5fbb916aa030834c877f58362b6fbc0a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Test Design and Documentation
Test Design and Documentation
 Test Design • Test design is to ensure that all requirements are met through a series of test procedures, increasing the probability of the software being capable of what is needed and wanted by the client. • Test design should start the moment the system requirements have been approved and baselined. • The test design changes/adapts during the system development lifecycle’s iterations
Test Design • Test design is to ensure that all requirements are met through a series of test procedures, increasing the probability of the software being capable of what is needed and wanted by the client. • Test design should start the moment the system requirements have been approved and baselined. • The test design changes/adapts during the system development lifecycle’s iterations
 Initial steps • We must first take into consideration the testing phase in which the test will be executed, as there are different types of test appropriate for testing: – – – Security Performance Usability Compatibility Functionality And other phases testing
Initial steps • We must first take into consideration the testing phase in which the test will be executed, as there are different types of test appropriate for testing: – – – Security Performance Usability Compatibility Functionality And other phases testing
 Initial Steps Continued • Once we have done this we then review the test plan, so as to understand the context and framework within the test objectives are defined. • To break down the testing tasks involved with test design we then have to ask ourselves the following questions:
Initial Steps Continued • Once we have done this we then review the test plan, so as to understand the context and framework within the test objectives are defined. • To break down the testing tasks involved with test design we then have to ask ourselves the following questions:
 What to test? • This should have been documented during the test planning phase so all we have to do is to review our test plan. When should test procedures be developed? • As already stated test procedures should be developed as soon as the requirements are approved. This question is more to do with what order tests should be developed. Higher priority test should be the first to be completed. The only exception to this rule is pre-cursor functions, as these are ran early regardless of there priority.
What to test? • This should have been documented during the test planning phase so all we have to do is to review our test plan. When should test procedures be developed? • As already stated test procedures should be developed as soon as the requirements are approved. This question is more to do with what order tests should be developed. Higher priority test should be the first to be completed. The only exception to this rule is pre-cursor functions, as these are ran early regardless of there priority.
 How should test procedures be designed? • Generally there is no single solution to testing a whole system. What usually happens is each part of the system and how each part is integrated is analysed and then we use the most appropriate and effective test for each part. Who should develop the tests? • Once we have determined when, what and how something is to be tested, it should be reasonably clear who should be responsible for the different testing.
How should test procedures be designed? • Generally there is no single solution to testing a whole system. What usually happens is each part of the system and how each part is integrated is analysed and then we use the most appropriate and effective test for each part. Who should develop the tests? • Once we have determined when, what and how something is to be tested, it should be reasonably clear who should be responsible for the different testing.
 More Questions We now have to consider the following: • What type of testing techniques shall we use? – i. e. Black box or white box testing • What test should be automated? – i. e. Tedious repetitive data entry ones, cost analysis • What kind of test data is needed?
More Questions We now have to consider the following: • What type of testing techniques shall we use? – i. e. Black box or white box testing • What test should be automated? – i. e. Tedious repetitive data entry ones, cost analysis • What kind of test data is needed?
 Test Procedure Template • A test procedure template should be mandated as soon as it is possible to be applied. This is to ensure: – Consistency – Completeness – Repeatability
Test Procedure Template • A test procedure template should be mandated as soon as it is possible to be applied. This is to ensure: – Consistency – Completeness – Repeatability

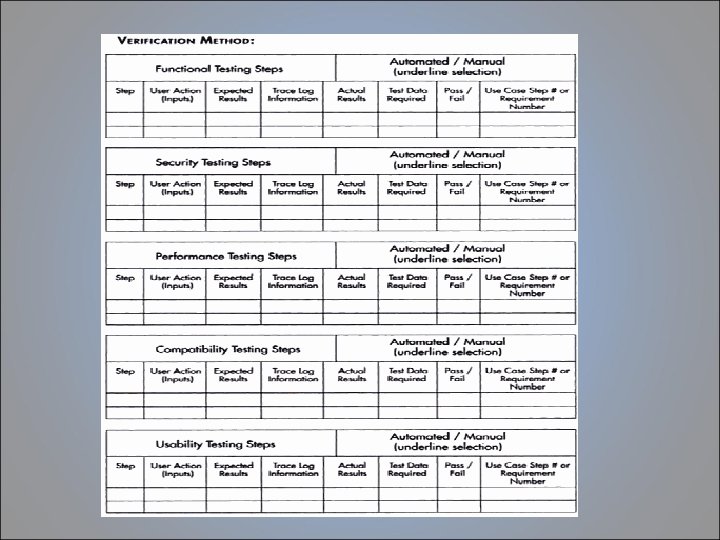
 Test Procedure Standards • It is important that test design standards are documented, communicated and followed by the whole development team. This is so that the required test information is produced. • These guidelines are necessary whether they are manual or automated test procedures. • The standards for manual test procedures should include an example of how much detail the procedure should go in. • The standards for automated test design are pretty similar to those of best coding practises.
Test Procedure Standards • It is important that test design standards are documented, communicated and followed by the whole development team. This is so that the required test information is produced. • These guidelines are necessary whether they are manual or automated test procedures. • The standards for manual test procedures should include an example of how much detail the procedure should go in. • The standards for automated test design are pretty similar to those of best coding practises.
 Test Procedure Standards • While it is important to maintain and mandate a test procedure template it is worth noting that the template should remain in a generic manner, omitting test data which is too specific. • This could lead to unnecessary duplication which could become both costly and time consuming.
Test Procedure Standards • While it is important to maintain and mandate a test procedure template it is worth noting that the template should remain in a generic manner, omitting test data which is too specific. • This could lead to unnecessary duplication which could become both costly and time consuming.
 Test-Design Techniques • The amount of test variations is endless, to narrow down the amount of necessary test procedures we use certain test-design techniques: • Functional Analysis – Involves analysing expected behaviour against functional specifications, then generating one or more test procedure for each function • Equivalence Partitioning – Identifies ranges of inputs and initial conditions that produce expected similar results. It eliminates tests that are similar and hence narrows down the amount of tests to be concluded.
Test-Design Techniques • The amount of test variations is endless, to narrow down the amount of necessary test procedures we use certain test-design techniques: • Functional Analysis – Involves analysing expected behaviour against functional specifications, then generating one or more test procedure for each function • Equivalence Partitioning – Identifies ranges of inputs and initial conditions that produce expected similar results. It eliminates tests that are similar and hence narrows down the amount of tests to be concluded.
 Test Design Techniques • Path Analysis – Is used by testing the internal paths, connections and structure of a product and can be applied at two levels (code based, white-box testing during unit tests & functional/black-box testing by testers or users i. e. manually) • Boundary Value – Used primarily for testing input edit logic, i. e. tests that the checks used for filtering out invalid data are working correctly.
Test Design Techniques • Path Analysis – Is used by testing the internal paths, connections and structure of a product and can be applied at two levels (code based, white-box testing during unit tests & functional/black-box testing by testers or users i. e. manually) • Boundary Value – Used primarily for testing input edit logic, i. e. tests that the checks used for filtering out invalid data are working correctly.
 Test Design Techniques • Orthogonal Arrays – Allows the maximum amount of test coverage with the minimum amount of test coverage, very useful for when there is a large amount of test input data or combinations of this data
Test Design Techniques • Orthogonal Arrays – Allows the maximum amount of test coverage with the minimum amount of test coverage, very useful for when there is a large amount of test input data or combinations of this data
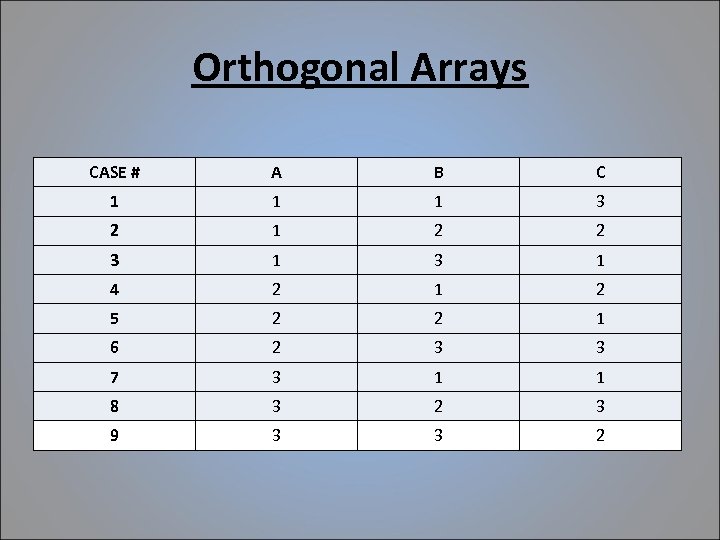 Orthogonal Arrays CASE # A B C 1 1 1 3 2 1 2 2 3 1 4 2 1 2 5 2 2 1 6 2 3 3 7 3 1 1 8 3 2 3 9 3 3 2
Orthogonal Arrays CASE # A B C 1 1 1 3 2 1 2 2 3 1 4 2 1 2 5 2 2 1 6 2 3 3 7 3 1 1 8 3 2 3 9 3 3 2
 Exploratory Testing • Exploratory testing is used in order to gain knowledge required for designing appropriate and effective tests. • It is most appropriate when detailed design are either absent or not complete. • Exploratory testing produces test conditions with each iteration of the development lifecycle. • If a pattern occurs in the problems found early in exploratory testing , it helps focus the efforts of the later tests.
Exploratory Testing • Exploratory testing is used in order to gain knowledge required for designing appropriate and effective tests. • It is most appropriate when detailed design are either absent or not complete. • Exploratory testing produces test conditions with each iteration of the development lifecycle. • If a pattern occurs in the problems found early in exploratory testing , it helps focus the efforts of the later tests.
 Summary • Test design is to ensure all requirements are met through a set of procedures • We then review the test plan and ask ourselves what to test, when to test, how to test and who to test? • How to test in more detail, what tests should be automated, what type of testing techniques to use, what data do we need to be produced
Summary • Test design is to ensure all requirements are met through a set of procedures • We then review the test plan and ask ourselves what to test, when to test, how to test and who to test? • How to test in more detail, what tests should be automated, what type of testing techniques to use, what data do we need to be produced
 More Summary • Testing techniques – Functional analysis – Equivalence partitioning – Path analysis – Boundary value – Orthogonal arrays • Exploratory testing
More Summary • Testing techniques – Functional analysis – Equivalence partitioning – Path analysis – Boundary value – Orthogonal arrays • Exploratory testing


