant Chemistry
No of regulatory staff needed for licensing of NPP ( cont. d) 6. Radiological Control (2 -3 p) Radiation Protection, Radiation Safety, Radiological Consequences, Dosimeter, Environmental Protection, Waste Management, Quality Assurance 7. Electrical Systems (1 -2 p) Electric Power Supply, Network Equipment, Quality Assurance 8. Nuclear Safety (1 -2 p) Safety Analysis, Probabilistic Safety Assessment, Reliability, System Integration. 9. Reactor Operation Safety (1 -2 p) Reactor Operation, Human Factors, Fire Protection, Plant Chemistry
 No of regulatory staff needed for licensing of NPP ( cont. d) 10. Safeguard (1 -2 p) MC&A, Physical Protection, Quality Assurance 11. Facility Support : Maintenance & Surveillance (4 p) Emergency Planning & Preparedness (1 -2 p) Management Organization & Control and Safety Culture (1 p) Training of Personnel (1 -2 p) Transportation (1 p) 12. Legislation and Regulation (7 -10) 13. QA/QC Including Surveillance, Audits and Inspection (2 -3) Total No. Proposed= 90/120 QP FOR REVIEWING, ASSESSMENT, INSPECTION
No of regulatory staff needed for licensing of NPP ( cont. d) 10. Safeguard (1 -2 p) MC&A, Physical Protection, Quality Assurance 11. Facility Support : Maintenance & Surveillance (4 p) Emergency Planning & Preparedness (1 -2 p) Management Organization & Control and Safety Culture (1 p) Training of Personnel (1 -2 p) Transportation (1 p) 12. Legislation and Regulation (7 -10) 13. QA/QC Including Surveillance, Audits and Inspection (2 -3) Total No. Proposed= 90/120 QP FOR REVIEWING, ASSESSMENT, INSPECTION
 On Job Training Needs For NRRA Quality Assurance And Regulations Branch Regulations Auditing Quality assurance program Quality control during manufacturing phase Quality control during construction phase 5 P 3 P 2 P 4 P 4 P
On Job Training Needs For NRRA Quality Assurance And Regulations Branch Regulations Auditing Quality assurance program Quality control during manufacturing phase Quality control during construction phase 5 P 3 P 2 P 4 P 4 P
 TRAINING NEEDS FOR REGULATORY INSPECTION OF NPPs Construction phase In house training (civil, mechanical, electrical, nuclear work) Fabrication Phase On job training abroad (mechanical, electrical, nuclear equipment and components)
TRAINING NEEDS FOR REGULATORY INSPECTION OF NPPs Construction phase In house training (civil, mechanical, electrical, nuclear work) Fabrication Phase On job training abroad (mechanical, electrical, nuclear equipment and components)
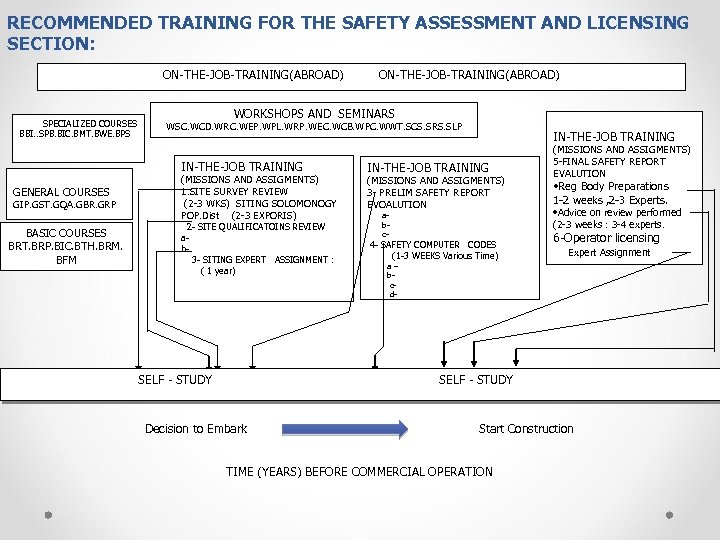 RECOMMENDED TRAINING FOR THE SAFETY ASSESSMENT AND LICENSING SECTION: ON-THE-JOB-TRAINING(ABROAD) SPECIALIZED COURSES BBI. . SPB. BIC. BMT. BWE. BPS WORKSHOPS AND SEMINARS WSC. WCD. WRC. WEP. WPL. WRP. WEC. WCB. WPC. WWT. SCS. SRS. SLP IN-THE-JOB TRAINING GENERAL COURSES GIP. GST. GQA. GBR. GRP BASIC COURSES BRT. BRP. BIC. BTH. BRM. BFM ON-THE-JOB-TRAINING(ABROAD) (MISSIONS AND ASSIGMENTS) 1. SITE SURVEY REVIEW (2 -3 WKS) SITING SOLOMONOGY POP. Dist (2 -3 EXPORIS) 2 - SITE QUALIFICATOINS REVIEW ab 3 - SITING EXPERT ASSIGNMENT : ( 1 year) SELF - STUDY IN-THE-JOB TRAINING (MISSIONS AND ASSIGMENTS) 3 - PRELIM SAFETY REPORT EVOALUTION abc- 4 - SAFETY COMPUTER CODES (1 -3 WEEKS Various Time) (MISSIONS AND ASSIGMENTS) 5 -FINAL SAFETY REPORT EVALUTION • Reg Body Preparations 1 -2 weeks , 2 -3 Experts. • Advice on review performed (2 -3 weeks : 3 -4 experts. 6 -Operator licensing Expert Assignment a– bcd- SELF - STUDY Decision to Embark Start Construction TIME (YEARS) BEFORE COMMERCIAL OPERATION
RECOMMENDED TRAINING FOR THE SAFETY ASSESSMENT AND LICENSING SECTION: ON-THE-JOB-TRAINING(ABROAD) SPECIALIZED COURSES BBI. . SPB. BIC. BMT. BWE. BPS WORKSHOPS AND SEMINARS WSC. WCD. WRC. WEP. WPL. WRP. WEC. WCB. WPC. WWT. SCS. SRS. SLP IN-THE-JOB TRAINING GENERAL COURSES GIP. GST. GQA. GBR. GRP BASIC COURSES BRT. BRP. BIC. BTH. BRM. BFM ON-THE-JOB-TRAINING(ABROAD) (MISSIONS AND ASSIGMENTS) 1. SITE SURVEY REVIEW (2 -3 WKS) SITING SOLOMONOGY POP. Dist (2 -3 EXPORIS) 2 - SITE QUALIFICATOINS REVIEW ab 3 - SITING EXPERT ASSIGNMENT : ( 1 year) SELF - STUDY IN-THE-JOB TRAINING (MISSIONS AND ASSIGMENTS) 3 - PRELIM SAFETY REPORT EVOALUTION abc- 4 - SAFETY COMPUTER CODES (1 -3 WEEKS Various Time) (MISSIONS AND ASSIGMENTS) 5 -FINAL SAFETY REPORT EVALUTION • Reg Body Preparations 1 -2 weeks , 2 -3 Experts. • Advice on review performed (2 -3 weeks : 3 -4 experts. 6 -Operator licensing Expert Assignment a– bcd- SELF - STUDY Decision to Embark Start Construction TIME (YEARS) BEFORE COMMERCIAL OPERATION
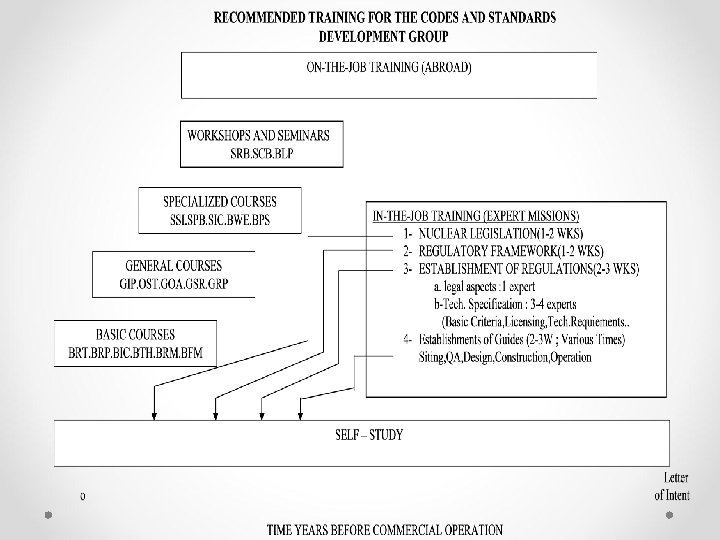
 Basic/Practical Courses (3 to 6 Months) (. )(x)(-) - BRT : Basic Reactor Technology (. )(x)(-) - BRP : Basic Radiation Protection (. )(x)(-) - BIC : Basic Instrumentation & Control (. )(x)(-) - BTH : Thermal-Hydraulics of Reactor Systems (. )(x)(-) - BRM : Reactor Materials (. )(x)(-) - BFM : Basic Fuel Management (x) BCI : Concrete Technology & Codes (x) BWI : Welding Technology & Codes (x) BND : Non-Destructive Examination (. ) Safety Assessment & Licensing Section (x) Inspection Section (-) Codes & Standards Group
Basic/Practical Courses (3 to 6 Months) (. )(x)(-) - BRT : Basic Reactor Technology (. )(x)(-) - BRP : Basic Radiation Protection (. )(x)(-) - BIC : Basic Instrumentation & Control (. )(x)(-) - BTH : Thermal-Hydraulics of Reactor Systems (. )(x)(-) - BRM : Reactor Materials (. )(x)(-) - BFM : Basic Fuel Management (x) BCI : Concrete Technology & Codes (x) BWI : Welding Technology & Codes (x) BND : Non-Destructive Examination (. ) Safety Assessment & Licensing Section (x) Inspection Section (-) Codes & Standards Group
 General Training Courses Ø Ø Ø Ø (. )( x)(-) GIP : Introduction To Nuclear Power (. )( x)(-) GST : Safety Technology Of Nuclear Power Plants (. )( x)(-) GST : Quality Assurance For Nuclear Plants (. )( x)(-) GSR : Safety Analysis Review (x)(-) GSL : Safety Inspection and Surveillance for a NPP (x)(- ) GOS : Operational Safety of Nuclear Power Plants (. )( x)(-) GRP : Radiation Protection in Nuclear Power Plants (. ) Safety Assessment & Licensing Section (x) Inspection Section (-) Codes & Standards Group
General Training Courses Ø Ø Ø Ø (. )( x)(-) GIP : Introduction To Nuclear Power (. )( x)(-) GST : Safety Technology Of Nuclear Power Plants (. )( x)(-) GST : Quality Assurance For Nuclear Plants (. )( x)(-) GSR : Safety Analysis Review (x)(-) GSL : Safety Inspection and Surveillance for a NPP (x)(- ) GOS : Operational Safety of Nuclear Power Plants (. )( x)(-) GRP : Radiation Protection in Nuclear Power Plants (. ) Safety Assessment & Licensing Section (x) Inspection Section (-) Codes & Standards Group
 Specialized Training Courses Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø SEP : Energy Planning and Economics (With Special Attention to Nuclear Energy) (. )(x)(-)SSI : Safety In Siting of Nuclear Power Plants (. )(x)(-) SPB : Technology and Safety of pressure-Bearing Systems and Components (. )(x)(-) SIC : Technology and Safety of NPP Instrumentation and Control Systems (. )(x)SMT : Maintenance and Periodic Testing for Safety of Nuclear Power Plants (x)SCH : Chemistry in NPP Operation (. )(x)(-) SWE: Radioactive waste and Effluent Control for NPPs (. )(-)SPS : Probabilistic Safety Analysis in Safety Review SEP : Emergency Planning and Preparedness (. ) Safety Assessment & Licensing Section (x) Inspection Section (-) Codes & Standards Group
Specialized Training Courses Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø SEP : Energy Planning and Economics (With Special Attention to Nuclear Energy) (. )(x)(-)SSI : Safety In Siting of Nuclear Power Plants (. )(x)(-) SPB : Technology and Safety of pressure-Bearing Systems and Components (. )(x)(-) SIC : Technology and Safety of NPP Instrumentation and Control Systems (. )(x)SMT : Maintenance and Periodic Testing for Safety of Nuclear Power Plants (x)SCH : Chemistry in NPP Operation (. )(x)(-) SWE: Radioactive waste and Effluent Control for NPPs (. )(-)SPS : Probabilistic Safety Analysis in Safety Review SEP : Emergency Planning and Preparedness (. ) Safety Assessment & Licensing Section (x) Inspection Section (-) Codes & Standards Group
 Workshop Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø (. )(x) (. )(x) WSC: Seismic Characteristics and data in safety analysis Reports WCD: Core Nuclear Design and Reactivity Controls WRC: Reactor Coolant system Design and Engineered safeguards WEP: Electric Power supply performance Analysis WPL: Plant Layout Influence on safely WRP: Radiation Protection (ALARA Consideration) WEC: Energy Conversion and Auxiliary Systems WCS: Containment System Design WPC: Reactor Protection and Control System WWT: Effluent Waste Treatment Systems (. ) Safety Assessment & Licensing Section (x) Inspection Section
Workshop Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø (. )(x) (. )(x) WSC: Seismic Characteristics and data in safety analysis Reports WCD: Core Nuclear Design and Reactivity Controls WRC: Reactor Coolant system Design and Engineered safeguards WEP: Electric Power supply performance Analysis WPL: Plant Layout Influence on safely WRP: Radiation Protection (ALARA Consideration) WEC: Energy Conversion and Auxiliary Systems WCS: Containment System Design WPC: Reactor Protection and Control System WWT: Effluent Waste Treatment Systems (. ) Safety Assessment & Licensing Section (x) Inspection Section
 Seminars Ø Ø Ø Ø (. )(x)(-)SCS: Safety Codes and Standards (. )(x)(-) SRP: Regulatory Body Organization and management (. )(x)(-) SLP: Regulatory Licensing Process (x) SRI: Regulatory Inspection (x) SQA: QA for Nuclear power Projects (x) SMO: Management for Operation of NPPS SAC: Diagnosis and Response in Abnormal Occurrences SPM: Project Management (. ) Safety Assessment & Licensing Section (x) Inspection Section (-) Codes & Standards Group
Seminars Ø Ø Ø Ø (. )(x)(-)SCS: Safety Codes and Standards (. )(x)(-) SRP: Regulatory Body Organization and management (. )(x)(-) SLP: Regulatory Licensing Process (x) SRI: Regulatory Inspection (x) SQA: QA for Nuclear power Projects (x) SMO: Management for Operation of NPPS SAC: Diagnosis and Response in Abnormal Occurrences SPM: Project Management (. ) Safety Assessment & Licensing Section (x) Inspection Section (-) Codes & Standards Group
 Practical Training (6 To 12 months) Ø OJ : On-the-Job Training in Organization involved in Nuclear Power Projects (e. g. Regulatory Body , Utility , Architect. Engineer) in Countries With Nuclear Programs Ø OS : Participation in Plant Activities on- Site (e. g. Systems Installation , Commissioning Tests , Procedures Preparation)
Practical Training (6 To 12 months) Ø OJ : On-the-Job Training in Organization involved in Nuclear Power Projects (e. g. Regulatory Body , Utility , Architect. Engineer) in Countries With Nuclear Programs Ø OS : Participation in Plant Activities on- Site (e. g. Systems Installation , Commissioning Tests , Procedures Preparation)
 Related IAEA Safety Standards Ø IAEA Safety Requirements GS-R-1, Governmental, Legal and Regulatory Framework for Safety Ø IAEA GS-R-3, Management System for Facilities and Activities Ø IAEA GS-G-3. 1, Application of the Management System for Facilities and Activities Ø IAEA GS-G-1. 1, Organization and Staffing of the Regulatory Body for Nuclear Facilities Ø IAEA Draft safety guide DSS 424 Establishing the Safety Infrastructure for a Nuclear Power Program Ø IAEA-TECDOC-1254, Training the staff of the regulatory body for nuclear facilities: A competency framework Ø IAEA Draft Safety Report, “A Framework for Managing a Regulatory Body’s Competence”
Related IAEA Safety Standards Ø IAEA Safety Requirements GS-R-1, Governmental, Legal and Regulatory Framework for Safety Ø IAEA GS-R-3, Management System for Facilities and Activities Ø IAEA GS-G-3. 1, Application of the Management System for Facilities and Activities Ø IAEA GS-G-1. 1, Organization and Staffing of the Regulatory Body for Nuclear Facilities Ø IAEA Draft safety guide DSS 424 Establishing the Safety Infrastructure for a Nuclear Power Program Ø IAEA-TECDOC-1254, Training the staff of the regulatory body for nuclear facilities: A competency framework Ø IAEA Draft Safety Report, “A Framework for Managing a Regulatory Body’s Competence”
 Conclusion Egypt is NOW preparing for entering in NPP field and has now established an independent regulatory body and will take the necessary arrangements for constructing a more efficient & effective RB through good regulations and high quality regulatory management with sufficient competent staff and well qualified inspectors. 48
Conclusion Egypt is NOW preparing for entering in NPP field and has now established an independent regulatory body and will take the necessary arrangements for constructing a more efficient & effective RB through good regulations and high quality regulatory management with sufficient competent staff and well qualified inspectors. 48
 Thank you for your attention
Thank you for your attention


