b00a8e8ecea8c48d63f53e76467b8589.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Testing Techniques Testing with Finite State Machines Ed Brinksma course 2004
Testing Techniques Testing with Finite State Machines Ed Brinksma course 2004
 This Lecture : Overview l Testing with formal methods: n Generic framework n Testing based on Labelled Transition Systems - ioco n Testing based on Finite State Machines (FSM) l Now: FSM n State based testing n H. Ural, Formal methods for test sequence generation, Computer Communications, 15(5), 1992. n Other literature: D. Lee and M. Yannakakis, Principles and methods of testing finite state machines - A survey. The Proceedings of the IEEE 84, August 1996. © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 2
This Lecture : Overview l Testing with formal methods: n Generic framework n Testing based on Labelled Transition Systems - ioco n Testing based on Finite State Machines (FSM) l Now: FSM n State based testing n H. Ural, Formal methods for test sequence generation, Computer Communications, 15(5), 1992. n Other literature: D. Lee and M. Yannakakis, Principles and methods of testing finite state machines - A survey. The Proceedings of the IEEE 84, August 1996. © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 2
 State Machines l Many systems can be specified / modelled as state machines l State machines as the basis for testing : n FSM : Finite State Machine n black box n specification based n reactive systems : l communication protocols l control systems l embedded systems © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 3
State Machines l Many systems can be specified / modelled as state machines l State machines as the basis for testing : n FSM : Finite State Machine n black box n specification based n reactive systems : l communication protocols l control systems l embedded systems © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 3
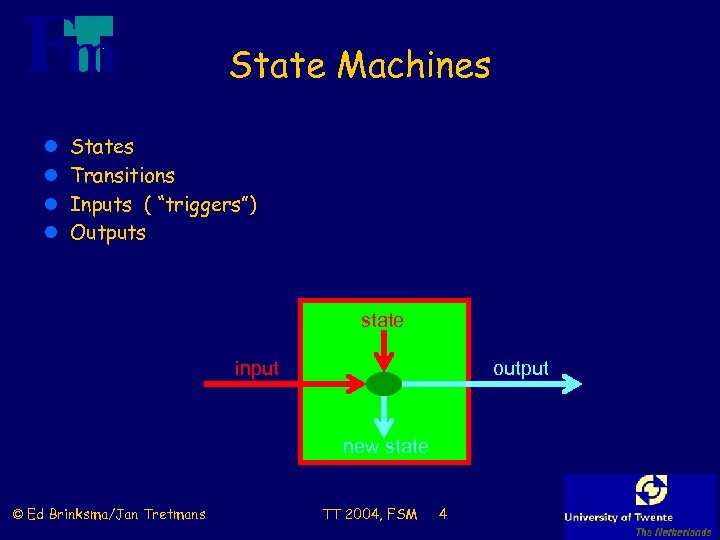 State Machines l l States Transitions Inputs ( “triggers”) Outputs state input output new state © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 4
State Machines l l States Transitions Inputs ( “triggers”) Outputs state input output new state © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 4
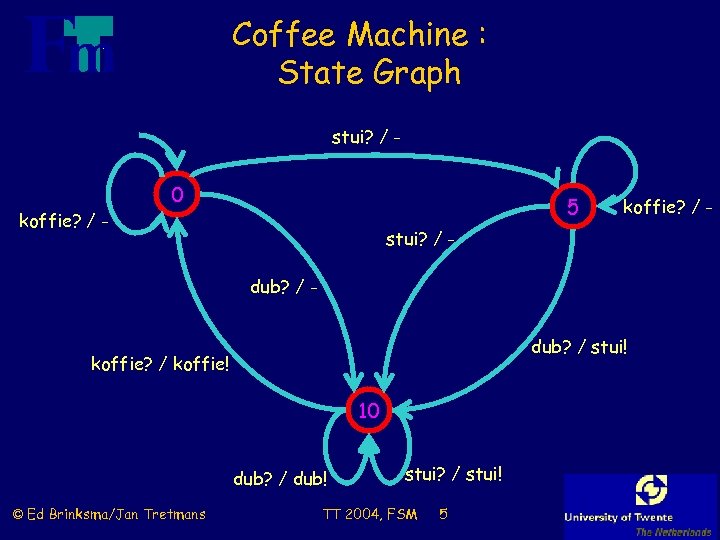 Coffee Machine : State Graph stui? / - koffie? / - 0 5 koffie? / - stui? / dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! TT 2004, FSM 5
Coffee Machine : State Graph stui? / - koffie? / - 0 5 koffie? / - stui? / dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! TT 2004, FSM 5
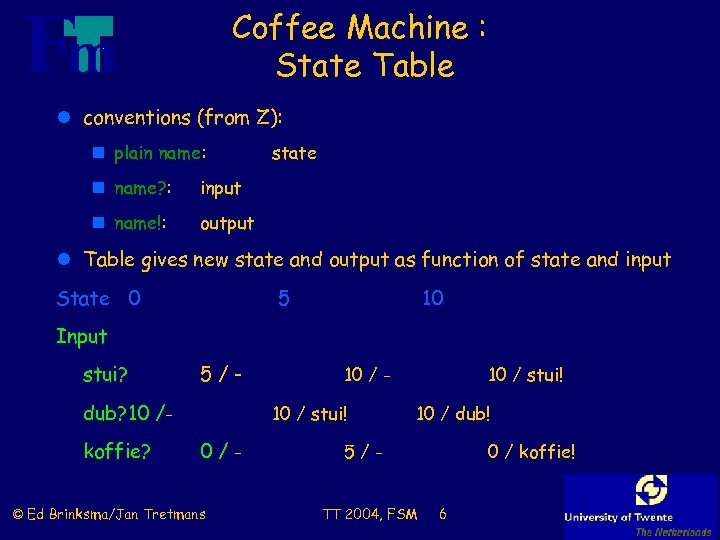 Coffee Machine : State Table l conventions (from Z): n plain name: n name? : input n name!: state output l Table gives new state and output as function of state and input State 0 5 10 Input stui? 5/- dub? 10 /koffie? 10 / stui! 0/- © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans 10 / stui! 10 / dub! 5/TT 2004, FSM 0 / koffie! 6
Coffee Machine : State Table l conventions (from Z): n plain name: n name? : input n name!: state output l Table gives new state and output as function of state and input State 0 5 10 Input stui? 5/- dub? 10 /koffie? 10 / stui! 0/- © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans 10 / stui! 10 / dub! 5/TT 2004, FSM 0 / koffie! 6
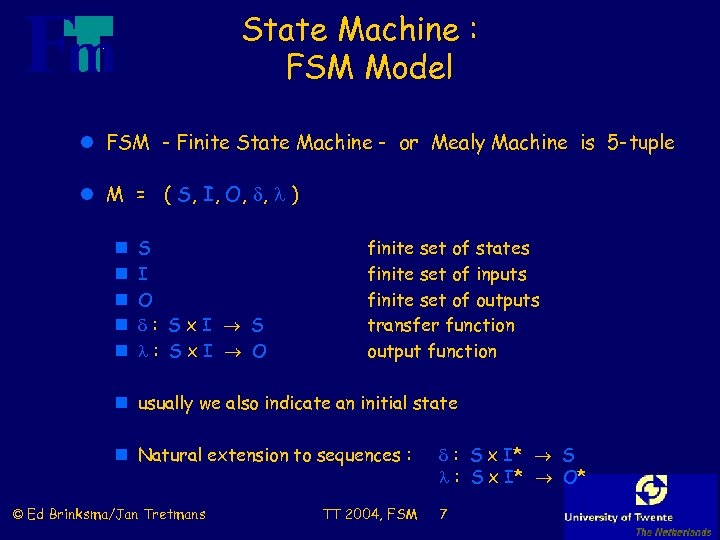 State Machine : FSM Model l FSM - Finite State Machine - or Mealy Machine is 5 -tuple l M = ( S, I, O, , ) n n n S I O : Sx. I S : Sx. I O finite set of states finite set of inputs finite set of outputs transfer function output function n usually we also indicate an initial state n Natural extension to sequences : © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM : S x I* S : S x I* O* 7
State Machine : FSM Model l FSM - Finite State Machine - or Mealy Machine is 5 -tuple l M = ( S, I, O, , ) n n n S I O : Sx. I S : Sx. I O finite set of states finite set of inputs finite set of outputs transfer function output function n usually we also indicate an initial state n Natural extension to sequences : © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM : S x I* S : S x I* O* 7
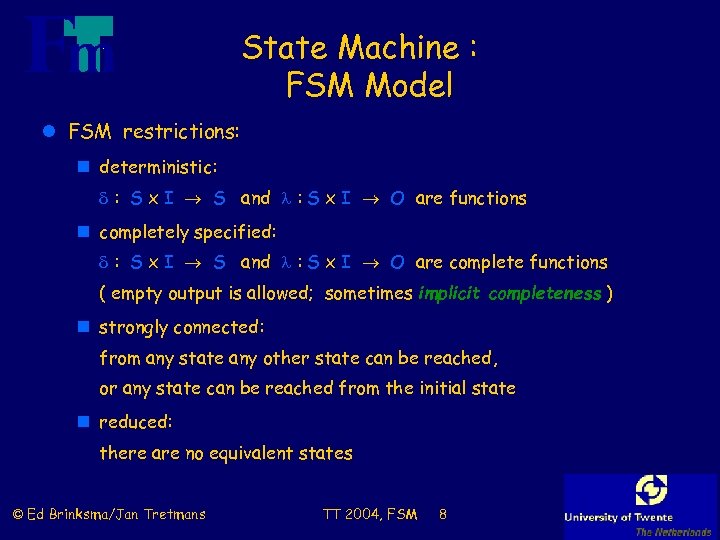 State Machine : FSM Model l FSM restrictions: n deterministic: : S x I S and : S x I O are functions n completely specified: : S x I S and : S x I O are complete functions ( empty output is allowed; sometimes implicit completeness ) n strongly connected: from any state any other state can be reached, or any state can be reached from the initial state n reduced: there are no equivalent states © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 8
State Machine : FSM Model l FSM restrictions: n deterministic: : S x I S and : S x I O are functions n completely specified: : S x I S and : S x I O are complete functions ( empty output is allowed; sometimes implicit completeness ) n strongly connected: from any state any other state can be reached, or any state can be reached from the initial state n reduced: there are no equivalent states © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 8
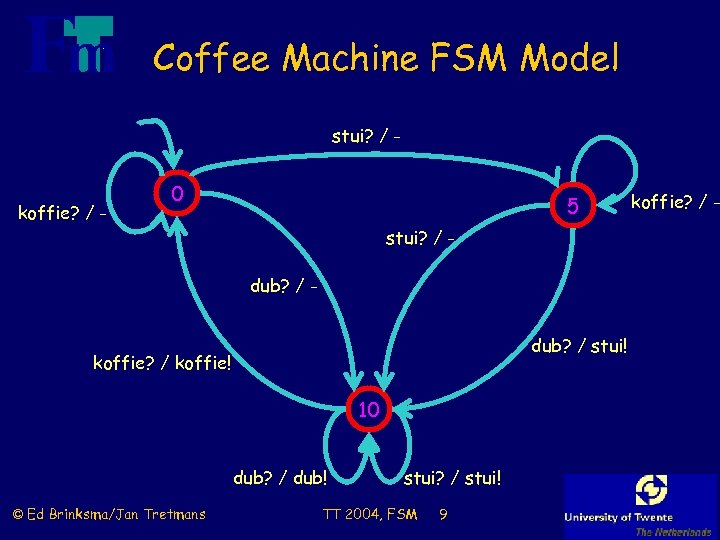 Coffee Machine FSM Model stui? / - koffie? / - 0 5 stui? / dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! TT 2004, FSM 9 koffie? / -
Coffee Machine FSM Model stui? / - koffie? / - 0 5 stui? / dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! TT 2004, FSM 9 koffie? / -
 Testing with FSM l Given: n a specification FSM MS n a ( black box ) implementation FSM MI l l determine whether MI conforms to MS i. e. , MI behaves in accordance with MS i. e. , whether outputs of MI are the same as of MS i. e. , whether the reduced MI is equivalent to MS l Possible errors: n extra or missing states n output fault n transition fault l to other state l to new state © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 10
Testing with FSM l Given: n a specification FSM MS n a ( black box ) implementation FSM MI l l determine whether MI conforms to MS i. e. , MI behaves in accordance with MS i. e. , whether outputs of MI are the same as of MS i. e. , whether the reduced MI is equivalent to MS l Possible errors: n extra or missing states n output fault n transition fault l to other state l to new state © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 10
 FSM Testing l Test with paths of the (specification) FSM l Path = sequence of inputs with expected outputs ( cf. path testing as white-box technique) l Infinitely many paths : how to select ? l Different strategies : n test every state : state coverage (of specification !) n test every transition : transition coverage l test output of every transition l test output + resulting state of every transition © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 11
FSM Testing l Test with paths of the (specification) FSM l Path = sequence of inputs with expected outputs ( cf. path testing as white-box technique) l Infinitely many paths : how to select ? l Different strategies : n test every state : state coverage (of specification !) n test every transition : transition coverage l test output of every transition l test output + resulting state of every transition © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 11
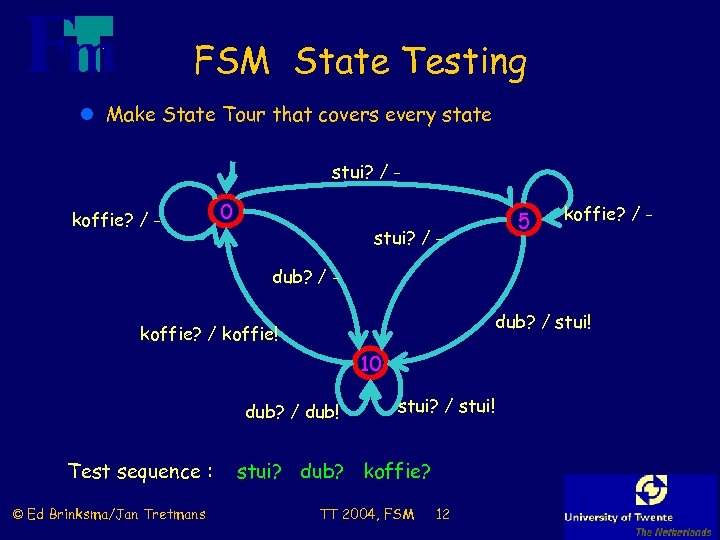 FSM State Testing l Make State Tour that covers every state stui? / koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! Test sequence : © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! stui? dub? koffie? TT 2004, FSM 12
FSM State Testing l Make State Tour that covers every state stui? / koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! Test sequence : © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! stui? dub? koffie? TT 2004, FSM 12
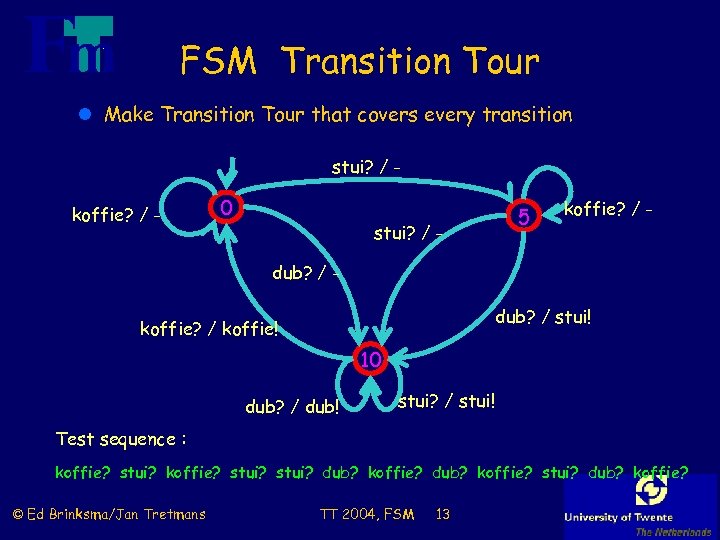 FSM Transition Tour l Make Transition Tour that covers every transition stui? / koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! stui? / stui! Test sequence : koffie? stui? dub? koffie? stui? dub? koffie? © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 13
FSM Transition Tour l Make Transition Tour that covers every transition stui? / koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! stui? / stui! Test sequence : koffie? stui? dub? koffie? stui? dub? koffie? © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 13
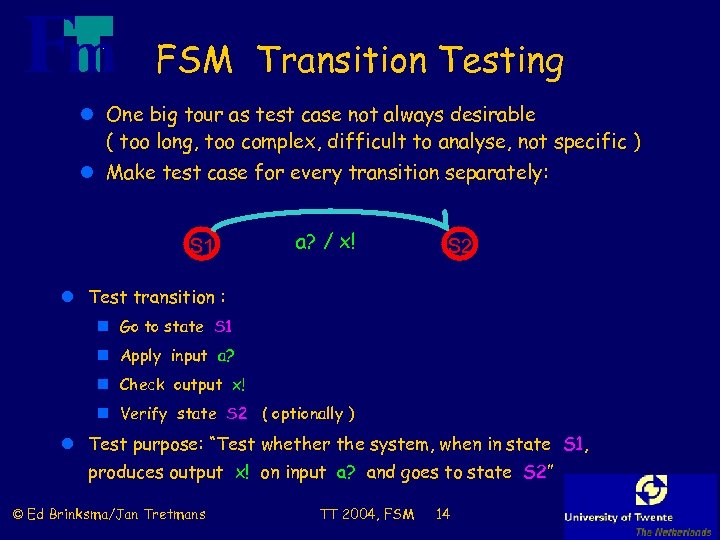 FSM Transition Testing l One big tour as test case not always desirable ( too long, too complex, difficult to analyse, not specific ) l Make test case for every transition separately: S 1 a? / x! S 2 l Test transition : n Go to state S 1 n Apply input a? n Check output x! n Verify state S 2 ( optionally ) l Test purpose: “Test whether the system, when in state S 1, produces output x! on input a? and goes to state S 2” © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 14
FSM Transition Testing l One big tour as test case not always desirable ( too long, too complex, difficult to analyse, not specific ) l Make test case for every transition separately: S 1 a? / x! S 2 l Test transition : n Go to state S 1 n Apply input a? n Check output x! n Verify state S 2 ( optionally ) l Test purpose: “Test whether the system, when in state S 1, produces output x! on input a? and goes to state S 2” © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 14
 FSM Transition Testing l Go to state S 1 : n synchronizing sequence brings machine to particular state, say S 0, from any state ( but synchronizing sequence may not exist ) n or: use reset transition if available n go from S 0 to S 1 ( always possible because of determinism and completeness ) © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 15
FSM Transition Testing l Go to state S 1 : n synchronizing sequence brings machine to particular state, say S 0, from any state ( but synchronizing sequence may not exist ) n or: use reset transition if available n go from S 0 to S 1 ( always possible because of determinism and completeness ) © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 15
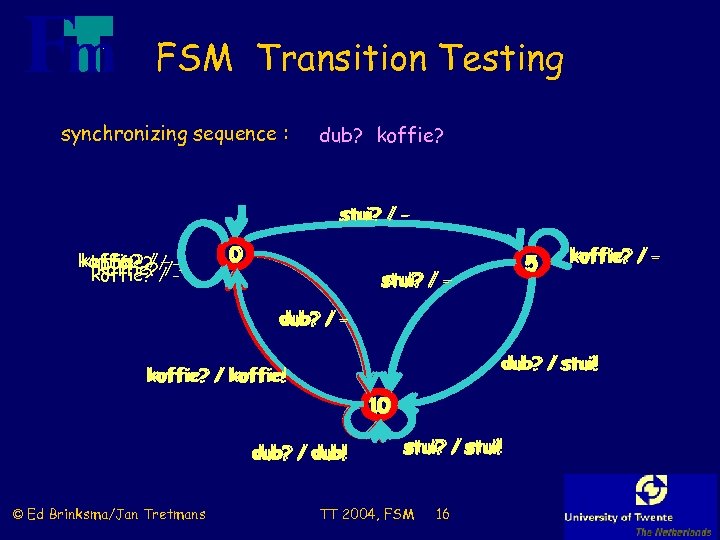 FSM Transition Testing synchronizing sequence : dub? koffie? stui? / koffie? / //-koffie? / koffie? / - 0 0 5 5 stui? / - koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 10 dub? / dub! © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! TT 2004, FSM 16
FSM Transition Testing synchronizing sequence : dub? koffie? stui? / koffie? / //-koffie? / koffie? / - 0 0 5 5 stui? / - koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 10 dub? / dub! © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! TT 2004, FSM 16
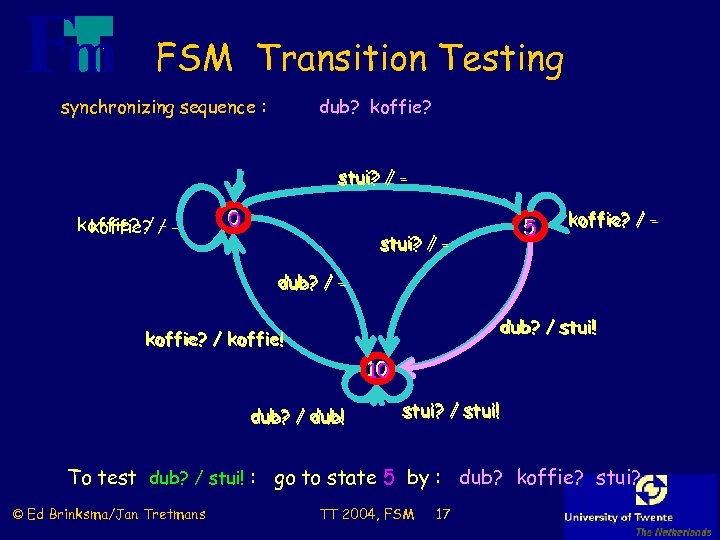 FSM Transition Testing synchronizing sequence : dub? koffie? stui? / koffie? / / koffie? - 0 5 stui? / - koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! stui? / stui! To test dub? / stui! : go to state 5 by : dub? koffie? stui? © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 17
FSM Transition Testing synchronizing sequence : dub? koffie? stui? / koffie? / / koffie? - 0 5 stui? / - koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! stui? / stui! To test dub? / stui! : go to state 5 by : dub? koffie? stui? © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 17
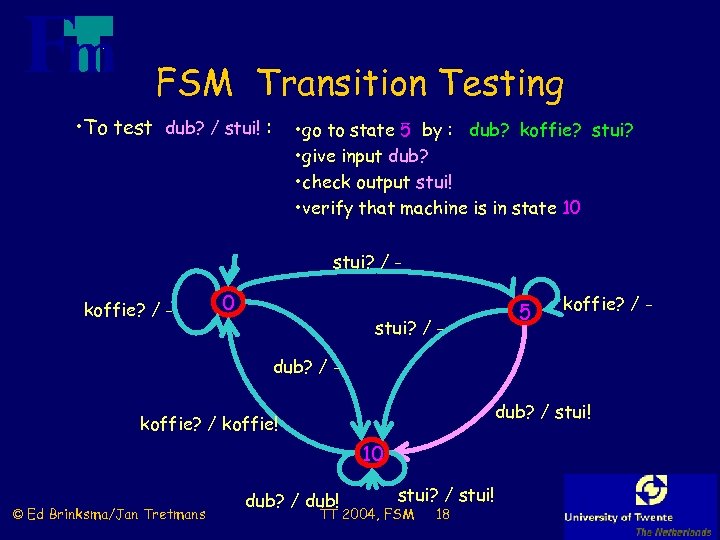 FSM Transition Testing • To test dub? / stui! : • go to state 5 by : dub? koffie? stui? • give input dub? • check output stui! • verify that machine is in state 10 stui? / - koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans dub? / dub! stui? / stui! TT 2004, FSM 18
FSM Transition Testing • To test dub? / stui! : • go to state 5 by : dub? koffie? stui? • give input dub? • check output stui! • verify that machine is in state 10 stui? / - koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans dub? / dub! stui? / stui! TT 2004, FSM 18
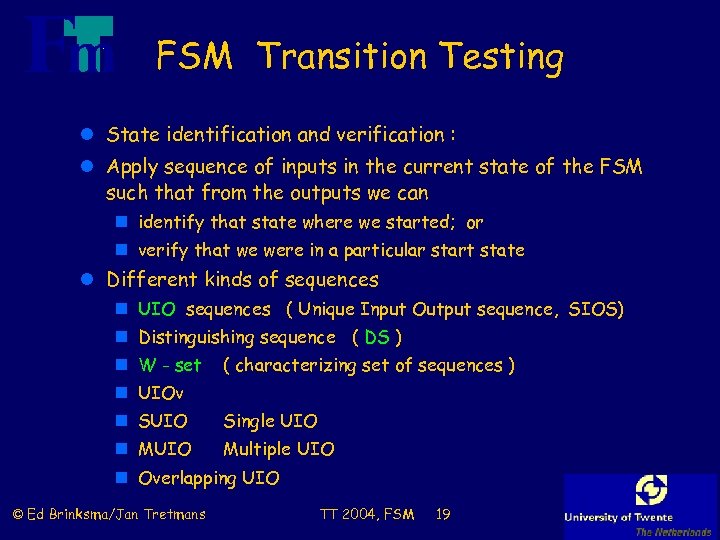 FSM Transition Testing l State identification and verification : l Apply sequence of inputs in the current state of the FSM such that from the outputs we can n identify that state where we started; or n verify that we were in a particular start state l Different kinds of sequences n UIO sequences ( Unique Input Output sequence, SIOS) n Distinguishing sequence ( DS ) n W - set ( characterizing set of sequences ) n UIOv n SUIO Single UIO n MUIO Multiple UIO n Overlapping UIO © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 19
FSM Transition Testing l State identification and verification : l Apply sequence of inputs in the current state of the FSM such that from the outputs we can n identify that state where we started; or n verify that we were in a particular start state l Different kinds of sequences n UIO sequences ( Unique Input Output sequence, SIOS) n Distinguishing sequence ( DS ) n W - set ( characterizing set of sequences ) n UIOv n SUIO Single UIO n MUIO Multiple UIO n Overlapping UIO © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 19
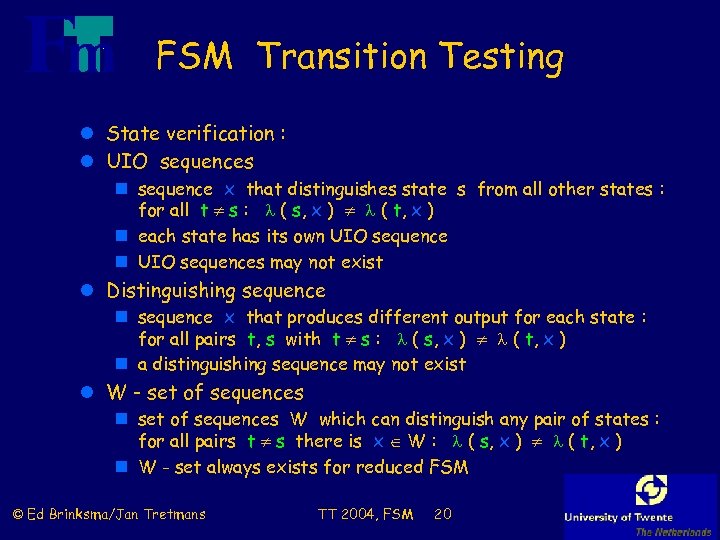 FSM Transition Testing l State verification : l UIO sequences n sequence x that distinguishes state s from all other states : for all t s : ( s, x ) ( t, x ) n each state has its own UIO sequences may not exist l Distinguishing sequence n sequence x that produces different output for each state : for all pairs t, s with t s : ( s, x ) ( t, x ) n a distinguishing sequence may not exist l W - set of sequences n set of sequences W which can distinguish any pair of states : for all pairs t s there is x W : ( s, x ) ( t, x ) n W - set always exists for reduced FSM © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 20
FSM Transition Testing l State verification : l UIO sequences n sequence x that distinguishes state s from all other states : for all t s : ( s, x ) ( t, x ) n each state has its own UIO sequences may not exist l Distinguishing sequence n sequence x that produces different output for each state : for all pairs t, s with t s : ( s, x ) ( t, x ) n a distinguishing sequence may not exist l W - set of sequences n set of sequences W which can distinguish any pair of states : for all pairs t s there is x W : ( s, x ) ( t, x ) n W - set always exists for reduced FSM © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 20
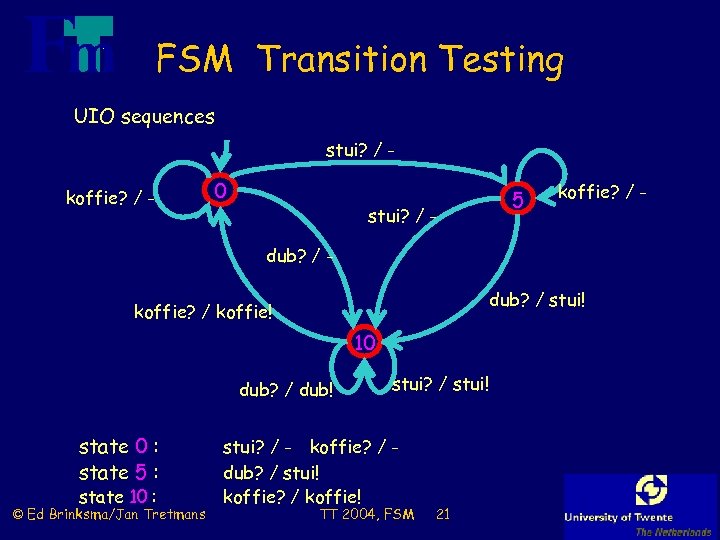 FSM Transition Testing UIO sequences stui? / koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! state 0 : state 5 : state 10 : © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! stui? / - koffie? / dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! TT 2004, FSM 21
FSM Transition Testing UIO sequences stui? / koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! state 0 : state 5 : state 10 : © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! stui? / - koffie? / dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! TT 2004, FSM 21
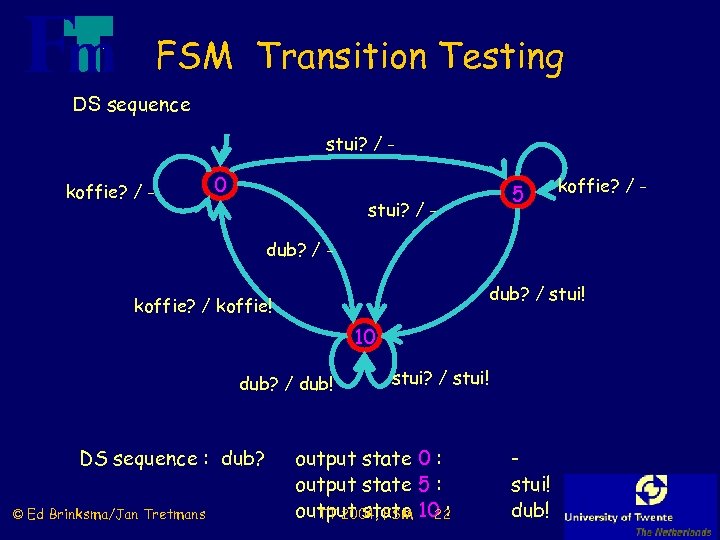 FSM Transition Testing DS sequence stui? / koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! DS sequence : dub? © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! output state 0 : output state 5 : output state 10 : TT 2004, FSM 22 stui! dub!
FSM Transition Testing DS sequence stui? / koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! DS sequence : dub? © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! output state 0 : output state 5 : output state 10 : TT 2004, FSM 22 stui! dub!
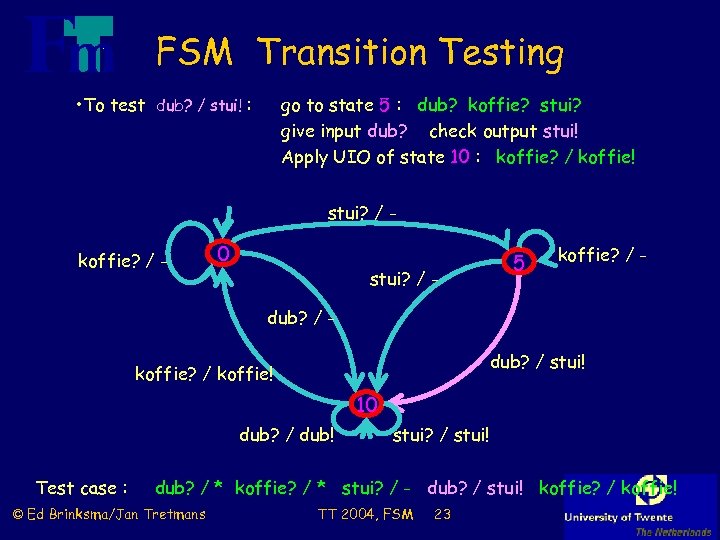 FSM Transition Testing • To test dub? / stui! : go to state 5 : dub? koffie? stui? give input dub? check output stui! Apply UIO of state 10 : koffie? / koffie! stui? / - koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! Test case : stui? / stui! dub? / * koffie? / * stui? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 23
FSM Transition Testing • To test dub? / stui! : go to state 5 : dub? koffie? stui? give input dub? check output stui! Apply UIO of state 10 : koffie? / koffie! stui? / - koffie? / - 0 stui? / - 5 koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! Test case : stui? / stui! dub? / * koffie? / * stui? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 23
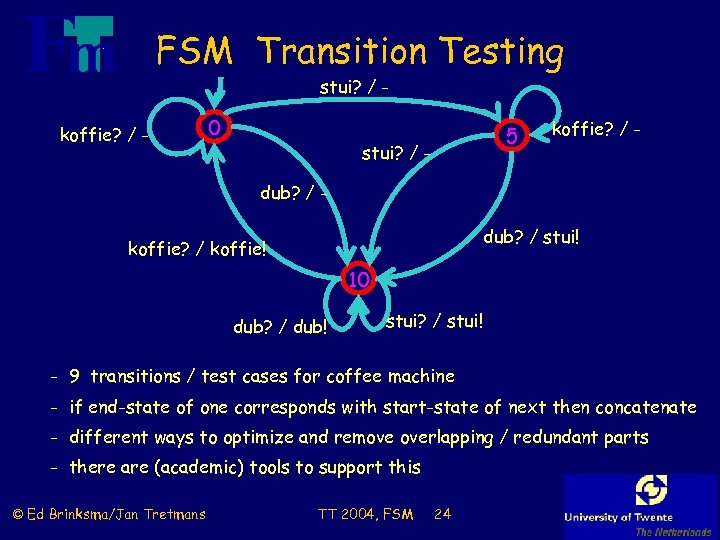 FSM Transition Testing stui? / - koffie? / - 0 5 stui? / - koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! stui? / stui! - 9 transitions / test cases for coffee machine - if end-state of one corresponds with start-state of next then concatenate - different ways to optimize and remove overlapping / redundant parts - there are (academic) tools to support this © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 24
FSM Transition Testing stui? / - koffie? / - 0 5 stui? / - koffie? / - dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! stui? / stui! - 9 transitions / test cases for coffee machine - if end-state of one corresponds with start-state of next then concatenate - different ways to optimize and remove overlapping / redundant parts - there are (academic) tools to support this © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 24
 FSM Transition Testing l Test transition : n Go to state S 1 n Apply input a? n Check output x! n Verify state S 2 l Checks every output fault and transfer fault (to existing state) l If we assume that the number of states of the implementation machine MI is less than or equal to the number of states of the specification machine to MS. then testing all transitions in this way leads to equivalence of reduced machines, i. e. , complete conformance © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 25
FSM Transition Testing l Test transition : n Go to state S 1 n Apply input a? n Check output x! n Verify state S 2 l Checks every output fault and transfer fault (to existing state) l If we assume that the number of states of the implementation machine MI is less than or equal to the number of states of the specification machine to MS. then testing all transitions in this way leads to equivalence of reduced machines, i. e. , complete conformance © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 25
 FSM: variations on this theme l there exists many variations on this theme: n Moore machines: output determined by state instead of transition n Infinite state machines: infinite number of states (e. g. state contains variable) n Non-deterministic FSM: transition relation instead of transition function Labelled Transition Systems - ioco n. . . © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 26
FSM: variations on this theme l there exists many variations on this theme: n Moore machines: output determined by state instead of transition n Infinite state machines: infinite number of states (e. g. state contains variable) n Non-deterministic FSM: transition relation instead of transition function Labelled Transition Systems - ioco n. . . © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 26
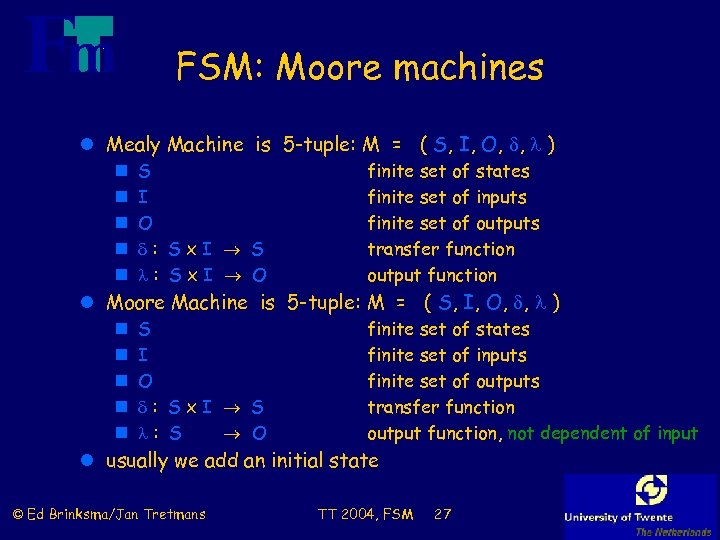 FSM: Moore machines l Mealy Machine is 5 -tuple: M = ( S, I, O, , ) n n n S I O : Sx. I S : Sx. I O finite set of states finite set of inputs finite set of outputs transfer function output function l Moore Machine is 5 -tuple: M = ( S, I, O, , ) n n n S I O : Sx. I S : S O finite set of states finite set of inputs finite set of outputs transfer function output function, not dependent of input l usually we add an initial state © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 27
FSM: Moore machines l Mealy Machine is 5 -tuple: M = ( S, I, O, , ) n n n S I O : Sx. I S : Sx. I O finite set of states finite set of inputs finite set of outputs transfer function output function l Moore Machine is 5 -tuple: M = ( S, I, O, , ) n n n S I O : Sx. I S : S O finite set of states finite set of inputs finite set of outputs transfer function output function, not dependent of input l usually we add an initial state © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 27
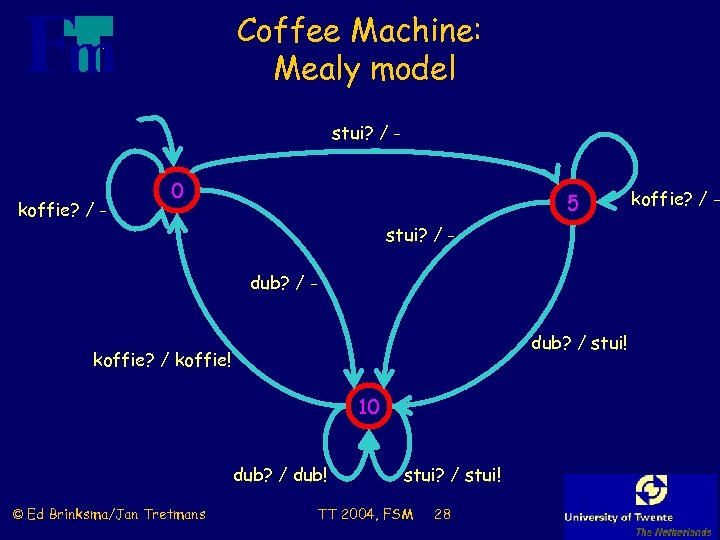 Coffee Machine: Mealy model stui? / - koffie? / - 0 5 stui? / dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! TT 2004, FSM 28 koffie? / -
Coffee Machine: Mealy model stui? / - koffie? / - 0 5 stui? / dub? / stui! koffie? / koffie! 10 dub? / dub! © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans stui? / stui! TT 2004, FSM 28 koffie? / -
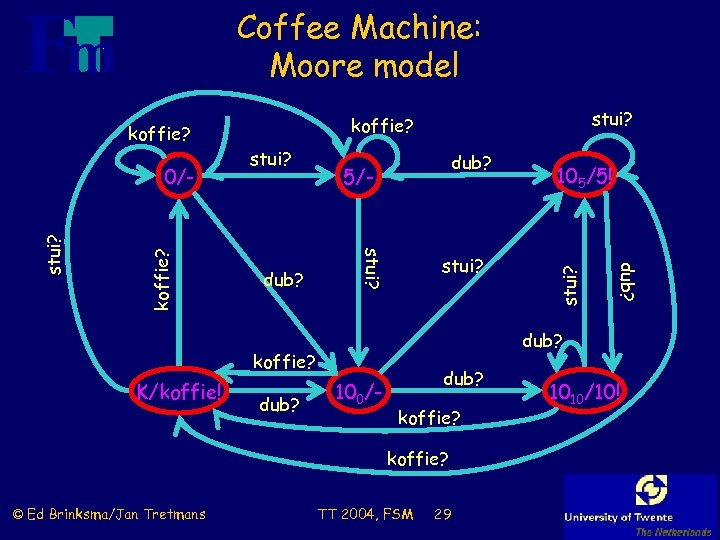 Coffee Machine: Moore model koffie? stui? dub? koffie? K/koffie! dub? 100/- dub? koffie? © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans 105/5! dub? 5/- stui? koffie? 0/- stui? koffie? TT 2004, FSM 29 1010/10!
Coffee Machine: Moore model koffie? stui? dub? koffie? K/koffie! dub? 100/- dub? koffie? © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans 105/5! dub? 5/- stui? koffie? 0/- stui? koffie? TT 2004, FSM 29 1010/10!
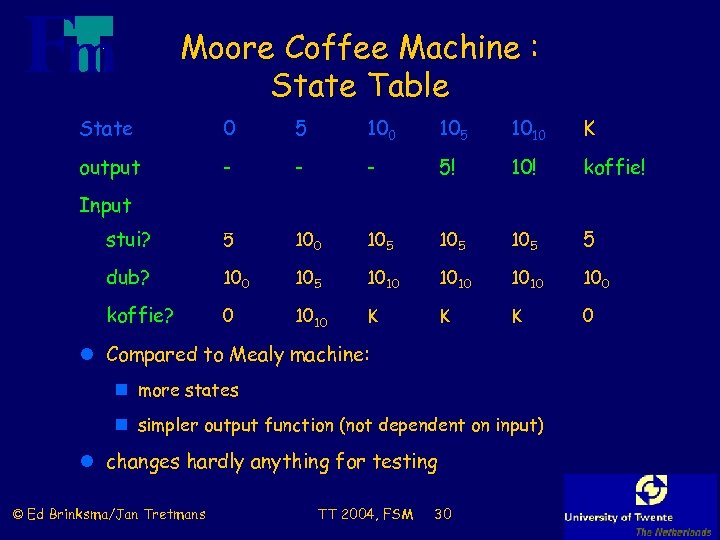 Moore Coffee Machine : State Table State 0 5 100 105 1010 K output - - - 5! 10! koffie! stui? 5 100 105 105 5 dub? 100 105 1010 100 koffie? 0 1010 K K K 0 Input l Compared to Mealy machine: n more states n simpler output function (not dependent on input) l changes hardly anything for testing © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 30
Moore Coffee Machine : State Table State 0 5 100 105 1010 K output - - - 5! 10! koffie! stui? 5 100 105 105 5 dub? 100 105 1010 100 koffie? 0 1010 K K K 0 Input l Compared to Mealy machine: n more states n simpler output function (not dependent on input) l changes hardly anything for testing © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 30
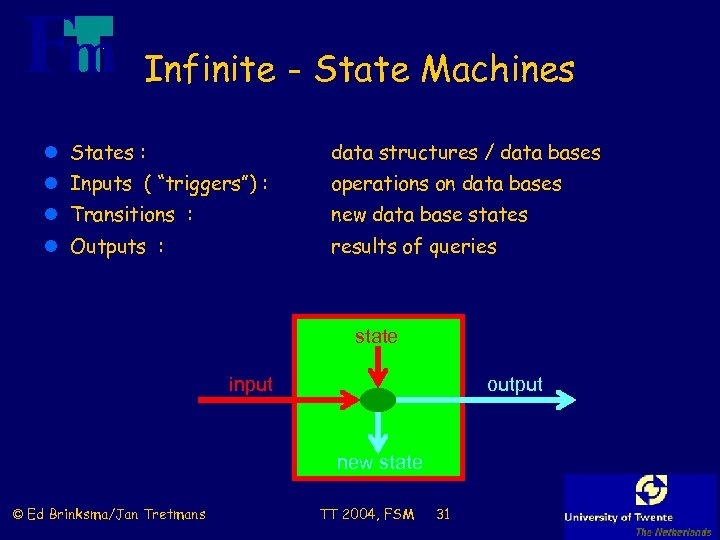 Infinite - State Machines l States : data structures / data bases l Inputs ( “triggers”) : operations on data bases l Transitions : new data base states l Outputs : results of queries state input output new state © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 31
Infinite - State Machines l States : data structures / data bases l Inputs ( “triggers”) : operations on data bases l Transitions : new data base states l Outputs : results of queries state input output new state © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 31
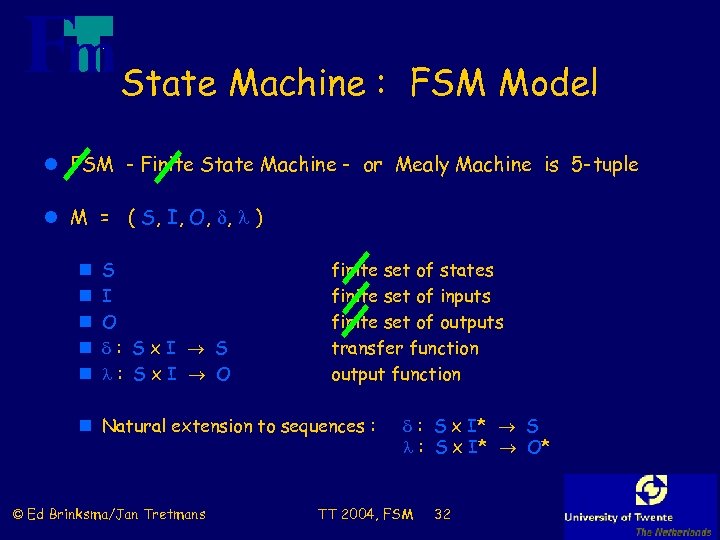 State Machine : FSM Model l FSM - Finite State Machine - or Mealy Machine is 5 -tuple l M = ( S, I, O, , ) n n n S I O : Sx. I S : Sx. I O finite set of states finite set of inputs finite set of outputs transfer function output function n Natural extension to sequences : © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans : S x I* S : S x I* O* TT 2004, FSM 32
State Machine : FSM Model l FSM - Finite State Machine - or Mealy Machine is 5 -tuple l M = ( S, I, O, , ) n n n S I O : Sx. I S : Sx. I O finite set of states finite set of inputs finite set of outputs transfer function output function n Natural extension to sequences : © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans : S x I* S : S x I* O* TT 2004, FSM 32
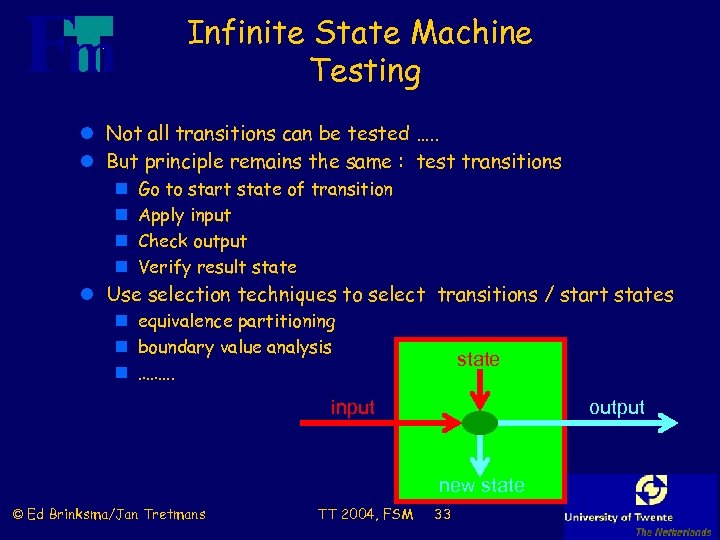 Infinite State Machine Testing l Not all transitions can be tested …. . l But principle remains the same : test transitions n n Go to start state of transition Apply input Check output Verify result state l Use selection techniques to select transitions / start states n equivalence partitioning n boundary value analysis n ……. . . state input output new state © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 33
Infinite State Machine Testing l Not all transitions can be tested …. . l But principle remains the same : test transitions n n Go to start state of transition Apply input Check output Verify result state l Use selection techniques to select transitions / start states n equivalence partitioning n boundary value analysis n ……. . . state input output new state © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 33
 FSM Testing vs. Inf. SM Testing l Restrictions on FSM: n deterministic n completeness l FSM has always alternation between input and output l Difficult to specify interleaving in FSM l FSM is not compositional l FSM has “more intuitive” theory l FSM test suite is complete -- but only w. r. t. assumption on number of states l FSM test theory has been around for a number of years © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 34
FSM Testing vs. Inf. SM Testing l Restrictions on FSM: n deterministic n completeness l FSM has always alternation between input and output l Difficult to specify interleaving in FSM l FSM is not compositional l FSM has “more intuitive” theory l FSM test suite is complete -- but only w. r. t. assumption on number of states l FSM test theory has been around for a number of years © Ed Brinksma/Jan Tretmans TT 2004, FSM 34


