5620b73c2214033114ec41fd60d27084.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 96
 *** Text information storage and retrieval and the CDS/ISIS program Paul NIEUWENHUYSEN pnieuwen@vub. ac. be University Library, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlaan 2, B-1050 Brussel, Belgium
*** Text information storage and retrieval and the CDS/ISIS program Paul NIEUWENHUYSEN pnieuwen@vub. ac. be University Library, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlaan 2, B-1050 Brussel, Belgium
 *** What is a database? • A database is a collection of similar data records stored in a common file (or collection of files).
*** What is a database? • A database is a collection of similar data records stored in a common file (or collection of files).
 *** Software type = information retrieval software • Software for information storage and retrieval (ISR software) • Text(-oriented) database management systems (Text-DBMS) • Text information management systems (TIMS) • Document retrieval systems • Document management systems
*** Software type = information retrieval software • Software for information storage and retrieval (ISR software) • Text(-oriented) database management systems (Text-DBMS) • Text information management systems (TIMS) • Document retrieval systems • Document management systems
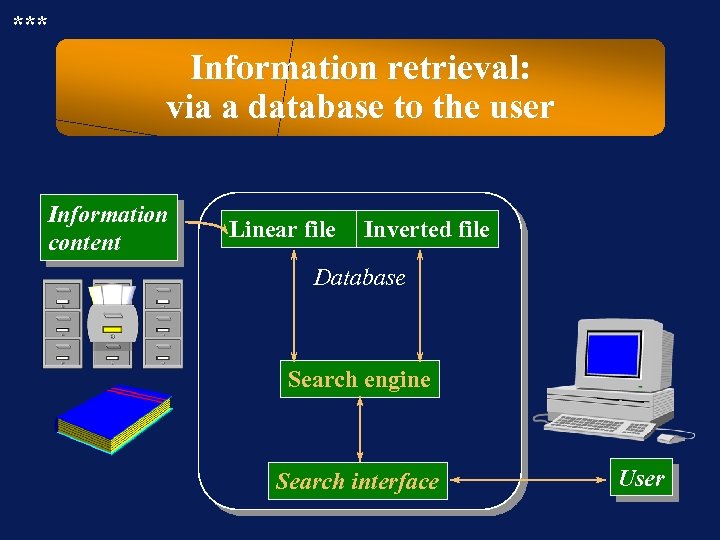 *** Information retrieval: via a database to the user Information content Linear file Inverted file Database Search engine Search interface User
*** Information retrieval: via a database to the user Information content Linear file Inverted file Database Search engine Search interface User
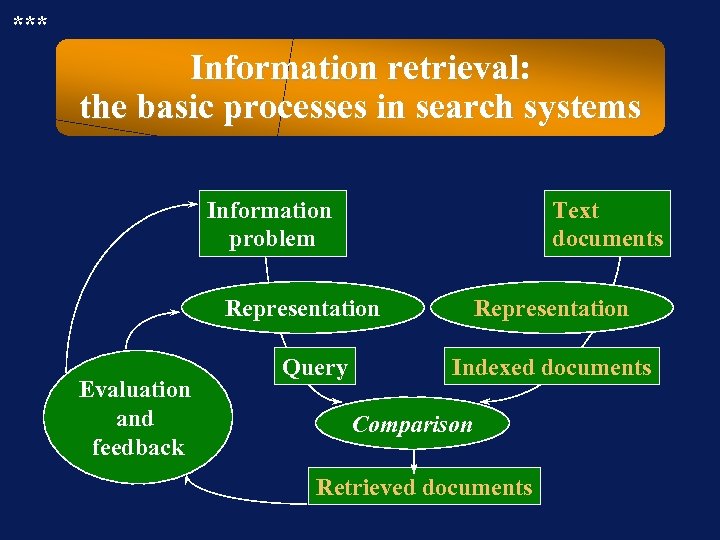 *** Information retrieval: the basic processes in search systems Information problem Text documents Representation Evaluation and feedback Query Representation Indexed documents Comparison Retrieved documents
*** Information retrieval: the basic processes in search systems Information problem Text documents Representation Evaluation and feedback Query Representation Indexed documents Comparison Retrieved documents
 *** Information retrieval systems: many components make up a system • Any retrieval system is built up of many more or less independent components. • These components can be modified to increase the quality of the results more or less independently.
*** Information retrieval systems: many components make up a system • Any retrieval system is built up of many more or less independent components. • These components can be modified to increase the quality of the results more or less independently.
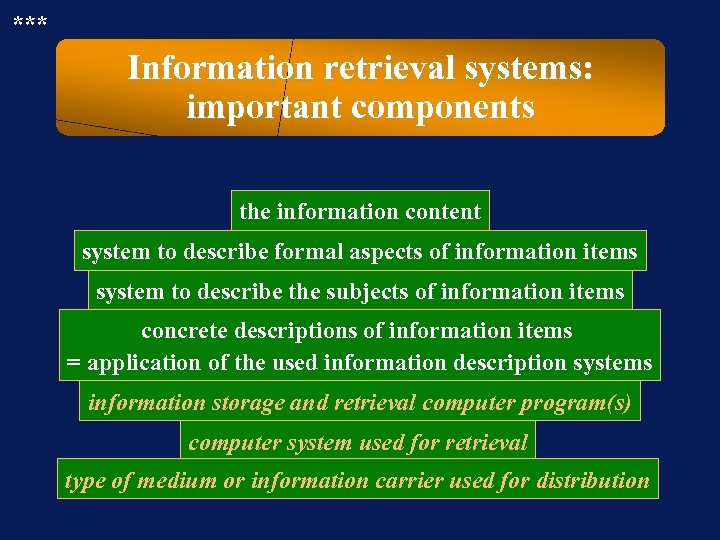 *** Information retrieval systems: important components the information content system to describe formal aspects of information items system to describe the subjects of information items concrete descriptions of information items = application of the used information description systems information storage and retrieval computer program(s) computer system used for retrieval type of medium or information carrier used for distribution
*** Information retrieval systems: important components the information content system to describe formal aspects of information items system to describe the subjects of information items concrete descriptions of information items = application of the used information description systems information storage and retrieval computer program(s) computer system used for retrieval type of medium or information carrier used for distribution
 *** Information retrieval systems: the information content • The information content is the information that is created or gathered by the producer. • The information content is independent of software and of distribution media. • The information content is input into the retrieval system using » a system (rules) to describe the formal aspects » a system (rules) to describe the contents (classification, thesaurus, . . . )
*** Information retrieval systems: the information content • The information content is the information that is created or gathered by the producer. • The information content is independent of software and of distribution media. • The information content is input into the retrieval system using » a system (rules) to describe the formal aspects » a system (rules) to describe the contents (classification, thesaurus, . . . )
 *** Information retrieval systems: media used for distribution • Hard copy (for information retrieval systems only in the broad sense) » Print » Microfiche • For computers: (for information retrieval systems strictu sensu) » Magnetic tape » Floppy disk; optical disk (CD-ROM, CD-i, Photo-CD, . . . ) » Online
*** Information retrieval systems: media used for distribution • Hard copy (for information retrieval systems only in the broad sense) » Print » Microfiche • For computers: (for information retrieval systems strictu sensu) » Magnetic tape » Floppy disk; optical disk (CD-ROM, CD-i, Photo-CD, . . . ) » Online
 *** Information retrieval systems: the computer program The information retrieval program consists of several modules, including: • The module that allows the creation of the inverted file(s) = index file(s) = dictionary file(s). • The search engine provides the search features and power that allow the inverted file(s) to be searched. • The interface between the system and the user determines how they (can) interact to search the database (using menus and/or icons and/or templates and/or commands).
*** Information retrieval systems: the computer program The information retrieval program consists of several modules, including: • The module that allows the creation of the inverted file(s) = index file(s) = dictionary file(s). • The search engine provides the search features and power that allow the inverted file(s) to be searched. • The interface between the system and the user determines how they (can) interact to search the database (using menus and/or icons and/or templates and/or commands).
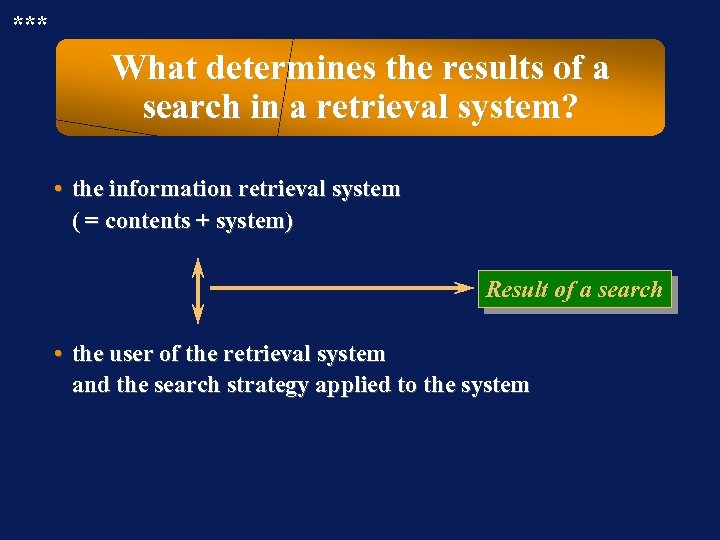 *** What determines the results of a search in a retrieval system? • the information retrieval system ( = contents + system) Result of a search • the user of the retrieval system and the search strategy applied to the system
*** What determines the results of a search in a retrieval system? • the information retrieval system ( = contents + system) Result of a search • the user of the retrieval system and the search strategy applied to the system
 *** Characteristics / definition of structured text-information • The text information is structured. (files, records, fields, sub-fields, links/relations among records, . . . ) • The length of records and fields can be “long”. • Some fields are multi-valued, i. e. they occur more than once.
*** Characteristics / definition of structured text-information • The text information is structured. (files, records, fields, sub-fields, links/relations among records, . . . ) • The length of records and fields can be “long”. • Some fields are multi-valued, i. e. they occur more than once.
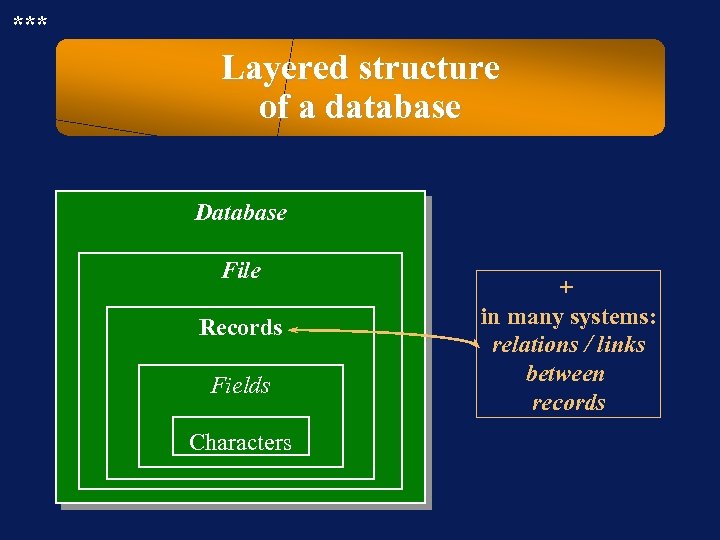 *** Layered structure of a database Database File Records Fields Characters + in many systems: relations / links between records
*** Layered structure of a database Database File Records Fields Characters + in many systems: relations / links between records
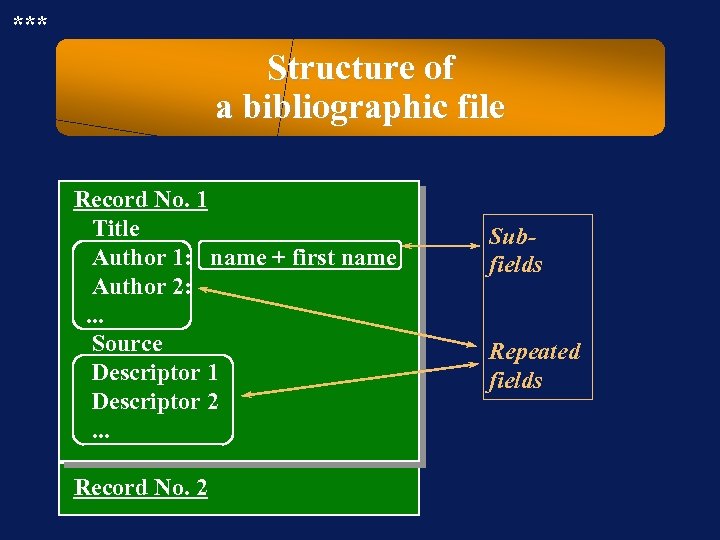 *** Structure of a bibliographic file Record No. 1 Title Author 1: name + first name Author 2: . . . Source Descriptor 1 Descriptor 2. . . Record No. 2 Subfields Repeated fields
*** Structure of a bibliographic file Record No. 1 Title Author 1: name + first name Author 2: . . . Source Descriptor 1 Descriptor 2. . . Record No. 2 Subfields Repeated fields
 *** Thesaurus: description • Thesaurus = » system to control a vocabulary + » the contents of this vocabulary • Thesaurus program = program to create, manage, modify and/or search a thesaurus using a computer
*** Thesaurus: description • Thesaurus = » system to control a vocabulary + » the contents of this vocabulary • Thesaurus program = program to create, manage, modify and/or search a thesaurus using a computer
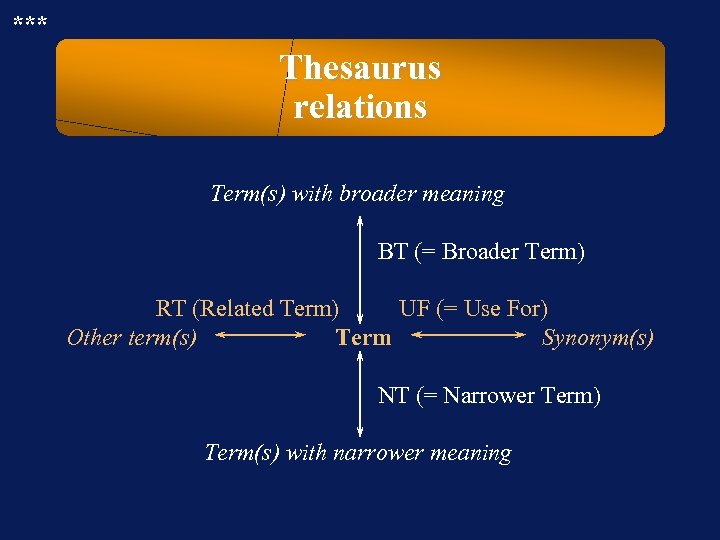 *** Thesaurus relations Term(s) with broader meaning BT (= Broader Term) RT (Related Term) UF (= Use For) Other term(s) Term Synonym(s) NT (= Narrower Term) Term(s) with narrower meaning
*** Thesaurus relations Term(s) with broader meaning BT (= Broader Term) RT (Related Term) UF (= Use For) Other term(s) Term Synonym(s) NT (= Narrower Term) Term(s) with narrower meaning
 *** Thesaurus applications • To find/choose index terms to add these to items, when terms are taken from a controlled vocabulary • To find more and/or better terms to search a database (to increase recall and precision) • To find more and/or better terms during writing • To understand the meaning of a term, by inspecting » the scope note of the term and/or » the relations with other terms
*** Thesaurus applications • To find/choose index terms to add these to items, when terms are taken from a controlled vocabulary • To find more and/or better terms to search a database (to increase recall and precision) • To find more and/or better terms during writing • To understand the meaning of a term, by inspecting » the scope note of the term and/or » the relations with other terms
 *** Database systems: why study this subject briefly ? • To achieve a better understanding of the inner workings of the external information retrieval systems that you use, so that you can exploit these more efficiently • To be able to evaluate the quality of database systems you are confronted with, so that you can » make better choices among available systems, » offer constructive suggestions to the manager, » . . .
*** Database systems: why study this subject briefly ? • To achieve a better understanding of the inner workings of the external information retrieval systems that you use, so that you can exploit these more efficiently • To be able to evaluate the quality of database systems you are confronted with, so that you can » make better choices among available systems, » offer constructive suggestions to the manager, » . . .
 **- Database systems: why study this subject in detail? To acquire the knowledge and skills to create / set up / manage your own local database system on a computer
**- Database systems: why study this subject in detail? To acquire the knowledge and skills to create / set up / manage your own local database system on a computer
 *** Database systems: definition A database (management) system is a program or set of programs, providing a means by which a user can easily store and retrieve data in the form of “databases”.
*** Database systems: definition A database (management) system is a program or set of programs, providing a means by which a user can easily store and retrieve data in the form of “databases”.
 **- Information retrieval software: related terms • Software for information storage and retrieval (ISR software) • Text(-oriented) database management systems (Text-DBMS) • Text information management systems (TIMS) • Document retrieval systems • Document management systems
**- Information retrieval software: related terms • Software for information storage and retrieval (ISR software) • Text(-oriented) database management systems (Text-DBMS) • Text information management systems (TIMS) • Document retrieval systems • Document management systems
 **- Information retrieval software: applications (Part 1) • Documentation centres • Archives • Libraries Documents • Musea • Medical files • Marketing departments Objects / Books /. . . • Schools • Bibliographic databases Courses / Teachers Archived documents Books / Documents Patient’s histories Clients / Potential clients Publications /. . .
**- Information retrieval software: applications (Part 1) • Documentation centres • Archives • Libraries Documents • Musea • Medical files • Marketing departments Objects / Books /. . . • Schools • Bibliographic databases Courses / Teachers Archived documents Books / Documents Patient’s histories Clients / Potential clients Publications /. . .
 **- Information retrieval software: applications (Part 2) • Meeting calendars • Product information • Laboratories • Personal documentation • Patent office • Co-operating information networks • . . . Meetings = conferences Product descriptions Recipes Documents Patents Documents / Persons / Institutes / Events /. . .
**- Information retrieval software: applications (Part 2) • Meeting calendars • Product information • Laboratories • Personal documentation • Patent office • Co-operating information networks • . . . Meetings = conferences Product descriptions Recipes Documents Patents Documents / Persons / Institutes / Events /. . .
 **- Cataloguing: hard copy versus computer-based • Hard copy » “Input” , i. e. cataloguing, on cards determines directly the “ouput”, i. e. the format of the data on the card as presented to the user » Summarized: INPUT=OUTPUT • Computer-based » Input in the database in fields allows later output in various formats for presentation » Summarized: 1. INPUT, 2. various OUTPUTs
**- Cataloguing: hard copy versus computer-based • Hard copy » “Input” , i. e. cataloguing, on cards determines directly the “ouput”, i. e. the format of the data on the card as presented to the user » Summarized: INPUT=OUTPUT • Computer-based » Input in the database in fields allows later output in various formats for presentation » Summarized: 1. INPUT, 2. various OUTPUTs
 *** Text-information management systems: characteristics and definition The information in the database is text oriented. Therefore, several features are required: » ability to store relatively long blocks of texts » ability to retrieve items in which specific words or terms occur anywhere
*** Text-information management systems: characteristics and definition The information in the database is text oriented. Therefore, several features are required: » ability to store relatively long blocks of texts » ability to retrieve items in which specific words or terms occur anywhere
 **- Text-information management: from free-form to structure Free form text information without structure Text database with information structured in files, records, fields, sub-fields, with links/relations among records, . . . (Ideally, each fields is repeatable = can be multi-valued, = can occur more than once in each record. )
**- Text-information management: from free-form to structure Free form text information without structure Text database with information structured in files, records, fields, sub-fields, with links/relations among records, . . . (Ideally, each fields is repeatable = can be multi-valued, = can occur more than once in each record. )
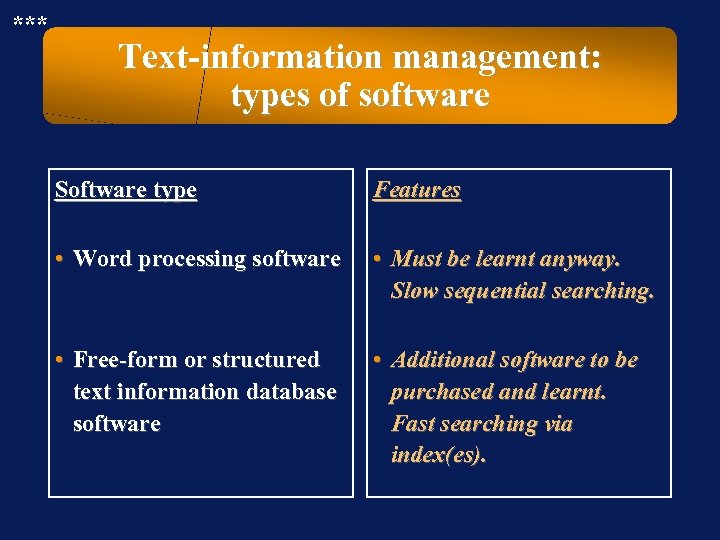 *** Text-information management: types of software Software type Features • Word processing software • Must be learnt anyway. Slow sequential searching. • Free-form or structured text information database software • Additional software to be purchased and learnt. Fast searching via index(es).
*** Text-information management: types of software Software type Features • Word processing software • Must be learnt anyway. Slow sequential searching. • Free-form or structured text information database software • Additional software to be purchased and learnt. Fast searching via index(es).
 **- Advantages of structured text-retrieval versus X-base systems Feature Text- X-base • Many long fields, forming long records retrieval systems Yes No • Repeatable fields Yes No • Subfields • Variable field lengths • Fast searching any word in all fields • Thesaurus to help searching Yes No
**- Advantages of structured text-retrieval versus X-base systems Feature Text- X-base • Many long fields, forming long records retrieval systems Yes No • Repeatable fields Yes No • Subfields • Variable field lengths • Fast searching any word in all fields • Thesaurus to help searching Yes No
 *** Hierarchy in the use of a database Database structure Input / Editing Searching / Output
*** Hierarchy in the use of a database Database structure Input / Editing Searching / Output
 *** Functions of database management software • Input / edit using keyboard or batch input • Indexing of the database(s) • Browse / Search / Select / Retrieve data from database • Output (Sort / Display / Print to file / Print to paper) + • Export / Import
*** Functions of database management software • Input / edit using keyboard or batch input • Indexing of the database(s) • Browse / Search / Select / Retrieve data from database • Output (Sort / Display / Print to file / Print to paper) + • Export / Import
 *** !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? Which advantages offers a document management system on computer?
*** !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? Which advantages offers a document management system on computer?
 *** Advantages of a document system on computer, for the user(s) JAccess to information is easier. JAccess to information is faster. JOnline access is possible even when centre is closed. JOnline access is possible from a distance. JIntegration in search module with data on loan status. JMore elements of the records can serve as search term. JCombinations of search terms can be used. JResults /selections can be stored as computer files.
*** Advantages of a document system on computer, for the user(s) JAccess to information is easier. JAccess to information is faster. JOnline access is possible even when centre is closed. JOnline access is possible from a distance. JIntegration in search module with data on loan status. JMore elements of the records can serve as search term. JCombinations of search terms can be used. JResults /selections can be stored as computer files.
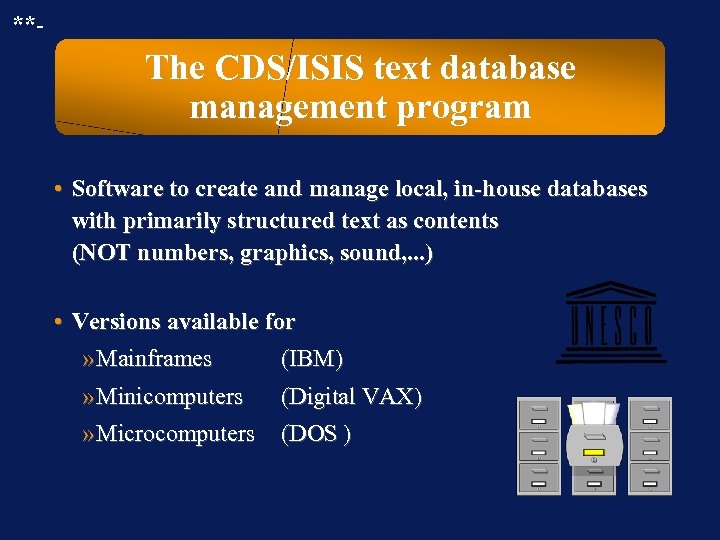 **- The CDS/ISIS text database management program • Software to create and manage local, in-house databases with primarily structured text as contents (NOT numbers, graphics, sound, . . . ) • Versions available for » Mainframes (IBM) » Minicomputers » Microcomputers (Digital VAX) (DOS )
**- The CDS/ISIS text database management program • Software to create and manage local, in-house databases with primarily structured text as contents (NOT numbers, graphics, sound, . . . ) • Versions available for » Mainframes (IBM) » Minicomputers » Microcomputers (Digital VAX) (DOS )
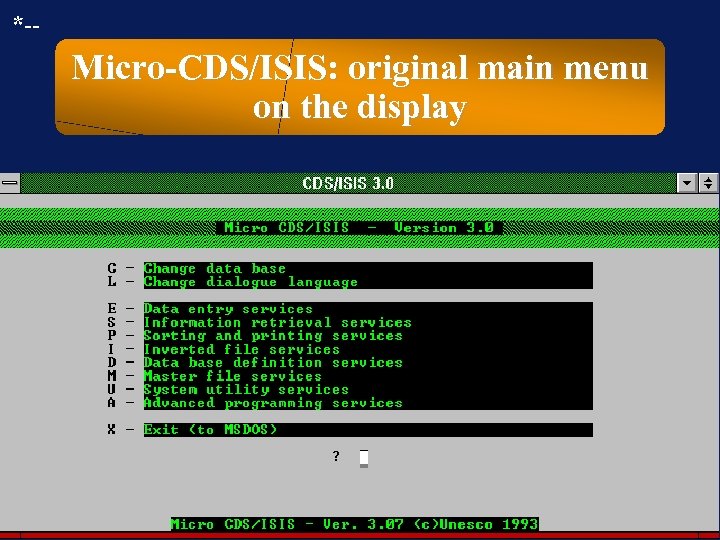 *-- Micro-CDS/ISIS: original main menu on the display
*-- Micro-CDS/ISIS: original main menu on the display
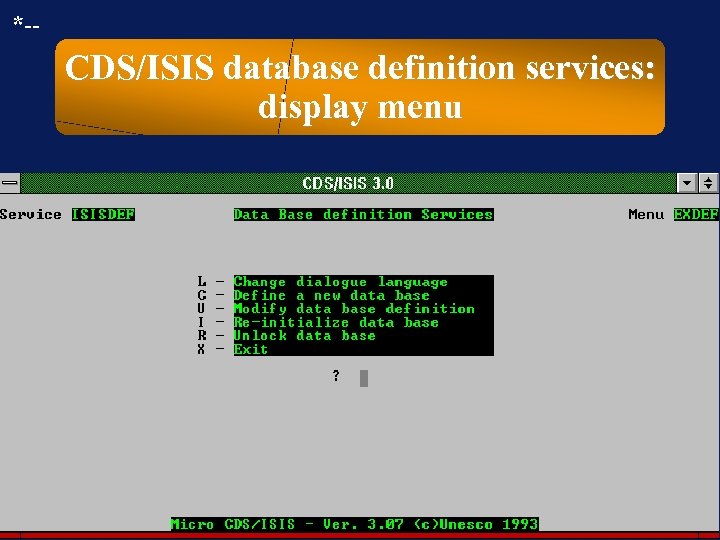 *-- CDS/ISIS database definition services: display menu
*-- CDS/ISIS database definition services: display menu
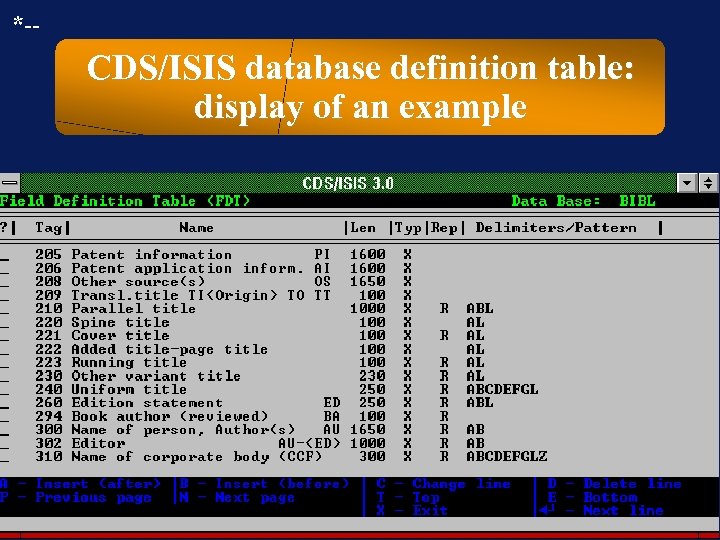 *-- CDS/ISIS database definition table: display of an example
*-- CDS/ISIS database definition table: display of an example
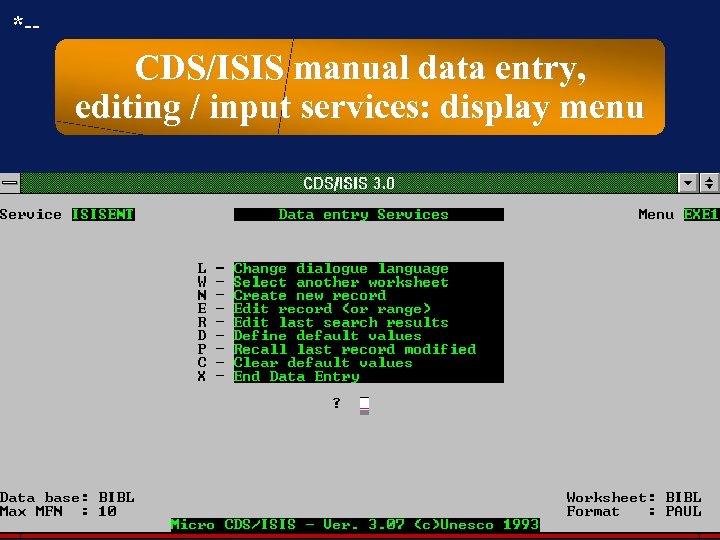 *-- CDS/ISIS manual data entry, editing / input services: display menu
*-- CDS/ISIS manual data entry, editing / input services: display menu
 **- Batch input / Import • Is batch input possible? • Is a format conversion program included or available? • . . .
**- Batch input / Import • Is batch input possible? • Is a format conversion program included or available? • . . .
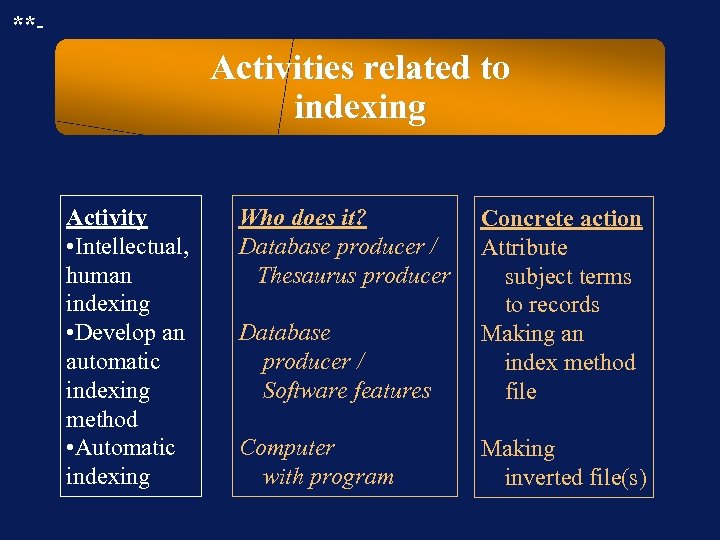 **- Activities related to indexing Activity • Intellectual, human indexing • Develop an automatic indexing method • Automatic indexing Who does it? Database producer / Thesaurus producer Database producer / Software features Concrete action Attribute subject terms to records Making an index method file Computer with program Making inverted file(s)
**- Activities related to indexing Activity • Intellectual, human indexing • Develop an automatic indexing method • Automatic indexing Who does it? Database producer / Thesaurus producer Database producer / Software features Concrete action Attribute subject terms to records Making an index method file Computer with program Making inverted file(s)
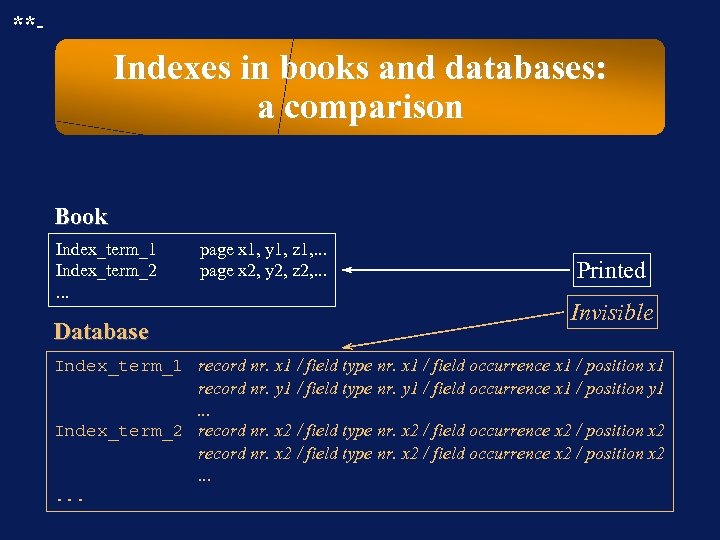 **- Indexes in books and databases: a comparison Book Index_term_1 Index_term_2. . . Database page x 1, y 1, z 1, . . . page x 2, y 2, z 2, . . . Printed Invisible Index_term_1 record nr. x 1 / field type nr. x 1 / field occurrence x 1 / position x 1 record nr. y 1 / field type nr. y 1 / field occurrence x 1 / position y 1. . . Index_term_2 record nr. x 2 / field type nr. x 2 / field occurrence x 2 / position x 2. . .
**- Indexes in books and databases: a comparison Book Index_term_1 Index_term_2. . . Database page x 1, y 1, z 1, . . . page x 2, y 2, z 2, . . . Printed Invisible Index_term_1 record nr. x 1 / field type nr. x 1 / field occurrence x 1 / position x 1 record nr. y 1 / field type nr. y 1 / field occurrence x 1 / position y 1. . . Index_term_2 record nr. x 2 / field type nr. x 2 / field occurrence x 2 / position x 2. . .
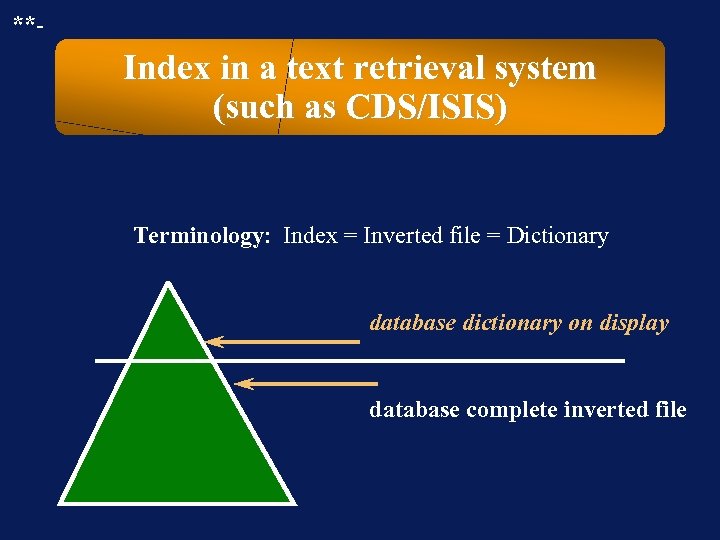 **- Index in a text retrieval system (such as CDS/ISIS) Terminology: Index = Inverted file = Dictionary database dictionary on display database complete inverted file
**- Index in a text retrieval system (such as CDS/ISIS) Terminology: Index = Inverted file = Dictionary database dictionary on display database complete inverted file
 **- Methods of inverted file creation ÆWord indexing J Simple / automatic / no indication required L Loss of word context J A field structure is not required ÆPhrase indexing L Indication of phrases during input is required J Richer than separate words J A field structure is not required ÆField indexing J Simple / automatic / no indication required J Context is better preserved L A field structure is required
**- Methods of inverted file creation ÆWord indexing J Simple / automatic / no indication required L Loss of word context J A field structure is not required ÆPhrase indexing L Indication of phrases during input is required J Richer than separate words J A field structure is not required ÆField indexing J Simple / automatic / no indication required J Context is better preserved L A field structure is required
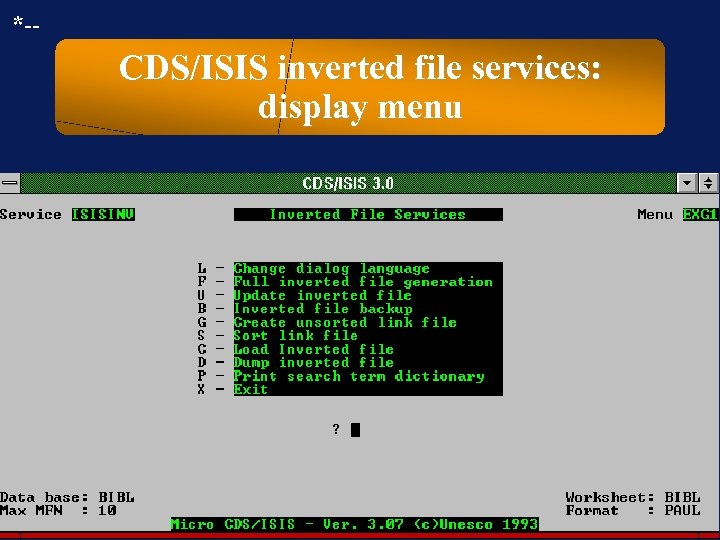 *-- CDS/ISIS inverted file services: display menu
*-- CDS/ISIS inverted file services: display menu
 **- Automatic indexing (file inversion) • • Word indexing? with proximity indexing? Field indexing? Sub-field indexing? Phrase indexing? Possible? Obligatory? ÆMaximum length of index entry? ÆList of stopwords available? ÆImmediately after input or in batch? (Slow down. . . ? ) ÆIndexing speed? ÆAdding prefixes/tags possible? ÆModification of indexing possible?
**- Automatic indexing (file inversion) • • Word indexing? with proximity indexing? Field indexing? Sub-field indexing? Phrase indexing? Possible? Obligatory? ÆMaximum length of index entry? ÆList of stopwords available? ÆImmediately after input or in batch? (Slow down. . . ? ) ÆIndexing speed? ÆAdding prefixes/tags possible? ÆModification of indexing possible?
 **- !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? Why can the index of a database be so large in comparison with the size of the database?
**- !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? Why can the index of a database be so large in comparison with the size of the database?
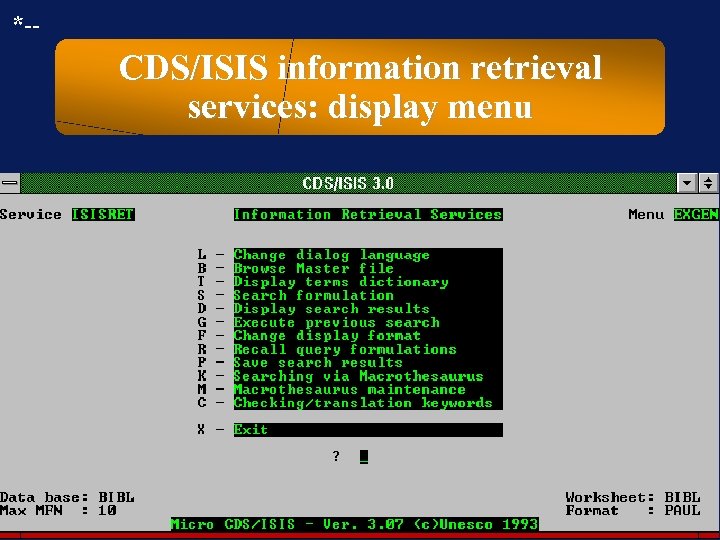 *-- CDS/ISIS information retrieval services: display menu
*-- CDS/ISIS information retrieval services: display menu
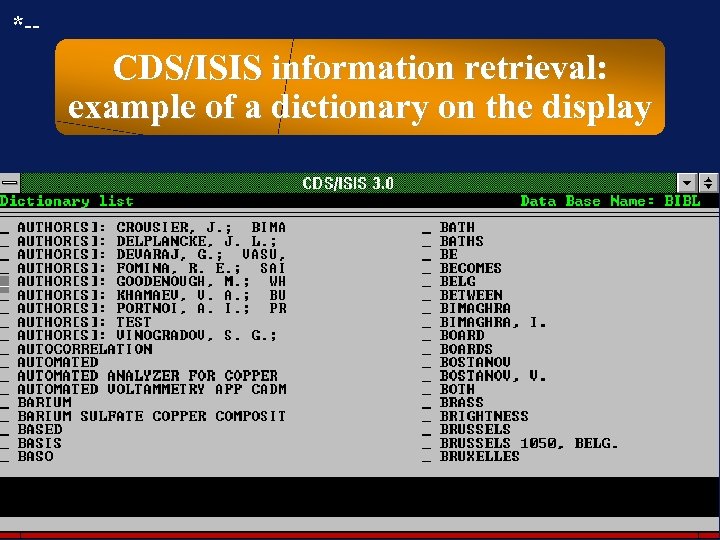 *-- CDS/ISIS information retrieval: example of a dictionary on the display
*-- CDS/ISIS information retrieval: example of a dictionary on the display
 **- Output from a database to various “devices” • to video display • to printer • to computer file (“printing” to a file) =< ;
**- Output from a database to various “devices” • to video display • to printer • to computer file (“printing” to a file) =< ;
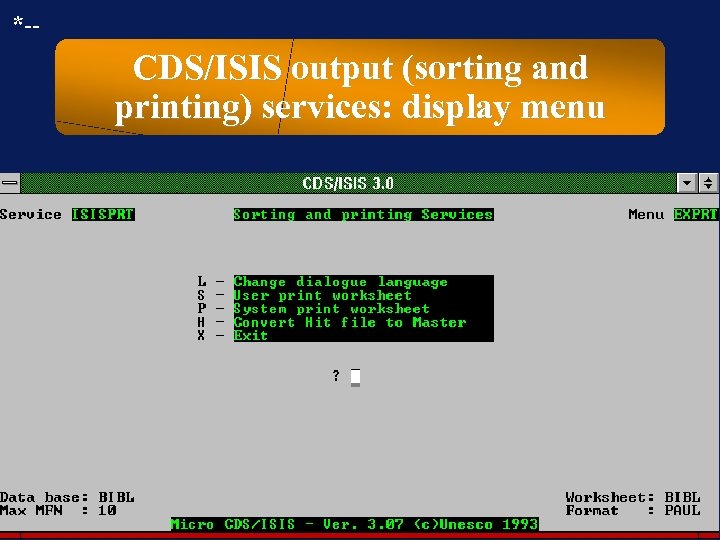 *-- CDS/ISIS output (sorting and printing) services: display menu
*-- CDS/ISIS output (sorting and printing) services: display menu
 **- Formatting of data within each record in output • Independent of output device: » Determine the sequence of the fields in each record. » Omit specific fields from each record. » Add field names or tags to the fields in each record. » Indicate the search term(s) in each record. • Dependent of output device: » Specify character formats in each (sub)field: typeface + size + bold/italic/underline
**- Formatting of data within each record in output • Independent of output device: » Determine the sequence of the fields in each record. » Omit specific fields from each record. » Add field names or tags to the fields in each record. » Indicate the search term(s) in each record. • Dependent of output device: » Specify character formats in each (sub)field: typeface + size + bold/italic/underline
 **- Sorting / arranging of records in the whole output • Can the user determine the sequence of the records? • Which elements can be used as a basis for sorting? • Can stopwords be omitted as a basis for sorting? • What is the maximum number of sort levels? • Can the user choose between ascending or descending order? • Can duplicate records be eliminated? (If yes: Can the user determine the meaning of duplicate? ) • Can output formats (styles) be stored?
**- Sorting / arranging of records in the whole output • Can the user determine the sequence of the records? • Which elements can be used as a basis for sorting? • Can stopwords be omitted as a basis for sorting? • What is the maximum number of sort levels? • Can the user choose between ascending or descending order? • Can duplicate records be eliminated? (If yes: Can the user determine the meaning of duplicate? ) • Can output formats (styles) be stored?
 **- Thesaurus program module: purpose • Does the database management program offer a thesaurus module which allows the user to create, modify, store, and delete relations between terms used in the database? • This is mainly used to establish relations among controlled subject indexing terms. • If more than one controlled vocabulary is used, these should be managed separately.
**- Thesaurus program module: purpose • Does the database management program offer a thesaurus module which allows the user to create, modify, store, and delete relations between terms used in the database? • This is mainly used to establish relations among controlled subject indexing terms. • If more than one controlled vocabulary is used, these should be managed separately.
 **- Structure of a thesaurus database record (Fields for “good” terms) • “Good” term • Controlled vocabulary to which the term belongs (if more than 1 is used in the same database) • Scope note (= definition of the controlled term) • Date of creation or modification of the term • Notes
**- Structure of a thesaurus database record (Fields for “good” terms) • “Good” term • Controlled vocabulary to which the term belongs (if more than 1 is used in the same database) • Scope note (= definition of the controlled term) • Date of creation or modification of the term • Notes
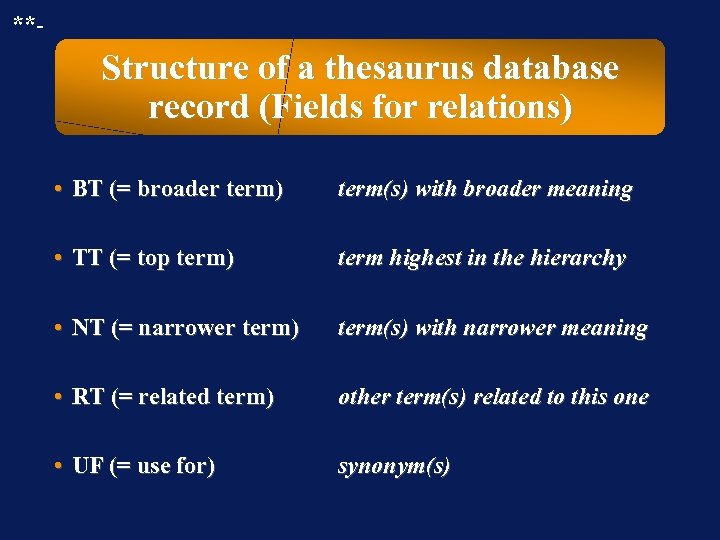 **- Structure of a thesaurus database record (Fields for relations) • BT (= broader term) term(s) with broader meaning • TT (= top term) term highest in the hierarchy • NT (= narrower term) term(s) with narrower meaning • RT (= related term) other term(s) related to this one • UF (= use for) synonym(s)
**- Structure of a thesaurus database record (Fields for relations) • BT (= broader term) term(s) with broader meaning • TT (= top term) term highest in the hierarchy • NT (= narrower term) term(s) with narrower meaning • RT (= related term) other term(s) related to this one • UF (= use for) synonym(s)
 **- Structure of a thesaurus database record (Fields forbidden terms) • Forbidden term • US (= use instead) “good” term in the controlled vocabulary
**- Structure of a thesaurus database record (Fields forbidden terms) • Forbidden term • US (= use instead) “good” term in the controlled vocabulary
 **- Structure of a thesaurus database record (Fields for candidate terms) • Candidate “good” term in the controlled vocabulary • (Other fields as in the case of “good” terms)
**- Structure of a thesaurus database record (Fields for candidate terms) • Candidate “good” term in the controlled vocabulary • (Other fields as in the case of “good” terms)
 **- Structure of a multilingual thesaurus database record Each type of field in a thesaurus record occurs for each language.
**- Structure of a multilingual thesaurus database record Each type of field in a thesaurus record occurs for each language.
 **- Thesaurus program: desirable properties (Part 1) • Multilingual user interface = menus and messages in more than 1 language • Multilingual contents = terms in more than 1 language • When a term in thesaurus database is added, changed or deleted, the program automatically makes the corresponding changes throughout the whole thesaurus database, there where that term occurs • The program controls the creation of impossible (= forbidden) or undesirable relations
**- Thesaurus program: desirable properties (Part 1) • Multilingual user interface = menus and messages in more than 1 language • Multilingual contents = terms in more than 1 language • When a term in thesaurus database is added, changed or deleted, the program automatically makes the corresponding changes throughout the whole thesaurus database, there where that term occurs • The program controls the creation of impossible (= forbidden) or undesirable relations
 **- Thesaurus program: desirable properties (Part 2) • Can thesaurus contents be formatted and printed or sent to file? • Can more than 1 thesaurus be managed, linked to the same database? • Can a thesaurus database can be used with more than 1 primary database? • Can the program signal the presence of orphan terms (= terms without relation)?
**- Thesaurus program: desirable properties (Part 2) • Can thesaurus contents be formatted and printed or sent to file? • Can more than 1 thesaurus be managed, linked to the same database? • Can a thesaurus database can be used with more than 1 primary database? • Can the program signal the presence of orphan terms (= terms without relation)?
 **- Thesaurus program: integration with input/editing of the primary database How simply and quickly can the user » search thesaurus during manual input/editing? (for instance to use it as an authority list) » copy a term from a thesaurus and paste into a database record? » copy a term from the database and paste into a thesaurus? » . . .
**- Thesaurus program: integration with input/editing of the primary database How simply and quickly can the user » search thesaurus during manual input/editing? (for instance to use it as an authority list) » copy a term from a thesaurus and paste into a database record? » copy a term from the database and paste into a thesaurus? » . . .
 **- Thesaurus program: integration with searching of the primary database • Can the user browse thesaurus during a search in the database? • Can the program automatically formulate a query, when the user selects terms in thesaurus module? • Does the program allow to include easily and quickly synonyms, narrower terms and broader terms in a query? • . . .
**- Thesaurus program: integration with searching of the primary database • Can the user browse thesaurus during a search in the database? • Can the program automatically formulate a query, when the user selects terms in thesaurus module? • Does the program allow to include easily and quickly synonyms, narrower terms and broader terms in a query? • . . .
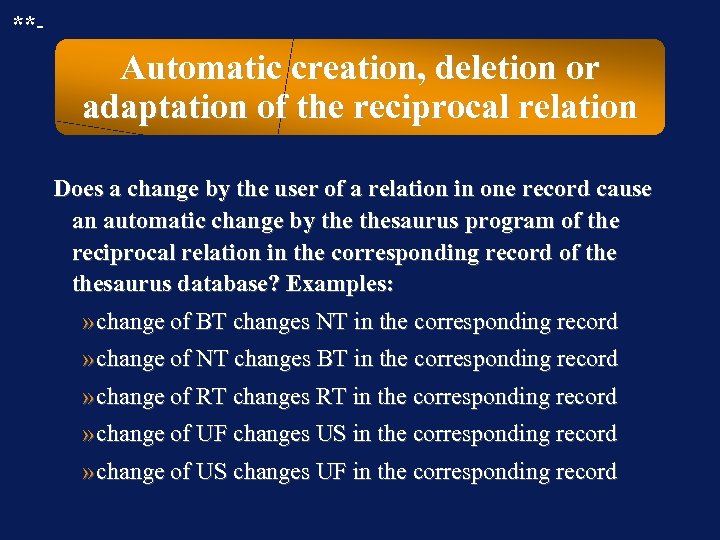 **- Automatic creation, deletion or adaptation of the reciprocal relation Does a change by the user of a relation in one record cause an automatic change by thesaurus program of the reciprocal relation in the corresponding record of thesaurus database? Examples: » change of BT changes NT in the corresponding record » change of NT changes BT in the corresponding record » change of RT changes RT in the corresponding record » change of UF changes US in the corresponding record » change of US changes UF in the corresponding record
**- Automatic creation, deletion or adaptation of the reciprocal relation Does a change by the user of a relation in one record cause an automatic change by thesaurus program of the reciprocal relation in the corresponding record of thesaurus database? Examples: » change of BT changes NT in the corresponding record » change of NT changes BT in the corresponding record » change of RT changes RT in the corresponding record » change of UF changes US in the corresponding record » change of US changes UF in the corresponding record
 **- Automatic control of the creation of impossible or undesirable relations Does thesaurus program avoid the creation of impossible or undesirable relations, or does it warn the user? Examples of this kind of relations: » circular hierarchy (a NT b, b NT c, c NT a, or longer) » circular synonym relation (a UF b, b UF a) » iterative synonym relations (a US b, b US c, or longer) » incomplete relations (a RT b, while b does not exist) » term related to itself (for instance: a NT a) » . . .
**- Automatic control of the creation of impossible or undesirable relations Does thesaurus program avoid the creation of impossible or undesirable relations, or does it warn the user? Examples of this kind of relations: » circular hierarchy (a NT b, b NT c, c NT a, or longer) » circular synonym relation (a UF b, b UF a) » iterative synonym relations (a US b, b US c, or longer) » incomplete relations (a RT b, while b does not exist) » term related to itself (for instance: a NT a) » . . .
 *-- Trilingual thesaurus program module for CDS/ISIS: properties • It is an additional program in CDS/ISIS Pascal language • Usage is free of charge, as in the case of CDS/ISIS • Thesaurus database management is based on CDS/ISIS • The thesaurus program, as well as CDS/ISIS, offers a user interface in English, French, and Spanish • The contents of a thesaurus database is trilingual : each term in English, French, and Spanish (each one replaceable by another language)
*-- Trilingual thesaurus program module for CDS/ISIS: properties • It is an additional program in CDS/ISIS Pascal language • Usage is free of charge, as in the case of CDS/ISIS • Thesaurus database management is based on CDS/ISIS • The thesaurus program, as well as CDS/ISIS, offers a user interface in English, French, and Spanish • The contents of a thesaurus database is trilingual : each term in English, French, and Spanish (each one replaceable by another language)
 *-- Trilingual thesaurus program for CDS/ISIS: the relations among terms • The available relations are: US, UF, NT, BT, TT, RT • Unlimited number of occurrences for each type of relations in each record • After a change of a relation, the program automatically adapts the corresponding relation in the corresponding thesaurus term records
*-- Trilingual thesaurus program for CDS/ISIS: the relations among terms • The available relations are: US, UF, NT, BT, TT, RT • Unlimited number of occurrences for each type of relations in each record • After a change of a relation, the program automatically adapts the corresponding relation in the corresponding thesaurus term records
 *-- Trilingual thesaurus program for CDS/ISIS: control of relations The program avoids the creation of some impossible or undesirable relations: » circular synonym relation (a UF b, b UF a) » iterative synonym relations (a US b, b US c, or longer) » incomplete relations (a RT b, while b does not exist)
*-- Trilingual thesaurus program for CDS/ISIS: control of relations The program avoids the creation of some impossible or undesirable relations: » circular synonym relation (a UF b, b UF a) » iterative synonym relations (a US b, b US c, or longer) » incomplete relations (a RT b, while b does not exist)
 *-- Trilingual thesaurus for CDS/ISIS: integration with searching • The user can browse thesaurus during a search in the primary database. • The program automatically formulates a query in the primary database, when the user selects terms in thesaurus module. • The program allows to include easily and quickly synonyms, narrower terms and broader terms in a query. • The thesaurus database can be used for searching with more than 1 primary database.
*-- Trilingual thesaurus for CDS/ISIS: integration with searching • The user can browse thesaurus during a search in the primary database. • The program automatically formulates a query in the primary database, when the user selects terms in thesaurus module. • The program allows to include easily and quickly synonyms, narrower terms and broader terms in a query. • The thesaurus database can be used for searching with more than 1 primary database.
 *-- Trilingual thesaurus program module for CDS/ISIS: further properties • In each record describing a term, a field for a scope note is present. • A field for date of term creation is present. • Several printout formats are included.
*-- Trilingual thesaurus program module for CDS/ISIS: further properties • In each record describing a term, a field for a scope note is present. • A field for date of term creation is present. • Several printout formats are included.
 *-- How to obtain the trilingual thesaurus program for CDS/ISIS? • the national distributor in your country • UNESCO Headquarters, General Information Programme, 1 rue Miollis, Paris, France • . . .
*-- How to obtain the trilingual thesaurus program for CDS/ISIS? • the national distributor in your country • UNESCO Headquarters, General Information Programme, 1 rue Miollis, Paris, France • . . .
 *-- Trilingual thesaurus program module for CDS/ISIS: conclusions - Negative: Not well integrated with the input/editing module of CDS/ISIS + Positive: Exceptionally interesting price/quality ratio
*-- Trilingual thesaurus program module for CDS/ISIS: conclusions - Negative: Not well integrated with the input/editing module of CDS/ISIS + Positive: Exceptionally interesting price/quality ratio
 **- Security / privacy / protection of databases • Password for searching specific database(s) and / or fields and / or record • Password for editing specific database(s) and / or fields and / or records • Password for changing » database structure » input and modification work sheets » sort and print formats of data in records » sort and print formats of records in a selection
**- Security / privacy / protection of databases • Password for searching specific database(s) and / or fields and / or record • Password for editing specific database(s) and / or fields and / or records • Password for changing » database structure » input and modification work sheets » sort and print formats of data in records » sort and print formats of records in a selection
 *-- Security / privacy / protection provided by DOS can make files » read-only » hidden
*-- Security / privacy / protection provided by DOS can make files » read-only » hidden
 *-- Security / privacy / protection in CDS/ISIS • SYSPAR. PAR file (entry 0) asks for a password, which can limit access to a particular » database » set of worksheets » set of menus » set of additional CDS/ISIS programs • Using the read-only version, named ISISCD. EXE, prevents modifications. • Menus can be changed or removed to prevent access.
*-- Security / privacy / protection in CDS/ISIS • SYSPAR. PAR file (entry 0) asks for a password, which can limit access to a particular » database » set of worksheets » set of menus » set of additional CDS/ISIS programs • Using the read-only version, named ISISCD. EXE, prevents modifications. • Menus can be changed or removed to prevent access.
 **- Passwords and usage tracking • Does the use of passwords linked to users or user groups allow usage tracking by a systems manager? “Usage” = for instance, number and types of search and/or edit actions. • This can be useful for studies and system management.
**- Passwords and usage tracking • Does the use of passwords linked to users or user groups allow usage tracking by a systems manager? “Usage” = for instance, number and types of search and/or edit actions. • This can be useful for studies and system management.
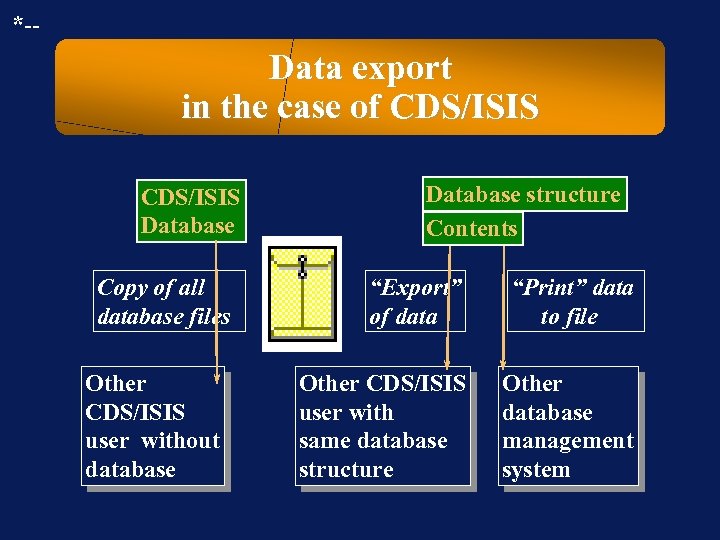 *-- Data export in the case of CDS/ISIS Database Copy of all database files Other CDS/ISIS user without database Database structure Contents “Export” of data “Print” data to file Other CDS/ISIS user with same database structure Other database management system
*-- Data export in the case of CDS/ISIS Database Copy of all database files Other CDS/ISIS user without database Database structure Contents “Export” of data “Print” data to file Other CDS/ISIS user with same database structure Other database management system
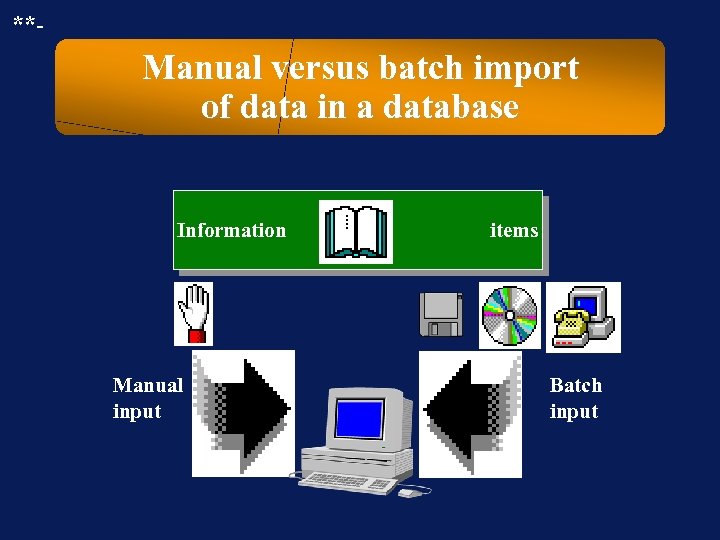 **- Manual versus batch import of data in a database Information Manual input items Batch input
**- Manual versus batch import of data in a database Information Manual input items Batch input
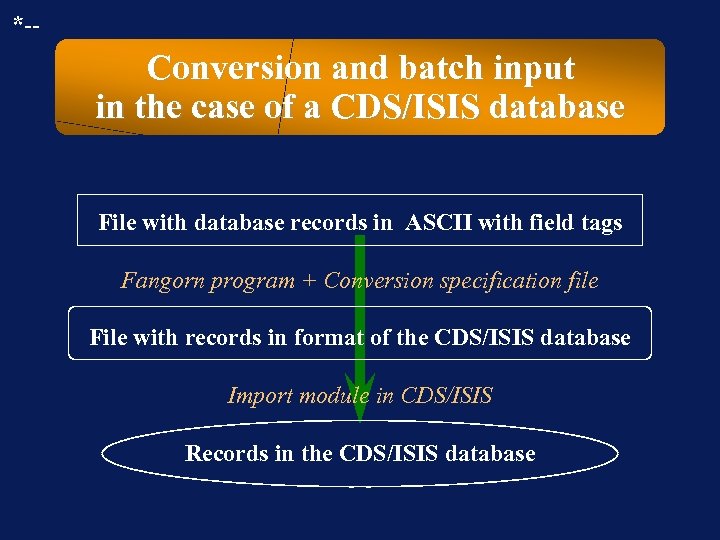 *-- Conversion and batch input in the case of a CDS/ISIS database File with database records in ASCII with field tags Fangorn program + Conversion specification file File with records in format of the CDS/ISIS database Import module in CDS/ISIS Records in the CDS/ISIS database
*-- Conversion and batch input in the case of a CDS/ISIS database File with database records in ASCII with field tags Fangorn program + Conversion specification file File with records in format of the CDS/ISIS database Import module in CDS/ISIS Records in the CDS/ISIS database
 *-- Format conversion program Fangorn • Authors: Besemer and Nieuwenhuysen • Available via anonymous ftp from » PCWS 1. SCI. SNS. IT » ftp. vub. ac. be in the directory pubprojectsDocinfopaulcursusisis » …
*-- Format conversion program Fangorn • Authors: Besemer and Nieuwenhuysen • Available via anonymous ftp from » PCWS 1. SCI. SNS. IT » ftp. vub. ac. be in the directory pubprojectsDocinfopaulcursusisis » …
 *-- Specification of a format conversion in the case of Fangorn for CDS/ISIS
*-- Specification of a format conversion in the case of Fangorn for CDS/ISIS
 **- !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? Which software packages for storage and retrieval of structured text do YOU know?
**- !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? Which software packages for storage and retrieval of structured text do YOU know?
 **-Examples Microcomputers software packages for structured text retrieval: examples • ask. Sam • Bib-Search • CAIRS • Notes (Lotus / IBM) • Personal Librarian • Pro-Cite • Cardbox-Plus • CDS / ISIS • Headfast • Reference Manager • Strix • STATUS • Idea. List • Inmagic • Topic (Verity) • . . .
**-Examples Microcomputers software packages for structured text retrieval: examples • ask. Sam • Bib-Search • CAIRS • Notes (Lotus / IBM) • Personal Librarian • Pro-Cite • Cardbox-Plus • CDS / ISIS • Headfast • Reference Manager • Strix • STATUS • Idea. List • Inmagic • Topic (Verity) • . . .
 **- !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? How can you use a word processing program together with a text retrieval system?
**- !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? How can you use a word processing program together with a text retrieval system?
 **- Word processing program to assist a retrieval program F To polish text data before import in the database managed by the retrieval program $ To inspect output to printer before real printing 2 To accept output from the retrieval program for further and better formatting, followed by printing
**- Word processing program to assist a retrieval program F To polish text data before import in the database managed by the retrieval program $ To inspect output to printer before real printing 2 To accept output from the retrieval program for further and better formatting, followed by printing
 **- !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? Which benefits offers a field structure to databases?
**- !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? Which benefits offers a field structure to databases?
 **- Field structure in records: benefits concerning input • The indication of fields in input worksheets guides the input. • Default values can be assigned to fields which can avoid errors and can make input faster. • The existence of fields allows control of the contents format of each specific field during input. • . . .
**- Field structure in records: benefits concerning input • The indication of fields in input worksheets guides the input. • Default values can be assigned to fields which can avoid errors and can make input faster. • The existence of fields allows control of the contents format of each specific field during input. • . . .
 **- Field structure in records: benefits concerning searching • User can limit search to specific fields. • Field type adds information to contents. • Field-indexing keeps data together in index. • . . .
**- Field structure in records: benefits concerning searching • User can limit search to specific fields. • Field type adds information to contents. • Field-indexing keeps data together in index. • . . .
 **- Field structure in records: benefits concerning output • Field structure makes output easier to understand. • In output, each field can be indicated with tag/prefix. • Records can be sorted based on contents of a field. • In output, the fields can be sorted in each record. • In output, some fields can be omitted. • . . .
**- Field structure in records: benefits concerning output • Field structure makes output easier to understand. • In output, each field can be indicated with tag/prefix. • Records can be sorted based on contents of a field. • In output, the fields can be sorted in each record. • In output, some fields can be omitted. • . . .
 **- !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? Besides all the benefits offered by a field structure in a database, which problems does this cause?
**- !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? Besides all the benefits offered by a field structure in a database, which problems does this cause?
 **- Field structure in records: problems (Part 1) • In the short term, it is more expensive and time consuming, than handling less structured data. • Initially, the database manager who wants to create a new database has to make decisions: » which fields to create to subdivide the database records, » which field tags or names to use for the internal housekeeping of the database by the chosen database management software package.
**- Field structure in records: problems (Part 1) • In the short term, it is more expensive and time consuming, than handling less structured data. • Initially, the database manager who wants to create a new database has to make decisions: » which fields to create to subdivide the database records, » which field tags or names to use for the internal housekeeping of the database by the chosen database management software package.
 **- Field structure in records: problems (Part 2) • The exchange of data, i. e. importing data in a database, which have been exported from another database, is hindered when the databases structures are not identical or compatible. • . . .
**- Field structure in records: problems (Part 2) • The exchange of data, i. e. importing data in a database, which have been exported from another database, is hindered when the databases structures are not identical or compatible. • . . .
 *** Exchange formats and standards for text database systems • Usage and aims: » to allow efficient exchange of information among databases without loss of structural information » to guide database managers in the creation of a database structure (records divided in fields and subfields) • Examples: (MARC = machine readable catalogue) » LC-MARC (=Library of Congress MARC); UNIMARC » Common Communication Format (of UNESCO) » SGML
*** Exchange formats and standards for text database systems • Usage and aims: » to allow efficient exchange of information among databases without loss of structural information » to guide database managers in the creation of a database structure (records divided in fields and subfields) • Examples: (MARC = machine readable catalogue) » LC-MARC (=Library of Congress MARC); UNIMARC » Common Communication Format (of UNESCO) » SGML
 **- Common Communication Format (CCF): description • Developed by the Unesco - General Information Programme for international application • Includes a system of numeric tags indicating » the location of fields and subfields in the records » the meaning of the fields and subfields
**- Common Communication Format (CCF): description • Developed by the Unesco - General Information Programme for international application • Includes a system of numeric tags indicating » the location of fields and subfields in the records » the meaning of the fields and subfields
 **- Common Communication Format (CCF): availability Published and made available free of charge by the Unesco - General Information Programme » Printed manuals » Printed implementation notes » Example CDS/ISIS database structured according to the Common Communication Format
**- Common Communication Format (CCF): availability Published and made available free of charge by the Unesco - General Information Programme » Printed manuals » Printed implementation notes » Example CDS/ISIS database structured according to the Common Communication Format
 **- Exchange of data among systems: requirements • Subject thesaurus (relation-structure + contents) • Subject classification scheme + level of usage • Contents of fields (and subfields) in the records (in the case of bibliographic databases: cataloguing input rules) • Database structure: records, fields, subfields, . . . as seen by the database manager • Version of the program for database management • Type of program for database management • Alphabet used for the data
**- Exchange of data among systems: requirements • Subject thesaurus (relation-structure + contents) • Subject classification scheme + level of usage • Contents of fields (and subfields) in the records (in the case of bibliographic databases: cataloguing input rules) • Database structure: records, fields, subfields, . . . as seen by the database manager • Version of the program for database management • Type of program for database management • Alphabet used for the data
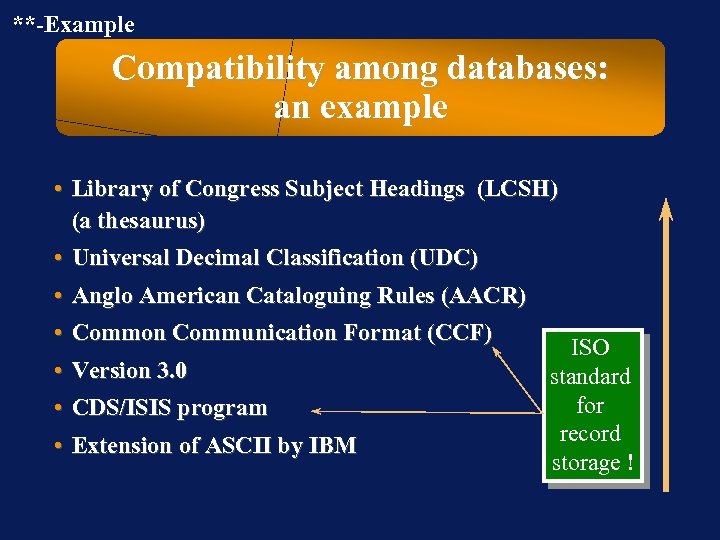 **-Example Compatibility among databases: an example • Library of Congress Subject Headings (LCSH) (a thesaurus) • Universal Decimal Classification (UDC) • Anglo American Cataloguing Rules (AACR) • Common Communication Format (CCF) ISO • Version 3. 0 standard for • CDS/ISIS program record • Extension of ASCII by IBM storage !
**-Example Compatibility among databases: an example • Library of Congress Subject Headings (LCSH) (a thesaurus) • Universal Decimal Classification (UDC) • Anglo American Cataloguing Rules (AACR) • Common Communication Format (CCF) ISO • Version 3. 0 standard for • CDS/ISIS program record • Extension of ASCII by IBM storage !



