05d3357df4e0833819108a4ee37e8e76.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 85
 th 5 Generation Distance Education Professor J C Taylor Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Global Learning Services) The University of Southern Queensland Australia
th 5 Generation Distance Education Professor J C Taylor Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Global Learning Services) The University of Southern Queensland Australia
 1982 ICDE Conference in Vancouver: “Technology’s the answer, but what is the question? ” Today, the technology has changed, but the question hasn’t.
1982 ICDE Conference in Vancouver: “Technology’s the answer, but what is the question? ” Today, the technology has changed, but the question hasn’t.
 Joseph Schumpeter (1934) predicted that every 50 years or so, technological revolutions would cause "gales of creative destruction” in which old industries would be swept away and replaced by new ones.
Joseph Schumpeter (1934) predicted that every 50 years or so, technological revolutions would cause "gales of creative destruction” in which old industries would be swept away and replaced by new ones.
 Technological Changes § Steam Power - 1780 s to the 1840 s § The Railways - 1840 s to the 1890 s § Electric Power - 1890 s to the 1930 s § The Motor Car - 1930 s to the 1980 s § Information Technology - 1980 s to ?
Technological Changes § Steam Power - 1780 s to the 1840 s § The Railways - 1840 s to the 1890 s § Electric Power - 1890 s to the 1930 s § The Motor Car - 1930 s to the 1980 s § Information Technology - 1980 s to ?
 Pace of Change 1. Radio: 50 million users in 38 years 2. Television: 50 million users in 13 years 3. The Internet: 50 million users in 5 years Current prediction: One billion users by the year 2003
Pace of Change 1. Radio: 50 million users in 38 years 2. Television: 50 million users in 13 years 3. The Internet: 50 million users in 5 years Current prediction: One billion users by the year 2003
 Internet Access in Australia An estimated 6 million adults (43% of Australia’s adult population) accessed the Internet in the year prior to February 2000. Source: ABS, February 2000
Internet Access in Australia An estimated 6 million adults (43% of Australia’s adult population) accessed the Internet in the year prior to February 2000. Source: ABS, February 2000
 Internet Access in Australia The likelihood that an adult is an Internet user decreases dramatically with age. In the 12 months prior to February 2000, 77% of 18 -24 year olds accessed the Internet compared to 13% of adults aged 55 or over. Source: ABS, February 2000
Internet Access in Australia The likelihood that an adult is an Internet user decreases dramatically with age. In the 12 months prior to February 2000, 77% of 18 -24 year olds accessed the Internet compared to 13% of adults aged 55 or over. Source: ABS, February 2000
 Internet Access at Home § 167. 1 million - USA § 27. 1 million - Germany § 23. 4 million - United Kingdom § 18. 1 million - Italy § 11. 6 million - Taiwan § 9. 2 million - Australia Source: Cyberatlas, June 2000
Internet Access at Home § 167. 1 million - USA § 27. 1 million - Germany § 23. 4 million - United Kingdom § 18. 1 million - Italy § 11. 6 million - Taiwan § 9. 2 million - Australia Source: Cyberatlas, June 2000
 Internet Access at Home % With Internet Access at Home § § § Australia 50% France 22% New Zealand 51% Sweden 61% UK 46% USA 60% Source: A C Nielsen, June 2000
Internet Access at Home % With Internet Access at Home § § § Australia 50% France 22% New Zealand 51% Sweden 61% UK 46% USA 60% Source: A C Nielsen, June 2000
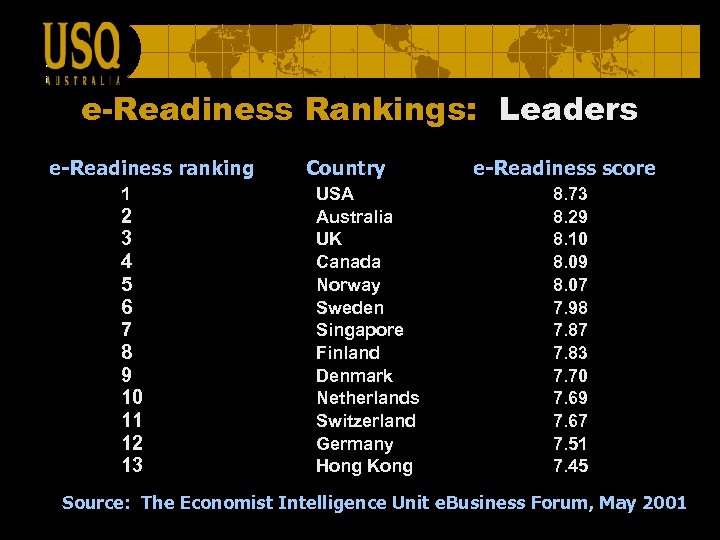 e-Readiness Rankings: Leaders e-Readiness ranking 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Country USA Australia UK Canada Norway Sweden Singapore Finland Denmark Netherlands Switzerland Germany Hong Kong e-Readiness score 8. 73 8. 29 8. 10 8. 09 8. 07 7. 98 7. 87 7. 83 7. 70 7. 69 7. 67 7. 51 7. 45 Source: The Economist Intelligence Unit e. Business Forum, May 2001
e-Readiness Rankings: Leaders e-Readiness ranking 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Country USA Australia UK Canada Norway Sweden Singapore Finland Denmark Netherlands Switzerland Germany Hong Kong e-Readiness score 8. 73 8. 29 8. 10 8. 09 8. 07 7. 98 7. 87 7. 83 7. 70 7. 69 7. 67 7. 51 7. 45 Source: The Economist Intelligence Unit e. Business Forum, May 2001
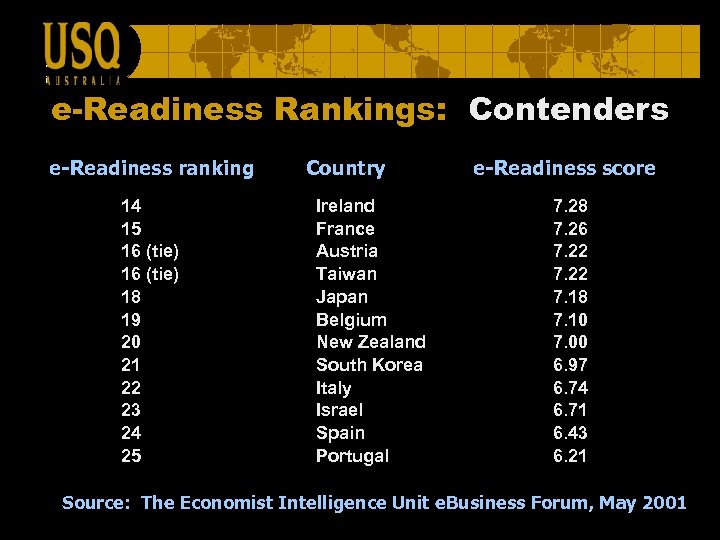 e-Readiness Rankings: Contenders e-Readiness ranking 14 15 16 (tie) 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Country Ireland France Austria Taiwan Japan Belgium New Zealand South Korea Italy Israel Spain Portugal e-Readiness score 7. 28 7. 26 7. 22 7. 18 7. 10 7. 00 6. 97 6. 74 6. 71 6. 43 6. 21 Source: The Economist Intelligence Unit e. Business Forum, May 2001
e-Readiness Rankings: Contenders e-Readiness ranking 14 15 16 (tie) 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Country Ireland France Austria Taiwan Japan Belgium New Zealand South Korea Italy Israel Spain Portugal e-Readiness score 7. 28 7. 26 7. 22 7. 18 7. 10 7. 00 6. 97 6. 74 6. 71 6. 43 6. 21 Source: The Economist Intelligence Unit e. Business Forum, May 2001
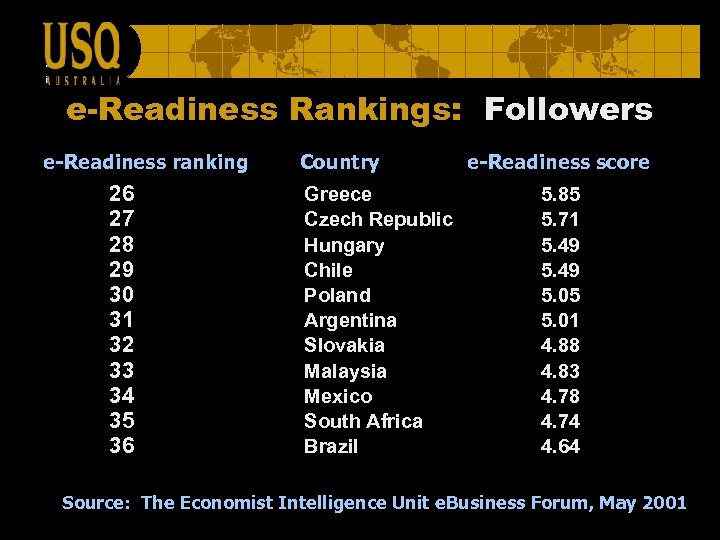 e-Readiness Rankings: Followers e-Readiness ranking 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Country Greece Czech Republic Hungary Chile Poland Argentina Slovakia Malaysia Mexico South Africa Brazil e-Readiness score 5. 85 5. 71 5. 49 5. 05 5. 01 4. 88 4. 83 4. 78 4. 74 4. 64 Source: The Economist Intelligence Unit e. Business Forum, May 2001
e-Readiness Rankings: Followers e-Readiness ranking 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Country Greece Czech Republic Hungary Chile Poland Argentina Slovakia Malaysia Mexico South Africa Brazil e-Readiness score 5. 85 5. 71 5. 49 5. 05 5. 01 4. 88 4. 83 4. 78 4. 74 4. 64 Source: The Economist Intelligence Unit e. Business Forum, May 2001
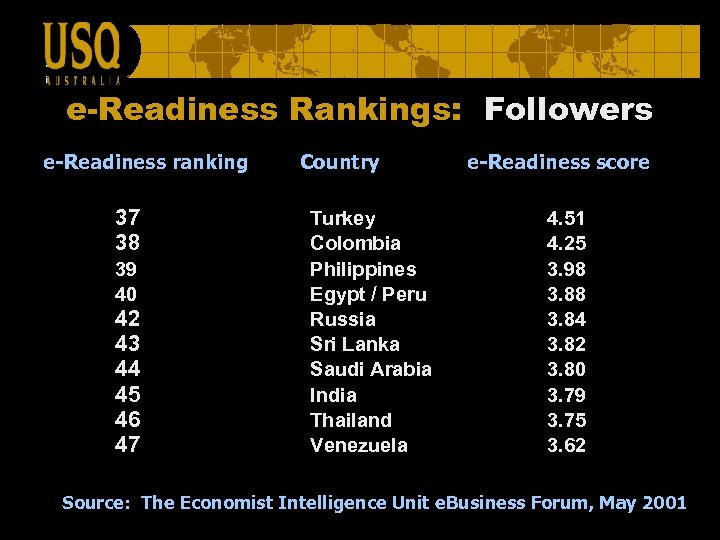 e-Readiness Rankings: Followers e-Readiness ranking 37 38 39 40 42 43 44 45 46 47 Country Turkey Colombia Philippines Egypt / Peru Russia Sri Lanka Saudi Arabia India Thailand Venezuela e-Readiness score 4. 51 4. 25 3. 98 3. 84 3. 82 3. 80 3. 79 3. 75 3. 62 Source: The Economist Intelligence Unit e. Business Forum, May 2001
e-Readiness Rankings: Followers e-Readiness ranking 37 38 39 40 42 43 44 45 46 47 Country Turkey Colombia Philippines Egypt / Peru Russia Sri Lanka Saudi Arabia India Thailand Venezuela e-Readiness score 4. 51 4. 25 3. 98 3. 84 3. 82 3. 80 3. 79 3. 75 3. 62 Source: The Economist Intelligence Unit e. Business Forum, May 2001
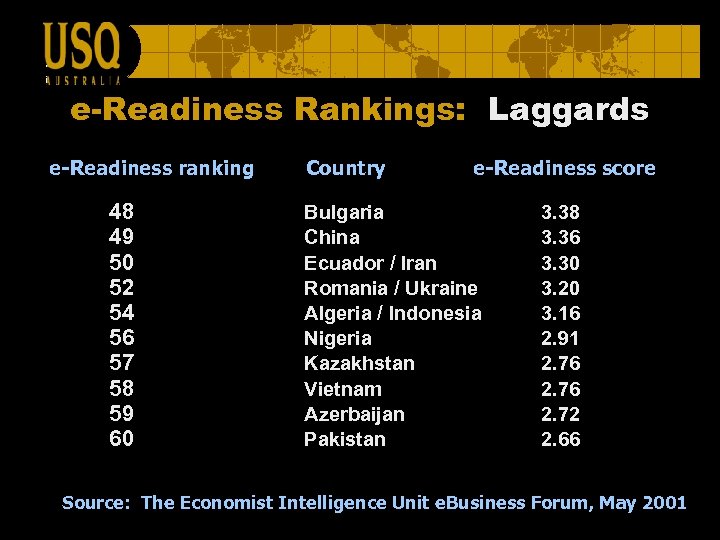 e-Readiness Rankings: Laggards e-Readiness ranking 48 49 50 52 54 56 57 58 59 60 Country e-Readiness score Bulgaria China Ecuador / Iran Romania / Ukraine Algeria / Indonesia Nigeria Kazakhstan Vietnam Azerbaijan Pakistan 3. 38 3. 36 3. 30 3. 20 3. 16 2. 91 2. 76 2. 72 2. 66 Source: The Economist Intelligence Unit e. Business Forum, May 2001
e-Readiness Rankings: Laggards e-Readiness ranking 48 49 50 52 54 56 57 58 59 60 Country e-Readiness score Bulgaria China Ecuador / Iran Romania / Ukraine Algeria / Indonesia Nigeria Kazakhstan Vietnam Azerbaijan Pakistan 3. 38 3. 36 3. 30 3. 20 3. 16 2. 91 2. 76 2. 72 2. 66 Source: The Economist Intelligence Unit e. Business Forum, May 2001
 Prediction: 'The death of distance as a determinant of the cost of communications will probably be the single most important economic force shaping society in the first half of the 21 st century'. Cairncross (1997)
Prediction: 'The death of distance as a determinant of the cost of communications will probably be the single most important economic force shaping society in the first half of the 21 st century'. Cairncross (1997)
 Getting It Wrong § In the 1940 s the Chairman of IBM predicted that the world market for computers would be approximately five. § In 1977, the CEO of Digital could not comprehend why anyone should need a personal computer.
Getting It Wrong § In the 1940 s the Chairman of IBM predicted that the world market for computers would be approximately five. § In 1977, the CEO of Digital could not comprehend why anyone should need a personal computer.
 “Mr Bell. Thank you for the demonstration. Don’t call us, we’ll call you”.
“Mr Bell. Thank you for the demonstration. Don’t call us, we’ll call you”.
 Education must lay the foundation for the success of the global economy.
Education must lay the foundation for the success of the global economy.
 Fast, Flexible and Fluid The transition from the Industrial to the Information Age was encapsulated by Dolence and Norris (1995), who argued that to survive organisations would need to change from rigid, formula driven entities to organisations that were “fast, flexible and fluid”.
Fast, Flexible and Fluid The transition from the Industrial to the Information Age was encapsulated by Dolence and Norris (1995), who argued that to survive organisations would need to change from rigid, formula driven entities to organisations that were “fast, flexible and fluid”.
 Institutional e-Readiness Trying to change a university is like trying to move a graveyard --- it is extremely difficult and you don’t get much internal support.
Institutional e-Readiness Trying to change a university is like trying to move a graveyard --- it is extremely difficult and you don’t get much internal support.
 Institutional Inertia Why should universities change? Increasing competition on a global scale.
Institutional Inertia Why should universities change? Increasing competition on a global scale.
 Increasing Competition Unext (Business education only) § London School of Economics and Political Science § University of Chicago § Carnegie Mellon University § Columbia University § Stanford University
Increasing Competition Unext (Business education only) § London School of Economics and Political Science § University of Chicago § Carnegie Mellon University § Columbia University § Stanford University
 Increasing Competition Britain’s e-University The Higher Education Funding Council and the Department of Education and Employment has asked Treasury to provide an extra £ 100 million (AU$260 million) to fund the e-University.
Increasing Competition Britain’s e-University The Higher Education Funding Council and the Department of Education and Employment has asked Treasury to provide an extra £ 100 million (AU$260 million) to fund the e-University.
 Increasing Competition The Cambridge e-MBA Cambridge University’s business school has joined forces with FT Knowledge, part of the global communications group Pearson plc, to offer this new degree from September 2001.
Increasing Competition The Cambridge e-MBA Cambridge University’s business school has joined forces with FT Knowledge, part of the global communications group Pearson plc, to offer this new degree from September 2001.
 Fast, Flexible and Fluid? 791 years ago Cambridge University passed a rule requiring all students to reside in the town of Cambridge, England. Last year that rule was revoked. The 800 year-old rulebook had to be altered to make way for the university’s first Internet-enabled program, the global e-MBA.
Fast, Flexible and Fluid? 791 years ago Cambridge University passed a rule requiring all students to reside in the town of Cambridge, England. Last year that rule was revoked. The 800 year-old rulebook had to be altered to make way for the university’s first Internet-enabled program, the global e-MBA.
 Increasing Competition UCLA’s Online. Learning. net § offers more than 1, 000 online courses and has enrolled over 12, 000 students. § offers 1, 000 American Airlines frequent flyer points when you enrol in an online course.
Increasing Competition UCLA’s Online. Learning. net § offers more than 1, 000 online courses and has enrolled over 12, 000 students. § offers 1, 000 American Airlines frequent flyer points when you enrol in an online course.
 Online Library: Fathom. com The following six institutions will invest AU$133 million to create an online library: § London School of Economics and Political § § § Science Cambridge University Press The British Library New York Public Library Columbia University Smithsonian Institute’s National Museum of Natural History
Online Library: Fathom. com The following six institutions will invest AU$133 million to create an online library: § London School of Economics and Political § § § Science Cambridge University Press The British Library New York Public Library Columbia University Smithsonian Institute’s National Museum of Natural History
 Book publishing may again become a cottage industry: § Charles Dickens sold his novels, chapter by chapter, in his own magazine, “Household Words”. § Stephen King recently offered his new 16, 000 word ghost story, “Riding the Bullet”, for exclusive sale via the Internet at US$2. 50 per copy. § Readers were able to download the text onto their computers or e-books. § King sold 400, 000 copies during the first day.
Book publishing may again become a cottage industry: § Charles Dickens sold his novels, chapter by chapter, in his own magazine, “Household Words”. § Stephen King recently offered his new 16, 000 word ghost story, “Riding the Bullet”, for exclusive sale via the Internet at US$2. 50 per copy. § Readers were able to download the text onto their computers or e-books. § King sold 400, 000 copies during the first day.
 e-Publishing § Frederick Forsyth will publish five short stories online from mid-October 2000. § URL: http: //www. onlineoriginals. com § Cost of each story: £ 2 § Forsyth: “If people want to log on and chit chat about the stories, that’s fine. ”
e-Publishing § Frederick Forsyth will publish five short stories online from mid-October 2000. § URL: http: //www. onlineoriginals. com § Cost of each story: £ 2 § Forsyth: “If people want to log on and chit chat about the stories, that’s fine. ”
 The Big Picture § Change is the only constant. § Growth is the only certainty.
The Big Picture § Change is the only constant. § Growth is the only certainty.
 Future Projections § A recent IBM report forecasts a threefold (US$4. 5 trillion) jump in global education expenditure during the next 13 years. § The World Bank expects the number of higher education students will more than double from 70 million to 160 million by 2025. (Source: Richard Gluyas, New Nabs e-School Deal http: //finance. news. com. au, 22 April 2000).
Future Projections § A recent IBM report forecasts a threefold (US$4. 5 trillion) jump in global education expenditure during the next 13 years. § The World Bank expects the number of higher education students will more than double from 70 million to 160 million by 2025. (Source: Richard Gluyas, New Nabs e-School Deal http: //finance. news. com. au, 22 April 2000).
 The Global Lifelong Learning Economy Will USQ survive? Will USQ prosper?
The Global Lifelong Learning Economy Will USQ survive? Will USQ prosper?
 University Resources § USQ is a “Public” Australian University set up under State legislation via the “University of Southern Queensland Act” § It receives approximately 65% of its annual income as an “operating grant” from the Federal Government (including HECS payments) § The remaining income is generated from research and enterprise activities
University Resources § USQ is a “Public” Australian University set up under State legislation via the “University of Southern Queensland Act” § It receives approximately 65% of its annual income as an “operating grant” from the Federal Government (including HECS payments) § The remaining income is generated from research and enterprise activities
 Enrolled Students Semester 1, 2001 § All students § External § Percentage External 20, 625 15, 194* 76% *includes currently enrolled off-shore students 3, 480
Enrolled Students Semester 1, 2001 § All students § External § Percentage External 20, 625 15, 194* 76% *includes currently enrolled off-shore students 3, 480
 USQ’s Australian Off-Campus Students 2001 § § § § Queensland New South Wales & ACT Victoria Western Australia South Australia Northern Territory Tasmania Australian’s living overseas TOTAL 8, 184 1, 687 450 214 191 145 137 706 11, 714
USQ’s Australian Off-Campus Students 2001 § § § § Queensland New South Wales & ACT Victoria Western Australia South Australia Northern Territory Tasmania Australian’s living overseas TOTAL 8, 184 1, 687 450 214 191 145 137 706 11, 714
 USQ’s Off-Shore Students 2001 § § § § § Singapore Malaysia China South Africa Pacific Islands Zimbabwe United Arab Emirates Canada Total, including students from 60 other countries 1, 165 943 340 199 114 93 76 73 3, 480
USQ’s Off-Shore Students 2001 § § § § § Singapore Malaysia China South Africa Pacific Islands Zimbabwe United Arab Emirates Canada Total, including students from 60 other countries 1, 165 943 340 199 114 93 76 73 3, 480
 Semester 2, 2001 § A total of 4, 767 international students are now enrolled § 1, 515 additional domestic students have enrolled
Semester 2, 2001 § A total of 4, 767 international students are now enrolled § 1, 515 additional domestic students have enrolled
 Schendler (2000) The Internet has “reached a stage that isn’t so much about vision and proprietary innovation, as about execution and competition”.
Schendler (2000) The Internet has “reached a stage that isn’t so much about vision and proprietary innovation, as about execution and competition”.
 Five Generations of Distance Education Technology § The Correspondence Model § The Multimedia Model § The Telelearning Model § The Flexible Learning Model § The Intelligent Flexible Learning Model
Five Generations of Distance Education Technology § The Correspondence Model § The Multimedia Model § The Telelearning Model § The Flexible Learning Model § The Intelligent Flexible Learning Model
 Variable costs tend to increase or decrease directly (often linearly) with fluctuations in the volume of activity. In traditional distance education delivery, the distribution of packages of self-instructional materials (printed study guides, audiotapes, videotapes, etc) is a variable cost, which varies in direct proportion to the number of students enrolled.
Variable costs tend to increase or decrease directly (often linearly) with fluctuations in the volume of activity. In traditional distance education delivery, the distribution of packages of self-instructional materials (printed study guides, audiotapes, videotapes, etc) is a variable cost, which varies in direct proportion to the number of students enrolled.
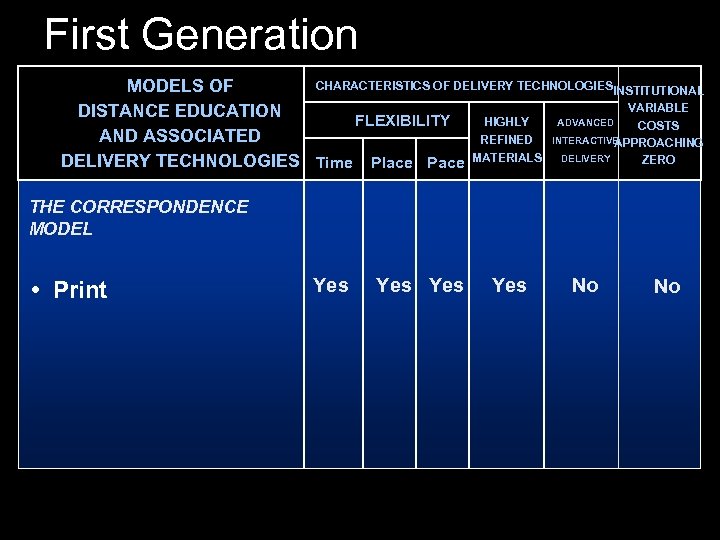 First Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE CORRESPONDENCE MODEL • Print Yes Yes No No
First Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE CORRESPONDENCE MODEL • Print Yes Yes No No
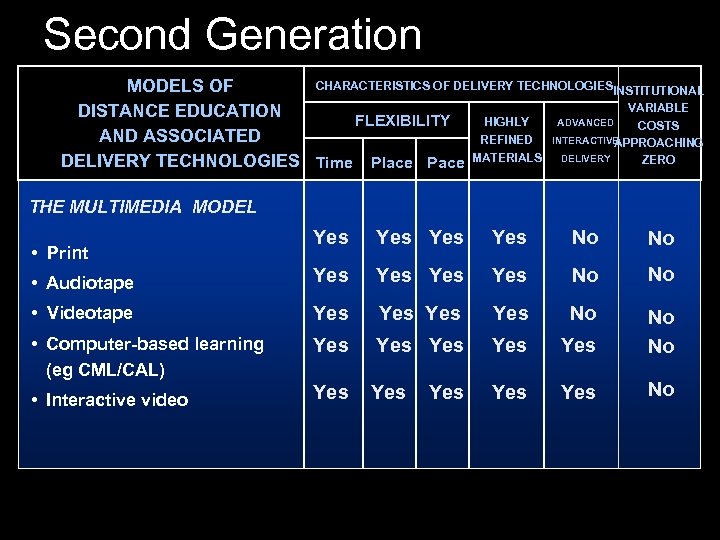 Second Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE MULTIMEDIA MODEL Yes Yes No No • Audiotape Yes Yes No No • Videotape Yes Yes No • Computer-based learning (eg CML/CAL) Yes Yes Yes No No • Interactive video Yes Yes No • Print Yes
Second Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE MULTIMEDIA MODEL Yes Yes No No • Audiotape Yes Yes No No • Videotape Yes Yes No • Computer-based learning (eg CML/CAL) Yes Yes Yes No No • Interactive video Yes Yes No • Print Yes
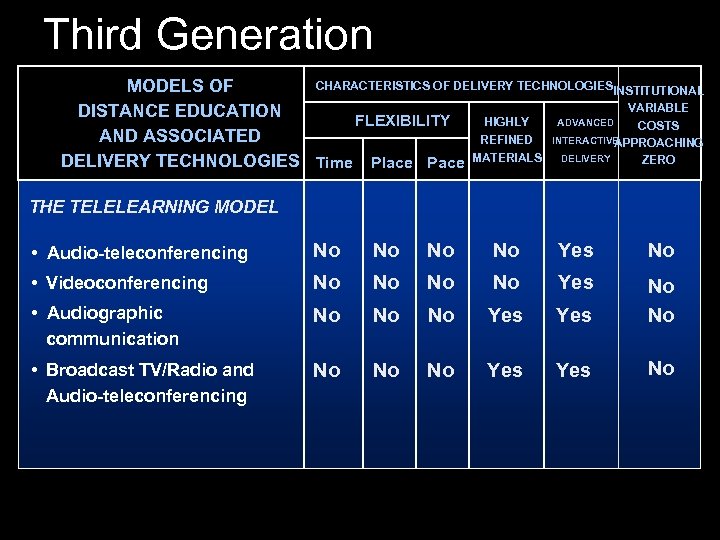 Third Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE TELELEARNING MODEL • Audio-teleconferencing No No Yes No • Videoconferencing No No Yes • Audiographic communication No No No Yes No No • Broadcast TV/Radio and Audio-teleconferencing No No No Yes No
Third Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE TELELEARNING MODEL • Audio-teleconferencing No No Yes No • Videoconferencing No No Yes • Audiographic communication No No No Yes No No • Broadcast TV/Radio and Audio-teleconferencing No No No Yes No
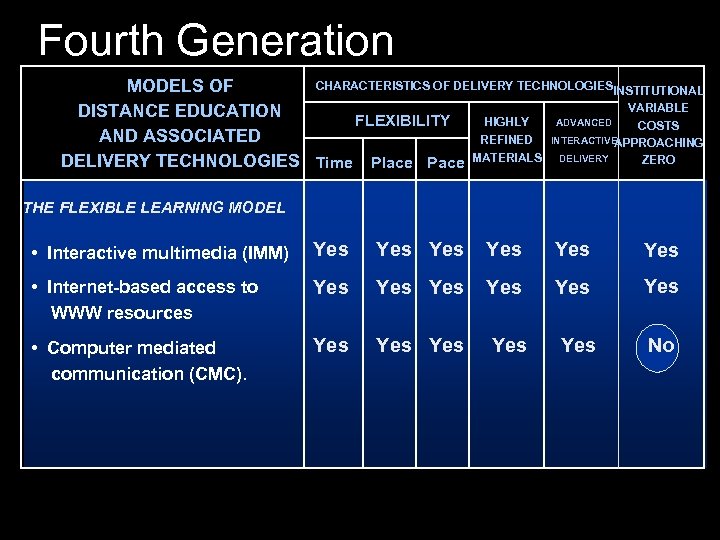 Fourth Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE FLEXIBLE LEARNING MODEL • Interactive multimedia (IMM) Yes Yes Yes • Internet-based access to WWW resources Yes Yes Yes • Computer mediated communication (CMC). Yes Yes Yes No
Fourth Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE FLEXIBLE LEARNING MODEL • Interactive multimedia (IMM) Yes Yes Yes • Internet-based access to WWW resources Yes Yes Yes • Computer mediated communication (CMC). Yes Yes Yes No
 The current applications of fourth generation Internetbased delivery tend to generate resource allocation models similar to tutorial-based on- campus teaching.
The current applications of fourth generation Internetbased delivery tend to generate resource allocation models similar to tutorial-based on- campus teaching.
 The underlying resource model is not significantly different from conventional on campus teaching, with a staff member being necessary to manage groups of approximately 20 students to maintain a reasonable quality of interaction and academic support.
The underlying resource model is not significantly different from conventional on campus teaching, with a staff member being necessary to manage groups of approximately 20 students to maintain a reasonable quality of interaction and academic support.
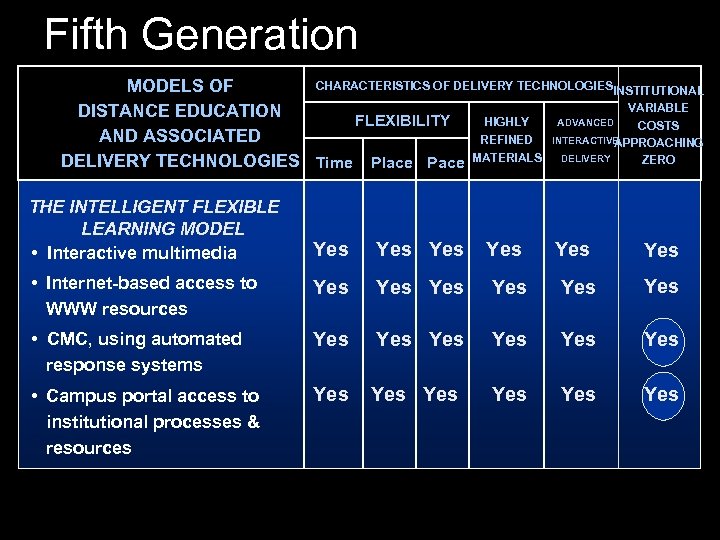 Fifth Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE INTELLIGENT FLEXIBLE LEARNING MODEL • Interactive multimedia Yes Yes Yes • Internet-based access to WWW resources Yes Yes Yes • CMC, using automated response systems Yes Yes Yes • Campus portal access to institutional processes & resources Yes Yes Yes
Fifth Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE INTELLIGENT FLEXIBLE LEARNING MODEL • Interactive multimedia Yes Yes Yes • Internet-based access to WWW resources Yes Yes Yes • CMC, using automated response systems Yes Yes Yes • Campus portal access to institutional processes & resources Yes Yes Yes


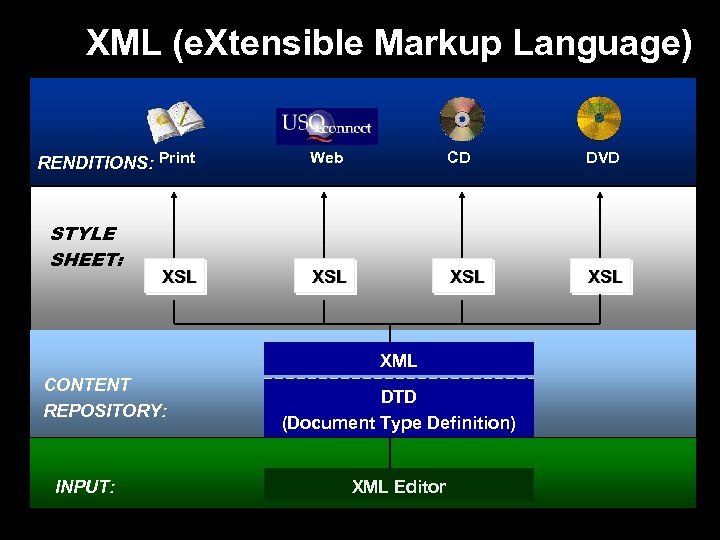 XML (e. Xtensible Markup Language) RENDITIONS: Print STYLE SHEET: XSL Web CD DVD XSL XSL XML CONTENT REPOSITORY: INPUT: DTD (Document Type Definition) XML Editor
XML (e. Xtensible Markup Language) RENDITIONS: Print STYLE SHEET: XSL Web CD DVD XSL XSL XML CONTENT REPOSITORY: INPUT: DTD (Document Type Definition) XML Editor

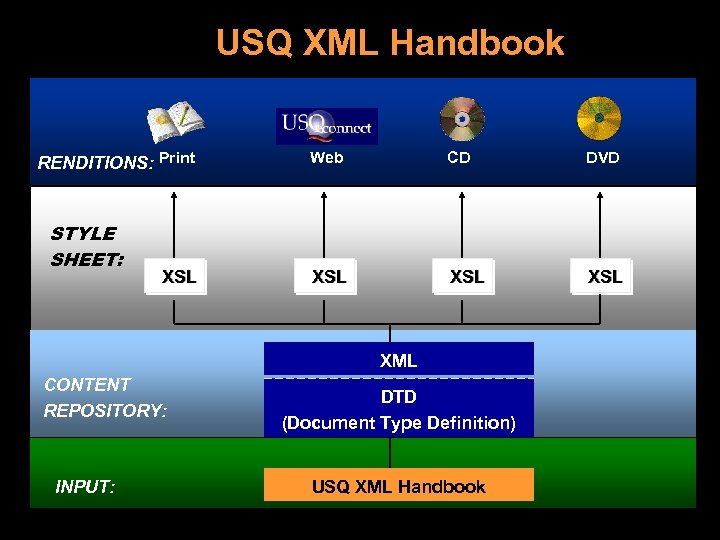 USQ XML Handbook RENDITIONS: Print STYLE SHEET: XSL Web CD DVD XSL XSL XML CONTENT REPOSITORY: INPUT: DTD (Document Type Definition) USQ XML Handbook
USQ XML Handbook RENDITIONS: Print STYLE SHEET: XSL Web CD DVD XSL XSL XML CONTENT REPOSITORY: INPUT: DTD (Document Type Definition) USQ XML Handbook




 USQOnline demonstration…….
USQOnline demonstration…….
 Garrison (1997) “The reflective and explicit nature of the written word is a disciplined and rigorous form of thinking and communicating …… it allows time for reflection and, thereby, facilitates learners making connections amongst ideas and constructing coherent knowledge structures”.
Garrison (1997) “The reflective and explicit nature of the written word is a disciplined and rigorous form of thinking and communicating …… it allows time for reflection and, thereby, facilitates learners making connections amongst ideas and constructing coherent knowledge structures”.
 Automating e-Learning § In the USQ approach, many teaching staff make use of discussion groups, which entail students posting “reflections” via the asynchronous CMC system. § Storing such interactions with appropriate metadata tags in a database is technically straightforward, and provides a rich resource for mining by key word/matching, using an automated response system.
Automating e-Learning § In the USQ approach, many teaching staff make use of discussion groups, which entail students posting “reflections” via the asynchronous CMC system. § Storing such interactions with appropriate metadata tags in a database is technically straightforward, and provides a rich resource for mining by key word/matching, using an automated response system.
 Automated Response Systems § Responses can be directed to the whole cohort of students, or at individuals; § They have the advantage of providing moreor-less immediate feedback to students at minimal variable cost; § As the intelligent object databases become more comprehensive, the institutional variable costs for the provision of effective tuition will tend towards zero.
Automated Response Systems § Responses can be directed to the whole cohort of students, or at individuals; § They have the advantage of providing moreor-less immediate feedback to students at minimal variable cost; § As the intelligent object databases become more comprehensive, the institutional variable costs for the provision of effective tuition will tend towards zero.
 e-Learner Relationship Management Using intelligent databases, the knowledge generated by solving student problems/enquiries is being progressively stored so that students with similar problems can have their enquiries dealt with immediately through the self-help, automated response capacity of the USQAssist system.
e-Learner Relationship Management Using intelligent databases, the knowledge generated by solving student problems/enquiries is being progressively stored so that students with similar problems can have their enquiries dealt with immediately through the self-help, automated response capacity of the USQAssist system.
 USQAssist As the intelligent databases become more comprehensive, the institutional variable costs for the provision of effective student support will tend towards zero.
USQAssist As the intelligent databases become more comprehensive, the institutional variable costs for the provision of effective student support will tend towards zero.


 The PC-e. Phone
The PC-e. Phone



 Organisational Development In many universities the development of web-based initiatives is not systemic, but is often the result of random acts of innovation initiated by risk-taking individual academics.
Organisational Development In many universities the development of web-based initiatives is not systemic, but is often the result of random acts of innovation initiated by risk-taking individual academics.
 The USQ Approach USQ’s institution-wide approach reflects one element of the corporate mission statement: “To be a leader in flexible learning and the use of information and communications technologies”.
The USQ Approach USQ’s institution-wide approach reflects one element of the corporate mission statement: “To be a leader in flexible learning and the use of information and communications technologies”.
 The USQ Approach The USQ approach is to give people: What they want, Where they want it, When they want it. WWW is purely incidental!
The USQ Approach The USQ approach is to give people: What they want, Where they want it, When they want it. WWW is purely incidental!
 USQ Case Study As a case study, the USQ experience exemplifies the necessary institution– wide corporate approach for an organization to become “fast, flexible and fluid” as it strives to develop the capacity to implement fifth generation distance education.
USQ Case Study As a case study, the USQ experience exemplifies the necessary institution– wide corporate approach for an organization to become “fast, flexible and fluid” as it strives to develop the capacity to implement fifth generation distance education.
 5 th Generation The fifth generation model of distance education has the potential to provide students with a valuable, personalized pedagogical experience at much lower cost than traditional approaches to distance education and conventional face-to-face education.
5 th Generation The fifth generation model of distance education has the potential to provide students with a valuable, personalized pedagogical experience at much lower cost than traditional approaches to distance education and conventional face-to-face education.
 5 th Generation If this can be achieved on a sufficiently large scale, then tuition costs can be significantly lowered, thereby engendering much greater access to higher education opportunities to many students throughout the world, who presently cannot afford to pay current prices.
5 th Generation If this can be achieved on a sufficiently large scale, then tuition costs can be significantly lowered, thereby engendering much greater access to higher education opportunities to many students throughout the world, who presently cannot afford to pay current prices.
 5 th Generation In effect, fifth generation distance education is not only less expensive, it also provides students with better quality tuition and more effective pedagogical and administrative support services at lower cost.
5 th Generation In effect, fifth generation distance education is not only less expensive, it also provides students with better quality tuition and more effective pedagogical and administrative support services at lower cost.
 The e-Revolution “Any new technology environment eventually creates a totally new human environment”. Marshall Mc. Luhan
The e-Revolution “Any new technology environment eventually creates a totally new human environment”. Marshall Mc. Luhan
 “Clicks and Mortar” are not enough The Internet is set to connect virtually everyone and everything – the Web is turning into humanity’s collective brain. Any organisation hoping to survive must mirror the Internet itself. It must become: open non-hierarchical democratic experimental tightly networked endlessly adaptable
“Clicks and Mortar” are not enough The Internet is set to connect virtually everyone and everything – the Web is turning into humanity’s collective brain. Any organisation hoping to survive must mirror the Internet itself. It must become: open non-hierarchical democratic experimental tightly networked endlessly adaptable
 “Clicks and Mortar” are not enough To survive and prosper organisations need to mirror the Internet and to develop a collective brain capable of - “habitual and radical innovation”. (Gary Hamel, Inside the Revolution, 2001)
“Clicks and Mortar” are not enough To survive and prosper organisations need to mirror the Internet and to develop a collective brain capable of - “habitual and radical innovation”. (Gary Hamel, Inside the Revolution, 2001)
 Aussie Rules……. OK?
Aussie Rules……. OK?
 USQ’s th 5 Generation “It is easier to create the future than it is to predict it. ” (Taylor, Census Night, 2001)
USQ’s th 5 Generation “It is easier to create the future than it is to predict it. ” (Taylor, Census Night, 2001)


