ebca05dfae4697d657a098496a00835c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Testing Cactus and JUnit By Bill Dudney and Jonathan Lehr Neal O’Brien 10/27/04

Table of Contents Overview Article Outline Thesis JUnit Background Cactus Background Pitfalls 1 -6 Comparable Products Conclusion

Overview Junit and Cactus are popular tools for automating testing of Java classes and web-based components Automation accomplished using ANT (Java Make utility) and often tested every time project built These tools enable testers to “verify” the code is written correctly – it was built right Automated tests are very useful to show code works correctly esp. after refactoring which is central to XP I picked this article because deals with JUnit & Cactus, offers a critique of the tools, and was practical, not just theoretical As this article describes, the tests themselves must be built right in order to validate the code being tested
Article Outline Theme: Pitfalls when testing with JUnit & Cactus Pitfall 1: No assert Pitfall 2: Unreasonable assert Pitfall 3: Console-Based Testing Pitfall 4: Unfocused Test Method Pitfall 5: Failure To Isolate Each Test Pitfall 6: Failure to Isolate Subject

Thesis – Analysis of article Thesis: critique was correct but wordy, repetive, and incomplete – missing some bigger pitfalls Pitfalls 1 -3 are all the same – use assert correctly Pitfall 4 is programming rule – write focused method Pitfall 5 is JUnit rule – Use set. Up and tear. Down Pitfall 6 is incomplete analysis of Cactus vs Mock. Obj Overview of Junit and Cactus, then discuss pitfalls, and finally look at unmentioned pitfalls & issues

JUnit Overview Popular and simple Java framework / library for automating testing Integrates well with ANT – Java Make utility General idea: write one test class per testee Write one method to verify each main feature Test class must extend Test. Case and each test method must start with “test” Order of test method execution varies Use assert. True() and assert. Equals() to verify code Use set. Up() & tear. Down() prepare testcase testfixture

JUnit code example Following test cases test the collection methods, is. Empty() and add() import junit. framework. *; public class Simple. Test extends Test. Case { private java. uti. Collection collection; protected void set. Up() { collection = new Array. List(); } // instantiates collection test fixture protected void tear. Down() { collection. clear(); } public void test. Empty. Collection() { assert. True(collection. is. Empty()); } public void test. One. Item. Collection() { collection. add("item. A"); assert. Equals(1, collection. size()); } }

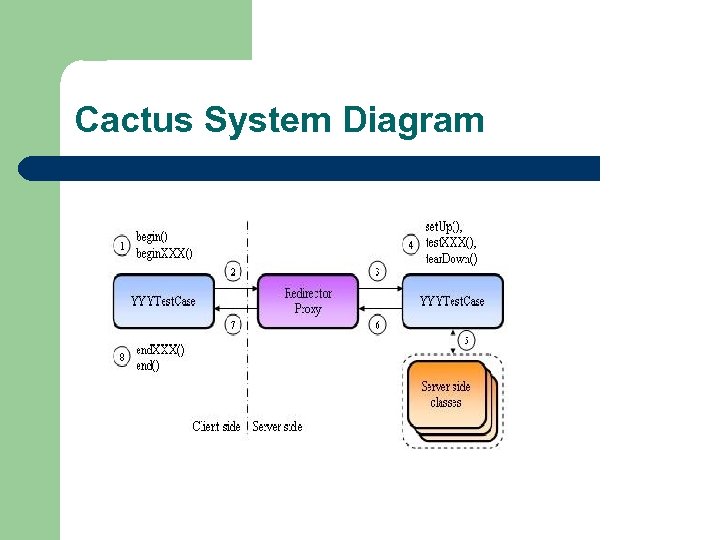
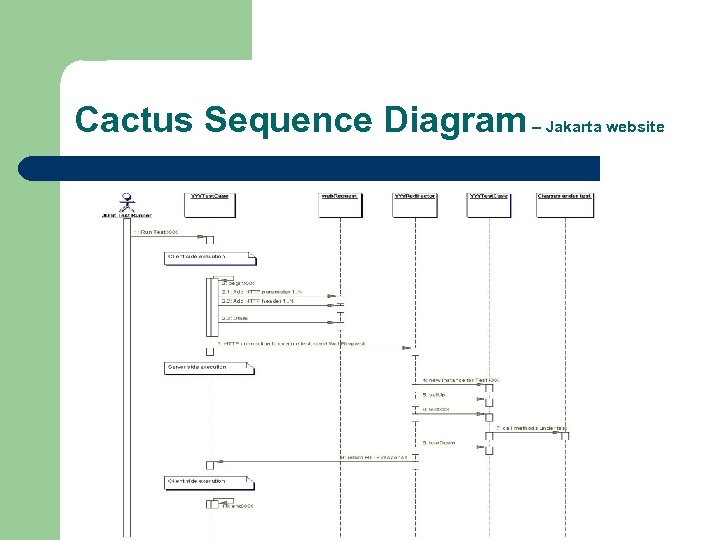
Cactus Overview Built on Junit framework Intended to test JSP, Servlets, EJBs, Filters, and custom tags Complex architecture that has client JVM call the J 2 EE application server JVM via redirector Testcase classes must reside on client and server Adds two methods to Junit architecture, begin. XX() and end. XX() which get called on client, rest on server
Cactus System Diagram
Cactus Sequence Diagram – Jakarta website
Pitfalls 1 -3 – No assert, Unreasonable assert, Console-Based Testing Pitfalls 1 -3 are all the same – use assert correctly Very important and author points out a major guideline – – test what is written in the javadocs for the testee implies javadocs must be up-to-date with requirements Author also points out to write a test case if encounter a defect before it is corrected However, using assert. True() and assert. Equals() is obvious These are the prominent features of the JUnit

Pitfall 4 – Unfocused Test Methods Writing focused tests is really just writing good code General rule of programming to make methods succinct, this applies equally to test methods Writing focused test methods is the whole point

Pitfall 5 – Failure To Isolate Each Test Pitfall 5 is really saying to use set. Up() and tear. Down() to prepare/release test fixture, an obvious suggestion – example from JUnit site Bigger pitfall is automating creation of the test fixture in distributed environments import junit. framework. *; public class Simple. Test extends Test. Case { private java. uti. Collection collection; protected void set. Up() { collection = new Array. List(); } // instantiates collection test fixture for 2 tests protected void tear. Down() { collection. clear(); } public void test. Empty. Collection() { assert. True(collection. is. Empty()); } public void test. One. Item. Collection() { collection. add("item. A"); assert. Equals(1, collection. size()); } }

Pitfall 6 – Failure to Isolate Subject Author points out one drawback of Cactus is that does not isolate test case as Mock. Objects does Mock. Objects simulates the Servlet container – – Mock Object framework does isolate test but at big expense Massive amount of stubs needed, more code to maintain While Cactus may be better than Mock. Objects, it may NOT be better than Http. Unit, why not compare these?

My pitfalls Does not mention major issues like creating this complex automated testing API is itself a software project and has high upfront resource commitments It will slow the development process Upkeep of test code is costly Tests must be documented, reside in source control, and be included in the project planning Junit testcases must reside in same package or parrallel package to access private/package methods – complicating code structure Testers often analysts, not programmers

My Pitfalls – continued Cactus can only test J 2 EE web objects - JSP/EJB/etc, cannot test ASP. NET, PHP, etc. Goal of Cactus not clear – Web or Unit tests? – Cactus is unnecessarily complex – – JUnit is better for unit testing business objects mucky interface: test code must reside on two JVMs Should call via web server like user does, else white box ** Many business websites may have distributed nature of data/objects to be tested, it may be very difficult to set. Up the test cases – Possibly data to be tested is on server not owned/managed by the testing team, data could be volatile

Alternative tools Http. Unit cleaner, simpler tool than Cactus Http. Unit is black box testing by calling webserver – Test code resides ONLY on client JVM Various interfaces like JWeb. Unit (Java API) and Web. Test (XML) integrate well with ANT Use Junit for unit tests and Http. Unit for functional Features to analyze HTML, ie. table element tests Features to input HTML form elements http: //www. junit. org/news/extension/index. htm

JWeb. Unit example – JWeb. Unit. sourceforge. net // The tests perform a google search for the Http. Unit home page, navigate to that page from Google, // and validate that there is a link to the user manual on the Http. Unit home page. package net. sourceforge. jwebunit. sample; import net. sourceforge. jwebunit. Web. Test. Case; public class JWeb. Unit. Search. Example extends Web. Test. Case { public JWeb. Unit. Search. Example(String name) { super(name); } public void set. Up() { get. Test. Context(). set. Base. Url("http: //www. google. com"); } public void test. Search() { begin. At("/"); set. Form. Element("q", "httpunit"); submit("btn. G"); click. Link. With. Text("Http. Unit"); assert. Title. Equals("Http. Unit"); assert. Link. Present. With. Text("User's Manual"); } }

Webtest – XML interface to Http. Unit, easy to automate test by inlining with ANT, verifies logon This XML file can easily be called from ANT Generic interfaces like XMLSPY can be used by non programmers to create the XML test files <target name="login" > <test. Spec name="normal" > <steps> <invoke stepid="get Login Page" url="login. jsp" /> <verifytitle stepid="we should see the login title" text="Login Page" /> <setinputfield stepid="set user name" name="username“ value="scott" /> <setinputfield stepid="set password" name="password" value="tiger" /> <clickbutton stepid="Click the submit button" label="let me in" /> <verifytitle stepid="Home Page follows if login ok" text="Home Page" /> </steps> </test. Spec> </target>

Conclusion Article lists some useful guidelines & pitfalls in an wordy fashion Many pitfalls were obvious and important ones not mentioned Important pitfalls not mentioned include – – – Cost, complexity, difficulty of distributed tests not mentioned Performs white box tests, yet, JUnit already does this Does not test HTTP interface (tests presentation layer poorly) Test code must reside in same package as testee & both JVMs Testers must be programmers JWeb. Unit & Web. Test better for web unit testing At times unclear when addressing Junit vs. Cactus and unnecessarily complex coding examples However, automating testing can save time and money in the long run These tools, while not perfect, are major players for automated Java testing and can verify functionality during development and refactoring
ebca05dfae4697d657a098496a00835c.ppt