2a6230816d2c46d97ac60b75e0f13481.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 87
 TH GRADE 8 ENERGY UNIT
TH GRADE 8 ENERGY UNIT
 What is ENERGY? • ENERGY – The ability to do work or create a change. • Law of Conservation: Energy is neither created nor destroyed…only changes form & position. • WORK – Force exerted on an object (matter) that causes it to move…energy is needed! • W : force x distance moved = ____ joules
What is ENERGY? • ENERGY – The ability to do work or create a change. • Law of Conservation: Energy is neither created nor destroyed…only changes form & position. • WORK – Force exerted on an object (matter) that causes it to move…energy is needed! • W : force x distance moved = ____ joules
 Kinetic Energy • Kinetic Energy (KE) – The energy of an object due to its motion. • How to find kinetic energy: KE: Mass of object x Velocity ² ÷ 2 =____Joules
Kinetic Energy • Kinetic Energy (KE) – The energy of an object due to its motion. • How to find kinetic energy: KE: Mass of object x Velocity ² ÷ 2 =____Joules
 Potential Energy / GPE • Potential Energy – Energy that is stored and held in readiness. • Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE) – Potential energy that depends on the height of object from surface. • GPE: height of object (h) x mass (m) =
Potential Energy / GPE • Potential Energy – Energy that is stored and held in readiness. • Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE) – Potential energy that depends on the height of object from surface. • GPE: height of object (h) x mass (m) =
 LAB Reviews • Transfer of energy means to pass energy from one place to another (one object to another) without changing forms. • Transformation of energy means that energy has changed from one form to another.
LAB Reviews • Transfer of energy means to pass energy from one place to another (one object to another) without changing forms. • Transformation of energy means that energy has changed from one form to another.
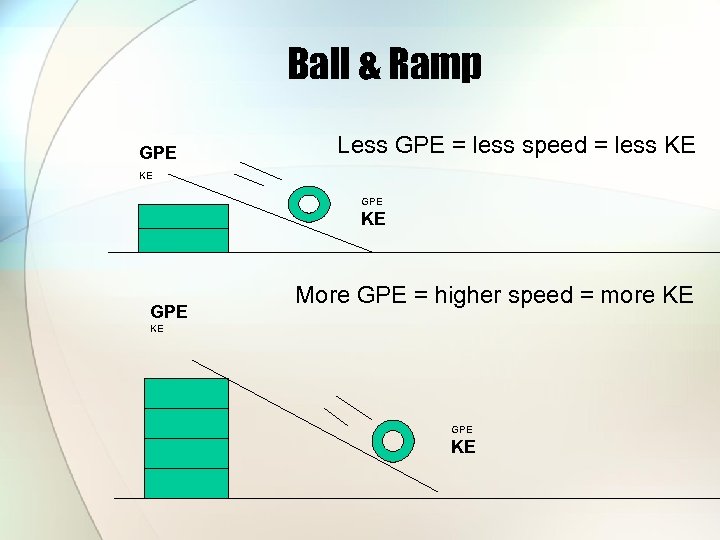 Ball & Ramp GPE Less GPE = less speed = less KE KE GPE More GPE = higher speed = more KE KE GPE KE
Ball & Ramp GPE Less GPE = less speed = less KE KE GPE More GPE = higher speed = more KE KE GPE KE
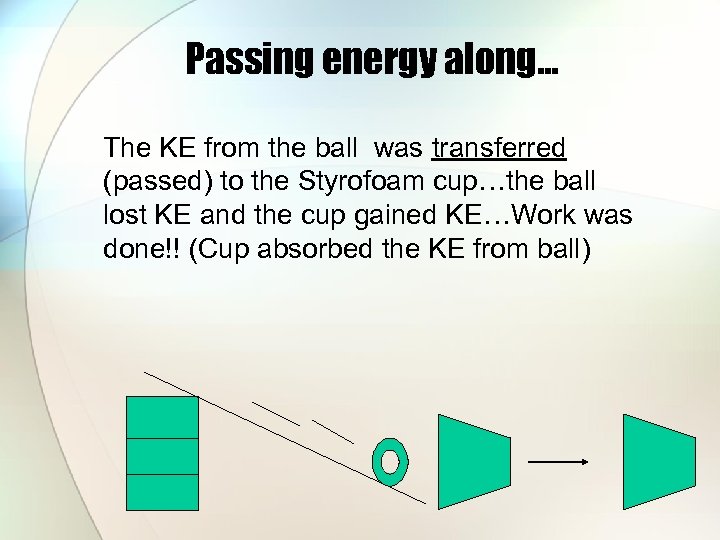 Passing energy along… The KE from the ball was transferred (passed) to the Styrofoam cup…the ball lost KE and the cup gained KE…Work was done!! (Cup absorbed the KE from ball)
Passing energy along… The KE from the ball was transferred (passed) to the Styrofoam cup…the ball lost KE and the cup gained KE…Work was done!! (Cup absorbed the KE from ball)
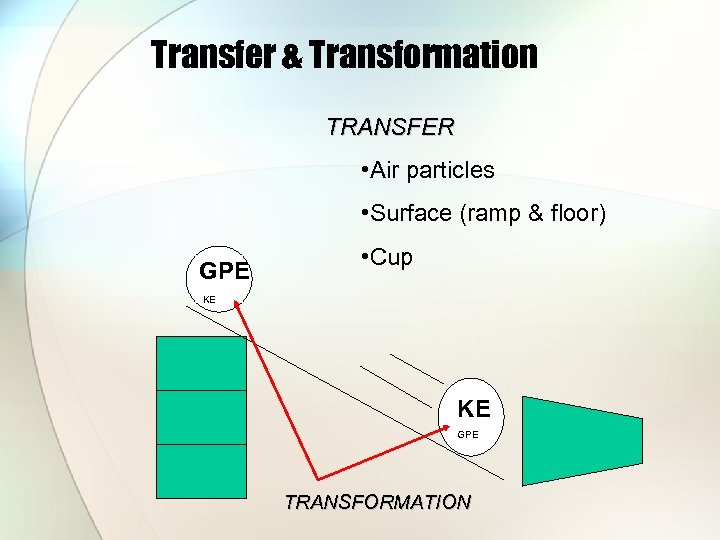 Transfer & Transformation TRANSFER • Air particles • Surface (ramp & floor) GPE • Cup KE KE GPE TRANSFORMATION
Transfer & Transformation TRANSFER • Air particles • Surface (ramp & floor) GPE • Cup KE KE GPE TRANSFORMATION
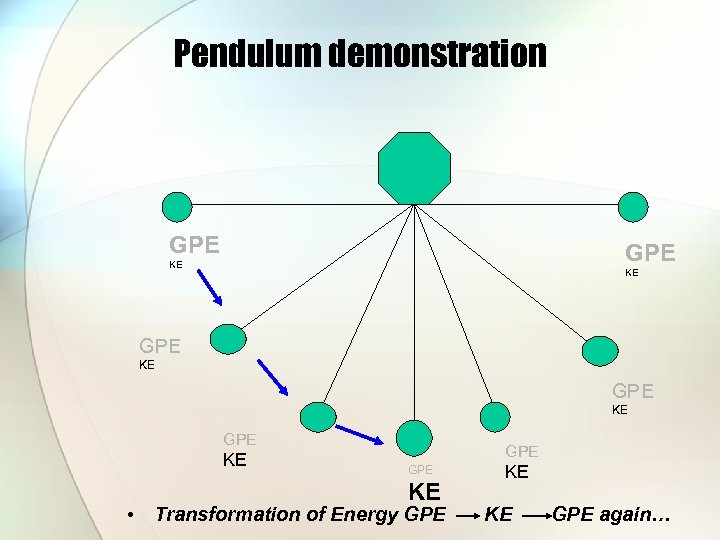 Pendulum demonstration GPE KE KE GPE KE • GPE KE Transformation of Energy GPE KE KE GPE again…
Pendulum demonstration GPE KE KE GPE KE • GPE KE Transformation of Energy GPE KE KE GPE again…
 Roller Coaster ‘W’ has the greatest GPE, so ‘X’ will have the greatest KE. The rest of the roller coaster ride will run fine because it has enough initial KE to make it over the rest of the smaller hills.
Roller Coaster ‘W’ has the greatest GPE, so ‘X’ will have the greatest KE. The rest of the roller coaster ride will run fine because it has enough initial KE to make it over the rest of the smaller hills.
 Energy transfer (absorbed) – activity #5 • How does type of surface affect energy transfer? • Surfaces whose particles are tightly packed can only absorb a little bit of energy at a time (many bounces) • Surfaces whose particles are loosely packed can absorb more energy at a time (less bounces)
Energy transfer (absorbed) – activity #5 • How does type of surface affect energy transfer? • Surfaces whose particles are tightly packed can only absorb a little bit of energy at a time (many bounces) • Surfaces whose particles are loosely packed can absorb more energy at a time (less bounces)
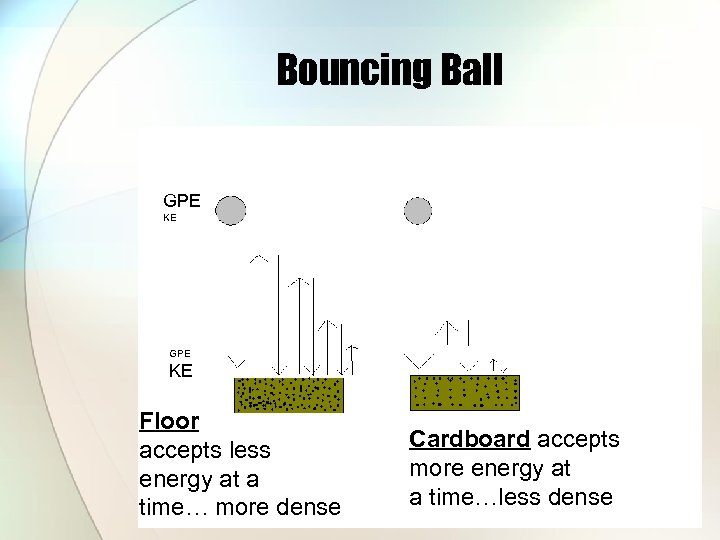 Bouncing Ball GPE KE Floor accepts less energy at a time… more dense Cardboard accepts more energy at a time…less dense
Bouncing Ball GPE KE Floor accepts less energy at a time… more dense Cardboard accepts more energy at a time…less dense
 Activity #7 (transfer of energy) KE is transferred from person rope wood.
Activity #7 (transfer of energy) KE is transferred from person rope wood.
 Activity #7 (transformation of energy Because of FRICTION between the rope and wood, the KE transformed into heat !! HOT
Activity #7 (transformation of energy Because of FRICTION between the rope and wood, the KE transformed into heat !! HOT
 Phase Change Particle Model Low KE medium KE High KE
Phase Change Particle Model Low KE medium KE High KE
 Phase change names melting freezing vaporization condensation
Phase change names melting freezing vaporization condensation
 What is Thermal Energy? • The TOTAL energy of all the particles that make up a substance (matter). • 3 Factors to find thermal energy: 1. Temp. 2. Amount (mass or volume) 3. Phase (solid, liquid, or gas)
What is Thermal Energy? • The TOTAL energy of all the particles that make up a substance (matter). • 3 Factors to find thermal energy: 1. Temp. 2. Amount (mass or volume) 3. Phase (solid, liquid, or gas)
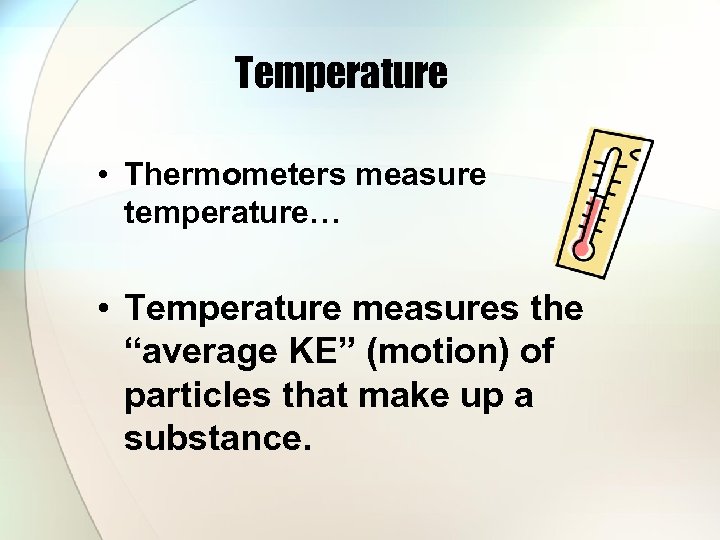 Temperature • Thermometers measure temperature… • Temperature measures the “average KE” (motion) of particles that make up a substance.
Temperature • Thermometers measure temperature… • Temperature measures the “average KE” (motion) of particles that make up a substance.
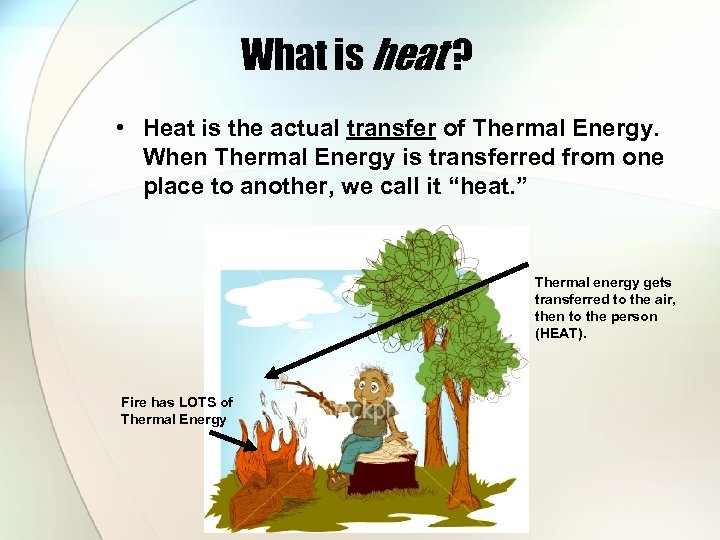 What is heat ? • Heat is the actual transfer of Thermal Energy. When Thermal Energy is transferred from one place to another, we call it “heat. ” Thermal energy gets transferred to the air, then to the person (HEAT). Fire has LOTS of Thermal Energy
What is heat ? • Heat is the actual transfer of Thermal Energy. When Thermal Energy is transferred from one place to another, we call it “heat. ” Thermal energy gets transferred to the air, then to the person (HEAT). Fire has LOTS of Thermal Energy
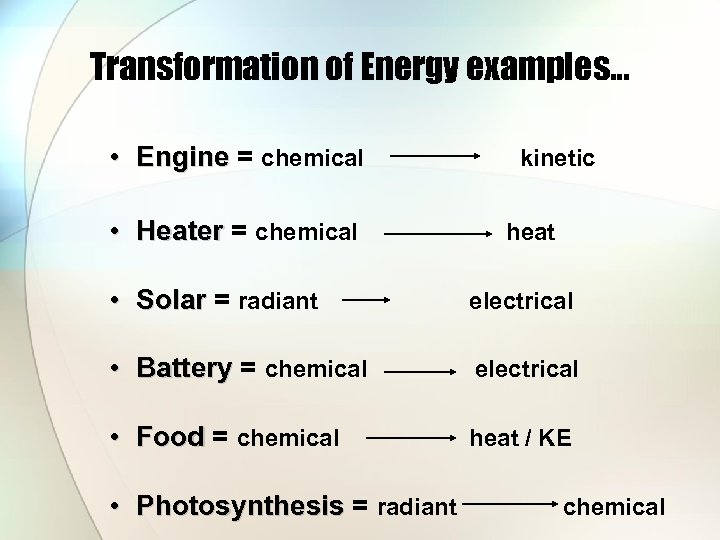 Transformation of Energy examples… • Engine = chemical kinetic Engine • Heater = chemical Heater • Solar = radiant Solar heat electrical • Battery = chemical electrical Battery • Food = chemical Food heat / KE • Photosynthesis = radiant chemical Photosynthesis
Transformation of Energy examples… • Engine = chemical kinetic Engine • Heater = chemical Heater • Solar = radiant Solar heat electrical • Battery = chemical electrical Battery • Food = chemical Food heat / KE • Photosynthesis = radiant chemical Photosynthesis
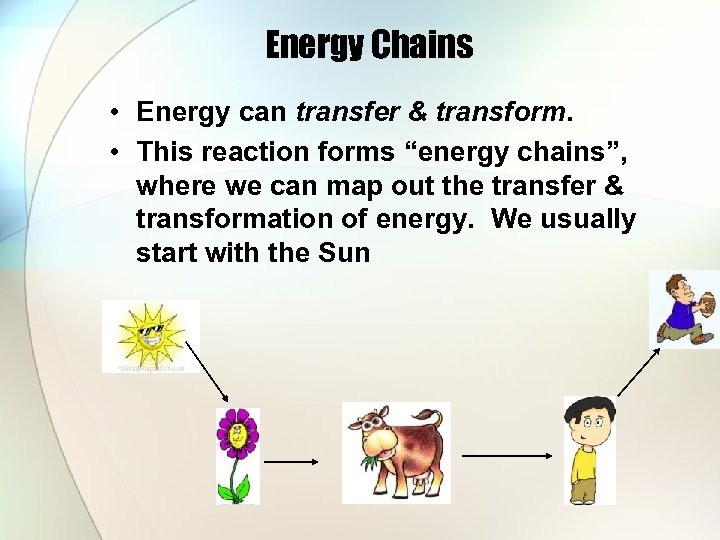 Energy Chains • Energy can transfer & transform. • This reaction forms “energy chains”, where we can map out the transfer & transformation of energy. We usually start with the Sun
Energy Chains • Energy can transfer & transform. • This reaction forms “energy chains”, where we can map out the transfer & transformation of energy. We usually start with the Sun
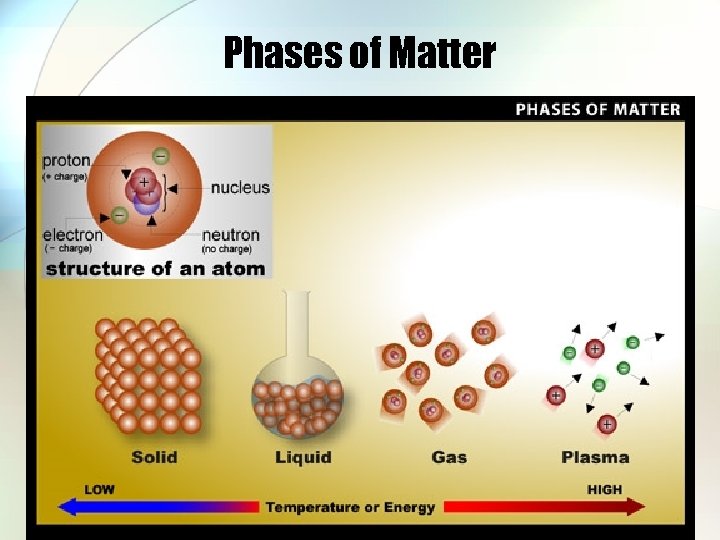 Phases of Matter
Phases of Matter
 What becomes of KE? What becomes of KE after it transfers? • When KE transfers from one place to another through physical contact, it not only gives the energy of motion, but also transforms into heat energy! • Friction – A resistance between 2 or more particles or objects causes KE to transfer.
What becomes of KE? What becomes of KE after it transfers? • When KE transfers from one place to another through physical contact, it not only gives the energy of motion, but also transforms into heat energy! • Friction – A resistance between 2 or more particles or objects causes KE to transfer.
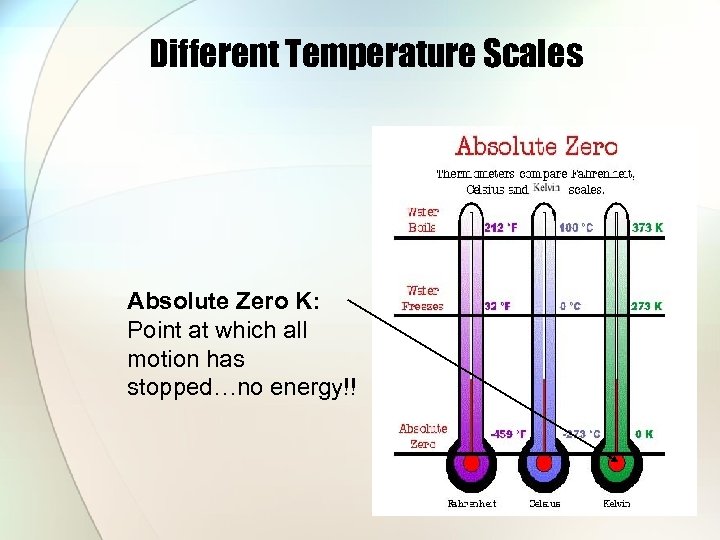 Different Temperature Scales Absolute Zero K: Point at which all motion has stopped…no energy!!
Different Temperature Scales Absolute Zero K: Point at which all motion has stopped…no energy!!
 Force • In order for KE to be transferred or transformed, there must be something making “matter” accelerate or change direction. • Force = is a push or pull that causes a substance with mass (takes up space) to accelerate in a certain direction. • Force can change amount of friction!!!
Force • In order for KE to be transferred or transformed, there must be something making “matter” accelerate or change direction. • Force = is a push or pull that causes a substance with mass (takes up space) to accelerate in a certain direction. • Force can change amount of friction!!!
 Thermal Expansion & Contraction • In physics, thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in length or volume in response to a change in temperature. When a substance is heated, its particles move around more vigorously and by doing so generally maintain a greater average separation. This requires more space!!
Thermal Expansion & Contraction • In physics, thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in length or volume in response to a change in temperature. When a substance is heated, its particles move around more vigorously and by doing so generally maintain a greater average separation. This requires more space!!
 1 st Law of Thermodynamics • States that energy is neither created nor destroyed…it is just passed along and/or transformed (conservation of energy). energy • All the energy that is in the universe right now can only change position or form!
1 st Law of Thermodynamics • States that energy is neither created nor destroyed…it is just passed along and/or transformed (conservation of energy). energy • All the energy that is in the universe right now can only change position or form!
 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics • Thermal energy flows (heat) spontaneously from a warmer body to a cooler one. • One cannot transfer or transform heat completely into useful work, some of the energy becomes unusable… • Every isolated system becomes disordered in time (entropy).
2 nd Law of Thermodynamics • Thermal energy flows (heat) spontaneously from a warmer body to a cooler one. • One cannot transfer or transform heat completely into useful work, some of the energy becomes unusable… • Every isolated system becomes disordered in time (entropy).
 3 ways Thermal Energy transfers (heat) 1. CONDUCTION 2. CONVECTION 3. RADIATION
3 ways Thermal Energy transfers (heat) 1. CONDUCTION 2. CONVECTION 3. RADIATION
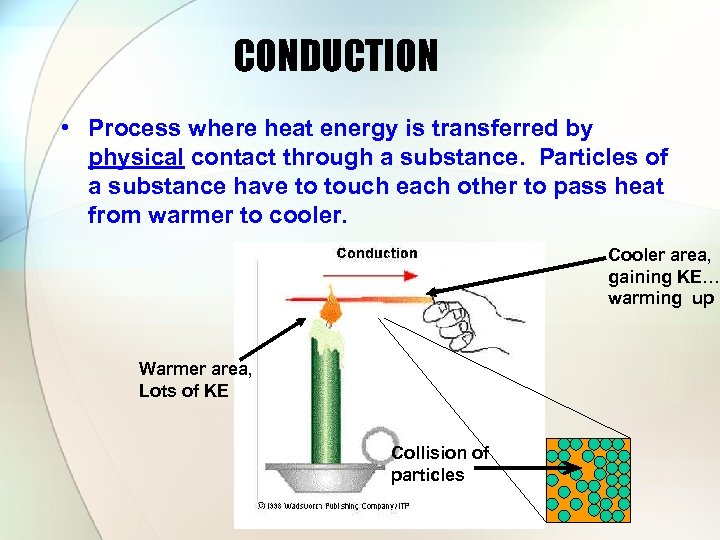 CONDUCTION • Process where heat energy is transferred by physical contact through a substance. Particles of a substance have to touch each other to pass heat from warmer to cooler. Cooler area, gaining KE… warming up Warmer area, Lots of KE Collision of particles
CONDUCTION • Process where heat energy is transferred by physical contact through a substance. Particles of a substance have to touch each other to pass heat from warmer to cooler. Cooler area, gaining KE… warming up Warmer area, Lots of KE Collision of particles
 Conductor vs. Insulator • Conductor – A substance that allows heat to transfer through it. • Insulator – A substance that does NOT allow heat to transfer to the cooler area easily.
Conductor vs. Insulator • Conductor – A substance that allows heat to transfer through it. • Insulator – A substance that does NOT allow heat to transfer to the cooler area easily.
 Insulators Fire gear: keeps heat from skin exposure Space suit keeps heat from sun minimal Ice actually slows the transfer of heat from inside to outside
Insulators Fire gear: keeps heat from skin exposure Space suit keeps heat from sun minimal Ice actually slows the transfer of heat from inside to outside
 CONVECTION • Transfer of heat by circulation or movement of the hot particles to cooler areas. Warmer, less dense fluids rise, while cooler, more dense fluids fall and replace. Warm, less dense air rises…cools Cool, more dense air falls…warms again
CONVECTION • Transfer of heat by circulation or movement of the hot particles to cooler areas. Warmer, less dense fluids rise, while cooler, more dense fluids fall and replace. Warm, less dense air rises…cools Cool, more dense air falls…warms again
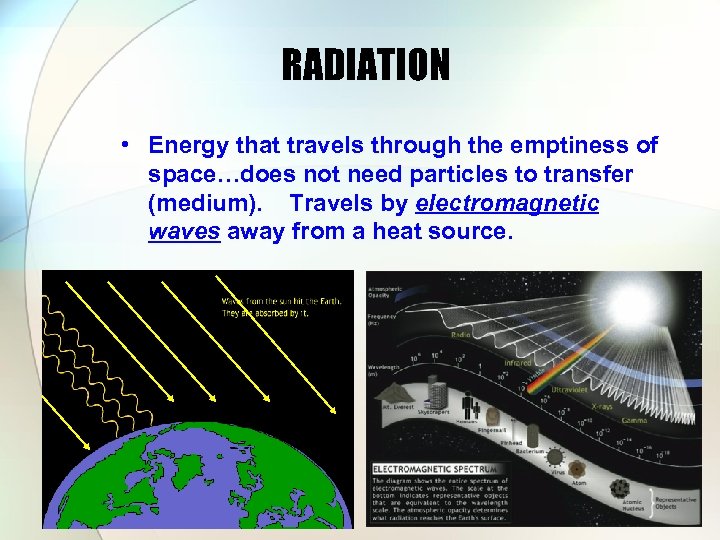 RADIATION • Energy that travels through the emptiness of space…does not need particles to transfer (medium). Travels by electromagnetic waves away from a heat source.
RADIATION • Energy that travels through the emptiness of space…does not need particles to transfer (medium). Travels by electromagnetic waves away from a heat source.
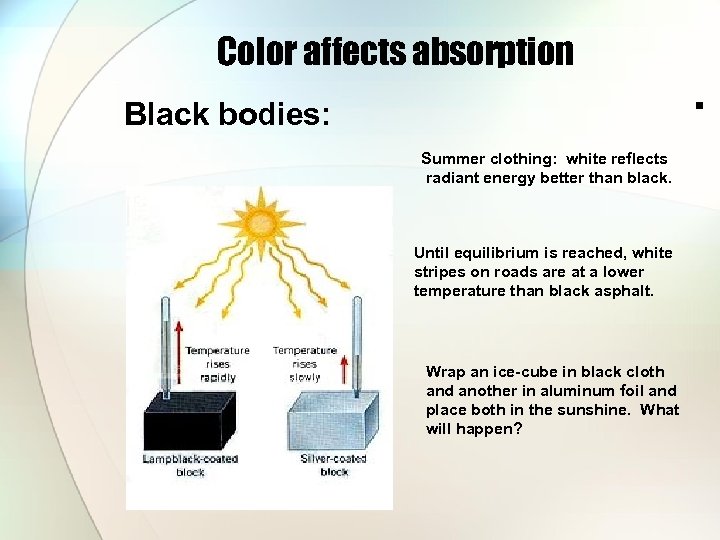 Color affects absorption Black bodies: Summer clothing: white reflects radiant energy better than black. Until equilibrium is reached, white stripes on roads are at a lower temperature than black asphalt. Wrap an ice-cube in black cloth and another in aluminum foil and place both in the sunshine. What will happen?
Color affects absorption Black bodies: Summer clothing: white reflects radiant energy better than black. Until equilibrium is reached, white stripes on roads are at a lower temperature than black asphalt. Wrap an ice-cube in black cloth and another in aluminum foil and place both in the sunshine. What will happen?
 What are Waves? • A wave is a disturbance when energy is transferred through a ‘medium’. • Medium is what energy is passing through (solid, liquid, gas, etc…) • This disturbance can cause the medium to become displaced • Sometimes permanently • Sometimes temporarily
What are Waves? • A wave is a disturbance when energy is transferred through a ‘medium’. • Medium is what energy is passing through (solid, liquid, gas, etc…) • This disturbance can cause the medium to become displaced • Sometimes permanently • Sometimes temporarily
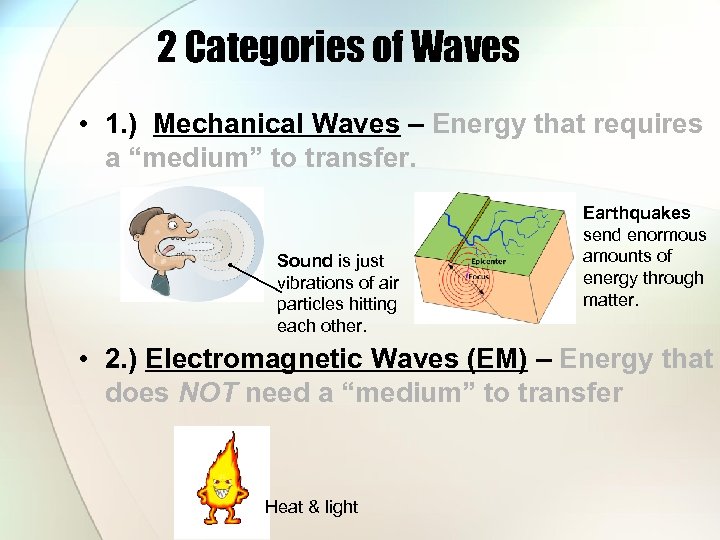 2 Categories of Waves • 1. ) Mechanical Waves – Energy that requires a “medium” to transfer. Sound is just vibrations of air particles hitting each other. Earthquakes send enormous amounts of energy through matter. • 2. ) Electromagnetic Waves (EM) – Energy that does NOT need a “medium” to transfer Heat & light
2 Categories of Waves • 1. ) Mechanical Waves – Energy that requires a “medium” to transfer. Sound is just vibrations of air particles hitting each other. Earthquakes send enormous amounts of energy through matter. • 2. ) Electromagnetic Waves (EM) – Energy that does NOT need a “medium” to transfer Heat & light
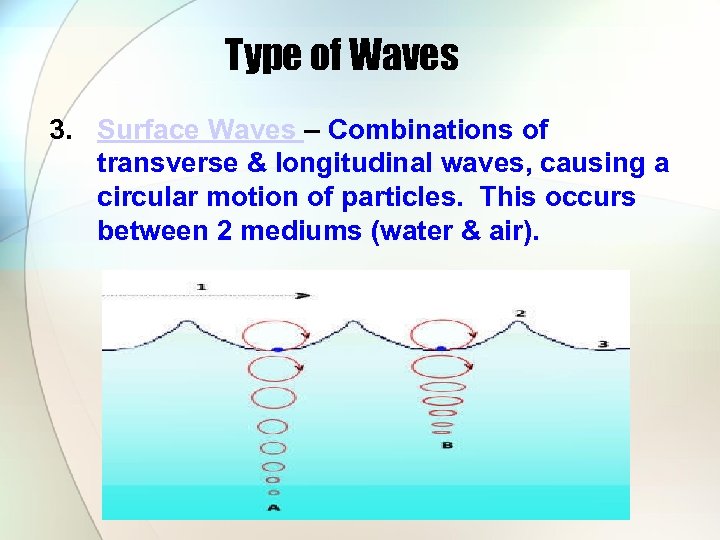 Type of Waves 3. Surface Waves – Combinations of transverse & longitudinal waves, causing a circular motion of particles. This occurs between 2 mediums (water & air).
Type of Waves 3. Surface Waves – Combinations of transverse & longitudinal waves, causing a circular motion of particles. This occurs between 2 mediums (water & air).
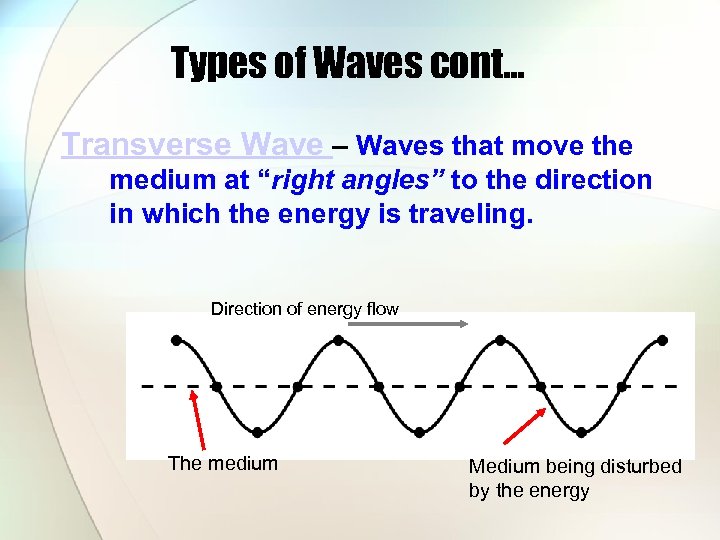 Types of Waves cont… Transverse Wave – Waves that move the medium at “right angles” to the direction in which the energy is traveling. Direction of energy flow The medium Medium being disturbed by the energy
Types of Waves cont… Transverse Wave – Waves that move the medium at “right angles” to the direction in which the energy is traveling. Direction of energy flow The medium Medium being disturbed by the energy
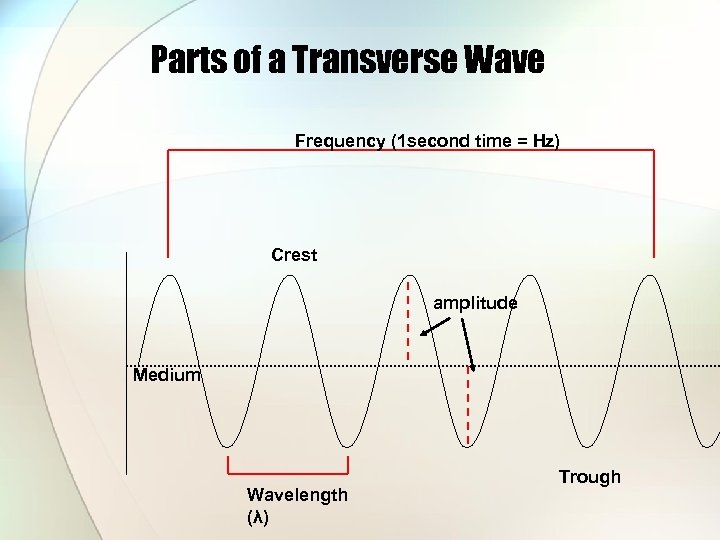 Parts of a Transverse Wave Frequency (1 second time = Hz) Crest amplitude Medium Wavelength (λ) Trough
Parts of a Transverse Wave Frequency (1 second time = Hz) Crest amplitude Medium Wavelength (λ) Trough
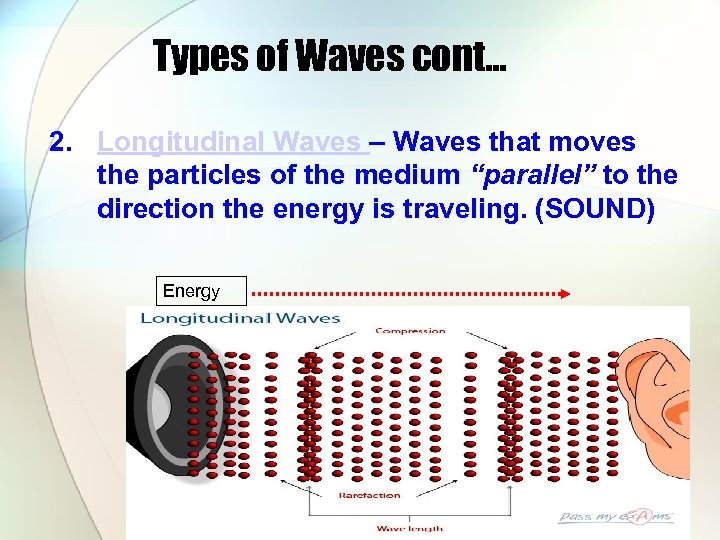 Types of Waves cont… 2. Longitudinal Waves – Waves that moves the particles of the medium “parallel” to the direction the energy is traveling. (SOUND) Energy
Types of Waves cont… 2. Longitudinal Waves – Waves that moves the particles of the medium “parallel” to the direction the energy is traveling. (SOUND) Energy
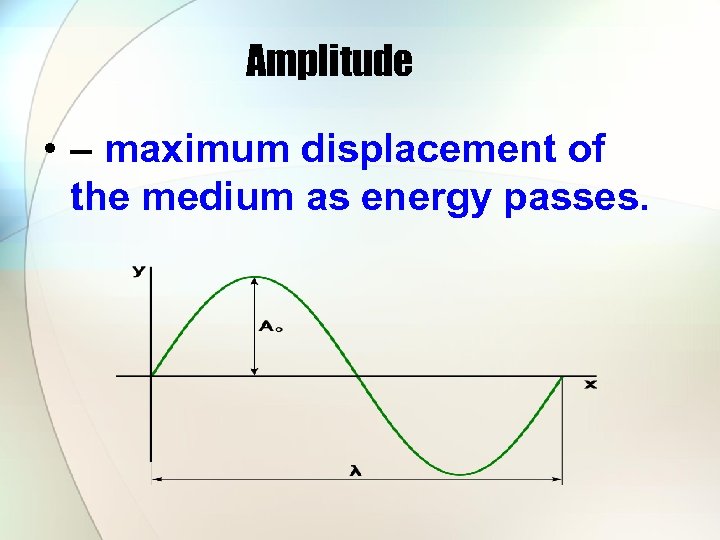 Amplitude • – maximum displacement of the medium as energy passes.
Amplitude • – maximum displacement of the medium as energy passes.
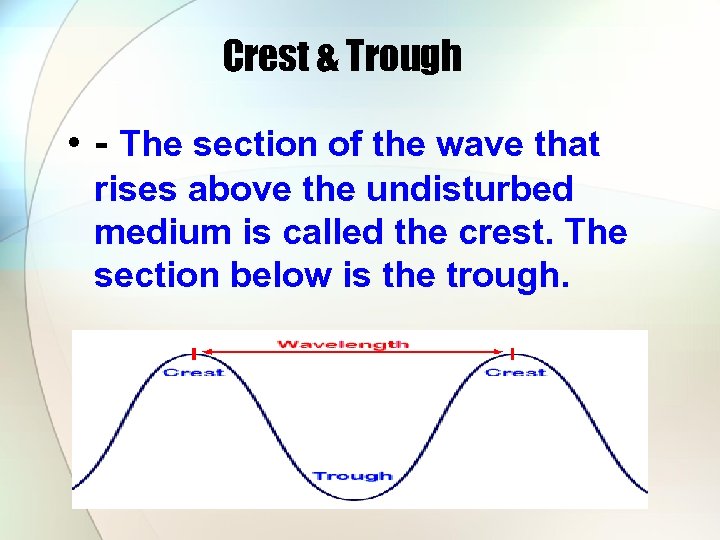 Crest & Trough • - The section of the wave that rises above the undisturbed medium is called the crest. The section below is the trough.
Crest & Trough • - The section of the wave that rises above the undisturbed medium is called the crest. The section below is the trough.
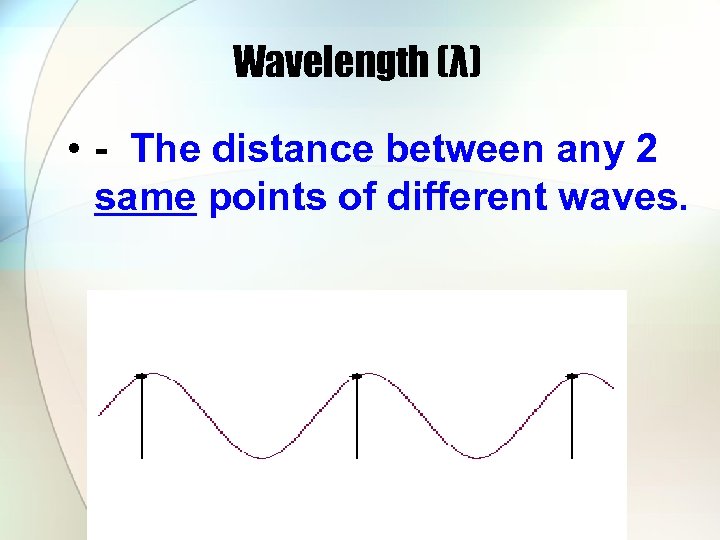 Wavelength (λ) • - The distance between any 2 same points of different waves.
Wavelength (λ) • - The distance between any 2 same points of different waves.
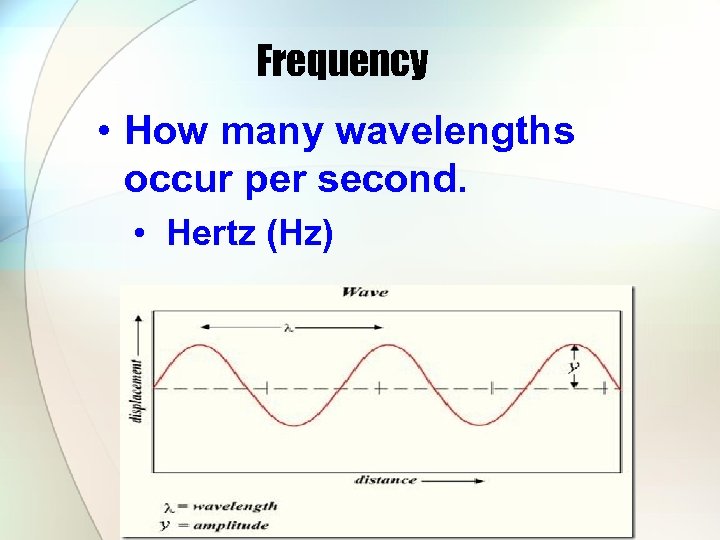 Frequency • How many wavelengths occur per second. • Hertz (Hz)
Frequency • How many wavelengths occur per second. • Hertz (Hz)
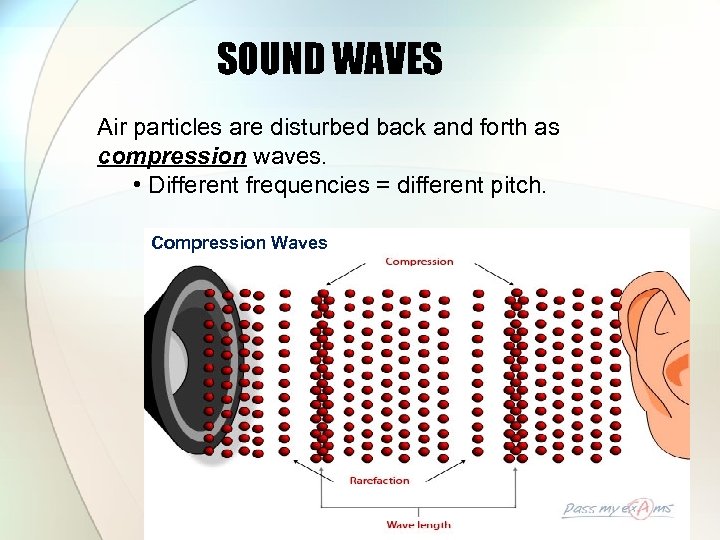 SOUND WAVES Air particles are disturbed back and forth as compression waves. • Different frequencies = different pitch. Compression Waves
SOUND WAVES Air particles are disturbed back and forth as compression waves. • Different frequencies = different pitch. Compression Waves
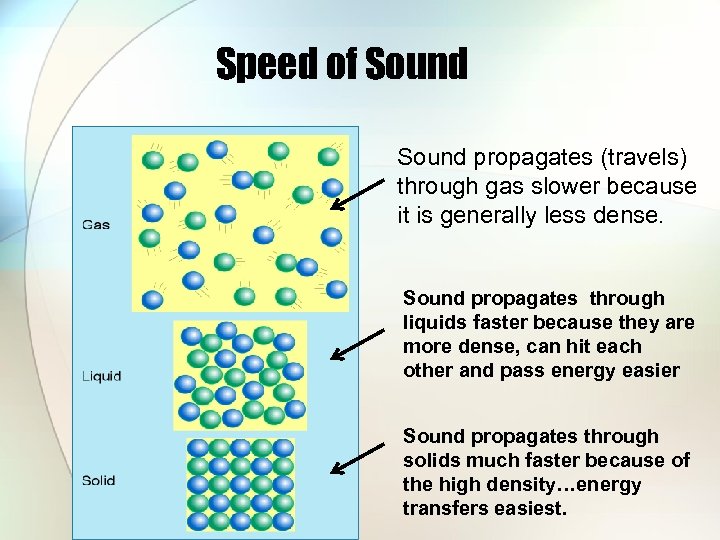 Speed of Sound propagates (travels) through gas slower because it is generally less dense. Sound propagates through liquids faster because they are more dense, can hit each other and pass energy easier Sound propagates through solids much faster because of the high density…energy transfers easiest.
Speed of Sound propagates (travels) through gas slower because it is generally less dense. Sound propagates through liquids faster because they are more dense, can hit each other and pass energy easier Sound propagates through solids much faster because of the high density…energy transfers easiest.
 Sound from stationary source Sound energy propagates outward (Compression waves) in all directions.
Sound from stationary source Sound energy propagates outward (Compression waves) in all directions.
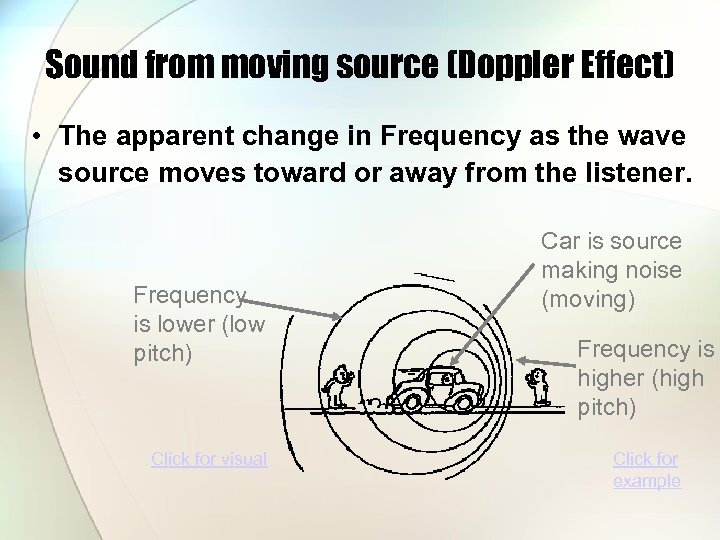 Sound from moving source (Doppler Effect) • The apparent change in Frequency as the wave source moves toward or away from the listener. Frequency is lower (low pitch) Click for visual Car is source making noise (moving) Frequency is higher (high pitch) Click for example
Sound from moving source (Doppler Effect) • The apparent change in Frequency as the wave source moves toward or away from the listener. Frequency is lower (low pitch) Click for visual Car is source making noise (moving) Frequency is higher (high pitch) Click for example
 Supersonic (breaking sound barrier) • When a wave source catches up and passes the outgoing waves of energy. Sound barrier Click for video example
Supersonic (breaking sound barrier) • When a wave source catches up and passes the outgoing waves of energy. Sound barrier Click for video example
 Electromagnetic Radiation (EM Waves) Energy that is coming from our star (The Sun). We have identified many different types of energy from the Sun and named them.
Electromagnetic Radiation (EM Waves) Energy that is coming from our star (The Sun). We have identified many different types of energy from the Sun and named them.
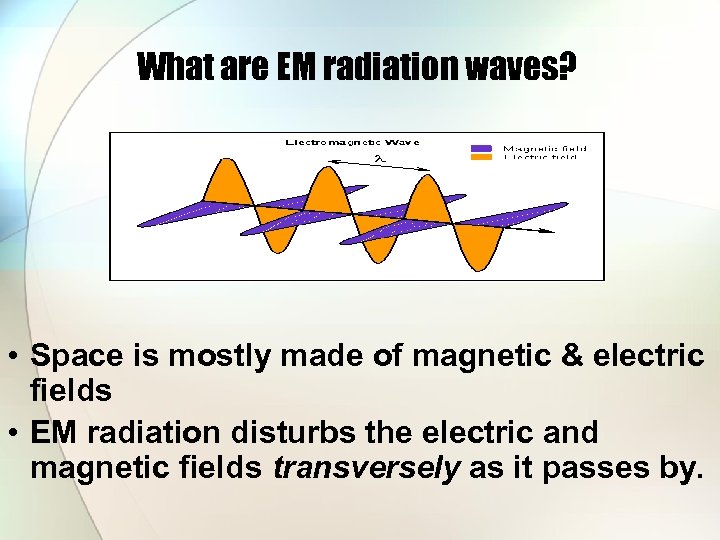 What are EM radiation waves? • Space is mostly made of magnetic & electric fields • EM radiation disturbs the electric and magnetic fields transversely as it passes by.
What are EM radiation waves? • Space is mostly made of magnetic & electric fields • EM radiation disturbs the electric and magnetic fields transversely as it passes by.
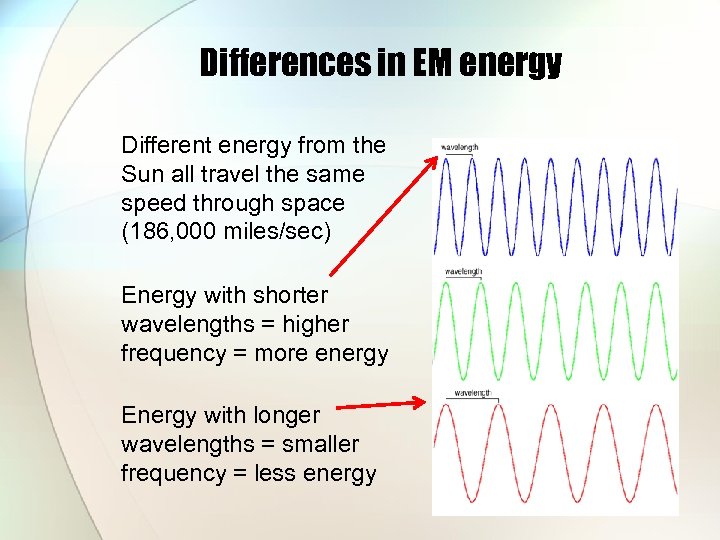 Differences in EM energy Different energy from the Sun all travel the same speed through space (186, 000 miles/sec) Energy with shorter wavelengths = higher frequency = more energy Energy with longer wavelengths = smaller frequency = less energy
Differences in EM energy Different energy from the Sun all travel the same speed through space (186, 000 miles/sec) Energy with shorter wavelengths = higher frequency = more energy Energy with longer wavelengths = smaller frequency = less energy
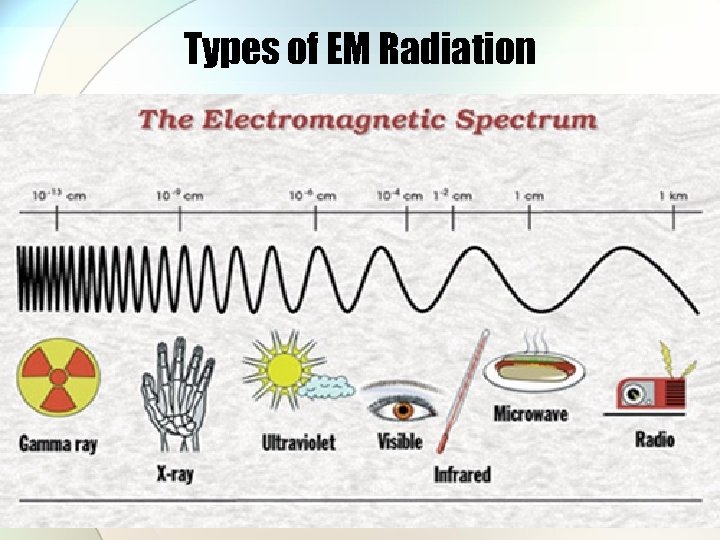 Types of EM Radiation
Types of EM Radiation
 How does energy travel through emptiness of space? ? ? • “Space particles” known as photons carry energy through space, but not matter. • Some photons carry lots of energy (gamma rays) • Some photons carry little energy (radio waves)
How does energy travel through emptiness of space? ? ? • “Space particles” known as photons carry energy through space, but not matter. • Some photons carry lots of energy (gamma rays) • Some photons carry little energy (radio waves)
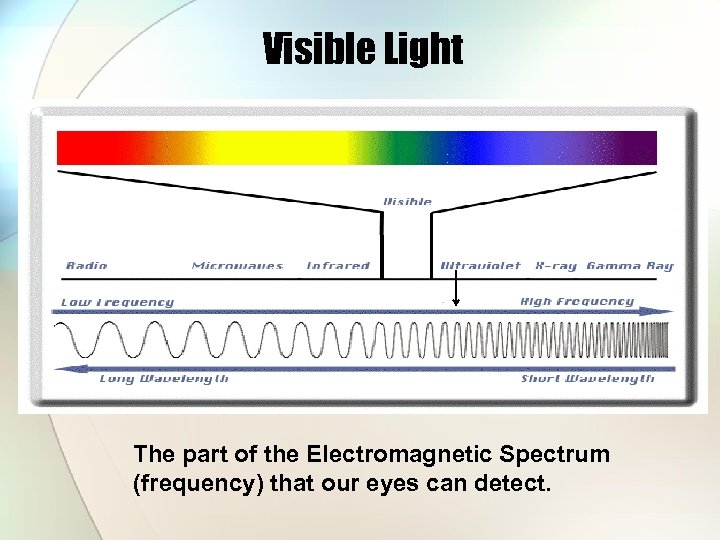 Visible Light The part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum (frequency) that our eyes can detect.
Visible Light The part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum (frequency) that our eyes can detect.
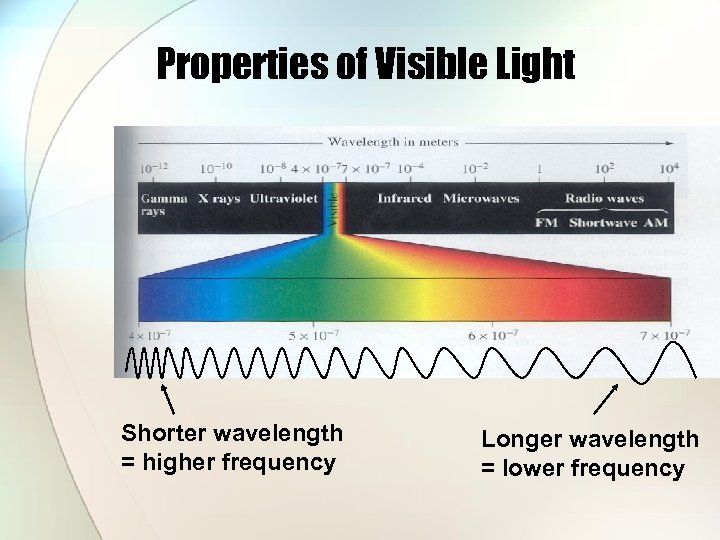 Properties of Visible Light Shorter wavelength = higher frequency Longer wavelength = lower frequency
Properties of Visible Light Shorter wavelength = higher frequency Longer wavelength = lower frequency
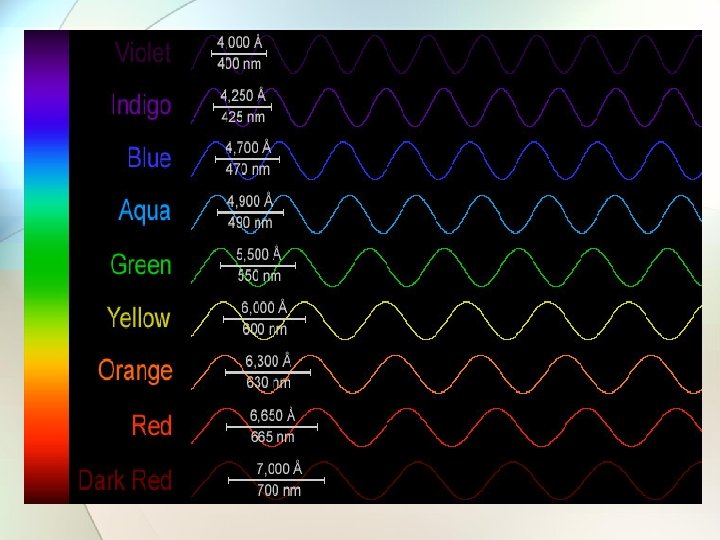
 Diffraction • Diffraction is the splitting of light energy to its individual frequencies (colors)
Diffraction • Diffraction is the splitting of light energy to its individual frequencies (colors)
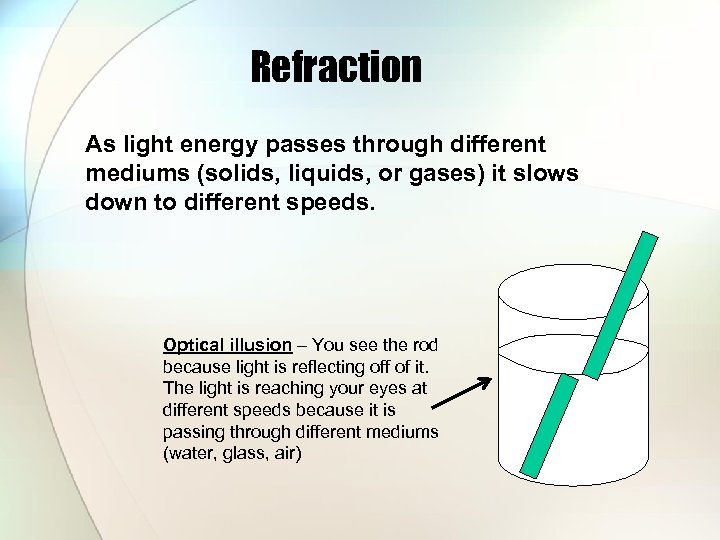 Refraction As light energy passes through different mediums (solids, liquids, or gases) it slows down to different speeds. Optical illusion – You see the rod because light is reflecting off of it. The light is reaching your eyes at different speeds because it is passing through different mediums (water, glass, air)
Refraction As light energy passes through different mediums (solids, liquids, or gases) it slows down to different speeds. Optical illusion – You see the rod because light is reflecting off of it. The light is reaching your eyes at different speeds because it is passing through different mediums (water, glass, air)
 Refraction cont… The Sun’s light energy is refracted when it enters our Earth’s atmosphere.
Refraction cont… The Sun’s light energy is refracted when it enters our Earth’s atmosphere.
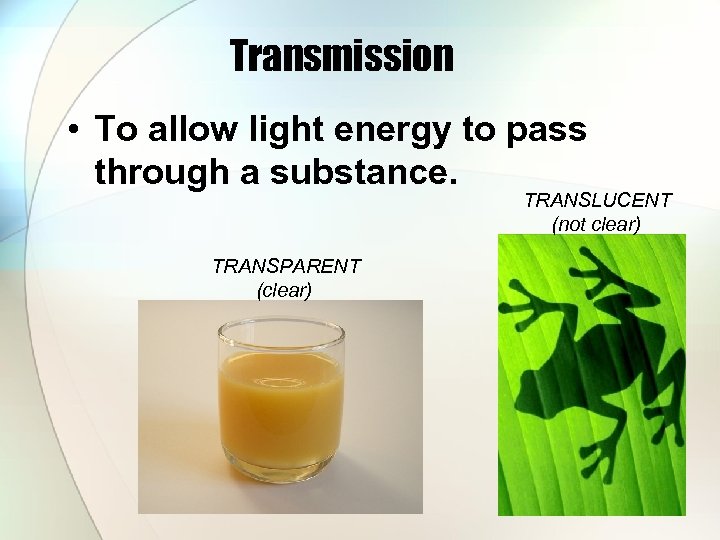 Transmission • To allow light energy to pass through a substance. TRANSLUCENT (not clear) TRANSPARENT (clear)
Transmission • To allow light energy to pass through a substance. TRANSLUCENT (not clear) TRANSPARENT (clear)
 Reflection • Regular Reflection – When parallel rays of light hit a smooth surface and all the rays bounce off the same direction & angle s bo e nc u
Reflection • Regular Reflection – When parallel rays of light hit a smooth surface and all the rays bounce off the same direction & angle s bo e nc u
 Reflection cont… • Diffuse Reflection – When parallel rays of light hit a bumpy or uneven surface they bounce off at different angles & direction.
Reflection cont… • Diffuse Reflection – When parallel rays of light hit a bumpy or uneven surface they bounce off at different angles & direction.
 Absorption • When visible light is absorbed, it is known as the “absence” of light…which is black. All absorbed Black h W te i
Absorption • When visible light is absorbed, it is known as the “absence” of light…which is black. All absorbed Black h W te i
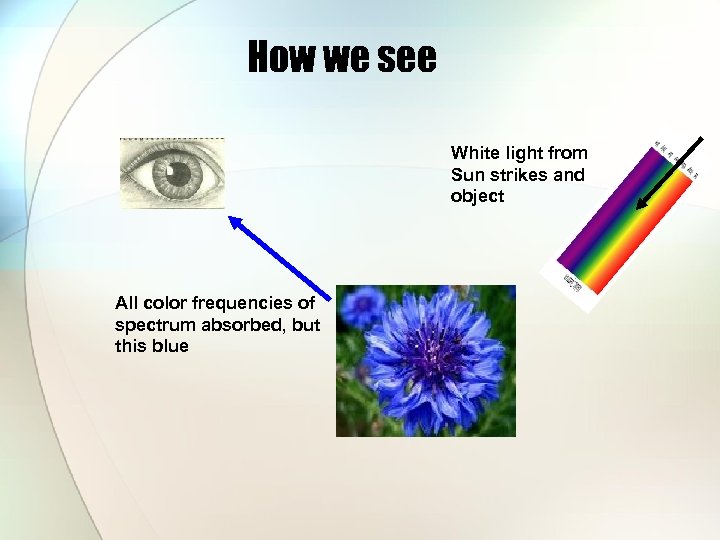 How we see White light from Sun strikes and object All color frequencies of spectrum absorbed, but this blue
How we see White light from Sun strikes and object All color frequencies of spectrum absorbed, but this blue
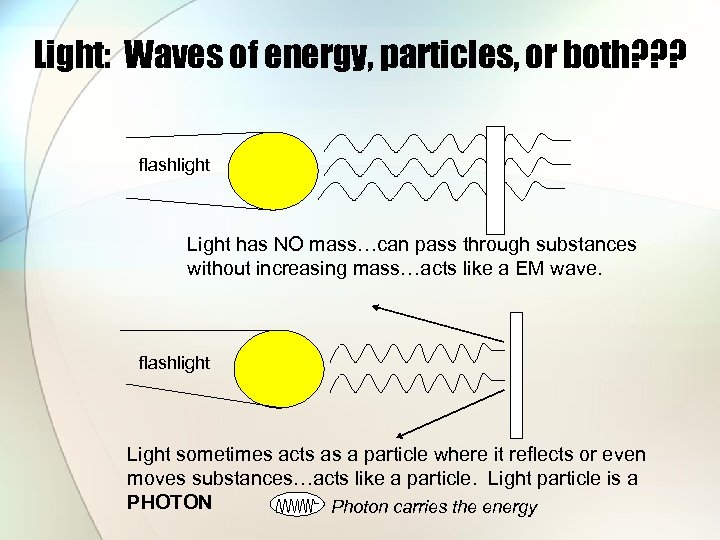 Light: Waves of energy, particles, or both? ? ? flashlight Light has NO mass…can pass through substances without increasing mass…acts like a EM wave. flashlight Light sometimes acts as a particle where it reflects or even moves substances…acts like a particle. Light particle is a PHOTON Photon carries the energy
Light: Waves of energy, particles, or both? ? ? flashlight Light has NO mass…can pass through substances without increasing mass…acts like a EM wave. flashlight Light sometimes acts as a particle where it reflects or even moves substances…acts like a particle. Light particle is a PHOTON Photon carries the energy
 Visible Light Hitting an Object 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Refraction Transmission Scattering Reflection Absorption
Visible Light Hitting an Object 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Refraction Transmission Scattering Reflection Absorption
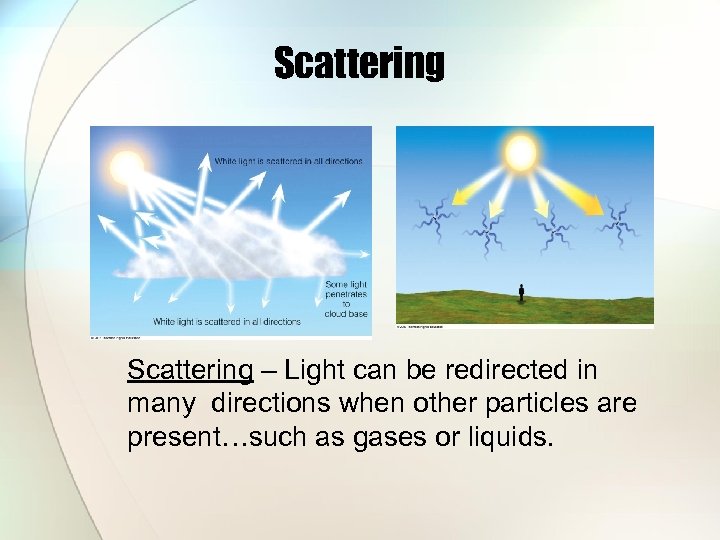 Scattering – Light can be redirected in many directions when other particles are present…such as gases or liquids.
Scattering – Light can be redirected in many directions when other particles are present…such as gases or liquids.
 TYPES OF ENERGY Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
TYPES OF ENERGY Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
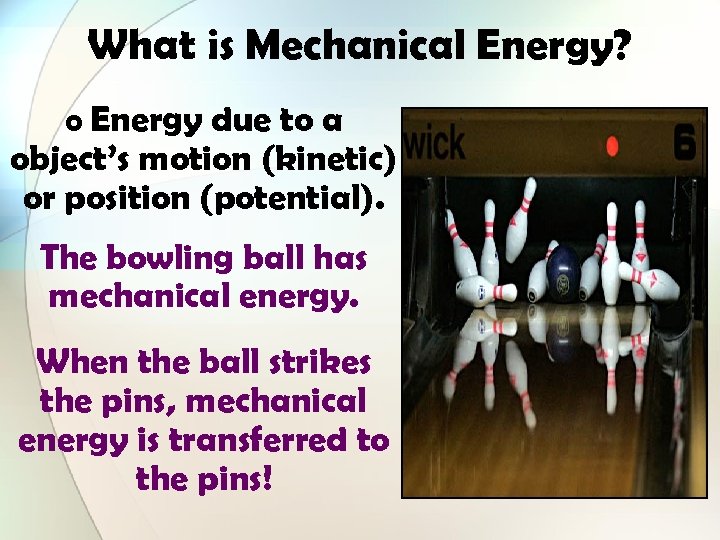 What is Mechanical Energy? o Energy due to a object’s motion (kinetic) or position (potential). The bowling ball has mechanical energy. When the ball strikes the pins, mechanical energy is transferred to the pins!
What is Mechanical Energy? o Energy due to a object’s motion (kinetic) or position (potential). The bowling ball has mechanical energy. When the ball strikes the pins, mechanical energy is transferred to the pins!
 Examples of Mechanical Energy
Examples of Mechanical Energy
 What is Electromagnetic Energy? o Light energy o Includes energy from gamma rays, xrays, ultraviolet rays, visible light, infrared rays, microwave and radio bands
What is Electromagnetic Energy? o Light energy o Includes energy from gamma rays, xrays, ultraviolet rays, visible light, infrared rays, microwave and radio bands
 What is Electrical Energy? o Energy caused by the movement of electrons o Easily transported through power lines and converted into other forms of energy
What is Electrical Energy? o Energy caused by the movement of electrons o Easily transported through power lines and converted into other forms of energy
 What is Chemical Energy? o Energy that is available for release from chemical reactions. The chemical bonds in a matchstick store energy that is transformed into thermal energy when the match is struck.
What is Chemical Energy? o Energy that is available for release from chemical reactions. The chemical bonds in a matchstick store energy that is transformed into thermal energy when the match is struck.
 Examples of Chemical Energy
Examples of Chemical Energy
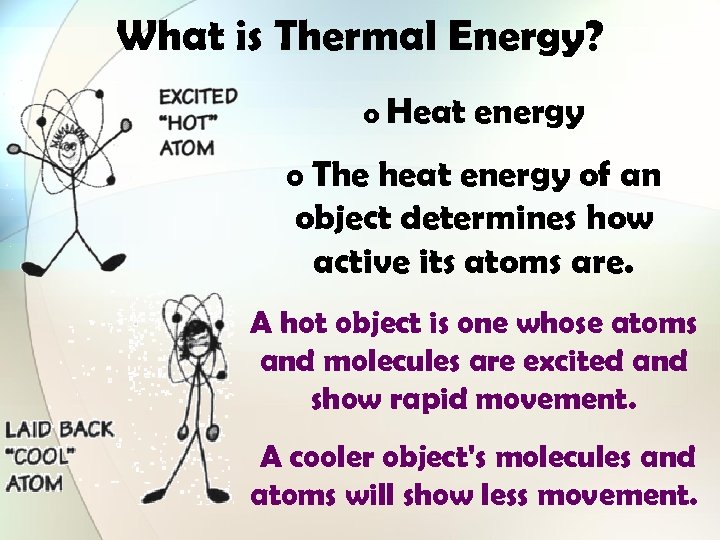 What is Thermal Energy? o Heat energy o The heat energy of an object determines how active its atoms are. A hot object is one whose atoms and molecules are excited and show rapid movement. A cooler object's molecules and atoms will show less movement.
What is Thermal Energy? o Heat energy o The heat energy of an object determines how active its atoms are. A hot object is one whose atoms and molecules are excited and show rapid movement. A cooler object's molecules and atoms will show less movement.
 QUIZ TIME! What type of energy cooks food in a microwave oven? ELECTROMAGNETIC ENERGY What type of energy is the spinning plate inside of a microwave oven? MECHANICAL ENERGY
QUIZ TIME! What type of energy cooks food in a microwave oven? ELECTROMAGNETIC ENERGY What type of energy is the spinning plate inside of a microwave oven? MECHANICAL ENERGY
 QUIZ TIME! Electrical energy is transported to your house through power lines. When you plug an electric fan to a power outlet, electrical energy is transform into what type of energy? MECHANICAL ENERGY
QUIZ TIME! Electrical energy is transported to your house through power lines. When you plug an electric fan to a power outlet, electrical energy is transform into what type of energy? MECHANICAL ENERGY
 QUIZ TIME! What energy transformation occurs when an electric lamp is turned on? ELECTRICAL ENERGY ELECTROMAGNETIC ENERGY
QUIZ TIME! What energy transformation occurs when an electric lamp is turned on? ELECTRICAL ENERGY ELECTROMAGNETIC ENERGY
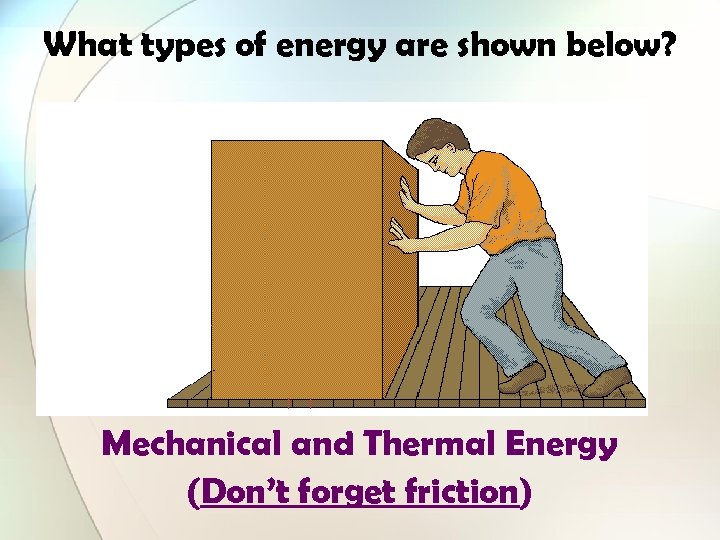 What types of energy are shown below? Mechanical and Thermal Energy (Don’t forget friction)
What types of energy are shown below? Mechanical and Thermal Energy (Don’t forget friction)
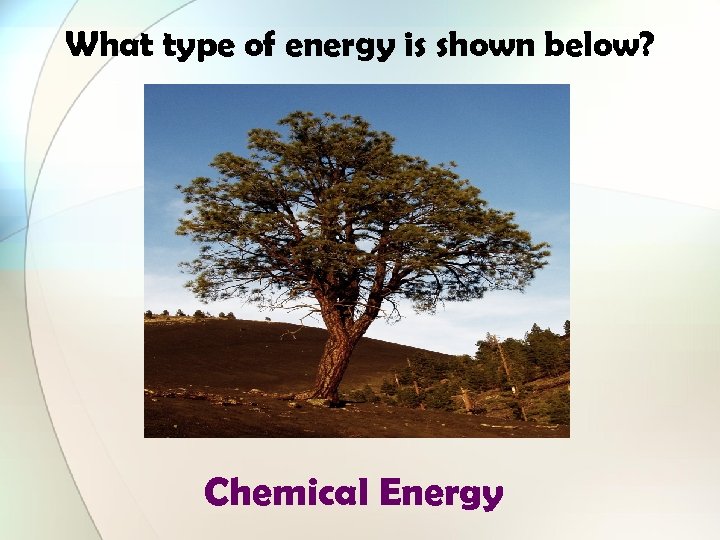 What type of energy is shown below? Chemical Energy
What type of energy is shown below? Chemical Energy
 What types of energy are shown below? Electrical, Mechanical and Electromagnetic Energy
What types of energy are shown below? Electrical, Mechanical and Electromagnetic Energy
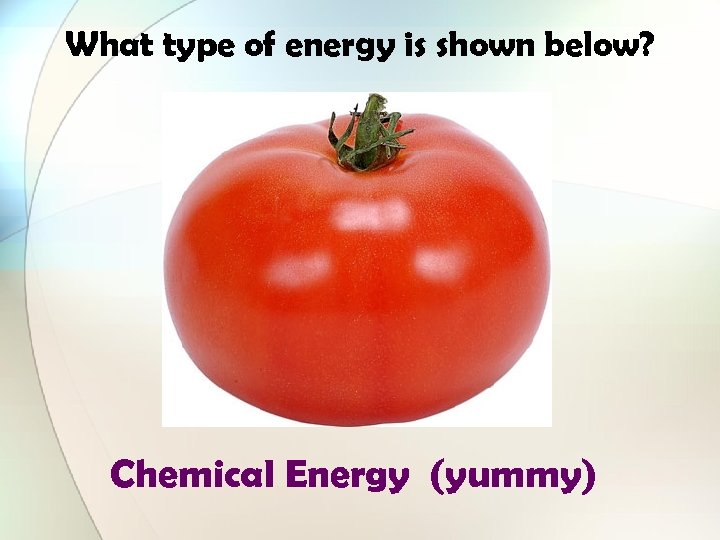 What type of energy is shown below? Chemical Energy (yummy)
What type of energy is shown below? Chemical Energy (yummy)
 What type of energy is shown below? Thermal Energy
What type of energy is shown below? Thermal Energy
 Flow of Energy • Draw a flow map showing the flow of energy transformations in a car from starting vehicle to driving. You should have 5 different types of energy.
Flow of Energy • Draw a flow map showing the flow of energy transformations in a car from starting vehicle to driving. You should have 5 different types of energy.
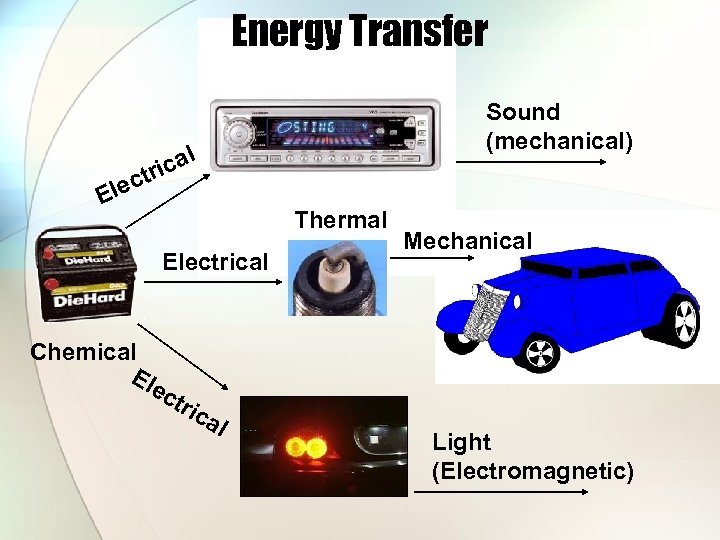 Energy Transfer Sound (mechanical) cal tri lec E Thermal Electrical Mechanical Chemical Ele ctr ica l Light (Electromagnetic)
Energy Transfer Sound (mechanical) cal tri lec E Thermal Electrical Mechanical Chemical Ele ctr ica l Light (Electromagnetic)


